Esci: Exogenic Processes of Weathering, Erosion & Deposition
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:14 PM on 1/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
Weathering
* involves the *physical breakdown* **(disintegration)** and *chemical alteration* **(decomposition)** of rock at or near the Earth’s surface
2
New cards
Mechanical Weathering
* __Accomplished by physical forces__ that break the rock into smaller and smaller pieces __without changing the rock’s mineral composition__.
* the disintegration of Earth's materials makes __*detrital sediments*__
* the disintegration of Earth's materials makes __*detrital sediments*__
3
New cards
Frost Wedging
* When water enters the joints, alternate freezing and thawing episodes ***pry the rock apart.***
* After water works its way into the cracks in the rock, t__he freezing water enlarges the cracks, and angular fragments are eventually produced__.
* After water works its way into the cracks in the rock, t__he freezing water enlarges the cracks, and angular fragments are eventually produced__.
4
New cards
Salt Crystal Growth
* __Force exerted by a salt crystal that forms as water evaporates__ from pore spaces or cracks in rocks can cause the rock to fall apart.
* __Infiltration of salty waters__ on rocks or soils from groundwaters or salty seawater.
* __Infiltration of salty waters__ on rocks or soils from groundwaters or salty seawater.
5
New cards
Sheeting
* Also known as ***exfoliation***, it is caused by the expansion(pressure release) of crystalline rock as erosion removes the overlying material(overburdened rock)
6
New cards
Abrasion
* Wearing away of rocks by the **constant collision of loose particles**
* This can be due to water, wind, or ice.
* This can be due to water, wind, or ice.
7
New cards
Biological Activity
* __Plants and animals__ as agents of mechanical weathering
* Wedges in rocks and soils form through plant growth (rooting) and motor activities of animals and even humans (like burrowing or shoveling).
* Wedges in rocks and soils form through plant growth (rooting) and motor activities of animals and even humans (like burrowing or shoveling).
8
New cards
Chemical Weathering
* Involves __a chemical transformation of rock__ into one or more new compounds.
* Decomposition of rocks and minerals by chemical processes
* Decomposition of rocks and minerals by chemical processes
9
New cards
Dissolution
* dissociation(splitting) of molecules into ions
* the process by which a mineral completely dissolves in water or other acidic solutions
* a common example includes the __________ of calcite and salt
* the process by which a mineral completely dissolves in water or other acidic solutions
* a common example includes the __________ of calcite and salt
10
New cards
Oxidation
* reaction between minerals and oxygen
dissolved in water
* the ***reaction of oxygen with iron-bearing minerals*** in rock.
dissolved in water
* the ***reaction of oxygen with iron-bearing minerals*** in rock.
11
New cards
Hydrolysis
* change in the composition of minerals
when they react with water
* occurs when silicate minerals react with water so that the mineral recombines with the water molecule to form a new mineral.
* For example, consider the mineral potassium feldspar
when they react with water
* occurs when silicate minerals react with water so that the mineral recombines with the water molecule to form a new mineral.
* For example, consider the mineral potassium feldspar
12
New cards
Spheroidal weathering
* A form of chemical weathering where a generally spherical boulder is c***racked & split off into curved layers*** on a much smaller scale
13
New cards
Climate
? Cold and dry
? High temperature and high rainfall
? Cold and dry
? High temperature and high rainfall
A factor that affects weathering:
* __The presence of water__ which is an important chemical weathering agent increases the rate of weathering.
* __High temperature__ enhances chemical reactions.
? What climate causes a slow rate of chemical weathering
? What climate causes a high rate of chemical weathering
\
* __The presence of water__ which is an important chemical weathering agent increases the rate of weathering.
* __High temperature__ enhances chemical reactions.
? What climate causes a slow rate of chemical weathering
? What climate causes a high rate of chemical weathering
\
14
New cards
Rock Type
A factor that affects weathering:
* The minerals that constitute rocks have different susceptibilities to weathering.
* Those most stable to surface conditions will be the most resistant to weathering.
* The minerals that constitute rocks have different susceptibilities to weathering.
* Those most stable to surface conditions will be the most resistant to weathering.
15
New cards
Rock Structure
A factor that affects weathering:
* rate of weathering is __*affected by the presence of joints, folds, faults,
bedding planes*__ through which agents of weathering enter a rock mass.
* rate of weathering is __*affected by the presence of joints, folds, faults,
bedding planes*__ through which agents of weathering enter a rock mass.
16
New cards
Topography
? Steep slopes
? Gentle slopes
? Steep slopes
? Gentle slopes
A factor that affects weathering:
* Weathering may occur more quickly on a steep slope than on a gentle one
? In what kind of slope is physical weathering faster
? In what kind of slope is chemical weathering faster
* Weathering may occur more quickly on a steep slope than on a gentle one
? In what kind of slope is physical weathering faster
? In what kind of slope is chemical weathering faster
17
New cards
Time
A factor that affects weathering:
* Longer exposure to weathering agents could mean a higher degree of weathering processes have occurred. The rock has been weakened; therefore, easier to be a break.
* Length of exposure to agents of weather determines the degree of weathering of a rock
* Longer exposure to weathering agents could mean a higher degree of weathering processes have occurred. The rock has been weakened; therefore, easier to be a break.
* Length of exposure to agents of weather determines the degree of weathering of a rock
18
New cards
Erosion
* the incorporation and transportation of material by a mobile agent such as water, wind, or ice
19
New cards
Deposition
* the settlement of material on a definite location; the inability of a mobile agent to transport deposits material.
20
New cards
* Running Water
* Ocean or Sea Waves
* Groundwater
* Glacier
* Wind
* Gravity
* Ocean or Sea Waves
* Groundwater
* Glacier
* Wind
* Gravity
* What are the basic agents that drive sediment transport?
21
New cards
Hydrologic Cycle
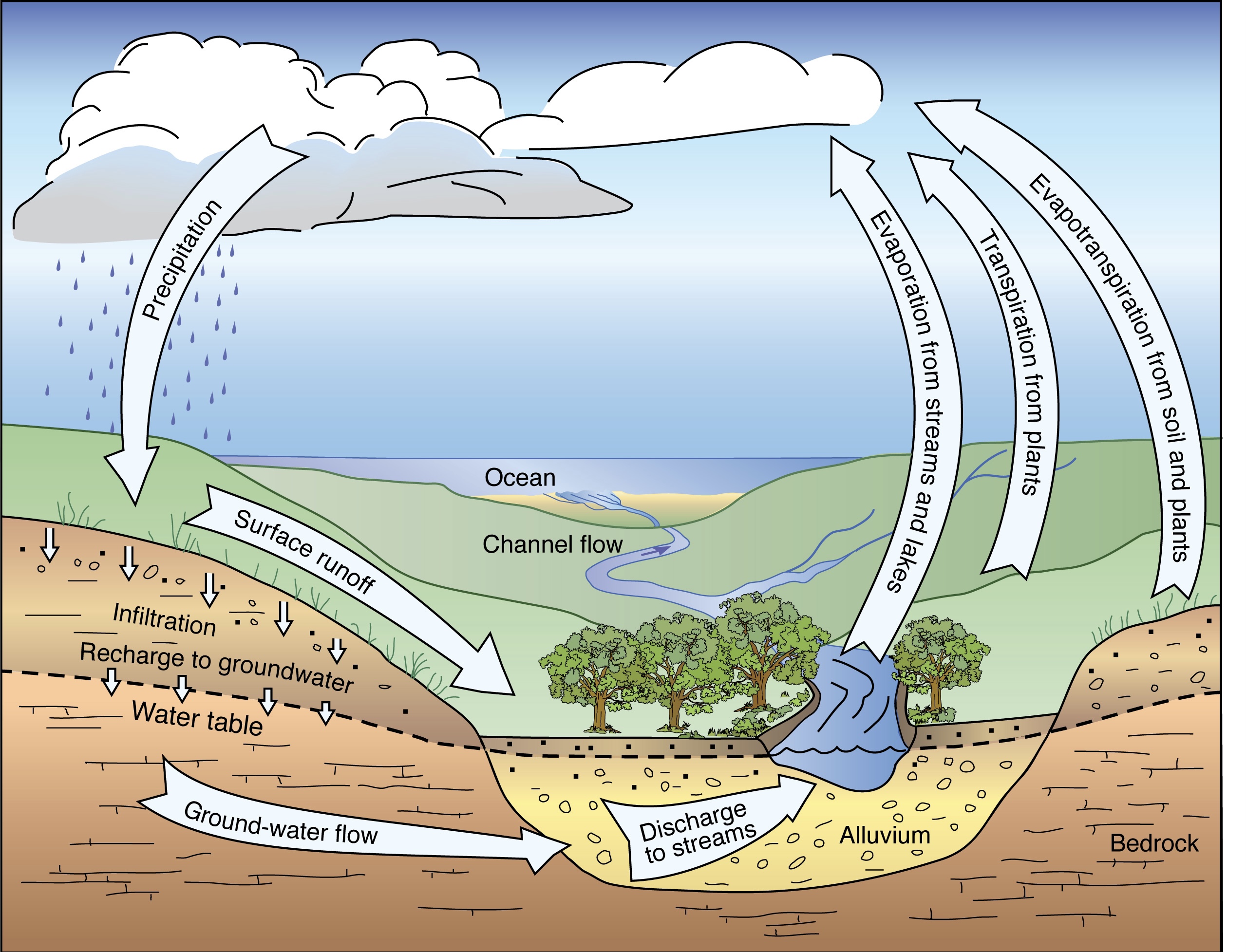
22
New cards
Drainage basin
* the area drained by a stream and its tributaries
23
New cards
Divides
* boundaries between drainage basins
24
New cards
Laminar flow
* fluid travels smoothly or in regular paths
25
New cards
Turbulent flow
* irregular fluctuations of liquid
* the speed of water is continuously undergoing changes in direction & magnitude
* the speed of water is continuously undergoing changes in direction & magnitude
26
New cards
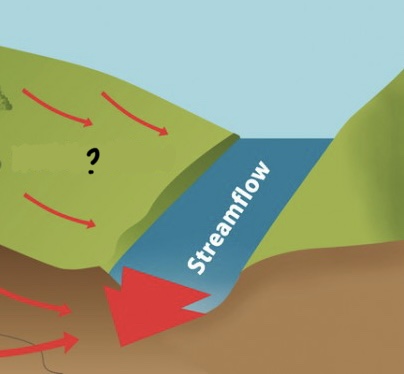
Overland flow
Encompassed by Running Water
* surface run-offs
* water flow down to a drainage basin due to a drainage divide, form rills and gullies on the surface due to erosion(rill & gully erosion)
* can erode before forming rills and gullies by sheet erosion
* surface run-offs
* water flow down to a drainage basin due to a drainage divide, form rills and gullies on the surface due to erosion(rill & gully erosion)
* can erode before forming rills and gullies by sheet erosion
27
New cards
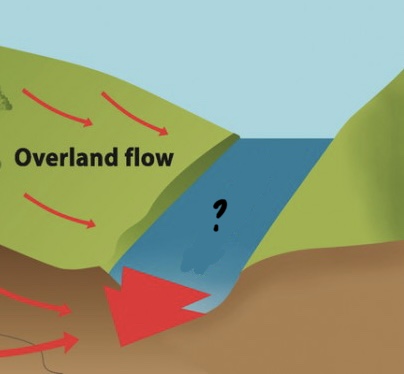
Streamflow
Encompassed by Running Water
* water flow in drainage basins(valley formation)
* turbulent flow of water is usually in river channels
* water flow in drainage basins(valley formation)
* turbulent flow of water is usually in river channels
28
New cards
Velocity
A factor affecting stream
* dictates the ability of a stream to erode & transport
* controlled by __*gradient, channel size & shape, channel roughness and the amount of water flowing in the channel*__
* dictates the ability of a stream to erode & transport
* controlled by __*gradient, channel size & shape, channel roughness and the amount of water flowing in the channel*__
29
New cards
Gradient
A factor affecting stream
* slope of the stream expressed as the vertical drop of a stream over a specified distance
* reserves much more enrgy the steeper it gets
* slope of the stream expressed as the vertical drop of a stream over a specified distance
* reserves much more enrgy the steeper it gets
30
New cards
Channel
A factor affecting stream
* stream path; straight channel can cause smooth stream(smooth erosion) while curved/banked channel can slow the stream and make it turbulent
* stream path; straight channel can cause smooth stream(smooth erosion) while curved/banked channel can slow the stream and make it turbulent
31
New cards
Discharge
A factor affecting stream
* volume of water passin through a cross-section of a stream during a given time
* as the discharge increases, the width of the channel, the depth of flow or flow velocity increase individually or simultaneously
* volume of water passin through a cross-section of a stream during a given time
* as the discharge increases, the width of the channel, the depth of flow or flow velocity increase individually or simultaneously
32
New cards
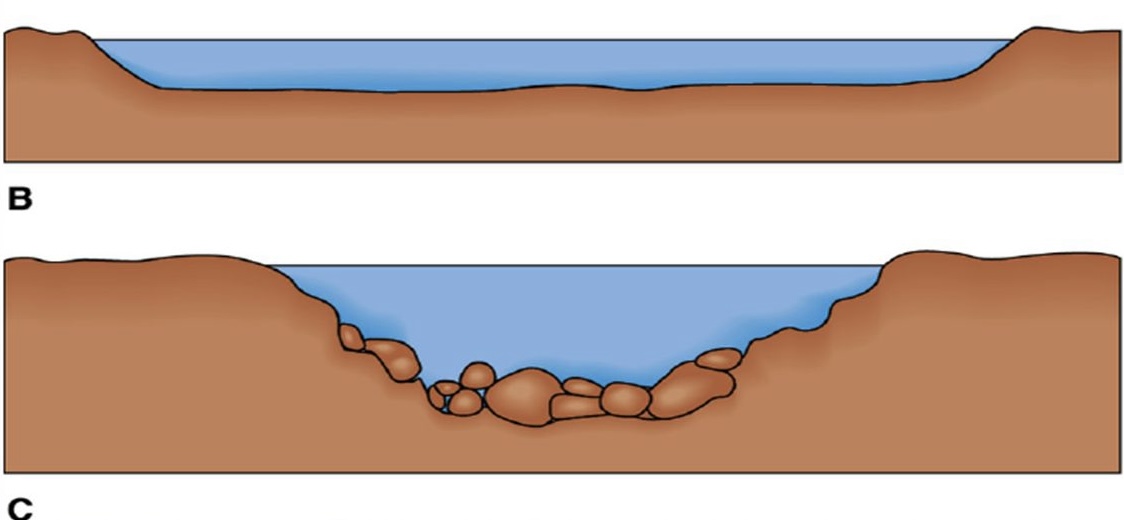
Slows the velocity
* What happens to the velocity when a channel is widened by soft rock and becomes rough & boulder strewn?
* what happens to the velocity when the channel is wide & shallow, increasing friction?
* what happens to the velocity when the channel is wide & shallow, increasing friction?
33
New cards
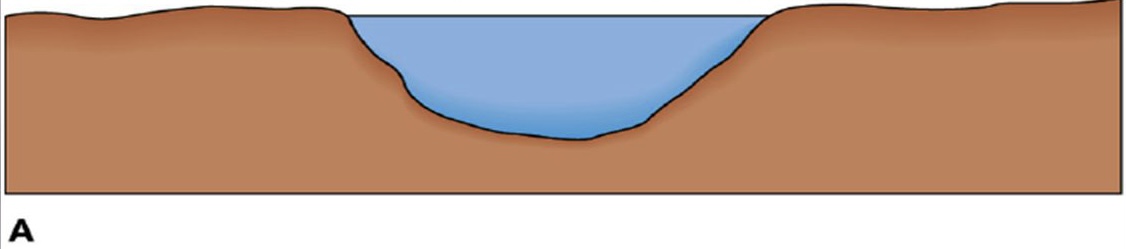
Stream velocity increases
* What happens to the velocity when a landslide narrows a channel?
* What happens to the velocity when a channel is semicircular?
* What happens to the velocity when bridge, piers or other obstructions are put up?
* What happens to the velocity when a channel is semicircular?
* What happens to the velocity when bridge, piers or other obstructions are put up?
34
New cards
Headward Erosion
Styles of erosion
* makes a river longer
* happens near its source
* surface run-off and flow cause erosion at the point where the water enters the valley head
* makes a river longer
* happens near its source
* surface run-off and flow cause erosion at the point where the water enters the valley head
35
New cards
Vertical Erosion
Style of erosion
* makes a river channel deeper
* this happen more in the upper stages of a river
* makes a river channel deeper
* this happen more in the upper stages of a river
36
New cards
Lateral erosion
Style of erosion
* makes a river wider
* this occurs mostly in the middle and lower stages of a river
* makes a river wider
* this occurs mostly in the middle and lower stages of a river
37
New cards
Quarrying
Erosion process in running water
* involves the removal of blocks from the bed of the channel
* involves the removal of blocks from the bed of the channel
38
New cards
Abrasion
Erosion process in running water
* bed & banks of a bedrock channel are ceaselessly bombarded by particles carried into the flow
* bed & banks of a bedrock channel are ceaselessly bombarded by particles carried into the flow
39
New cards
Corrosion/Solution
Erosion process in running water
* a procces in which rock is gradually dissolved by the flowing water
* a procces in which rock is gradually dissolved by the flowing water
40
New cards
Dissolved Load
Running Water: Transport sediment
* solution
* transportation of dissolved mineral which is moved and dispersed in stream
* usually came from groundwater
* solution
* transportation of dissolved mineral which is moved and dispersed in stream
* usually came from groundwater
41
New cards
Suspended Load
Running Water: Transport Sediment
* suspension
* fine sediments(such as clay) transported in streams as suspended sediments
* usually came from flooding/run-offs
* suspension
* fine sediments(such as clay) transported in streams as suspended sediments
* usually came from flooding/run-offs
42
New cards
Bed Load
Running Water: Transport Sediments
* coarse grains
* transportation by traction(rolling of gravels such as boulders) and saltation(skidding or jumping movements of smaller gravels such as pebbles)
* coarse grains
* transportation by traction(rolling of gravels such as boulders) and saltation(skidding or jumping movements of smaller gravels such as pebbles)
43
New cards
Bedrock Channel
Running Water: Channel Formation
* channel which consists and generally formed by rocks whereas its pattern is geologically structured
* definite and uniform structure
* channel which consists and generally formed by rocks whereas its pattern is geologically structured
* definite and uniform structure
44
New cards
Straight Channel
Running Water: Channel Formation; Bedrock Channel
* form where a stream erodes sediments in a constant patter without drstic change in its path/flow
* form where a stream erodes sediments in a constant patter without drstic change in its path/flow
45
New cards
Alluvial Channel
Running Water: Channel Formation
* watewr path whereas it has no definite patter and it changes its structure
* composed of unconsolidated sediments
* watewr path whereas it has no definite patter and it changes its structure
* composed of unconsolidated sediments
46
New cards
Braided Channel
Running Water: Channel Formation; Alluvial Channel
* form where alarge portion of a stream’s load consists of coarse material(sand & gravel) and the stream has a highly variable discharge
* form where alarge portion of a stream’s load consists of coarse material(sand & gravel) and the stream has a highly variable discharge
47
New cards
Meandering Channel
Running Water: Channel Formation; Alluvial Channel
* form where streams that transport much of their load in suspension generally move in sweeping bends
* form where streams that transport much of their load in suspension generally move in sweeping bends
48
New cards
* River valleys, waterfalls, potholes, terraces, gulley/rills
* Meanders(exhibit erosion & depositional features), oxybow lake, peneplain
* Meanders(exhibit erosion & depositional features), oxybow lake, peneplain
* What are the of Erosional Landforms from Running water as an agent of erosion
49
New cards
* Alluvial fans/cones, natural leeves, deltas
* What are the Depositional landforms from running water as an agent of erosion?
50
New cards
Deltas
Running Water: Deposits According to Agents of Erosion
* form where sediment-charged streams enters the realtively still water of a lake, an inland sea, or the ocean
* form where sediment-charged streams enters the realtively still water of a lake, an inland sea, or the ocean
51
New cards
Natural Levees
Running Water: Deposits According to Agents of Erosion
* meandering rivers that occupy valleys with broad floodplains, tend to build _____ ______ that parallel their channels on both banks
* meandering rivers that occupy valleys with broad floodplains, tend to build _____ ______ that parallel their channels on both banks
52
New cards
Alluvial Fan
Running Water: Deposits According to Agents of Erosion
* Are fan-shaped deposits that accumulate along steep mountain fronts
* When a mountain stream emerges onto a relatively flat lowland, its gradient drops and its deposits a large portion of sediment load
* Are fan-shaped deposits that accumulate along steep mountain fronts
* When a mountain stream emerges onto a relatively flat lowland, its gradient drops and its deposits a large portion of sediment load
53
New cards
Waves
Ocean or Sea Waves
* energy transported to a medium
* are caused by energy transferred by wind or storm in the ocean’s surface
* energy transported to a medium
* are caused by energy transferred by wind or storm in the ocean’s surface
54
New cards
* Wave Height
* Wavelength
* Wave period
* Wavelength
* Wave period
Characteristics of a Wave
* What do you call the vertical distance between trough and crest?
* What do you call the horizontal distance between successive crests(or troughs)?
* What do you call the time it takes one full wave to pass a fixed position?
* What do you call the vertical distance between trough and crest?
* What do you call the horizontal distance between successive crests(or troughs)?
* What do you call the time it takes one full wave to pass a fixed position?
55
New cards
* Wind speed
* Length of time the wind has blon
* Fetch or distance that the wind has traveled across open water
* Length of time the wind has blon
* Fetch or distance that the wind has traveled across open water
* What are the factors that affect the Height, Length & Period of a Wave?
56
New cards
Hydraulic Action
Shoreline Erosion Process of Ocean/Sea Waves:
* Rock wedging and disintegration due to wave slap
* Rock wedging and disintegration due to wave slap
57
New cards
Abrasion
Shoreline Erosion Process of Ocean/Sea Waves:
* the sawing and grinding action of the water armed with rock fragments
* the sawing and grinding action of the water armed with rock fragments
58
New cards
Corrosion
Shoreline Erosion Process of Ocean/Sea Waves:
* dissolution of rocks due to constant wave current
* dissolution of rocks due to constant wave current
59
New cards
Wave Refraction
Transportation by Waves and Currents:
* bending of waves making wave front parallel to the shore
* bending of waves making wave front parallel to the shore
60
New cards
Longshore Current
Transportation by Waves and Currents:
* erosion of sediments/soils by angled/oblique wave to the shore
* erosion of sediments/soils by angled/oblique wave to the shore
61
New cards
Rip Current
Transportation by Waves and Currents:
* Concentrated movement of water that flow in the opposite direction from breaking waves
* Concentrated movement of water that flow in the opposite direction from breaking waves
62
New cards
* Wave-cut Cliffs
* Wave-cut Platforms
* Marine Terraces
* Sea Arches
* Sea Stacks
* Wave-cut Platforms
* Marine Terraces
* Sea Arches
* Sea Stacks
* What are the Erosional Features from Ocean/Sea Waves as an agent of erosion
63
New cards
* Beach
* Spits
* Baymout bars
* Tombolo
* Barrier Island
* Spits
* Baymout bars
* Tombolo
* Barrier Island
* What are the Depositional Features from Ocean/Sea Waves as an agent of erosion
64
New cards
Glaciers
* a moving body of ice on land that moves downslope or outward from an area of accumulation
65
New cards
Ice Sheets(continental glaciers)
Types of glaciers:
* Cover large areas of the land surface
* unconfined by topography
* cover Antartica and Greenland
* Cover large areas of the land surface
* unconfined by topography
* cover Antartica and Greenland
66
New cards
Outlet glacier
* when a glacier flows out of an ice sheet, ice cap or icefield
67
New cards
Valley(Alpine) Glaciers
Types of glaciers; Ice Sheets:
* bounded by vallewys and tend to long and narrow
* can be formed when an outlet glacier forms and slides away from an icefield
* Can also be formed on their own, starting from high up on a mountain range and flowing down within the steep V between two peaks
* bounded by vallewys and tend to long and narrow
* can be formed when an outlet glacier forms and slides away from an icefield
* Can also be formed on their own, starting from high up on a mountain range and flowing down within the steep V between two peaks
68
New cards
Ice Shelf
Types of glaciers:
* a thick slab of ice, attached to a coastline and extending out over the ocean as a seaward extension of the grounded ice sheet
* a thick slab of ice, attached to a coastline and extending out over the ocean as a seaward extension of the grounded ice sheet
69
New cards
Cirque Glaciers
Types of glaciers:
* snow that accumulates in small depressions on the side of a mountain, eventually compacting into glacier ice
* when the glaciers are built up and shifted, they erode the depression to form bowl shaped valleys called corries or ______
* may sometimes accumulate enough ice to spill over and form valley glaciers
* snow that accumulates in small depressions on the side of a mountain, eventually compacting into glacier ice
* when the glaciers are built up and shifted, they erode the depression to form bowl shaped valleys called corries or ______
* may sometimes accumulate enough ice to spill over and form valley glaciers
70
New cards
Firn
Glaciers: Glacial Formation
* a recrystallized snow that is dense and is in granular form with a texture like coarse sand
* basic structure that is pressurized to form glacial ice
* a recrystallized snow that is dense and is in granular form with a texture like coarse sand
* basic structure that is pressurized to form glacial ice
71
New cards
* plastic flow
* basal slip
* basal slip
Glaciers: Glacial Movement
* Glaciers move to lower elevations by _______ ____ due to great stress on the ice at depth;
* and _____ ____ facilitated by meltwater which acts as a lubrican between the glacier and the surface over which it moves
* Glaciers move to lower elevations by _______ ____ due to great stress on the ice at depth;
* and _____ ____ facilitated by meltwater which acts as a lubrican between the glacier and the surface over which it moves
72
New cards
* Plucking
* Abrasion
* Abrasion
Glaciers: Glacial Erosion
* What do you call lifting piecies of bedrock beneath the glacier?
* What is the grinding and scraping by sediment already in ice called?
* What do you call lifting piecies of bedrock beneath the glacier?
* What is the grinding and scraping by sediment already in ice called?
73
New cards
* Glaciated Valleys
* Glacial Through
* Truncated Spurs
* Hanging Valleys
* Paster Noster Lake
* Cirque
* Tarn
* Col
* Aretes and Horns
* Rouches Moutonnees
* Glacial Through
* Truncated Spurs
* Hanging Valleys
* Paster Noster Lake
* Cirque
* Tarn
* Col
* Aretes and Horns
* Rouches Moutonnees
* What are the landforms created by glacial erosions?
74
New cards
Glacial Till
Glaciers: Glacial Deposits
* deposited as glacial ice melts and drops its load of rock fragments
* deposited as glacial ice melts and drops its load of rock fragments
75
New cards
Stratified Drift
Glaciers: Glacial Deposits
* deposited by the glacial meltwater and thus has experienced the sorting action of water
* deposited by the glacial meltwater and thus has experienced the sorting action of water
76
New cards
Wind
* a relatively insignificant erosional agent
* Dryness and scant vegetation are important prerequisites for it to be an effective errosional force
* Dryness and scant vegetation are important prerequisites for it to be an effective errosional force
77
New cards
Dunes(Sand Deposits)
Type of Wind Deposits:
* Hills or ridges of wind-blown sand
* Hills or ridges of wind-blown sand
78
New cards
Loess(Silt Deposit)
Type of Wind Deposits:
* Extensive blankets of silt that were once carried in suspension
* Extensive blankets of silt that were once carried in suspension
79
New cards
Barchan
Wind: Type of Sand Dune
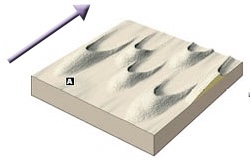
80
New cards
Transverse
Wind: Type of Sand Dune
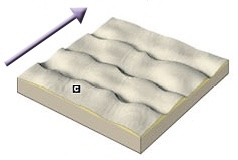
81
New cards
Barchanoid
Wind: Type of Sand Dune
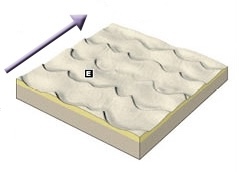
82
New cards
Longitudinal
Wind: Type of Sand Dune
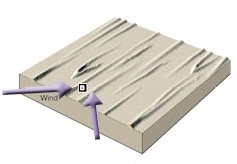
83
New cards
Parabolic
Wind: Type of Sand Dune
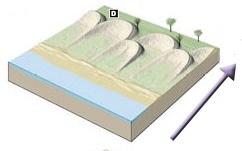
84
New cards
Star
Wind: Type of Sand Dune
85
New cards
Groundwater
* represents the largest reservoir of freshwater that is readily available to humans
* erodes sediments chemically rather tham mechanically(Weathering and movement of solution)
* erodes sediments chemically rather tham mechanically(Weathering and movement of solution)
86
New cards
Zone of soil moisture
Distribution of Groundwater
* area where water is molecularly atrracted and suspends
* area where water is molecularly atrracted and suspends
87
New cards
Unsaturated(Vadose) Zone
Distribution of Groundwater
* contains both air and water
* water cannot be extracted through wells
* contains both air and water
* water cannot be extracted through wells
88
New cards
Saturated(Phreatic) Zone
Distribution of Groundwater
* where all the open spaces in sediments and rocks are completely filled with water
* where all the open spaces in sediments and rocks are completely filled with water
89
New cards
Groundwater
Distribution of Groundwater
* water present in the phreatic zone
* water present in the phreatic zone
90
New cards
Water table
Distribution of Groundwater
* the upper limit of the phreatic zone(boundary with the valdose zone; “water level”)
* the upper limit of the phreatic zone(boundary with the valdose zone; “water level”)
91
New cards
Capillary fringe
Distribution of Groundwater
* Just above the water table
* zone where water can penetrate
* Just above the water table
* zone where water can penetrate
92
New cards
Graining Streams
Stream-Groundwater Interaction:
* inflow of groundwater through the streambed
* higher elevation of water table
* receive water from he groundwater system
* inflow of groundwater through the streambed
* higher elevation of water table
* receive water from he groundwater system
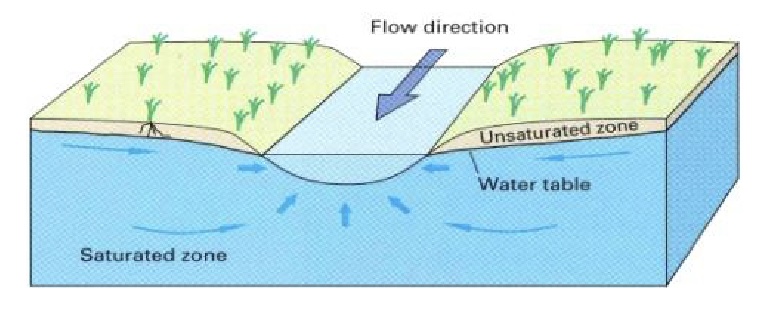
93
New cards
Losing Stream
Stream-Groundwater Interaction:
* lower elevation of water table
* water from streambed follow down to groundwater
* can be connected ot disconnected
* provide water to the groundwater system
* (disconnected) may form a buldge in the water table when it is separated from the groundwater system by the unsaturrated zone
* lower elevation of water table
* water from streambed follow down to groundwater
* can be connected ot disconnected
* provide water to the groundwater system
* (disconnected) may form a buldge in the water table when it is separated from the groundwater system by the unsaturrated zone
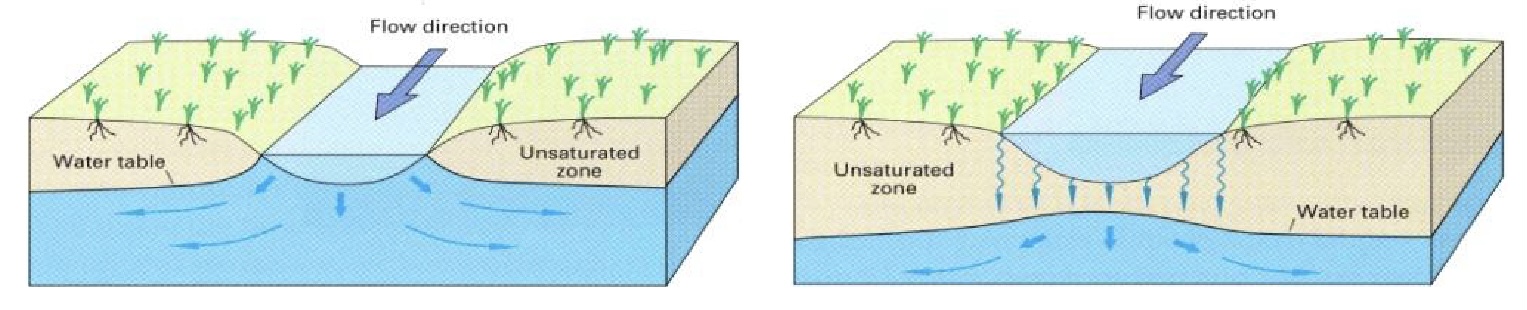
94
New cards
Porosity
* Factor affecting the storage and movement of groundwater
* percentage of total volume of rock or sediment containing pore spaces
* percentage of total volume of rock or sediment containing pore spaces
95
New cards
Permeability
* Factor affecting the storage and movement of groundwater
* the ability to transmit fluid
* the ability to transmit fluid
96
New cards
Aquitards
* Factor affecting the storage and movement of groundwater
* impermeable layers that hinders water movement
Ex. clays have mcuh smaller pores
* impermeable layers that hinders water movement
Ex. clays have mcuh smaller pores
97
New cards
Aquifiers
* Factor affecting the storage and movement of groundwater
* Permeable layers that transmit groundwater freely
Ex. Sand & gravels have much larger pores
* Permeable layers that transmit groundwater freely
Ex. Sand & gravels have much larger pores
98
New cards
Specific Retention
* Factor affecting the storage and movement of groundwater
* the ratio of the volume of water that a given body of rock or soil will old against the pull of gravity to the volume of the body itself
* the ratio of the volume of water that a given body of rock or soil will old against the pull of gravity to the volume of the body itself
99
New cards
Specific Yield
* Factor affecting the storage and movement of groundwater
* also known as the drainable porosity
* is a ration, less than or equal to the effective porosity
* also known as the drainable porosity
* is a ration, less than or equal to the effective porosity
100
New cards
Recharge area
Flow system
* water flow underground that replenishes water
* water flow underground that replenishes water