Chapters 1-3
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Pharmacology is the study of
drugs and their interactions with living organisms
pharmacotherapy is the use of medications to treat
different disease states
pharmacodynamics is the study of action of drugs on
living organisms
pharmacokinetics is the study of
what the body does to the drug
what does pharmacokinetics measure
the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of drug from the body
Toxicology is the study of
harmful effects of drugs on living tissues
Dental hygienists are typically the first to gather and evaluate
medication list and med history
T/F In ohio we can administer local anesthesia and nitrous oxide sedation
true
what should we know and understand to be able to explain to our patients ab medications
antibiotics (allergy concerns)
Fluoride (in office and prescriptions)
Pain meds (abuse concern)
Emergency drugs
Alterations of appointments involve
time of day, length of app, and positioning of pts
what are the treatment modifications
limit / no vasoconstrictors, evaluate bleeding, antibiotic prophylaxis
drug investigation process includes the (what names)
code name or chemical name
What is the trade name
a name given by a pharmaceutical company that created the drug
is the trade name capitalized or not capital
capitalized
how long is the trade name protected by the federal patent law
20 yrs
what is the generic name
the official name determined by the US adopted name council
is the generic name capitalized?
no
what do regulatory agencies do?
they grant approvals for drugs to be marketed after being deemed of safe and effective
what does the US food and drug administration determine ab a drug
if it is over the counter or prescription
what does the US federal trade commission do
regulate trade practices and prohibit false advertisment
What does the US Drug Enforcement Administration Regulate?
manufacturing and distribution of substances that may be abused
clinical testing phase I purpose
biological effect, metabolism, safe dose range, and toxic effects
clinical testing phase II purpose
test effectiveness
clinical testing phase III purpose
safety and efficacy demonstrated, dosage determined
clinical testing phase IV purpose
reporting of adverse reactions
scheduled drugs II-IV require
Rx
package inserts includes
information about the drug- chemical makeup, (contra)indications for use, warnings, adverse reactions, drug interactions, dose, administration
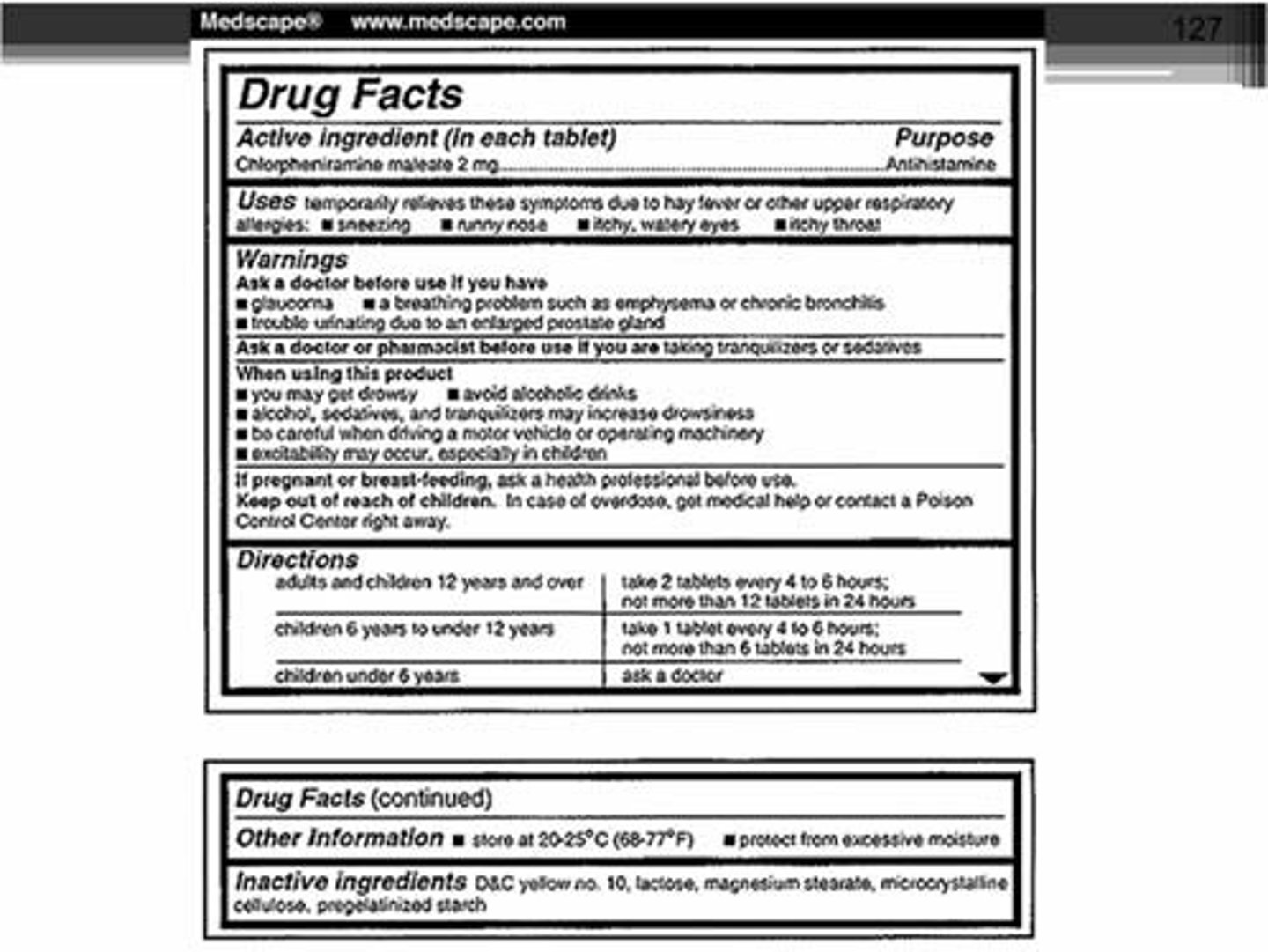
black box warning
serious safety concerns

drug recall is when there is a probability of
serious adverse effects
a drug is a biologically active substance that can modify
cellular function
what part of the cell interacts with the molecule and causes a chain of events
the receptor
Agonist
"perfect fit" full bind to receptor
antagonist
partially binds to receptor and prevents agonists from binding
partial agonist
partially binds to receptor and produced small response, prevents others
effective dose 50% is the dose required to produce
50% of maximal effect
Toxic dose 50% is the dose required to produce
50% of toxic effect
whats the therapeutic index
the safety zone of a drug
potency is the
amount of drug needed to produce an effect
effiicacy is the
maximum intensity of effect of a drug regardless of dose
what is the onset
the time it takes for the drug to have an effect
what is the duration
length of time the effect lasts
what does ADME stand for
absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion
Absorption is the process by which:
drugs are transferred from site of administration to the circulation (blood)
where are drugs usually absorbed
the small intestines
distribution is the passage of drugs from
blood stream to various body systems
metabolism is the
breakdown of the drug for easy excretion
where do drugs usually get metabolized (first pass)
in the liver
excretion is the _________of the drug
removal
what organ assists in removing the drug and how
kidneys and usually removed through urine
what are some factors that alter drug effects
patient adherence, tolerance, time of administration, sex, genetic variations, drug interactions, age/weight, environment
what does enteral mean
goes directly to GI tract (orally or rectally)
what does parenteral mean
bypasses the GI tract (inhalation, injection, topical)
disruption is the
initial breakdown of the outer shell/coating
Disintegration
breakdown of contents of tablet/capsule
Dispersion
concentrated drug is spread throughout the stomach/intestines
Dissolution
drug is dissolved in GI fluid
advantages of IV (injections)
most rapid response, more predictable blood vessles
advantages of intramuscular injection
long lasting effect, good absorption due to vascularity if skeletal muscles
examples of subcutaneous injections
insulin, LA's
what is intradermal injection and whats an example
into dermis of the skin, ex. TB test
inhalation causes a
rapid delivery
how are topicals used
applied to body surface
where are topicals most effective
in non-keratinized areas
an adverse drug reaction is a response to a drug that is
not desired, potentially harmful and occurs at therapeutic doses
toxic reaction is when the desired effect on the target organ is
excessive
side effect is the dose related effect on
a non targeted organ
idiosyncratic reaction is __________ related abnormal drug response
genetically
drug allergy is the
immunologic response resulting in rash or anaphylaxis
an interference with natural defense mechanism reduce the bodys ability to
fight infection
common oral side effects of drugs
gingival overgrowth, bleeding, xerostomia, or medication related osteonecrosis of the jaw