4.Bias, Sample Selection & Confounding
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from the lecture notes on bias, sampling frameworks, and confounding.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Bias
A systematic error in study design, conduct, or analysis that leads to an incorrect estimate of the association between exposure and risk of disease
Chance (random error)
Random fluctuations that cause variation in estimates due to sampling variability.
Confounding
A distortion of the exposure–outcome relationship caused by a third variable related to both exposure and outcome.
Selection bias
Systematic error from how participants are chosen, resulting in a non-representative sample.
Information bias
Systematic error in measuring exposure or disease status, leading to biased estimates.
Non-response bias
Bias due to differences between those who participate and those who do not respond.
Loss to follow-up bias
Bias from differential dropout, affecting incidence or risk estimates.
Sampling bias
Bias arising from non-random sampling, causing non-comparable groups.
Randomization
Assignment of participants to groups by chance to balance known and unknown confounders.
Matching
Design approach that pairs participants on specific characteristics to control confounding.
Restriction
Limiting the study to a homogeneous subgroup to reduce variability and confounding.
Stratification
Evaluate association within subgroups of confounding variable
Multivariate analysis
Technique that takes into account many variables at the same time that may confound the effect of exposure
Stratified analysis
Examining associations within each level of a confounding variable.
Odds ratio
A measure of association (odds of outcome with exposure vs without) often used in case-control studies.
Target population
The entire set of individuals of interest to the research question.
Sample
Subset of individuals in target population from which researchers will draw their conclusions about target population. following process of statistical interference
Probability sampling
Sampling where each member has a known probability of selection; includes random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling.
Non-probability sampling
Sampling without known probabilities, often leading to biased population estimates (e.g., snowball, convenience, purposive).
Simple random sampling
Each subject in a population has an equal chance of being selected.
Systematic random sampling
Selection of sampling has a known and equal predefined interval such as select every 4th animal in a herd from a random starting point.
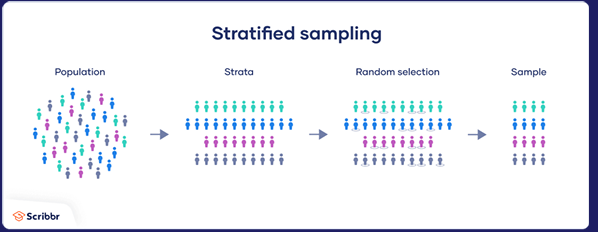
Stratified random sampling
Dividing the population into strata and taking random samples from each strata.
Cluster sampling
Population is split into clusters, and then a random sample of clusters is selected
Snowball sampling
recruited subjects refer others into the study.
Convenience sampling
Cheap and quick used for user opinion polls or pilot testing for a survey
Purposive sampling
Researcher chooses sample most useful to the purposes of the research and has clear criteria and rationale for inclusion
Recall bias
The ability of respondents to accurately remember exposure of pets
Interviewer bias
Interviewer interjects his or her bias into interview. the way questions are asked and perceived by respondents affects their response
Surveillance bias
One group is monitored much more closely than another group
Observer bias
Incorrect measurement technique and recording of values
Confounder
A variable in a study that distorts true relationship between an exposure and an outcome to seem more/less associated
Confounding variables
Age, sex, breed