Schizophrenia and Diagnosis of Mental Disorders
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
A TWIN STUDY: GOTTESMAN & SHIELDS (1966)
THE GENETIC CAUSE OF SCHIZOPHRENIA
Common triggers include:
Drug abuse (such as new types of potent cannabis)
Stress
Family tensions
Aims:
To find out if there is a genetic basis for schizophrenia.
Also, to replicate previous twin studies into schizophrenia to test their reliability. In particular, the researcher looks for concordance rates in MZ twins where one suffered from schizophrenia and compared these to concordance rates in DZ twins to see if there was a significant difference which would be explained by genes.
IV
This is an independent groups design, since it looks at the difference between DZ twins and MZ twins. Because zygocity is a occurring variable, this is a natural experiment.
DV
The researcher's measured the concordance rate for pairs of twins in four different categories.
Sample
62 schizophrenic patients, half male, half female and all aged 19 to 64. All had been patients at a large London hospital between 1948 and 1964 and all had a twin. The researchers originally identified 68 but had to reduce this because some were now out of the country or else it was impossible to tell if they were MZ or DZ twins.
Procedure
The researchers had to assign each twin pair to either MZ or DZ conditions. Zygocity was determined by:
fingerprint testing (different patterns suggest DZ)
blood testing (different blood groups means DZ)
physical resemblance (different hair/eye colour and sex means DZ)
24 MZ twin pairs and 33 DZ twin pairs were identified.
Mental health in the twin was measured by a range of tests:
hospital notes
questionnaires and semi-structured interviews with twins and parents
30 minute tape recording of speech, to identify language problems (a negative symptom)
personality testing
psychometric testing to measured disorganised thinking (a positive symptom)
Results:


In every category, there was a significant difference between MZ and DZ twins, with MZ twins being more likely to share a similar diagnosis of mental illness. The concordance was stronger for female twins than male twins and also stronger with more severe schizophrenia.
There seems to be a genetic component to schizophrenia because the closer the genetic link, the more likely both twins are to show schizophrenic symptoms. However, the MZ concordance rate was significantly lower than 100%. This means that, despite their shared genotype, MZ twins do not always share schizophrenic symptoms - 21% of MZ twins with a schizophrenic brother or (less commonly) sister were perfectly healthy. This suggests that genetics is not the only cause of schizophrenia.
Gottesman & Shields conclude that genes may predispose a person towards schizophrenia, but there needs to be an environmental trigger. This is called the diathesis-stress model (Rosenthal, 1963) and it takes into account nature and nurture.
STRENGTHS OF TWIN STUDY: GOTTESMAN & SHIELDS (1966)
Generalisability:
This study has a fairly large sample and covers a range of ages, from teenagers to men and women in their 60s. There's a 50/50 mix of men and women and even a high proportion of 'rare' MZ twins in the study.
Application:
The people need to know they have a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia so that they can avoid triggers (like drug abuse or excessive alcohol, highly stressful professions, etc). Armed with this research, doctors can monitor "at-risk" patients for early symptoms that might go unnoticed. Like most mental illnesses, schizophrenia cannot be cured but its harmfulness can be reduced if it is recognised early.
Validity:
Gottesman & Shields' findings tie in with earlier research and Rosenthal's theory of the diathesis-stress model of schizophrenia. This gives their research concurrent validity (they agree with the previous studies) and construct validity (they agree with the theory).
Ethics:
The participants in this study were mostly adults who agreed to take part knowing what was being researched. The youngest participants were teenagers and may have needed parental consent, but parents were heavily involved in the research process so that was surely given.
WEAKNESSES OF TWIN STUDY: GOTTESMAN & SHIELDS (1966)
Generalisability:
The sample may not be representative. Besides the problem of twins being unusual people, these particular twins were particularly unusual. Many of them were admitted to hospital in the '40s and '50s after their experiences in WWII. Some of them had been prisoners of war (POWs). These traumatic experiences might have led to all sorts of lifelong problems, not just "ordinary" schizophrenia.
Reliability:
By modern standards, the procedures are not reliable. Without DNA testing, assigning zygocity by physical resemblance and fingerprints is not accurate. However, in the Brendgen et al. (2005) study, Brendgen assigned zygocity based on appearance then checked this with DNA testing and found it to be 94% accurate, which is quite high.
If Gottesman & Shields were that accurate, then at most 2 or 3 twin pairs were mis-assigned, probably DZ twins being mis-assigned to MZ. In this case, the real difference between MZ and DZ twins might have been even greater than it appeared!
Validity:
The twins' illnesses might be nothing to do with schizophrenia - for example, having to care for a mentally ill twin is stressful and depressing, but that doesn't necessarily make you schizophrenic too.
Ethics:
There are some concerns about obtaining consent from mentally ill participants who may not be competent to understand and agree to the research. However, parents and carers may give presumptive consent instead.
This sort of research has a strong social responsibility to shed light on the causes of schizophrenia and perhaps help reduce the suffering it causes.
Heston (1966) - ADOPTION STUDY
Adoption studies use a correlational technique to see if there is a relationship between the children and their parents. These studies investigate if traits that children inherit are more determined by nurture (similar to their adoptive parents) or nature (similar to their biological parents).
Aim: To test whether schizophrenia and other mental disorders were a cause of nature or nurture by seeing how many adopted children of biological mothers with schizophrenia would go on to develop it themselves.
Conditions: The participants were all born between 1915 and 1945 to schizophrenic mothers in an American psychiatric hospital.
Children were selected if their mother:
● Had put them up for adoption
● Was diagnosed with schizophrenia
● Had evidence of behaviour consistent with schizophrenia
● Had no diseases
● The mother and child were separated from birth
Sample: 74 children satisfied the conditions, but 16 participants were dropped for reasons including death, contact with their mother, disease, and no control participant, which left 58 total participants. These 58 were matched with like controls on sex, type of eventual placement, and length of time in child care. A control group was used to possibly eliminate the fact that adoption itself was the cause of schizophrenia. However, due to further deaths and loss of contact via follow-up, there were a final 47 experimental participants (30 male, 17 female), and 50 controls (33 male, 17 female).
Procedure:
Conducted personal interviews with the participants in their homes
Conducted MMPI (Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory - a mental health personality test)
Collected their IQ scores (either from school/other records or one was conducted)
Looked at police/retail credit/school/psychiatric hospital records, criminal and civil court actions, and reviewed newspaper files.
Contacted relatives, friends, and employers
Noted the social class of the participant’s first home and their current social class
Results:
No differences in the number of participants, age, gender, adoption rate, or IQ.
No differences in children, divorces, marriage rates, school years, social groups, or years serving in the armed forces.
Differences found in psycho-social disability, schizophrenia, time spent in penal or psychiatric institutions, IQ deficiency, as well as sociopathic and neurotic personality disorder, crimes, and the number discharged from the armed forces due to psychiatric or behavioural issues.
The rate of schizophrenia to those with schizophrenic mothers was 10.6% compared to 0% in those not born to individuals with schizophrenia.
Conclusion:
The findings support the influence of genes in schizophrenia and that inheritance also contributes to psycho-social disability.
However, Heston also reports that ½ of the participants born to schizophrenic mothers were successful adults who possessed artistic talented and imaginative adaptations to life which was not found in the control group. Therefore, it can be concluded that there must be other possible factors influencing the development of schizophrenia.
Strengths of Heston (1966) - ADOPTION STUDY
Reliability:
Several aspects followed a standardised procedure which allows for replication, e.g.:
Each participant’s dossier was evaluated using the same approach (i.e., blindly and individually, then a third time by Heston). This allows for high inter-rater reliability as a total of 3 researchers confirmed the evaluative assessment of the adoptees and whether they had schizophrenia, making the study objective and removing bias with high scientific credibility.
The interviews were standardised with the same questions being asked to each participant, meaning the results will be easily comparable and the procedure itself can be replicated.
Application:
There is a clear genetic link for schizophrenia. This finding can be used to develop research in order to prevent schizophrenia being passed on.
Validity:
High ecological validity as the experiments were conducted in a natural environment (the participants’ home) so their behaviour will be quite natural.
Weaknesses of Heston (1966) - ADOPTION STUDY
Generalisability:
There was a small sample of 47 adopted participants from Oregon, meaning the findings/conclusions cannot be generalised to other cultures outside of the USA/Oregon, especially collectivist cultures.
Ethics:
Participants were contacted by letter asking if they'd like to take part, meaning informed consent was obtained. However, some questions could've caused stress as they were very personal.
Reliability of the DSM-3
Spitzer (2012) and his colleagues felt that 0.7 on Cohen’s kappa would indicate ‘good agreement’.
Johnstone and Miners (2014)
Suggests psychologists are turning to ‘formulation’ as an alternative to diagnosis. This involves building up a personal story that allows the clinician to understand how past traumatic experiences have caused current distress.
Regier and colleagues (2013)
3 disorders including PTSD had kappa values ranging from 0.60-0.79 (very good) while seven more diagnoses including schizophrenia had kappa values of 0.40-0.59 (good).
Major depressive disorder (MDD) had one of the least reliable diagnoses (0.28)
Cooper (2014)
DSM-5 task force classified kappa values 0.2-0.4 as ‘acceptable’, so the fall in standards suggests DSM is less reliable than previous versions because of the risk of error during diagnoses.
Pontizovsky et al. (2006)
Studied the admission and release of 998 Israel patients suffering depression and mood disorders and 1013 patients suffering from schizophrenia.
Strengths - Reliability of ICD:
Mood disorders had a kappa value of 0.68 whilst psychotic patients had a kappa value of 0.62.
Compared reliability of ICD-9 and ICD-10 using PPV (positive, predictive value) which is the proportion of people getting the same diagnosis when reassessed.
Galeazzi et al. (2004)
Strengths - Reliability of ICD:
Compared reliability of ICD-9 and ICD-10 using PPV (positive, predictive value) which is the proportion of people getting the same diagnosis when reassessed.
Mason et al. (1997)
Strengths - Validity of ICD:
Good predictive Validity for Schizophrenia
ICD-9 & ICD-10 were reasonably good at predicting disability in 99 people with schizophrenia 13 years later.
Luhrmann et al. (2015)
Cultural Differences in Hearing Voices:
Interviewed 60 American, Indian & Ghanaian people with schizophrenia
70% of Americans - harmful, destructive voices.
50% of Ghanaians - mainly positive voices.
20% of Ghanaians - voices told them to kill or fight.
Indian people tended to hear family members compared to only 10% of Americans.
Strengths - DSM-5 and ICD-10 are reliable because of consistent schizophrenia diagnosis
Regier et al. (2013) - Kappa value was 0.46 in field trials of DSM-5.
Sartorius et al. (1995) - high kappa value of 0.86.
Davis et al. (1991)
Dopamine Deficiency - Hypodopaminergia
ORIGINAL DOPAMINE HYPOTHESIS Suggests:
Excess Dopamine in the mesolimbic pathway - positive symptoms of schizophrenia
Limited Dopamine in the mesocortical pathway - negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Insel (2010)
Suggests schizophrenia stems from abnormalities in early brain development, starting in the first few weeks of gestation.
People who exhibit schizophrenic symptoms in their late teens & early 20s exhibit similar prodromal (pre-diagnostic symptoms).
Howes & Kapur (2009)
Dopamine Dysregulation & schizophrenic symptoms:
Describes dopamine dysregulation in the striatum as a common pathway to psychosis.
Tenn et al. (2003)
Strengths of Neurotransmitters (biological explanation of schizophrenia):
Research Support - Found rats given 9 amphetamine injections over 3 weeks showed various schizophrenic symptoms, which can be seen as social withdrawal.
Snyder (1985)
Strengths of Neurotransmitters (biological explanation of schizophrenia):
Support for D2 receptors - Chlorpromazine acts as an antagonist at many D1 & D2 dopamine receptors, has an antipsychotic effect.
Dépatie & Lal (2001)
Weaknesses of Neurotransmitters (biological explanation of schizophrenia):
Showed that apomorphine, a dopamine agonist that stimulates D2 receptors, does not include psychotic symptoms.
This challenges how hypodominergia is responsible for positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
Veling et al. (2008)
Weaknesses of Neurotransmitters (biological explanation of schizophrenia):
Second Generation Immigrants:
Showed Moroccan immigrants in the Netherlands were more likely to be diagnosed than Turkish Immigrants & correlated with the amount of actual & perceived discrimination faced by each group.
Hilker et al. (2018)
Schizophrenia: Genetic Influence (One other biological explanation)
A recent estimate for the heritability of schizophrenia is 79%.
Wright (2014)
Schizophrenia: Genetic Influence (One other biological explanation)
As many as 700 genes have been linked to schizophrenia.
Houston et al. (2008)
Schizophrenia: Genetic Influence (One other biological explanation)
Diathesis-Stress Model: Schizophrenia genes are only triggered by biological and environmental factors.
‘Stress’ was often seen as psychological, created by harsh parenting.
Stress is now seen as anything that risks triggering schizophrenia.
Susser & Lin (1992)
Schizophrenia: Genetic Influence (One other biological explanation)
Epigenetics: How genes are turned on and off by environmental stressors.
Reported that women who became pregnant during the famine had low birth weight babies who were twice as likely to develop schizophrenia.
Mil et al. (2006)
Schizophrenia: Genetic Influence (One other biological explanation)
Epigenetics:
Found MZ twins had up to 20% greater ‘methylation’ of two genes linked with schizophrenia.
Gottesman (1991)
Strengths for Schizophrenia: Genetic Influence (One other biological explanation)
Research Support:
Found a clear relationship between genetic similarity and an increase in two related individuals having schizophrenia.
48% concordance rate for MZ twins VS 17% only for DZ twins
Gottesman & Shields (1966)
Strengths for Schizophrenia: Genetic Influence (One other biological explanation)
Research Support:
Found a concordance rate of 42% for MZ twins and 9% for DZ twins.
Dahown et al. (2017)
Strengths for Schizophrenia: Genetic Influence (One other biological explanation)
Research Evidence on DISC1 and COMT genes:
Reviewed 14 studies and concluded that DISC1 is associated with presynaptic dopamine dysregulation, a key factor in schizophrenia.
Egan et al. (2001)
Strengths for Schizophrenia: Genetic Influence (One other biological explanation)
Research Evidence on DISC1 and COMT genes:
Proposed a link between decreased dopamine activity in the PFC and 1 form of the COMT gene.
Tienari et al. (1994)
Issues & Debates:
Strengths for Schizophrenia: Genetic Influence (One other biological explanation)
A 21-year longitudinal study supports the diathesis-stress model.
Adopted children whose biological mothers were diagnosed with schizophrenia were more sensitive to family dysfunction in adoptive homes than those from low-risk backgrounds.
Pederson & Mortensen (2006)
Weaknesses for Schizophrenia: Genetic Influence (One other biological explanation)
Research demonstrates the longer a person is exposed to urban life (dense population), the greater the risk of developing schizophrenia.
What are the 4D’s?
DEVIANCE: These are behaviours and emotions that are viewed as unacceptable. Extremely abnormal behaviour that deviates from social and statistical norms; people feel anxious or threatened by the person who is deviant.
DYSFUNCTION: This is when the abnormal behaviour is significantly interfering with everyday tasks and living your life.
DANGER: They are a threat to society
DISTRESS: This is the simple view that abnormality involves being unhappy: experiencing negative feelings like anxiety, isolation, confusion and fear. Abnormality is when these negative feelings occur inappropriately or persist longer than they should.
Rosenhan & Seligman (1989):
Loss of control
Irrationality
Violate moral standards
Causes discomfort to observers
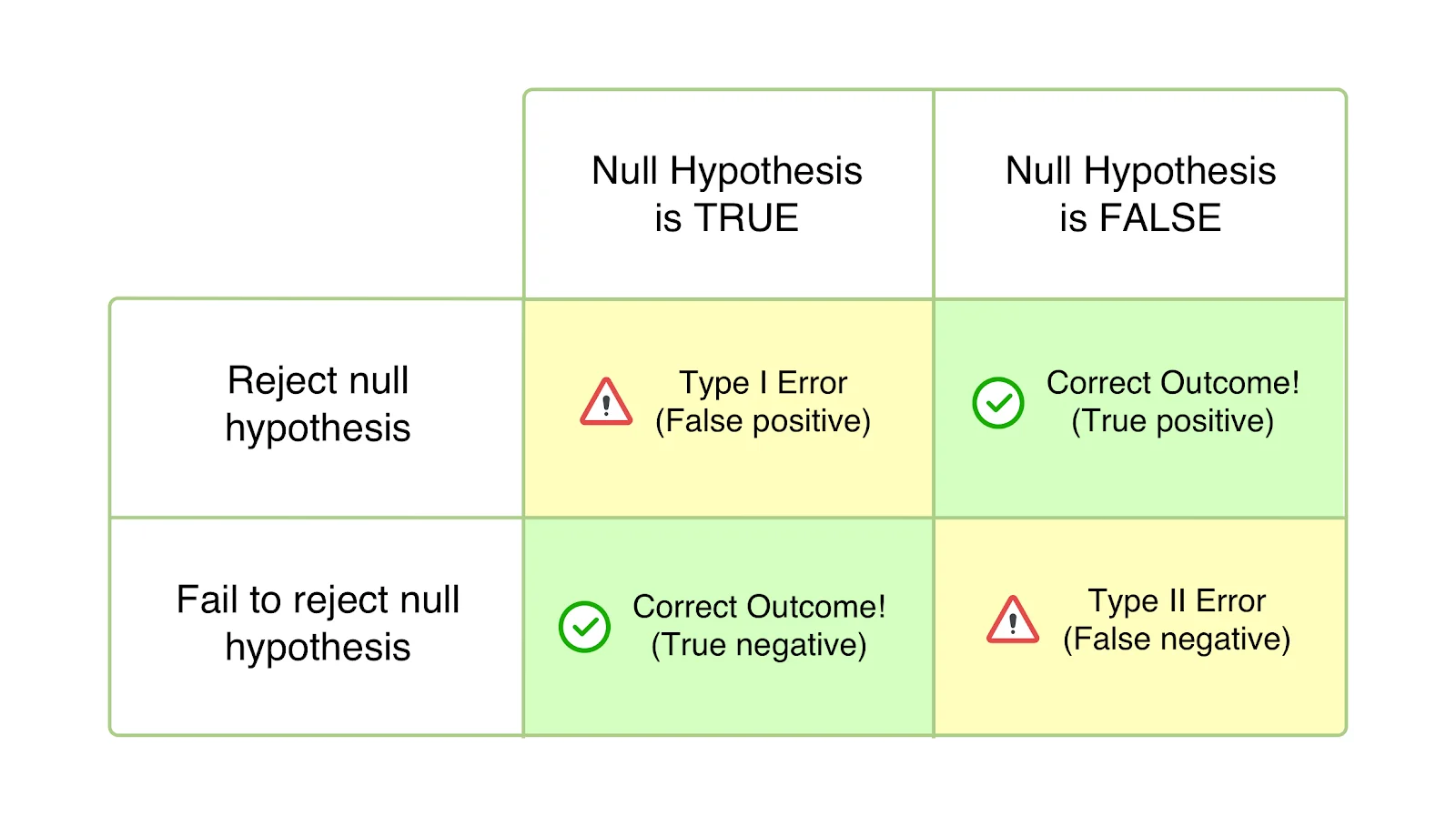
APPLYING DIAGNOSES TO REAL LIFE (A02)
A serious problem with the application of diagnosis is false diagnosis. These false into two types:
Type I Error or False Positive: diagnosing someone with a mental disorder when they are healthy
Type II Error or False Negative: diagnosing someone as healthy when in reality they are ill
False Positives come from "reading too much" into the client's behaviour. It can also come from the fear of the consequences of a False Negative (if a mentally ill person is told they are normal then goes and hurts or kills themselves). False Negatives can come from the suspicion that the client is faking their illness or the belief that their deviant behaviour is deliberate wickedness.
Cultural Problems:
People from other cultures presenting their symptoms to a Western doctor may express themselves in unfamiliar ways. For example, among African-Caribbeans it is not abnormal to talk to dead relatives while grieving. This can lead to them being diagnosed with a much more severe disorder than they really have (such as schizophrenia rather than mild depression) - a false positive diagnosis.
EVALUATING DIAGNOSES (A03)
Supporting Research:
The use of diagnostic systems means more communication between clinicians, which increases inter-rater reliability (Spitzer & Fleiss, 1974).
Factitious disorders (like Munchausen Syndrome) exist where people fake illness or psychological disorder to get medical attention. This indicates deviance from the norm, as well as distress felt by the individual through faking illness; there may be danger, as they may harm themselves to back up their claims; dysfunction may incur as faking the illness involves losing jobs, withdrawing from social life, etc.
Opposing Research:
There has been found to be only a 68% agreement (Andrews et al, 1999) between the ICD and DSM.
Rosenhan (1973) provides evidence that diagnoses are flawed, as staff were unable to tell mentally disordered patients apart from those who were healthy.
The lack of objectivity of the four Ds raise issues about reliability of diagnosis. If the four Ds are used by two different therapists, they may not reach the same diagnoses. For example, Dissociative Identity Disorder (multiple personality) is a recognised disorder in the USA but not in Britain.
Spitzer & Fleiss (1974) carried out a meta-analysis of 6 studies and found some similarities in how disorders were diagnosed by psychiatrists but many differences. They claim that reliability is not high for the diagnosis of any mental disorder and that reliability for schizophrenia is just 'fair' rather than 'good'.
Different Theories:
Davies proposes that a 5th D - Duration - needs to be included. Grief is a good example, because a period of grief is normal after the death of a loved one (in fact, not grieving would be abnormal) but if the grief goes on too long (like Queen Victoria) then that becomes abnormal instead.
Recovery Model - It grew out of a movement in the 1980s and '90s that rejected institutionalization and drug therapy and focused on the testimonies of people who "beat their illness" by changing their lives.
Arenella (2015) argues that the recovery model is gaining ground over the medical model because drugs and psychiatrists are expensive but social workers are much cheaper.
Application:
African-Caribbean people in the UK are 3-5 times more likely to be diagnosed with schizophrenia and hospitalised than other groups. You are also more likely to be diagnosed with serious mental disorders if you are poor. Women are more likely to be diagnosed than men.
Diagnosis
The process of matching a person’s behaviours, cognitions, feelings and desires to the signs and symptoms of a recognised mental disorder to provide information and prognosis.
The 4D’s of Diagnosis
Deviance:
Unusual, bizarre behaviours.
Statistical and social norms are necessary to determine how undesirable behaviour is.
Failure to conform to social norms may lead to negative attention and social exclusion.
Dysfunction:
Symptoms interfering with the ability to carry out daily responsibilities.
Objective measures are used by psychologists to assess everyday functioning and the abilities to follow routines.
Distress:
Symptoms causing emotional pain or anxiety.
Quantitative data is collected using Kessler Psychological Distress Scale
Danger:
Careless, hostile behaviour jeopardising safety
Predicting violent behaviours are hard, but a record makes another incident more likely
UK’s ‘Mental Health Act’ only needs 3 professionals to agree that an individual is a danger to themselves and others.
STRENGTHS OF Diagnoses using 4D’s
All 4 features help avoid erroneous diagnoses.
Avoids eccentric, harmless people being seen as abnormal, but common, debilitating symptoms of depression are missed.
WEAKNESSES OF Diagnoses using 4D’s
Lack of Objectivity:
Feelings are subjective when rated
Clinician requires information about the person and their community to apply the 4Ds properly.
Lowers reliability - different physicians might not get the same diagnosis
Fazel et al. (2009)
4D’s create labels - media distortion can cause schizophrenic people to seem more dangerous than normal people.
Social control over behaviour that might be seen as normal in certain cultures.
Ignores culture-bound syndromes → The DSM and ICD fail to consider cultural differences, like the Amok in Malaysia.
Classification Systems: DSM-5
Features:
Focuses more on mental and emotions
Important introductory step for appropriate support and treatment
Describes and classifies symptoms, features and associated risk factors of over 300 mental and behavioural disorders
Structure:
Consists of 3 sections:
1 - Guidance about using the new system
2 - Details of disorders, categorised according to current understanding of underlying causes and similarities
3 - Includes information about the impact of culture on the presentation of symptoms and how they are communicated.
Diagnosis using DSM:
Unstructured and structured clinical interviews based on symptoms
General practitioners can diagnose uncomplicated symptoms whilst difficult cases can take weeks or months.
Types of Validity for DSM-5
Descriptive Validity - 2 people with the same diagnosis exhibit similar symptoms
Aetiological Validity - 2 people with the same diagnosis have similar causal factors
Concurrent Validity - Clinician uses more than 1 method to reach the same diagnosis'
Predictive Validity - Accurately predicting outcomes
Implicit Bias - Clinicians may have pre-conceived ideas
STRENGTHS OF DSM-5
Good level of agreement for some disorders. Development of new criteria for PTSD.
Kim-Cohen et al. (2005) found that DSM has predictive validity for conduct disorders in children.
WEAKNESSES OF DSM-5
Issue of failing standards
Acceptable level of agreement has fallen, reducing reliability and validity.
Prone to cultural barriers, language barriers and miscommunication
Patients can choose to lie or withhold information from the clinician
Classification Systems: The ICD-10
Features:
It includes all diseases and disorders (physical and psychological), not just mental disorders. ICD-10 includes 10 groups of mental disorders, such as delusional disorders, mood disorders, clinical/personality disorders etc. It is bases its diagnoses around symptoms.
Each disorder has a code starting with ‘F’, listed consecutively and there are 11 sections.
Each section contains ‘leftover codes’ so new disorders can be added
Process:
Select key words from client interview relating to symptoms
Use alphabetical index
Locate sub-category
Weaknesses of ICD-10
Presentation, communication and interpretation of symptoms are shaped by language and culture.
Culture bias can lead to different diagnoses from physicians of different cultures.
Diagnostic practices and standards may differ internationally.
Nicholls et al. (2000) - neither the DSM or ICD-10 demonstrated good inter-rater reliability for children with eating disorders.
Strengths of ICD-10
PPV scores for schizophrenia increased from 68% in 1989 to 94.2% in 2003, showing high reliability of ICD.
Good predictive validity for schizophrenia.
APPLYING DIAGNOSTIC MANUALS (A02)
It's normal and healthy to grieve when a loved one dies. DSM-IV contains a "bereavement exclusion criterion" for Major Depressive Disorder. This meant that you couldn't be diagnosed as depressed if you had been bereaved (lost a loved one) up to 2 months ago. DSM-5 removes this exclusion, allowing for a grieving person to be diagnosed with a mental disorder.
EVALUATING DIAGNOSTIC MANUALS (A03)
Supporting Research:
Research by Rosenhan (1973) and Spitzer & Fleiss (1974) showed how important it was to make diagnosis more valid and reliable. Wilson (1993) suggests that DSM-III was developed precisely to tackle the unreliability of the previous systems.
There is evidence that the DSM is improving. Brown et al. (2001) tested the reliability of the DSM-IV. They studied anxiety and mood disorders in 326 out-patients in Boston, USA. The patients underwent two independent clinical interviews and there was high level agreement for most of the DSM-IV categories.
Opposing Research:
Normal grief being diagnosed as Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) because the bereavement exclusion criterion has been removed.
Forgetfulness in old age might be diagnosed as Mild Neurocognitive Disorder, leading to the "worried well" being diagnosed with dementia
Binge Eating Disorder will lead to a mental disorder being diagnosed for people who are just greedy. Behavioural Addiction is a diagnosis that be applied to anything we like doing a lot (like Pokemon Go).
This can create a lot of Type 1 errors, leading to unnecessary prescribing of medical drugs which is expensive and harmful.
Different Theory:
There has been found to be only a 68% agreement (Andrews et al, 1999) between the ICD-10 and DSM-IV on an assessment of 1500 patients. However, Andrews found agreement on diagnosis for depression, substance dependence and generalised anxiety.
Hoffman et al. (2015) compared DSM-5 and ICD-10 in a study of alcoholism among over 7000 prisoners. The two systems agreed in diagnosing healthy individuals and those with severe alcoholism. However, the diagnoses differed when it came to mild-to-moderate alcohol disorders. About a third of those with mild alcohol disorder according to DSM-5 received no diagnosis from ICD-10.
Application:
Patients increasingly self-diagnose using medical websites which are based on DSM-5
Diagnosis of Schizophrenia
DSM-5: The person must have at least 1 month of active symptoms and 6 months of disturbance to everyday functioning. Requires at least 2 of the 5 key symptoms.
ICD-10: Less focus on dysfunction and 6 months of disturbance is not necessary.
Brain damage/substance abuse could account for altered behaviour
Positive Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Additions to normal behaviour:
Delusions: Harmful fixed beliefs resistant to change
Hallucinations: Unrealistic perceptual experiences (sensory)
Thought Insertions: Believing thoughts are implanted by an external source
Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Absence of certain behaviours:
Disorganised thinking: Jumbled and unrelated thoughts leading to incoherent speech.
Flat Affect (Lack of emotion)
Mutism
Avolition (lack of goal-directed behaviour)
Nurture - Cultural Differences in Schizophrenia
Luhrmann et al. (2015) interviewed 60 American, Indian & Ghanaian people with schizophrenia
70% Americans heard destructive and harmful voices
50% Ghanaians heard mainly positive voices
20% of Ghanaians heard voices telling them to kill or fight
Indians tended to hear family members
Features of Schizophrenia
Onset slightly earlier in males than females
Prognosis is variable and hard to predict while only a minority recover
0.3-0.7% lifetime prevalence (uncommon)
Males have poorer prognosis than females, thus they suffer from a higher proportion of negative symptoms for a longer duration
Many participants show cognitive functioning deficits and mood abnormalities are common
Evaluation of Features & Symptoms of Schizophrenia
STRENGTHS:
Reliability - Schizophrenia diagnosis is highly consistent using DSM-5 & ICD-10. Sartorius et al. (1995) - Kappa value of 0.86
Detailed descriptors for reliable diagnosis
WEAKNESSES:
Hard to distinguish with other mental disorders
Accurate diagnosis requires awareness & sensitivity to cultural & linguistic differences
Biological Explanation of Schizophrenia
Desbonnet (2016) - ORIGINAL DOPAMINE HYPOTHESIS - HYPERDOPAMINERGIA
Found overactive dopamine D2 receptors in areas like the limbic system linked to positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
Negative schizophrenic symptoms can link to low functioning of dopamine D1 receptors in the PFC.
Causes of hyperdopaminergia:
Low levels of beta hydroxylase may build up excess dopamine in the synapse
Proliferation of D2 dopamine receptors in postsynaptic cells
Davis et al. (1991) - HYPODOPAMINERGIA
Positive symptoms - excess dopaminergic activity in the mesolimbic pathway
Negative Symptoms - lack of dopaminergic activity in the mesocortical pathway
Developmental Psychology:
Insel (2010) - schizophrenia stems from early abnormalities in brain development. Genetics overlap with other disorders.
Effect of Serotonin on Schizophrenia - CLOZAPINE
Clozapine binds to D1 & D4 receptors but weakly to D2.
Binds to serotonin receptors, greatly reducing positive & negative symptoms
Negative symptoms may be caused by irregular serotonin activity
Dopamine Dysregulation
Howes & Kapur (2009):
High presynaptic levels of dopamine can cause ‘psychosis proneness’ and not just schizophrenia
Dopamine dysregulation explains referential delusions and aberrant salience (can lead to hallucinations and delusions)
Evaluation Of Biological Explanation of Schizophrenia
STRENGTHS
Tenn et al. (2003): supported by research on rats treated with amphetamines
Rats given 9 amphetamine injections over 3 weeks showed various schizophrenic symptoms like social withdrawal, supporting original dopamine hypothesis
Snyder (1985): Support for D2 receptors
Chlorpromazine acts as an antagonist at many dopamine receptors and has an antipsychotic effect.
Haloperidol is a dopamine antagonist with a narrower range of biochemical effects.
Excess activity on D1 and D2 dopamine receptors can lead to development of schizophrenia
Application:
Atypical drugs and dopamine antagonists allow schizophrenic individuals to live in residential care.
Owens et al. (1978) found a higher density of D2 dopamine receptors in certain areas of the brain of schizophrenic patients
WEAKNESSES:
Dépatie & Lal (2001): apomorphine, a dopamine agonist that stimulates D2 receptors does not induce psychotic symptoms, showing how excess dopaminergic activity does not cause positive schizophrenia
Veling et al. (2008): Social stress can cause 2nd generation immigrants to be more prone to psychosis
Reductionist - only focuses on biological view
Unclear cause-and-effect explanation - Schizophrenia may cause chemical changes in the brain
One Other Biological Explanation of Schizophrenia - GENES
Hilker et al. (2018) - 79% heritability of schizophrenia
DiGeorge Syndrome - deletion of 30-40 neighbouring genes located on chromosome 22 has a 25% chance of developing schizophrenia
COMT Gene: COMT is an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the PFC, so the deletion of the COMT gene can cause schizophrenic symptoms due to poor dopamine regulation.
DISC1 Gene: Abnormality causes issues in the creation of GABA, a neurotransmitter that regulates glutamate and dopamine the limbic system, and people are 1.4 times more likely to develop schizophrenia (Kim et al. 2012).
Epigenetics: how genes are turned ‘on’ or ‘off’ by environmental stressors, which can change the way a genetic code is expressed, increasing vulnerability of developing schizophrenia.
Original Diathesis Stress Model: Genes are triggered by environmental factors. Stress was seen as a trigger for schizophrenia. Mil et al. (2006) found diagnosed MZ twins had up to 20% greater ‘methylation’ of 2 genes linked to schizophrenia.
Evaluation Of One Other Biological Explanation of Schizophrenia - GENES
STRENGTHS:
Empirical Support - Gottesman (1991) found a clear relationship between genetic similarity and an increase in 2 related individuals having schizophrenia.
Gottesman & Shields (1966) found a concordance rate of 42% for MZ twins and 9% for DZ twins.
Egan et al. (2001) proposed a link between hypodopaminergic activity in the PFC and 1 form of the COMT gene, which causes negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
Dahoun et al. (2017) reviewed 14 studies and found DISC1 gene was associated with presynaptic dopamine dysregulation.
Support for the original diathesis model: Tienari et al. (1994) found adopted children from schizophrenic biological mothers were more sensitive to family dysfunction compared to those from low-risked backgrounds, showing how social and environmental stressors can trigger genes for schizophrenia.
Heston (1966) found that the rate of schizophrenia to those with schizophrenic mothers was 10.6% compared to 0% in those not born to individuals with schizophrenia. This supports the influence of genes in schizophrenia and that inheritance also contributes to psycho-social disability.
Rosenthal (1963) - Quadruplets all developed schizophrenia but the girls also had a terrible social upbringing.
WEAKNESSES:
Other factors also increase risk of schizophrenia - Pederson & Mortensen (2006) demonstrated that the longer a person is exposed to urban life, the higher the risk of developing schizophrenia.
Culturally biased - most research is in Western countries
Reductionist theory - ignores social & cultural factors - concordance rate of MZ twins is not 100%
Deterministic - born with a gene suggests that inheriting schizophrenia is inevitable
One Non-Biological Explanation of Schizophrenia - SOCIAL FACTORS
Social Adversity - Basic human needs are not met by an individual. Eaton (1974) - city life is more stressful
Urbanicity - Increased competition & population density elicits schizophrenic symptoms. Lederbogen et al. (2011) found urban participants had greater activity in the amygdala and ACC compared to rural areas using fMRI scans, showing stress and emotional regulation is higher in urban participants.
Faris (1934) - Schizophrenia can cause social isolation, as the individual cuts off feedback from inappropriate thoughts or behaviours, causing strange behaviour.
Social Defeat Hypothesis - when a person or animal is exposed to hostile confrontations, causing high stress which increases the risk of schizophrenia.
The risk of first and second-generation immigrants having schizophrenia decreases as the number of people from the same ethnic background increases.
Evaluation Of One Non-Biological Explanation of Schizophrenia - SOCIAL FACTORS
STRENGTHS:
Support for social causation hypothesis: Vassos et al. (2012) performed a meta-analysis of data from 4 studies conducted in Sweden, Netherlands, and Denmark, consisting for 24,000 schizophrenia cases and found risk of schizophrenia was 2.37 times higher in urban than rural settings.
Veling et al. (2010) - Weak ethnic identity increases risk of developing schizophrenia.
Application - Importance of housing projects that encourage neighbourhood cohesion & cultural diversity.
Support for Social Defeat Hypothesis - Selten & Cantor-Graae (2005) → Studies with rats showed that when a male rat (intruder) is placed into another rat’s cage (resident), the resident generally attacked the intruder (outgroup). The intruder showed signs of submission and an increase of dopamine activity in the brain’s mesolimbic system which is linked to positive symptoms of schizophrenia
WEAKNESSES:
DIATHESIS STRESS MODEL: Environmental factors only trigger the onset of schizophrenia for people already genetically predisposed.
Meta-analysis data is only correction, and cannot provide a cause-and-effect explanation
Competing Argument → Schizophrenia may lead to urbanicity. The social drift hypothesis suggests schizophrenic individuals ‘drift’ into a lower social class than their family, causing migration to deprived inner-city areas.
One Biological Treatment
Typical Antipsychotics (FGAs):
Chlorpromazine is a dopamine antagonist that greatly reduces positive symptoms by blocking postsynaptic dopamine receptors.
Barlow & Durand (1995) - 40% of schizophrenic patients do not gain relief and still experienced negative symptoms. Side effects like tardive dyskinesia can cause relapse.
Other Side Effects:
Dryness of Mouth
Weight Gain
Drooling
Atypical Antipsychotics (SGAs):
Clozapine blocks dopamine, serotonin and glutamate receptors (antagonistic effect), reducing both positive and negative symptoms.
Lally & MacCabe (2015) - Provides relief for 60% but has fatal side effect of agranulocytosis.
Pickar et al. (1992) - Clozapine was the most effective in treating symptoms, even in patients who previously did not respond to treatment. More effective than placebo drug.
Risperidone - more recent SGA that binds stronger to dopamine receptors with less side effects.
TGAs:
Glutamate agonists
Trials: 118 schizophrenic people, 4 week double-blind trial. Random allocation to 3 conditions:
40 mg twice daily of new TGA
15mg of a SGA
Placebo
Both new TGA and SGA showed superior response rates compared to placebo.
Individual Differences: Texas Medication Algorithm Project (TMAP)
STAGES
Risperidone
Different SGA/FGA
Clozapine
Different combinations of FGAs and SGAs along with mood-stabilising drugs.
ECT shocks to non-dominant hemisphere of the brain
Patel et al. (2014) - Medication use should be early for higher effectiveness. Maintenance dosage should be maintained for 12 months after remission to prevent relapse (only 18-32% schizophrenic patients relapsed after taking maintenance dosage).
Evaluation Of One Biological Treatment
STRENGTHS:
Zhao et al. (2016) used a large meta-analysis and found 17 antipsychotics tested had significantly lower relapse rates than the placebo. This shows drug treatments are cheap and effective if medicine fails.
Application: Antipsychotics allow schizophrenic people to remain in the community and live normal lives without being institutionalised.
Drugs allow the patient to take on social treatments as well.
WEAKNESSES:
Patel found only 20% of schizophrenic patients showed consistent improvement after multiple FGA trials whilst 45% experienced partial improvement with severe side effects.
Drugs only suppress the symptoms
Drugs can be seen as a form of social control
One Non-Biological Treatment
Cognitive-Behavioural Treatment: 5-20 sessions in groups or individually.
Aim: CBT helps to change the way clients think, behave, and focuses on the present problems and difficulties to improve the client’s state of mind. CBT helps clients identify irrational thoughts & delusions, and change them. Changing negative thoughts can lead to improvements in behaviour and feelings.
Process: Therapist encourages self-awareness in clients so that they can recognise specific situations to precede decompensation (decline of normal functioning to psychosis). Stress management and coping strategies are used. The therapist may draw diagrams to show the clients the link between their thinking, behaviour, and emotions.
Verbally challenging the clients’ perceived reality through a recording.
Evidence is then discussed so their delusions can be debunked.
The course of CBT is very organised - 20 one-hour sessions with goals and plans discussed
EXAMPLE - Combs et al. (2007): LN
LN was hospitalised for aggressive behaviour out of the delusion that social services were stealing from her. This was based on getting several phone calls where the caller immediately hung up and seeing people in the shared carpark. This was debunked when a family member helped find 3 missing items.
Evaluation Of One Non-Biological Treatment
STRENGTHS:
NICE (2014) - A meta-analysis of CBT studies found that CBT was effective in reducing re-hospitalisation for up to 18 months and time spent in hospitals. CBT also reduced symptom severity and improved psychosocial functioning 12 months after treatment.
NICE (2004) - CBT caused a reduction in positive and negative symptoms
Kuipers et al. (1997) - conducted a randomised control trial on CBT & found drug-resistant clients improved when given CBT which targeted delusions and hallucinations.
Bradshaw (1998) - Carol benefited from CBT.
Lack of side effects
WEAKNESSES:
CBT overlooks individual differences - Bradshaw (1998) found that relationship between client and therapist was also important for the journey to self-recovery.
McKenna & Kingdon (2014) - CBT was only superior to routine treatment in 2/9 trials.
Challenging client’s delusions can be distressing - requires sharing unpleasant thoughts and feelings.
CBT requires commitment - participants may drop out
Classic Study: Rosenhan (1973)
Aim: To reveal deep flaws in process of psychiatric diagnosis by providing evidence to support the idea that mental disorders are subjectively determined by the person making the diagnosis.
Procedure:
3 males and 5 females as pseudopatients who complained of the same symptom at a psychiatric hospital
They claimed to hear same-sex, unfamiliar voice that said ‘empty’ and ‘hollow’ terms
12 hospitals in 5 states in the East and West coast
Pseudopatients proved they were sane by cooperating with staff and socialising with other patients
Pseudopatients then asked the staff about their release
Findings:
Initial study:
7 diagnosed with schizophrenia and 1 with bipolar disorder
19 day average hospitalisation
30% of patients voiced suspicion on pseudopatients
Follow-Up Study:
At least 1 member of staff wrongly reported 41/193 were fake.
Slater (2005) replica in 9 psychiatric wards was diagnosed with psychotic depression, which was later disagreed upon by many psychiatrists, showing how Rosenhan’s claims were not era-bound.
Conclusion:
Hospital environment created a set of situational factors that led to depersonalisation & segregation
Self-fulfilling prophecies
Evaluation Of Classic Study: Rosenhan (1973)
STRENGTHS:
Covert Observation allowed for quantitative and qualitative data to be collected
High ecological validity
WEAKNESSES:
Only 1 pseudopatient per hospital and pseudopatients only recorded negative interactions.
Clinicians were made to feel incompetent and real patients were discriminated against
Contemporary Study: Carlsson et al. (2000)
Aims: Biological Explanation of Schizophrenia
To provide an up-to-date review of current status of dopamine hypothesis
To test the effect of other neurotransmitters: Glutamate, serotonin & GABA
Research for new antipsychotics
Procedure:
Carlsson explains evidence from PET/SPECT that supports the Dopamine Hypothesis (dopaminergic dysfunction):
Findings:
Schizophrenic participants show more dopamine activity than a healthy control group, especially in a part of the brain called the basal ganglia
However, Laruelle et al. (1999) found that schizophrenia patients in remission (not showing symptoms) only had normal dopamine activity
Carlsson et al. point out the patients taking antipsychotics complain most about the side-effects while their symptoms are in remission - not surprising if their dopamine activity becomes normal during this time and the drugs are causing hypodopaminergia (too little dopamine)
Carlsson et al. focus on glutamate for two reasons:
Drugs like PCP ("angel dust") and ketamine produce psychotic symptoms, but instead of activating dopamine they stimulate glutamate receptors called NMDA
Lodge et al. (1989) claim glutamate activity at NMDA receptors produces psychotic reactions (it is "psychotogenic") in rats and humans
Low levels of glutamate (hypoglutamatergia) seems to link with both positive and negative schizophrenic symptoms. Carlsson found that hypoglutamatergia in the basal ganglia (reward centre) leads to positive symptoms and hypoglutamatergia in the cerebral cortex leads to negative symptoms (which includes the frontal lobe, where conscious behaviour happens).
The "treatment resistant" patients who don't respond to typical antipsychotics (that reduce dopamine) might have a more glutamatergic condition instead
Clozapine is an atypical antipsychotic that has better results with "treatment resistant" patients and this might be because it doesn't target dopamine (it targets serotonin instead)
Glutamate regulates dopamine activity
Miller & Abercrombie (1996) - increased dopamine is caused by reduction of glutamate
Conclusion: Carlsson suspects there are probably different groups of schizophrenia patients ("subpopulations") whose symptoms have different biological explanations - not always the Dopamine Hypothesis. There may be a subpopulation suffering from glutamatergic deficiency and these deserve "special attention". Lack of glutamate might cause patients to have an exaggerated response to dopamine at the post-synapse.
Evaluation Of Contemporary Study: Carlsson et al. (2000)
STRENGTHS:
Representative selection of PET studies makes research reliable and replicable (highly standardised).
Development of new antipsychotic drugs that focus on serotonin and glutamate
No ethical issues
WEAKNESSES:
Time-locked → His review of studies is not generalisable to modern society and research.
Evidence for dopamine hypothesis was based on acute schizophrenia but people with chronic schizophrenia may respond differently to drugs.
Research Methods
Case Study: Lavarenne et al. (2013)
Aim:
Previous research suggests that psychosis results from weak ego boundaries.
This study study attempts to investigate how out-patients use group sessions to provide firm boundaries which support them during their illness, to develop a feeling of connectedness.
To explore some of the group's core therapeutic actions against psychosis.
Examples of weak ego boundaries include
–a person fearing that they will break apart
–be annihilated
–wishing to be a part of someone else.
Procedure:
a single session of out-patient group therapy
six individuals with schizophrenia or schizoaffective illness
sessions usually had 10 members but only six attended the 45 minute session which was led by the three researchers
sessions were not recorded whilst a coding system recorded emotions, thoughts/behaviours.
Findings:
The six members of the group all had fragile ego boundaries, expressed in various different ways
EARL:
Description: Rejected Christmas gifts from Brett.
Interpretation: Earl has an underlying fear of being annihilated (self-disintegration) and accepting the gift may have triggered fragmentation fears.
Description: Showed grandiose, delusional ideas about a large-scale multinational engineering project.
Interpretation: The delusion is holding the fragmented pieces of Earl’s self together, so symbolises a boundary between Earl’s self and the selves of others. He may also wish to merge his identity with his father.
DAN:
Description: The previous evening had ‘an out-of-body experience and was very scared’ he would not be able to get his ‘spirit back into his body’.
Interpretation: He felt his Ego boundary to be very fragile during this frightening experience.
Description: Showed the group burns on his arms he had got from being distracted while cooking. He was currently trying to cope with a change in nature of his relationship with his girlfriend (a former fiancée).
Interpretation: He felt his Ego boundary to be extremely fragile and was asking for the boundaries of his relationship to be clearly defined.
Conclusions:
each group member struggles daily with the environmental, social, and biological factors in their schizophrenia
sessions enable development of stronger Ego defences for each member through object relations, which enables a relationship between ‘self’ and ‘others’ to form
Researchers saw their role as allies to the patients and that the group can serve as a buffer to prevent psychological crises which may lead to subsequent breakdown and rehospitalisation
All group members were working hard to hold themselves together
Impressive tolerance, acceptance and containment from group members
Group Therapy enabled group members to wrestle with their fragile egos and foster psychological growth
Interview: Vallentine et al. (2010)
Aim:
To determine the usefulness of group psychoeducation for offenders in a high security forensic psychiatric hospital.
Predictions; offenders will
Oshow improvements in general well-being and mental state
Odescribe benefits with regards their level of understanding and willingness to comply with other suggested treatments
Procedure:
42 male patients were referred to the ‘Understanding Mental Illness’ (UMI) group
Four 20-session UMI groups run over a period of 3 years
Findings:
CORE-OM and SCQ indicated no significant differences between pre- and post-group scores.
Individual patients did show “clinically significant change” on the CORE-OM
OSubjective well-being (N = 5)
OProblems/Symptoms (N = 5)
OSocial/life function (N = 6)
ORisk (N = 3).
Two Pps showed clinical significant change on the SCQ.
Only one Pp showed reliable change on the subjective well-being scale of the CORE-OM.
On the SCQ nearly half (N = 5) achieved significant reliable change
More than half of the participants showed a positive shift in scores
A proportion of participants demonstrated no change from pre to post scoring.
Some achieved a higher score reflecting a negative shift.
Two Pps reported negative reliable significant change.
Similar to the CORE-OM, over 50% of the participants also reported an improvement in self-esteem, with some reporting no change or a decrease in self-esteem; one participant reported negative reliable significant change.
Conclusions:
Important feedback on what was helpful and difficult and this has been acted on for future groups
Future research could investigate the type of information given to patients at first diagnosis and throughout their treatment.
Offender patients have an identified need for information; this was universally endorsed by participants.
Helpful in designing useful ways of relaying information to patients at various stages of their admission.
Development and distribution of easy reference handouts for patients to refer back to might be of benefit in the retention of information.
Limited positive change on qualitative measures and problems with retention of the information was highlighted by patients in post-group interviews, and suggests a need for future booster sessions or further therapy work in this area (e.g. CBT for psychosis) for this client group.
Feedback from patients emphasised the positive impact of the intervention on their sense of agency and empowerment.
Future research should focus on identifying the most effective way of targeting those patients who will benefit positively from this group and ways of relaying the information in a user-friendly format
Clinical Psych Key Question
‘How do Schizophrenia and Unipolar Depression overlap in societies?’
Schizophrenia is a psychotic disorder characterised by positive symptoms (delusions, hallucinations, disordered thoughts, and speech) and negative symptoms (lack of emotion and speech difficulties). Unipolar depression is an affective disorder characterised by low mood, loss of interest or enjoyment, and fatigue, and must be experienced for more than 2 weeks.
There is an overlap between certain negative symptoms of schizophrenia and depressive symptoms. In schizophrenia, negative symptoms are the absence of certain behaviors like disorganised thinking and flat affect, where individuals suffer from a lack of emotion and goal-directed behavior. This is similar to cognitive symptoms of unipolar depression where individuals suffer from self-deprecating, suicidal thoughts, and a lack of self-confidence, increasing the risk of developing other mental disorders. This is important because this suggests that schizophrenia and depression might be hard to distinguish, so proper classification systems like the ICD-10 and DSM-5 are necessary for accurate diagnoses. Understanding and providing support for symptoms can reduce stigmatisation. However, Chemerinski et al. (2008) found a link between depressive symptoms in elderly schizophrenic patients, suggesting that there is an overlap between both mental health disorders.
Furthermore, there might also be similar causal factors between depression and schizophrenia. Social adversity is when basic human needs like nutrition, shelter, warmth, and intellectual, and emotional support are not met, causing social withdrawal. Lower socio-economic families suffering from unemployment may be more vulnerable to schizophrenia and depression because of stress. Wicks et al. (2005) and Björkenstam (2017) found a higher prevalence of developing schizophrenia and depression if there was social adversity present in childhood. This shows how an environment that is high in stress can increase the risk of obtaining mental health disorders.
Schizophrenia and depressive symptoms have common features. The onset of schizophrenia is earlier in males than females and the prognosis is variable and hard to predict so only a minority recover. Depression is also highly prevalent, as 5% of the world’s population suffers from affective disorder, and hard to distinguish. Society could benefit from tailoring mental health services to account for these gender-based differences, ensuring treatment resources like CBT are equitably distributed, and increasing accessibility. However, researchers in Ethiopia found that roughly one in four and one in five patients (23.71%) with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, respectively, were misdiagnosed whilst depressive disorder was also commonly misdiagnosed half the time. This suggests that proper clinical interviews are necessary so that the overlap of negative symptoms does not lead to misdiagnosis. Early, comprehensive treatment is most effective for reducing symptoms and enhancing quality of life.
It is also important to note that there are some differences between depression and schizophrenia as they do not overlap genetically. Depression is caused by the monoamine depletion hypothesis. Schildkraut (1965) suggested abnormally low levels of monoamine neurotransmitters cannot regulate the functions of the amygdala, hypothalamus, and limbic system, which are important emotional and reward centers. Coppen (1967) found a link between low levels of serotonin and depression. Whereas, schizophrenia is mainly caused by inheritance as Hilker et al. (2018) found a recent estimate of the heritability of schizophrenia to be 79% whilst Wright (2014) indicated that over 700 genes are linked to the psychotic disorder. This shows how deletion of the COMT gene and abnormality of the DISC1 gene are more important in developing schizophrenia whereas depression is developed by a lack of monoamine neurotransmitters and BDNF.
Lastly, schizophrenia and unipolar depression also differ in treatments. Antipsychotics are used to treat schizophrenia because they act as antagonists by reducing the action of neurotransmitters. Chlorpromazine, a typical antipsychotic and dopamine antagonist, greatly reduces positive schizophrenic symptoms by blocking postsynaptic dopamine receptors, allowing the regulation of dopamine levels. Whereas, antidepressants work to increase the availability of serotonin, dopamine, and cortisol in the brain. For instance, monoamine oxidase inhibitors block the enzyme monoamine oxidase from breaking down neurotransmitters, allowing an increase in mood after reuptake. Therefore, schizophrenia and depression are also treated differently in society.
Overall, although there are many overlaps in terms of the causes and symptoms of schizophrenia and depression, they differ in genetics and treatment.