The biological impact of climate change
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
temperature coefficient (Q10)
a coefficient showing the effect of temperature on the rate of a reaction
Q10 = rate at higher temperature rate at lower temperature
what is optimum temperature
the temperature at which an enzyme works most efficiently
denature
to cause permanent changes in a protein by too high a temperature
effect of lower temperatures on enzymes
Lower temperatures either prevent reactions from proceeding or slow them down
Molecules move relatively slowly as they have less kinetic energy
Less kinetic energy results in a lower frequency of successful collisions between substrate molecules and the active sites of the enzymes which leads to less frequent enzyme-substrate complex formation
Substrates and enzymes also collide with less energy, making it less likely for bonds to be formed or broken
effect of higher temperatures on reactions
Higher temperatures cause reactions to speed up
Molecules move more quickly as they have more kinetic energy
Increased kinetic energy results in a higher frequency of successful collisions between substrate molecules and the active sites of the enzymes which leads to more frequent enzyme-substrate complex formation
Substrates and enzymes also collide with more energy, making it more likely for bonds to be formed or broken
does temperature effect enzyme controlled reactions
Changing air temperature can have a significant impact on the metabolism of living organisms due to the effect of temperature on enzyme activity
A Q10 value of 2 indicates that the reaction rate doubles with an increase in temperature of 10 C, while a value of 3 indicates that it trebles with every 10 C increase
Increase on rate of reaction by increase in temperature by 10 degrees Celsius
Any reaction between 0- 40 degrees has a Q10 value of 2.
This means that an increase of 10 degrees celcius will cause
a doubling of the rate of the reaction. Decrease in
temperature causes the rate of reaction to slow down
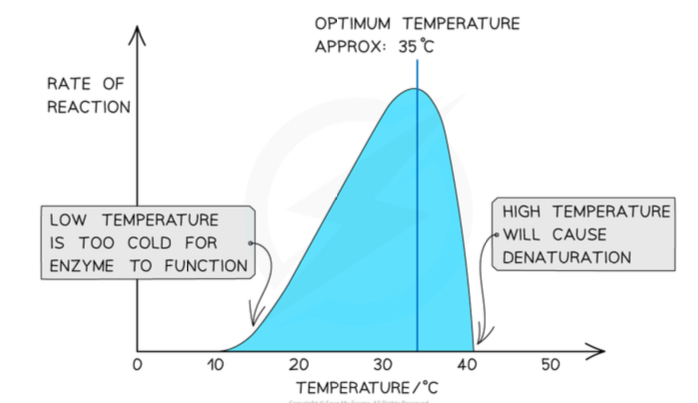
Effect of temperature on rate of enzyme controlled reactions?
As the temperature increases this will increase the rate of enzyme controlled reactions, organisms may grow and reproduce faster.
The rate of photosynthesis increases as it is also enzyme controlled; plants will take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere faster and grow more.
If it exceeds optimum temperature enzymes start to denature and these chemical reactions slow down, some organisms may die
how denaturation occurs
If temperatures continue to increase past a certain point, the rate at which an enzyme catalyses a reaction drops sharply as the enzymes begin to denature
The increased kinetic energy and vibration of an enzyme puts a strain on its bonds, eventually causing the weaker hydrogen and ionic bonds that hold the enzyme molecule in its precise shape to start to break
The breaking of bonds causes the tertiary structure of the enzyme to change
The active site is permanently damaged and its shape is no longer complementary to the substrate, preventing the substrate from binding
Denaturation has occurred if the substrate can no longer bind
Effect of temperature changes on organisms in trophic regions
Majority of plants and animal species live in the tropics and they have little tolerance for temperature change as their conditions are generally stable.
Temperature, rainfall and day length do not vary much over the course of the year. Main difference is volume of rainfall between wet season and dry season
Tropical organisms have not been subject to temperature selection pressure and rise or fall of a few degrees could lead to extinction of many species. Insects are pollinators if they die, plants die and animals which feed on the plants die
Effect of temperature change on organisms in temperate regions
Temperate regions see large variations in weather throughout the year. Organisms that live there are able to tolerate huge fluctuations in temperature even within a single day
Effect of changes due to global warming on plants
plants have optimal temperature especially those that form staple diet food
if climate chnages so temp falls or icnreases then this would mean plants may not grow as well
Temperature changes can also lead to increased rainfall that leads to flooding or decreased rainfall and droughts this could cause major problems for people
how seasonal changes can affect species
In higher altitudes seasonal changes affect life cycle and global warming is changing the beginning and end of seasons.
Affecting life cycle and distribution of species.
Warmer temperatures plants flower early. Insects and butterflies active earlier. The food is available for their caterpillars as the warmer temperatures caused plants to flower earlier and grow faster.
Some birds adapt to these changes and breeding cycles are
adjusted.
however birds breeding time can become earlier but caterpillars emerge even earlier and birds miss peak caterpillar population and few chicks surviving
As they breed earlier some animal species can have more
than one breeding cycle per year. So populations increase.
This could cause knock on effects on other organisms.
effect of increase in temperature on fish
Some fish eggs have been shown to develop more slowly at higher temperatures
Many species' successful egg development is dependent on temperature, with impacts such as
Extreme temperature fluctuations can reduce hatching rates in some invertebrates
effect of temp changes on reptiles
The sex of the young inside the egg of some species is determined by temperature, so increasing temperatures can affect the sex ratios in a species
E.g. in alligators
effect of flooding
Floods destroy homes, kill people and destroy farmland.
Increasing dry periods of drought.
Lack of rain and high temperatures
mean fewer crops and leading to local extinction of plants
and animals.
effect of low rainfall
Resovoirs are low and rainfall is erratic. This level drought
means even well adapted animals and plants will struggle.
effect of climate change on species distribution
Change in climate can affect the area in which many
different organisms can live.
Species may have to change their distribution in response to changing temperatures in order to survive
Species may migrate to higher altitudes or further from the equator to find cooler temperatures
Animals can move more easily than plants so will survive more easily than plants. Areas become warmer some animals may be able to extend their ranges north while becoming extinct in the southern areas.
If organisms that spread disease are affected then patterns
of health could change.