Clicker and quiz UNIT 3
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
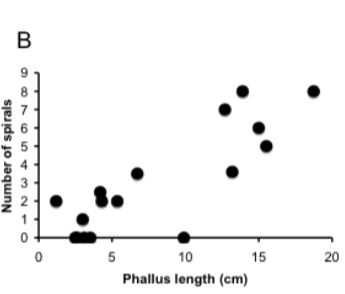
The graph shows the relationship of male genitalia (phallus length) to characteristics of the female genitalia. Each dot corresponds to
a different species in a group of animals. Which information does the graph relay?
A. Coevolution of male and female genitalia
B. Male genitalia evolving to be better at sperm competition
C. Male genitalia evolving to overcome female choice
D. A&C
E. All of the above
A&C
Which is support for the idea that gamete recognition is
Driven to some degree by sexual conflict:
A sperm is less choosy about which gametes they fuse with
With than are eggs
B. Genes involved in game recognition and fusion evolve
fairly slowly
C. The costs of fusing with a gamete from a different
Species is lower for eggs than it is for sperm
D.A&C
E. All of the above
A
Cannibalism is always classified as a form of interlocus sexual
conflict because:
A. The individual being cannibalized always loses fitness
B. Cannibalism is avoided at all costs during mating
C. Like infanticide, cannibalized individuals die
D. B&C
E. none of the above OR cannibalism is not always
interlocus conflict
E
One of the primary ways by which Wolbachia can be used to
combat the spread of mosquito-borne illnesses like Zika,
Dengue and Malaria is by:
A.Reducing mosquito populations up to 70-94%
B.Dramatically cutting fecundity of females in half
C. Increasing pathogen replication so the virus kills the host
before spreading
D.A&B
E. A&C
A
The identification of selfish genetic elements have made
Scientists realize which of the following?
A. All aspects of the genome should integrate to promote fitness of the organism
B. Some genetic regions can increase their own fitness at the
cost of others
C. Meiosis does not always result in 50:50 transmission of
alleles
D. A&B
E. B&C
E
The genome evolves counter measures to selfish genetic elements
because
A. They are almost always linked to disease-resistance genes that reduce lifespan
B. Selfish genetic elements have high crossover during meiosis, which negatively impacts the offspring
C. They always feminize to some degree, and selection favors a balanced sex ratio
D. A&C
E. None of the above
E
The genome evolves counter measures to selfish genetic
elements because
A. They are almost always linked to disease-resistance
genes that reduce lifespan (they can be linked, particularly if humans engineer them to be, but they operate as their own unit, without any need to be linked to any other allele)
B. Selfish genetic elements have high crossover during meiosis, which negatively impacts the offspring (they have low crossover)
C. They always feminize to some degree, and selection favors a balanced sex ratio (they do not always feminize, but they can feminize)
D. A&C
E. None of the above
E
1. Which is/are patterns that can be reliably used to identify the
presence of selfish genetic elements?
A. Increased transmission of the SGE at the cost of significantly reduced fitness in the organism
B. Mutations that have a negative effect on phenotype
C. Increased copies at different sites in the genome each generation
D. All of these
E. None of the above
E
What are true about selfish mitochondria?
A. Selection favors mitochondrial genome mutations that increase
resource allocation to female reproductive parts.
B. Selection shaping the nuclear genome will favor counter measures to selfish mitochondria that balance the sex ratio to 50:50
C. In general, nuclear genomes favor resource allocation biased
towards male reproductive parts, and selfish mitochondria counter
balance this.
D. A&B
E. All of these
D
Why are selfish genetic elements observed more often in hybrids
between strains or species?
A. Within a population, selfish genetic elements are often fixed, so
there is no variation among individuals by which to identify them
B. Often suppressors evolve in response to selfish genetic elements, and hybrids may not inherit both the selfish genetic
element and the suppressor.
C. Both of these
D. Neither of these
C
Cytoplasmic incompatibility related to Wolbachia infections:
A. Leads to a major decrease in offspring viability
B. Can occur even when both gametes that fuse are infected by
Wolbachia
C. Happens when Wolbachia-infected eggs fuse with uninfected eggs
sperm cells
D. A&B
E. All of the above
D
Which of the following are correct statements about selfish
genetic elements?
A. They can be used to manipulate crops to avoid self-
fertilization
B. Transposable elements are used to edit genetic mutations associated with human disease
C. Biased gene converter allow for the evolution of novel protein structures, for example in the different subunits of hemoglobin
D. A&B
E. All of these
A
Which are true about meiotic drive?
A. When gamete killers occur on a sex chromosome, they can bias
the sex ratio and novel sex determination mechanism can evolve to
counteract the killers
B. Gamete killers reduce the total viable sperm, and occur more
frequently in males because gametes are less costly to produce in males.
C. Meiotic drive occurs when the driver (the SGE) preferentially
migrates away from the functional oocyte and into the polar body, thus harming the organism due to reduced fertility.
D. A&B
E. All of these
D
Imprinting occurs most commonly in:
A.Genes that regulate growth and development
B.Certain regions of the brain like the hypothalamus
C. Birds and mammals
D.A&B
E. All of the above
D
When imprinting ‘goes wrong,’ which are likely to occur?
A.Over- or under-expression of one of the alleles at the
locus that is imprinted
B.Developmental disorders
C. The X chromosome in the male is not properly
inactivated
D.A&B
E. All of the above
D
X-inactivation
A. Leads to the homogeneous phenotype of all cells in a
heterozygous individual
B. It is a random process by which one or the other X
chromosome is inactivated early in development
C. Occurs more in males than females
D. A&B
E. None of the above
B
Imprinting occurs:
A. In genes regulating phenotypes like eye and hair color
B. When genetic sequences controlling growth and development
are edited after egg and sperm fuse.
C. Only in mammals
D. B&C
E. None of the above
E
Which represents reasons that imprinting has evolved in response to
intersexual conflict in mammals?
A. It evolved when mammals evolved
B. Imprinting occurs primarily in genes involved in early development,
when males and females are most aligned in the preferred level of
investment in offspring.
C. Live birth increases the gap in investment between males and
females
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
C
What are important steps in the process of imprinting?
A. Methylation patterns at imprinted loci are reset when germ
cell line forms
B. Chemicals like histones bind up the DNA in one copy of a gene
such that it cannot be transcribed
C. The phenotype at the imprinted locus becomes equally
influenced by the maternal and paternal alleles.
D. A&B
E. None of these
D
Negative birth and gestational outcome (e.g. preeclampsia or gestational diabetes) occur for which of the following reason(s)?
A. The paternal genome can hijack the system to overexpresses selfish genes causing negative effects in the female (genomic conflict is different than selfish genes, which conflict between a gene and the rest of the genome in which the gene resides)
B. The conflict between maternal and paternal genomes is not fully in balance (this happens when the paternally expressed genes cause over growth, or maternal undergrowth, that have negative consequences. When balanced, the growth is typical)
C. The fetus manipulates the expression of maternal genes (the placenta does release hormones that shift maternal phenotype, and this is necessary for pregnancy to proceed normally...it is only when the balance between maternally and paternally imprinted genes are off, like if the placenta implants too deeply, that problems arise)
D. A&B
E. All of the above
B
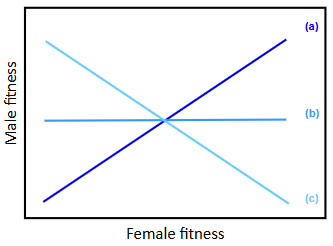
mf : genetic correlation between male and female fitness/trait. Which relationship among siblings is expected under unresolved intralocus sexual conflict?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. Cannot tell from graph
C
When there is intralocus sexual conflict, what are some evolutionary outcomes
that resolve (partially or wholly) this conflict?
A. Males and females express the same trait value because it generates
maximal fitness for both sexes simultaneously
B. A gene that mediates sex-specific expression of a trait evolves to
allow each sex to express the trait at a value closer to their optimum
(think of the lizards)
C. Both of theseD. Neither of these
B
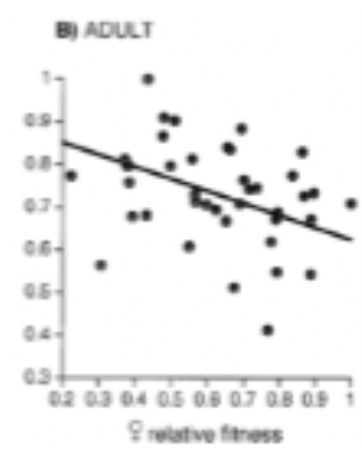
If the graph to the right illustrates intralocus sexual conflict, which would be the most appropriate label on the y-axes that would
demonstrate the conflict?
A. Female trait value : male trait value
B. Male trait value
C. Male relative fitness (when males have higher fitness, females have lower fitness – this graph was shown in class)
C
Cannibalism is considered interlocus sexual conflict when:
A. Cannibalism increases reproductive output in one sex to the detriment of the reproductive output other sex
B. The individuals that are cannibalizing receive benefits
C. Females kill the offspring of other females
D. A&B
E. All of these
A
Which of the following are important for intralocus sexual conflict to arise?
A. Males and females share a genome
B. Selection favors similar optima in both sexes
C. Sex-specific gene expression allows for the sexes to express traits at their optima
D. Selection favors one allele in males, with positive effects on females
E. All of the above
A
How might interlocus sexual conflict decrease female fitness?
A. Males may kill a female’s offspring so she is able to mate sooner
B. Males can transfer compounds with their sperm that reduce female
lifespan
C. Males provide nuptial gifts to help his offspring develop
D. A&B
E. All of the above
D
Which of the following are reasons behind, or outcomes of, sexual conflict over gamete recognition?
A. Sperm benefit more from indiscriminate gamete fusion than do eggs
B. Genes involved in gamete recognition and fusion evolve quickly
C. The costs of fusing with a gamete from a different species is lower for
eggs than it is for sperm
D. A&B
E. All of the above
D
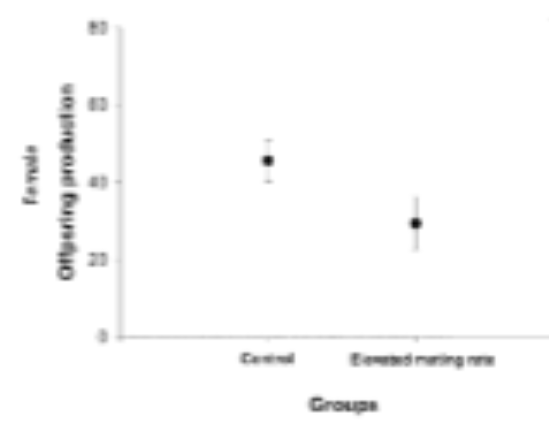
The following graph shows the reproductive output of females that are allowed to mate as often as they like (control group), or are forced to mate more often by males (elevated mating rate group). Why is this considered intersexual conflict?
A. Males are manipulating female mating rates at a significant cost to
females
B. Females experience increased fecundity and offspring viability with
additional matings.
C. Males that mated previously with females lose out on offspring she would have produced with them.
D. A&B
E. A&C
A
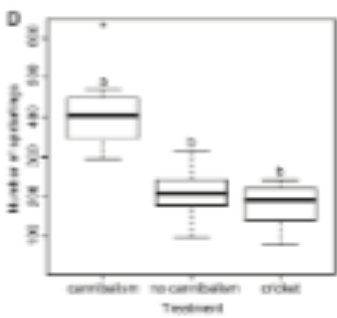
The following graph shows offspring number when (from left to right) males are cannibalized, when males are not cannibalized, and when females are fed a cricket after mating. Why is this NOT considered sexual conflict?
A. Males are losing reproductive output while females are gaining reproductive output.
B. Both males and females increase fitness with cannibalism.
C. Males are losing future reproductive opportunities by investing in the current one
D. All of these
E. None of these
B
Which of the following are true about interlocus sexual conflict?
A. It arises due to one sex gaining fitness by having a specific trait value, and the other sex losing fitness having that trait value
B. It evolves slowly as adaptations and counteradaptations evolve
C. It often favors persistence (over mating or fertilization) in males,
and resistance (to gain more control over mating or fertilization) in females
D. It can be resolved by sex-specific trait expression
E. All of these
C
Which is/are patterns that can be reliably used to identify the presence of selfish genetic elements?
A. Increased transmission of the SGE at the cost of significantly reduced fitness in the organism
B. Mutations that have a negative effect on phenotype
C. Increased copies at different sites in the genome each generation
D. All of these
E. None of the above
E
Killer Y sperm will kill all sperm that contain a Y chromosome. Despite the expectation that this will eventually lead to the loss of males in the population, males persist. What are the reasons for this seemingly contradictory outcome?
A. Males with Killer Y sperm do not have as many viable sperm
B. Females mate promiscuously
C. Females with the Killer Y allele have increased fecundity
D. A&B
E. All of these
D
What are true about selfish mitochondria?
A. Selection favors mitochondrial genome mutations that increase resource allocation to female reproductive parts.
B. Selection shaping the nuclear genome will favor countermeasures to selfish mitochondria that balance the sex ratio to 50:50
C. nuclear genomes generally favor resource allocation biased towards male reproductive parts, and selfish mitochondria counterbalance this.
D. A&B
E. All of these
D
Which type of genetic drive is illustrated by this example: Selfish genetic elements end up inserting copies of themselves in different locations in the genome
A. Gonotaxis
B. Biased gene converters
C. Transposable elements
D. Interference
C
Which type of genetic drive is illustrated by this example: Selfish genetic elements end up more often in the functional egg versus the polar bodies
A. Gonotaxis
B. Interference
C. Overreplication
D. Killer genes
A
Why are selfish genetic elements observed more often in hybrids between strains or species?
A. Within a population, selfish genetic elements are often fixed, so there is no variation among individuals by which to identify them
B. Often suppressors evolve in response to selfish genetic elements, and hybrids may not inherit both the selfish genetic element and the suppressor.
C. Both of these
D. Neither of these
C
Cytoplasmic incompatibility related to Wolbachia infections:
A. Leads to a major decrease in offspring viability
B. Can occur even when both gametes that fuse are infected by Wolbachia
C. Happens when Wolbachia-infected eggs fuse with uninfected sperm cells
D. A&B
E. All of the above
D
What is often true when selfish genetic elements arise?
A. An evolutionary arms race occurs between the selfish genetic element and other parts of the genome
B. They have strong negative or positive effects on organismal fitness
C. They spread quickly in a population and accumulate in the genome
D. A&B
E. A&C
E
Which of the following are correct statements about selfish genetic elements?
A. They can be used to manipulate crops to avoid self-fertilization
B. Transposable elements are used to edit genetic mutations associated with human disease
C. Biased gene converter allow for the evolution of novel protein structures, for example in the different subunits of hemoglobin
D. A&B
E. All of these
A
Which are true about meiotic drive?
A. When gamete killers occur on a sex chromosome, they can bias the sex ratio and novel sex determination mechanism can evolve to counteract the killers
B. Gamete killers reduce the total viable sperm, and occur more frequently in males because gametes are less costly to produce in males.
C. Meiotic drive occurs when the driver (the SGE) preferentially migrates away from the functional oocyte and into the polar body, thus harming the organism due to reduced fertility.
D. A&B
E. All of thes
D
What are some of the major consequences of selfish genetic elements?
A. Rapid evolution between selfish genetic elements and other regions of the genome that suppress positive effects of selfish genetic elements (suppresses the NEGATIVE effects)
B. The evolution of novel sex determination mechanisms (when feminization happens, this favors mutations recovering the production of male gametes)
C. Reduction in male fertility due to increased investment in female reproductive tissues (this specifically refers to the outcomes of selfish mitochondria)
D. B&C
E. All of the above
D
Which is/are correct statements about imprinting?
A. If methylation patterns for imprinted genes are not reset during early germ cell line formation, offspring may not properly express the imprinted gene .
B. In paternally imprinted genes, methylation binds up the allele from the mother such that the maternal allele cannot be expressed.
C. Paternally imprinted loci are expressed only in male offspring.
D. A&B
E. All of these
A
Imprinting is a mechanism by which:
A. Growth and development are regulated by either the paternal or maternal allele at a given locus, but not both
B. DNA editing occurs to regulate which alleles are actively expressed
C. Environmental stressors affect the expression of offspring phenotype
D. A&B
E. None of the above
A
Which represents evidence that intersexual conflict in mammals has contributed to genomic imprinting?
A. Imprinting occurs primarily in genes involved in early growth and development of the fetus, for which males and females have different optima
B. Paternally and maternally imprinted genes in humans are often related to the same developmental pathways but have counteractive effects
C. Removing patterns of imprinting allows for the development of larger, healthier offspring
D. A&B
E. None of the above
D
What occurs during, or as a result of, the process of imprinting?
A. One allele is expressed a little less than the other allele
B. One allele is expressed, whereas the other allele is silenced, and which allele is expressed (paternal vs maternal) is random, whether it is maternally or paternally imprinted, and the sex of the parent.
C. Selection on a given allele will depend upon the sex the allele was inherited.
D. A&B
E. None of these
C
What are the evolutionary consequences of imprinting?
A. Selection has a stronger effect on imprinted genes
B. Selection on the imprinted gene will depend on whether it is inherited from the mother or father
C. Mutations can have larger impacts on phenotypes controlled by imprinted genes
D. A&C
E. All of the above
E
What are important steps in the process of imprinting?
A. Methylation patterns at imprinted loci are reset when the embryo develops
B. One copy of an allele is methylated so it cannot be expressed
C. Phenotype will depend on whether an allele is inherited from maternally vs paternally
D. B&C
E. All of these
D
Killer Y sperm kill most or all other sperm that contain a Y chromosome. Why would this type of selfish genetic element evolve?
A. Males with Killer Y sperm do not have as many viable sperm
B. Evolution occurs at the level of different genes in the genome, rather than at the level of individuals
C. Females avoid mating with males with Killer Y sperm
D. A&C
E. All of the above
B
Investment in offspring in live-bearing animals results from which of the following:
A balance between maternal and paternal interests in the level of investment in the fetus.
B. A balance between maternal and offspring interests in the level of investment in the fetus.
C. Strategies for maximizing inclusive fitness for mother and offspring.
D. B&C
E. All of the above
E
When should maternal-paternal conflict over offspring investment be highest?
A. When offspring are mostly self-sufficient
B. When rates of polygamy are high
C. When offspring are closely related to their siblings.
D. B&C
E. All of the above
B
How does the fetus get enough glucose and oxygen if the pregnant female also needs those nutrients?
A. Fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen
B. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged through the placenta
C. The placenta releases hormones that increase insulin resistance in the pregnant
female
D. A&B
E. All of the above.
E
What makes the placenta unique and why?
A. It is a temporary organ, and this is the only organ that is temporary
B. It is comprised of tissue built from both maternal and paternal genomes, and the female does
not “reject” the organ (unlike organ transplant recipients)
C. It mediates the flow of nutrients from mother to offspring, and the level of flow is determined
by a balance between paternal/fetal interests and maternal interests.
D. A&B
E. All of the above
E
What benefits do sperm gain from cooperating with other sperm to reach the female gametes?
A. Even though only one sperm can fertilize the egg, cooperation increases the likelihood that a group of sperm will reach the egg.
B. Single sperm do not have to compete with other sperm if they reach the egg, but they are far more likely to reach the egg if cooperating.
C. Particularly in organisms with complex female reproductive tracks, cooperation increases the chances of fertilization by the male
D. A&B
E. All of the above.
E
Which of the following are reasons that sperm might not align with male interests?
A. Sperm might have DNA with selfish genetic elements that increase the male’s fitness
B. Selfish genetic elements are can reduce male fertility
C. Males prefer sperm with selfish genetic elements to fertilize the eggs, so if sperm without
do, the male can lose fitness.
D. All of these
E. None of these
B
Sperm RNA could provide which of the following benefits to females?
A. A nuptial gift that aids in the early stages of embryonic development
B. Increase in the likelihood that sperm from a single male will fertilize her eggs
C. Remove the burden of cryptic choice from the female
D. A&B
E. None of the above
A
Sperm RNA have odor receptors, which may aid in kin recognition of sperm from thesame male. Why would this function evolve?
A. Sperm that clump increase the chances that sperm from a given male will reach the female egg first in species that are monogamous.
B. Sperm that clump with other sperm from the same male have a small individual chance of fertilizing the eggs, but increase the chances of sperm from that male fertilizing.
C. Females discriminate against sperm that clump with sperm from non-related individuals.
D. A&B
E. All of the above
B
Which are properly described disorders related to the human placenta?
A. Placenta accreta is when the placenta embeds too deeply in the uterine lining, which can cause hemorrhaging
B. Placental abruption is when the placenta tears away from the uterine wall, reducing the nutrient and oxygen flow from the pregnant individual to the fetus.
C. Placenta previa is when the placenta is attached too far from the fetus and increases the risk of bleeding
D. A&B
E. All of the above
D
What can we learn from studying the placenta and why?
A. How to decrease organ transplant rejections because the placenta comprises tissue derived from both maternal genomes and paternal (non-self) genomes.
B. The mechanisms of cancers that embed in our tissues because the placenta avoids embedding in the uterine lining.
C. How to improve immune responses because the placenta can sense illness in the fetus and generate immunoglobulins in response.
D. A&B
E. All of the above
A
Morning sickness:
A. Is likely shaped by selection for pregnant humans to avoid ingesting foods that are harmful to the developing fetus
B. Is greatest late in pregnancy when risk of foodborne illness to fetal development is highest
C. Likely has no protective function
D. A&B
E. B&C
A
Which are the primary functions of the placenta
A. Generating hormones during pregnancy that regulate transmission of nutrients between the pregnant female and developing fetus
B. Functioning as a lung that allows the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the pregnancy female and fetus.
C. Functioning as a liver that allows the fetus to get rid of waste products
D. A&B
E. All of these
E
Which of these are likely to originate from a misbalance of the conflict between the paternal/fetal genomes and maternal genome and why?
A. Pre-eclampsia, which occurs due to abnormal placental growth that increase maternal blood pressure, because it increases blood supply to the placenta and greater nutrient flow to the fetus while reducing the pregnant female’s health
B. Gestational diabetes, which occurs when placental hormones increase the fetal insulin resistance, because it reduces the amount of glucose available in the bloodstream for the pregnant female.
C. Gestational diabetes, which occurs when placental hormones increase maternal insulin resistance, because it increases glucose supply to the fetus at the cost to the pregnant female’s health
D. A&B
E. A&C
E
Epigenetic inheritance
A. Involves mechanisms like histone binding of DNA that alters expression of alleles
B. Can influence fear responses and metabolic processes of offspring
C. Can influence the phenotype of individuals for generations because of alterations that do not affect the DNA sequence of a gene
D. A&B
E. All of the above
E
In which ways do epigenetic affect evolutionary processes?
A.Two individuals with exact DNA copies can have different epimutations that express different phenotypes
B.Responses to changes in the environment could involved epigenetic changes rather than changes in allele frequencies
C.Epigenetic changes can occur across several genes simultaneously
D.A&B
E.All of the above
E