Midterm 1
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
How many types of principal flow are there?
four
The image above represents which kind of flow?
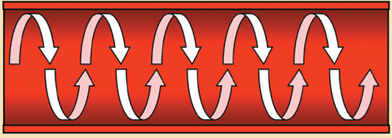
Spiral
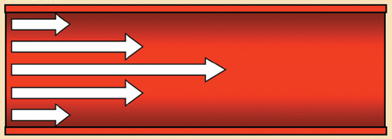
The Image above represents which kind of flow?
Laminar
The image above represents which kind of flow?
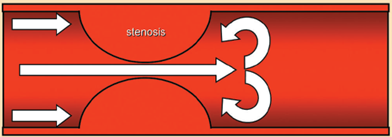
Vortex
Pre-sat bands can’t be brought into the FOV itself
false
The frequency difference between fat and water is called chemical shift
true
The frequency difference between fat and water at 1.5 T is:
220 Hz
Which type of saturation does the above image have?
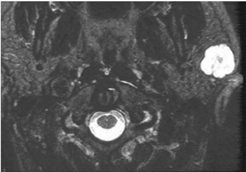
Fat
Ghosting or _ produces replications of moving anatomy
Phase mismapping
Ghosting only occurs along the ___ gradient
Phase encoding
Phase mipmapping occurs because of
Anatomy moving along the phase encoding gradient
According to the Nyquist theorem, frequencies must be sampled at least _____ per cycle to map them correctly
twice
Chemical shift artifact occurs along the frequency encoding axis
true
Truncation artifact produces a banding artefact at the interfaces of high and low signal
true
Magnetic susceptibility artifact is more prominent in
Gradient echo sequences
To reduce magnetic susceptibility artifact:
Use SE instead of GE, decrease TE, and reduce the FOV
Zipper artifact is caused by extraneous RF entering the room
True
The image above demonstrates which artifact?
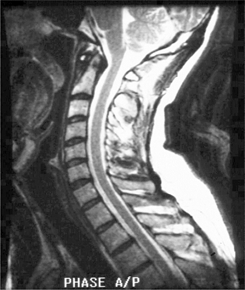
phase mismapping
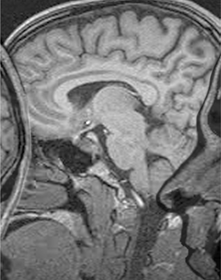
The image above demonstrates which artifact?
Magnetic susceptibility artifact
The image above demonstrates which artifact?
Aliasing
The image above demonstrates which artifact?
Zipper artifact
The image above demonstrates which artifact?
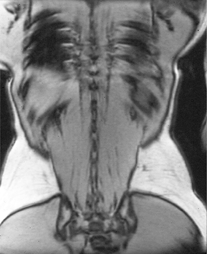
Chemical misregistration
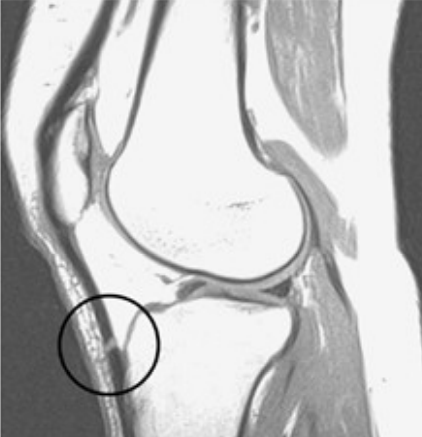
The image above demonstrates which artifact?
Magic angle artifact
MRI and MRA techniques rely on the anatomy of the vessel itself (rather than the motion of blood within the vessel).
False
MRCP stand for:
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography
Aluminum and gadolinium are examples of materials with what type of magnetism?
Paramagnetism
Once a ferromagnetic material is exposed to an external magnetic field it retains magnetization and therefore becomes magnetized.
True
Which type of materials display the greatest positive magnetic susceptibility?
Ferromagnetic
The magnetic field strength in superconducting magnets is maintained with cryogens at a temperature of:
4 K (450 F)
Passive magnetic shielding can be accomplished by lining the scan room walls with:
Steel
The type of MRI magnet that allows the highest field strength is a _______.
Superconductive magnet
In a typical superconducting (cylindrical bore) magnet, the direction of the magnetic field is:
horizontal
The direction of the magnetic field in a typical permanent magnet is:
vertical
What is the maximum field strength of commercially available MRI scanners traditionally used for clinical imaging of humans?
3T
Shielding reduces the magnetic fringe field
True
Since water has a high signal intensity in T2 weighted images, pathology is commonly evaluated using this type of weighting
True
The most commonly used contrast agents are __________ based.
Gadolinium
Gadolinium is an example of a T1 agent.
True
Gadolinium is highly toxic, but it can be made safe for use by binding or chelating the gadolinium to other molecules.
True
Gadolinium can cross the breakdowns in the blood–brain barrier (BBB)
True
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis is a fatal condition with virtually no cure
True
If bony lesions are to be evaluated with gadolinium on T1 weighted images, fat suppression techniques should be used.
True
The net displacement of molecules diffusing across an area of tissue per second is called
Diffusion
In areas of restricted diffusion, the ADC is low, whereas in areas of free diffusion it is high
True
The most common use of DWI is in the brain after infarction.
true
The directional term “Superior” denotes:
towards the head
The directional term “Lateral” denotes:
Away from the midsagittal plane
The directional term “Medial” denotes
towards the midsagittal plane
The directional term "Plantar" denotes
The sole of the foot
The directional term “Superficial” denotes
Near the body surface
The directional term “Proximal” denotes:
Toward a reference point or source within the body
The directional term “Anterior” denotes:
toward the front of the body
The regional term “Cephalic” denotes:
head
The regional term “Antecubital” denotes
anterior surface of the elbow area of the arm
The sella turcica houses the:
pituitary gland
Located in the ________ bone is the foramen magnum, which allows the brainstem to continue inferiorly as the spinal cord.
occipital
There are _______ vertebrae in the Cervical Spine.
7
Compared with conventional spin echo
sequences, the fast pulse sequences,
such as fast spin echo (FSE) or rapid
acquisition relaxation enhanced (RARE)
have ________RF deposition.
the same?
__ is technique in which a complete image is obtained from one selective excitation pulse
EPI
A 90° excitation pulse followed by one or more 180° rephasing pulses is called a
Spin echo
The pulse sequence interval from the 90° RF pulse to the collection of the MR signal is termed what?
TE (echo time)
The IR the sequence interval from the initial 180° RF pulse, used to flip the net magnetization into the negative “z” plane, to the 90° RF pulse is termed________.
TI
In a T1 weighted Image; a short TR is used to______.
maximize t1 effects
The vertical axis of K space represents which axis of the image?
phase encoding
In a T2 weighted Image; a long TE is used to______
maximize t2 effects
TOF effects depend on which of the following?
slice thickness, echo time, and velocity of flow
In a Spin Echo Sequence, TR is the time between each 90° excitation pulse for each slice and TE is the time between the 90° excitation pulse and the peak of the spin echo.
true
The superimposition of signal that occurs when a LARGE FOV is acquired is known as:
partial volume averaging
motion is seen as a smearing in the
phase encoding direction
The superimposition of signal that occurs when a SMALL FOV is acquired is known as:
wrap around/fold over/aliasing
Aliasing occurs because tissue outside the selected FOV is:
undersampled
Gibbs, or truncation artifact is seen as:
high and low signal intensity bands
Chemical shift occurs because the:
fat and water precesses at different frequencies
In order to compensate for aliasing
oversample & FOV can be enlarged
To correct for Gibbs artifact, the
number of phase encoding is increased
Chemical shift becomes more obvious as the
reciver bandwidth is decreased
Magnetic susceptibility effects are more prominent with
gradient echo sequences
A leak in the RF shielding can appear as a:
“zipper” artifact in the frequency direction
Susceptibility effects can be reduced by:
reducing the FOV and reducing the TE
Flow artifacts can be reduced by:
GMN, spatial pre-sat pulses, & shortening the TE
A decrease in voxel volume leads to a decrease in:
chemical shihft & partial volume averaging
As slice thickness increases, partial volume averaging
increases
As FOV increases, partial volume averaging:
increases
As TR increases, partial volume averaging:
stays the same (not affected, TR does not mess with voxel size)
Respiratory artifacts can be reduced by:
respiratory gating/triggering and Increasing the number of signals averaged
Motion artifact occurs due to period and/or aperiodic motion, whereby following motions are examples of what?
A. periodic motion
B. aperiodic motion
C. pulsatile motion
D. daily motion
Patient movement= B
Peristaltic motion= B & D
Respiratory motion = A
Cardiac motion= A & C
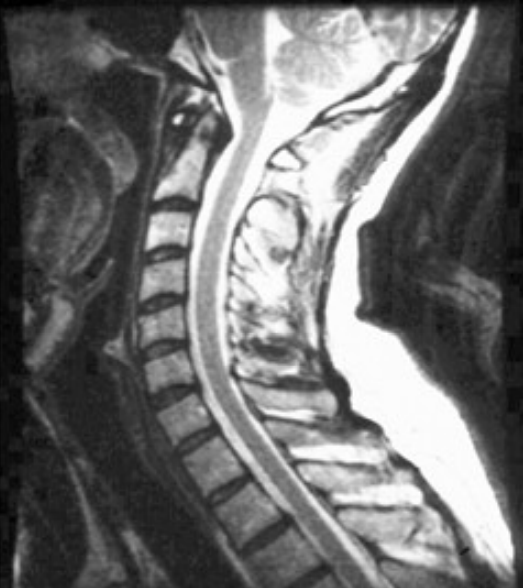
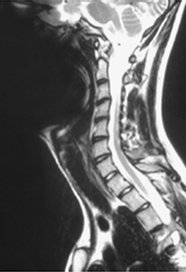
Which artifact?
phase mismapping
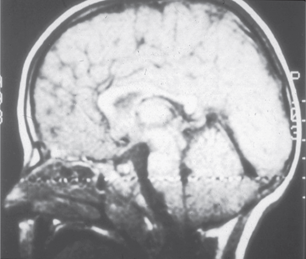
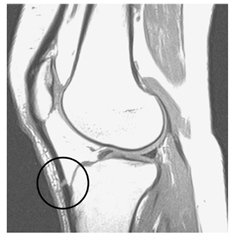
Which artifact?
Magic angle artifact
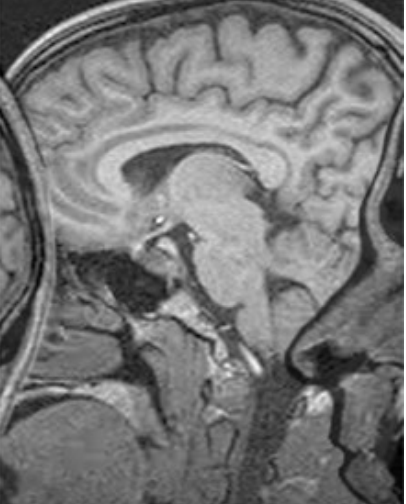
which artifact?
Aliasing
Chemical shift artifacts occur in which direction?
frequency encoding
Motion artifacts for conventional MR imaging occur in which direction?
phase encoding