Chemistry I Lesson 11: Solubility
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
CRB The van't Hoff factor (or ionizability factor i) tells you how many ions one molecule of a compound will produce in water. What is the van't Hoff factor for NH4I?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 5
(D) 6
(B) 2
In water, NH4I will dissociate into ammonium (NH4+) and iodide (I-).
CRB Which of the following statements about electrolytes are correct?
I. Strong electrolytes are solutes that will dissociate completely in a solvent and will dissolve.
II. Weak electrolytes may remain ion-paired to some extent.
III. Non-electrolytes are covalent compounds that do not dissociate into ions.
(A) II only
(B) I and III only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(C) II and III only
Strong electrolytes will dissociate completely, but do not necessarily have to be soluble. All ionic compounds are strong electrolytes.
Weak electrolytes may remain ion-paired to some extent and nonelectrolytes are covalent compounds that do not dissociate into ions.
How does Ksp relate to other equilibrium constants?
They are very similar! :)
The key difference is that, because the solvent is a liquid, it does not need to be considered in the calculations.
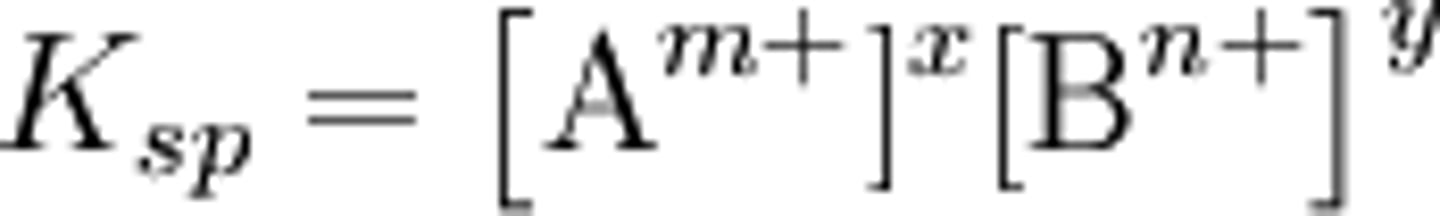
CRB Other equilibrium constants tend to follow the mass-action ratio. Write out this ratio of products and reactants that is equal to Keq or Q (if the reactants and products are not at equilibrium).
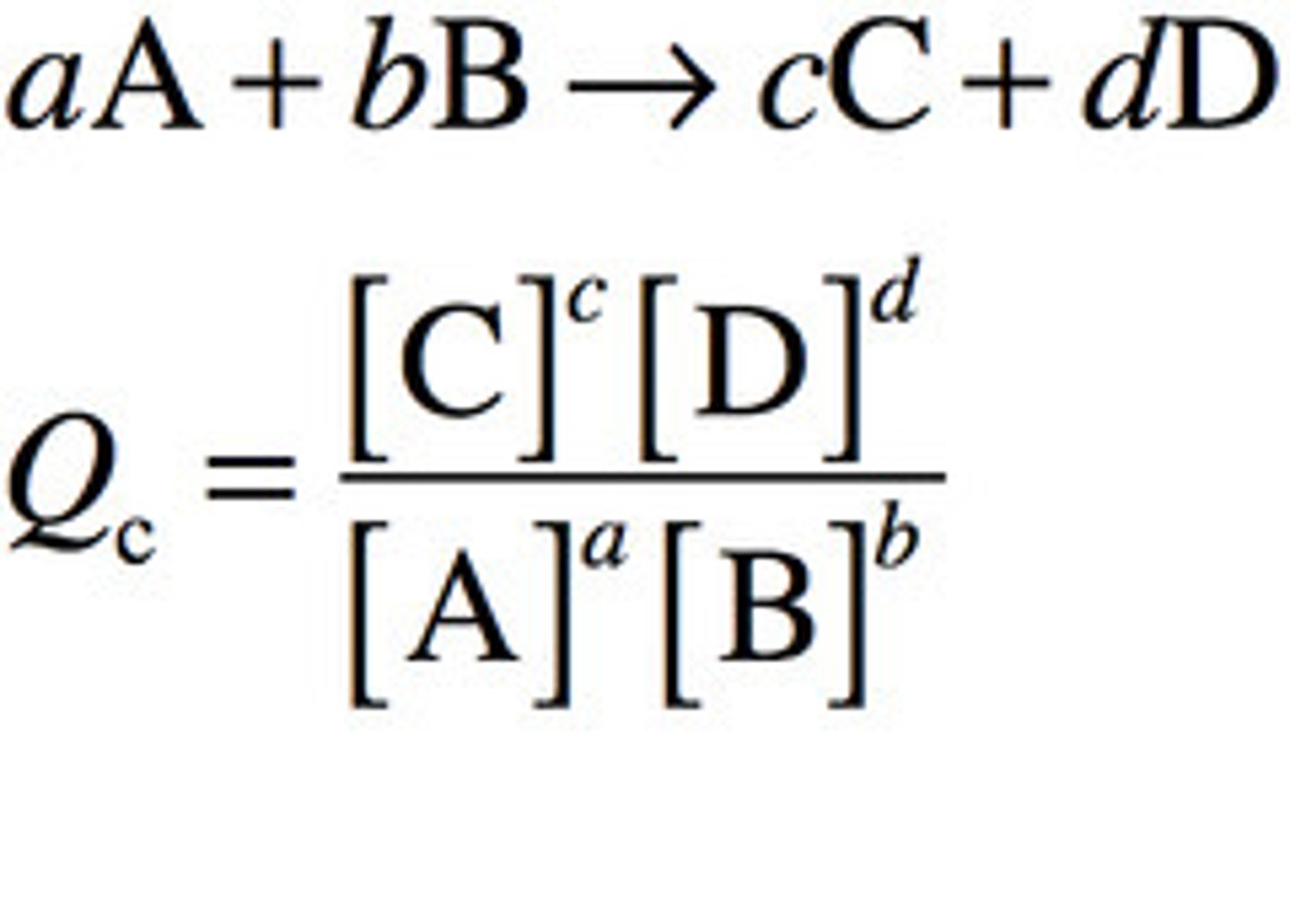
CRB In the previous question, which of the following is the proper name of Q, which represents mass-action ratio not at equilibrium?
(A) Pre-equilibrium factor
(B) Equilibrium factor
(C) Reaction quotient
(D) Reaction ratio
(C) Reaction quotient

CRB Given that the ion product, Qsp, is less than Ksp, which of the following will occur?
(A) More salt will dissolve
(B) No net change in salt dissolving
(C) Less salt will dissolve
(D) Not enough information given
(A) More salt will dissolve
Qsp and Ksp have the same relationship as Q and Keq. If there are less products than the equilibrium suggests should exist (Qsp << Ksp), then more products will form (i.e. salt will dissolve).
CRB True or false? It is not possible to have an ion product that is greater than the Ksp.
False. When the ion product is greater than the Ksp, then the solution is said to be "supersaturated". This often happens by dissolving a solute in a hot solvent and then cooling the solvent.

Calculate the Ksp of PbCl2 (MM = 278.1) assuming that .14 grams of PbCl2 enters solution upon addition of 14.98 grams of PbCl2 to 147 mL of water?
(A) 3.54 ⋅ 10^-9
(B) 7.98 ⋅ 10^-8
(C) 1.60 ⋅ 10^-7
(D) 3.45 ⋅ 10^-6
(C) 1.60 ⋅ 10^-7
.14 grams PbCl2 ⋅ 1 mol PbCl2 / 278.1 g PbCl2 = approx. 5⋅10^-4 moles PbCl2 (actual: 5.03 ⋅ 10^-4)
5 ⋅ 10^-4 moles / .147 L = approx. 3.5 ⋅ 10^-3 M PbCl2 (actual: 3.42 ⋅ 10^-3)
[Pb2+] = approx. 3.5 ⋅ 10^-3 M
[Cl-] = approx. 7 ⋅ 10^-3 M
Ksp = [Pb2+][Cl-]^2
Ksp = (3.5 ⋅ 10^-3)(7 ⋅ 10^-3)^2
Ksp = approx. 1.75 ⋅ 10^-7 (actual: 1.60 ⋅ 10^-7)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
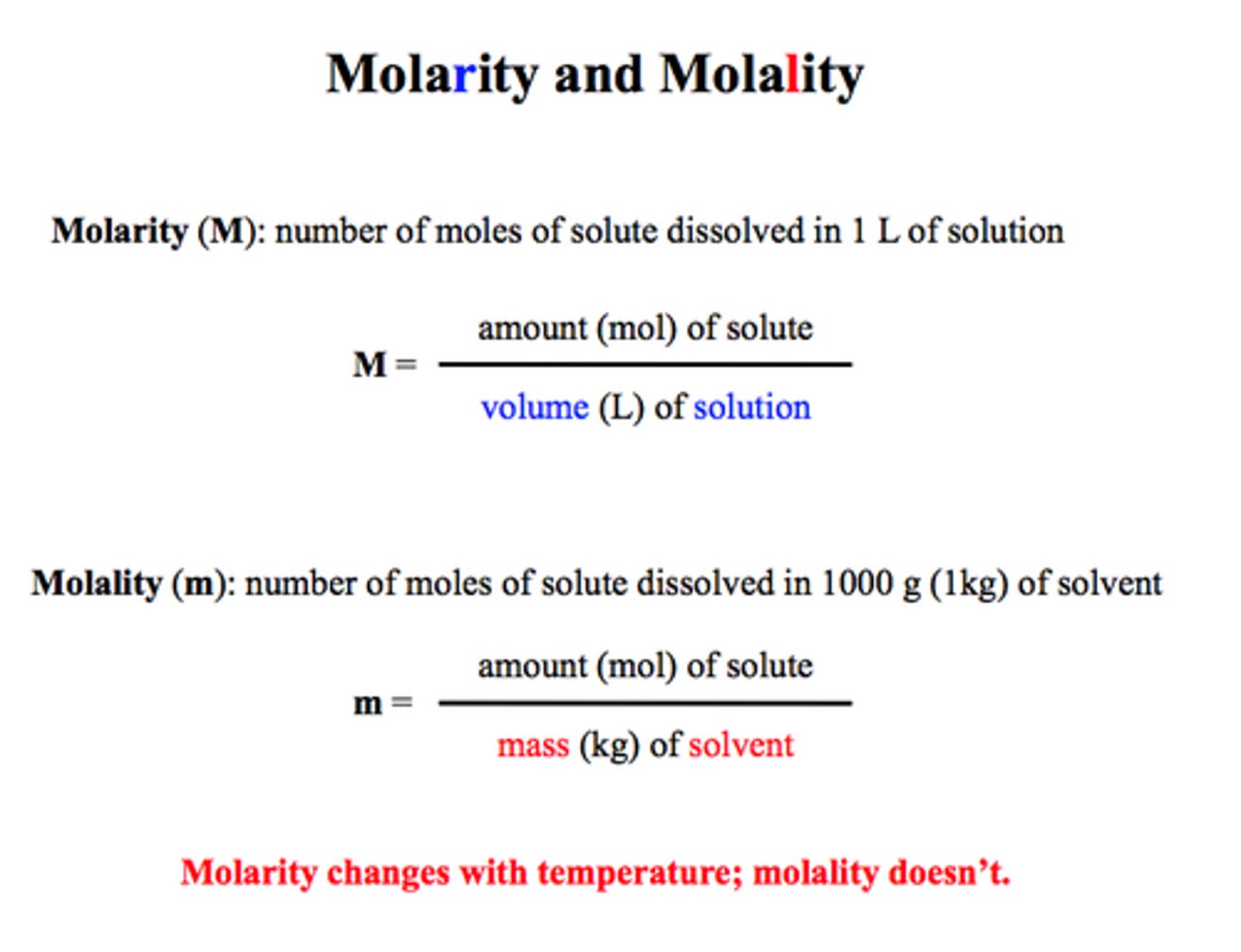
CRB Two common methods of defining the amount of solute in a solvent are molarity (M) and molality (m). Write out the definitions (equations) for each.
What is the concentration of Cu2+ at equillibrium upon the addition of Cu(OH)2 (Ksp = 2.2 ⋅ 10^-20)?
(A) 1.8 ⋅ 10^-7 M
(B) 6.9 ⋅ 10^-7 M
(C) 1.8 ⋅ 10^-8 M
(D) 6.9 ⋅ 10^-8 M
(A) 1.8 ⋅ 10^-7 M
Ksp = [Cu2+][OH-]^2
2.2 ⋅ 10^-20 = x * ^(2x)^2
2.2 ⋅ 10^-20 = 4x^3
approx. 5 ⋅ 10^-21 = x^3
x = approx. 2 ⋅ 10^-7 (actual: 1.8 ⋅ 10^-7)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
Which will dissolve to the greatest extent?
(A) PbCl2 (Ksp = 1.60 ⋅ 10^-5) added to a solution of KCl
(B) PbCl2 (Ksp = 1.60 ⋅ 10^-5) added to a solution of NaOH
(C) Cu2OH (Ksp = 2.2 ⋅ 10^-20) added to a solution of KCl
(D) Cu2OH (Ksp = 2.2 ⋅ 10^-20) added to a solution of NaOH
(B) PbCl2 (Ksp = 1.60 ⋅ 10^-5) added to a solution of NaOH
PbCl2 will dissolve more than Cu2OH because it has a greater Ksp value. PbCl2 being added to a solution of NaOH will dissolve more than being added to a solution of KCl because the extra Cl- in the solution will push the dissolution reaction backwards (recall the common ion effect).
CRB In the previous card, the common ion effect prevented some of the PbCl2 from dissolving. Removing Cl- from the solution would increase the solubility of PbCl2, pushing the reaction to the right, in accordance with which of the following?
(A) Hund's rule
(B) Le Chatelier's principle
(C) Huckel's rule
(D) Dalton's law
(B) Le Chatelier's principle
Le Chatelier's principle states that a system at equilibrium will try to neutralize the effects of change. Therefore, the initial removing Cl- would make more Cl- dissolve to mitigate the effects of the initial removing.
CRB Suppose that a partially soluble salt dissolving is exothermic. According to Le Chatelier's principle, which of the following would happen if the mixture was heated?
(A) There is no observable change of the salt
(B) There is net dissolving of the salt
(C) There is a net precipitation of the salt
(D) Not enough information is given
(C) There is a net precipitation of the salt
Because heat was added, the system will want to remove heat. If the salt dissolving was exothermic, then the salt precipitating would need to be endothermic and would occur.
PbCl2 (Ksp = 1.60 ⋅ 10^-5) is added to a 8.79 ⋅ 10^-2 M solution of KCl. What is the final concentration of Pb2+?
(A) .00021 M
(B) .0021 M
(C) .021 M
(D) .21 M
(B) .0021 M
Ksp = [Pb2+][Cl-]
1.60 ⋅ 10^-5 = (x)(8.79 ⋅ 10^-2 + 2x)^2 but 2x can be approximated as 0 as compared to the concentration of Cl-:
1.60 ⋅ 10^-5 = (x)(8.79 ⋅ 10^-2)^2
1.60 ⋅ 10^-5 = (x)(approx. 81 ⋅ 10^-4)
(1.6 ⋅ 10^-5)/(8.1 ⋅ 10^-3) = x
x = approx. .2 ⋅ 10^-2 M (actual: .21 ⋅ 10^-2 M)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
Does adding H+ to a solution of CaF2 result greater or less solubility of CaF2? Why?
Increased solubility because F- reacts with the H+, causing the solubility reaction to move forward according to Le Chatelier's principle (removing products).
Does adding NH3 to a solution of AgCl result greater or less solubility of AgCl? Why?
Increased solubility because NH3 reacts with the Ag to form a complex ion, causing the solubility reaction to move forward according to Le Chatelier's principle.
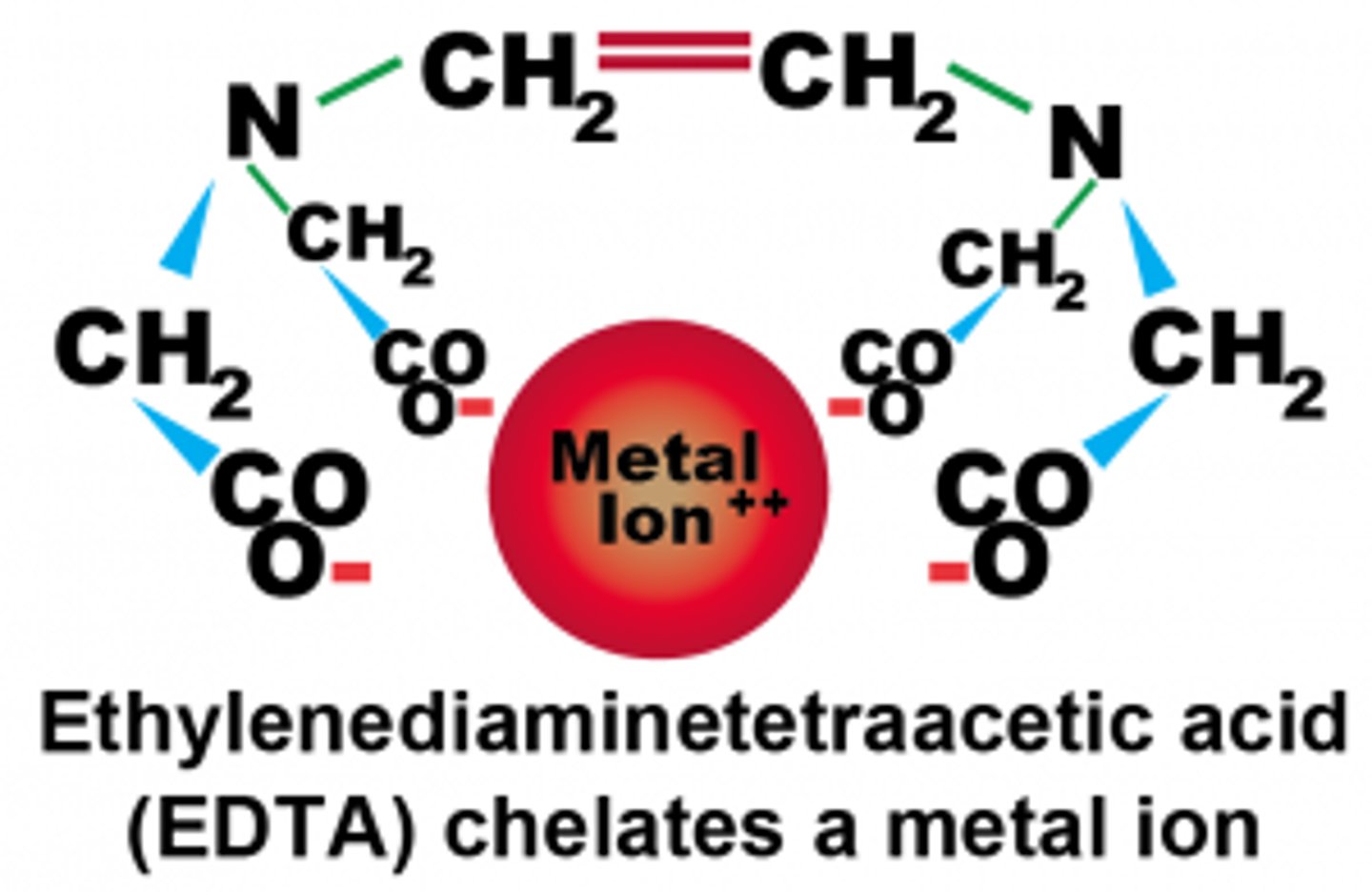
CRB In some complex ions, the central cation can bind to the same ligand in multiple places. A therapy based on this process is used to sequester toxic metals in the body. What is this process called?
(A) Coordination
(B) Chelation
(C) Association
(D) Complexing
(B) Chelation
Chelation is when a central cation can bind to the same ligand in multiple places, and often requires large organic ligands that could double back to interact with the central cation another time.
CRB Solutions are often thought of strictly as involving liquids as the solvent. Which of the following is the general term for a solution of a solid in a solid?
(A) Solenoid
(B) Colloids
(C) Ore
(D) Alloy
(D) Alloy
The majority of elements that are solids at common temperatures are metals. On a side note, ore is more of a mixture because the different compounds can be extracted rather easily, not truly being dissolved.

CRB Solutions can also have physical properties that do not depend on the chemical identity of the dissolved particles, but rather the amount of particles dissolved. What are these properties called?
(A) Amorphous properties
(B) Colligative properties
(C) Phase-dependent properties
(D) State-dependent properties
(B) Colligative properties
Colligative properties do not depend on the chemical identity of the dissolved particles, but rather the amount of particles dissolved.

CRB Which of the following is NOT a colligative property?
(A) Vapor pressure depression
(B) Boiling point depression
(C) Freezing point depression
(D) Osmotic pressure
(B) Boiling point depression
Colligative properties to know are: vapor pressure depression, boiling point ELEVATION, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure.
CRB Of the following colligative properties, which of the following does NOT have the van't Hoff factor in its equation?
(A) Vapor pressure depression
(B) Boiling point elevation
(C) Freezing point depression
(D) Osmotic pressure
(A) Vapor pressure depression
Vapor pressure depression is actually modeled by Raoult's law, which states PA = XA * PAo.
PA = Vapor pressure of solvent A when solutes are present
XA = Mole fraction of solvent A
PAo = Vapor pressure of solvent A in its pure state
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/