Rates of reaction
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is collision theory?
For particles to react, they have to collide with each other with sufficient energy (activation energy)
What is activation energy?
The minimum amount of energy needed for a reaction to take place
What factors affect the rate of reaction?
- Surface area
- Temperature
- Pressure / concentration
- Catalyst
How does surface area affect rate of reaction?
Rate of reaction increases with larger surface area
This is because there is more space for the particles to collide with each other, therefore increasing collision frequency
How does temperature affect rate of a reaction?
Rate of reaction increases with higher temperatures
This is the particles gain more KE which causes them to move faster, therefore increasing collision frequency
Additionally, the particles collide with more energy which increases the proportion of successful reactions
How does pressure / concentration affect rate of reaction?
Rate of reaction increases with a greater pressure / concentration
This is because there are more particles per unit of volume, therefore increasing collision frequency
What is a catalyst?
A substance that increases the rate of reaction & remains chemically unchanged by the end of the reaction
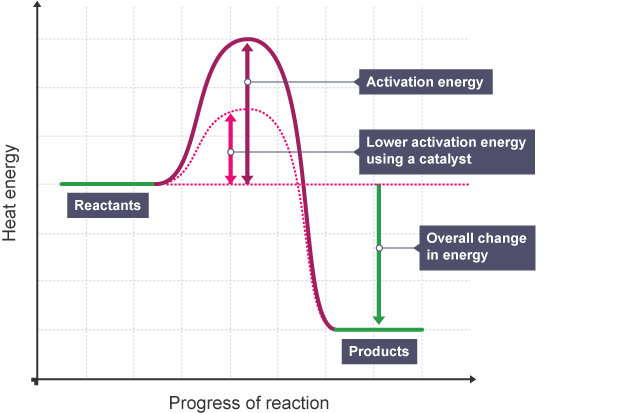
How does a catalyst work to increase the rate of reaction?
By providing an alternative reaction pathway that has lower activation energy, therefore increasing the proportion of successful reactions
How does using a catalyst affect a reaction profile?
The activation energy decreases
Practical: investigate the effect of changing the surface area of marble chips on the rate of reaction between marble chips & hydrochloric acid
- Pour 25cm3 HCl into a conical flask & place it on a top ban balance
- Quickly add in 1g of small marble chips & insert a cotton wool bung to prevent any HCl from spraying out but still allow CO2 produced to escape
- Immediately start a stop clock & record the total mass of the experiment in 30 second intervals until the reading on the top pan balance remains constant
- Repeat & then plot results on a graph
- Use this method again but with larger marble chips
Practical: investigate the effect of changing the concentration of hydrochloric acid on the rate of reaction between marble chips & hydrochloric acid
- Add 25cm3 HCl into a conical flask & place it on a top ban balance
- Quickly add in 1g of marble chips & insert a cotton wool bung to prevent any HCl from spraying out but still allow CO2 produced to escape
- Immediately start a stop clock & record the total mass of the experiment in 30s intervals until mass remains constant
- Repeat & plot results on a graph
- Use method again with different concentrations of HCl