review test1
1/692
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
693 Terms
ilium
what is 1
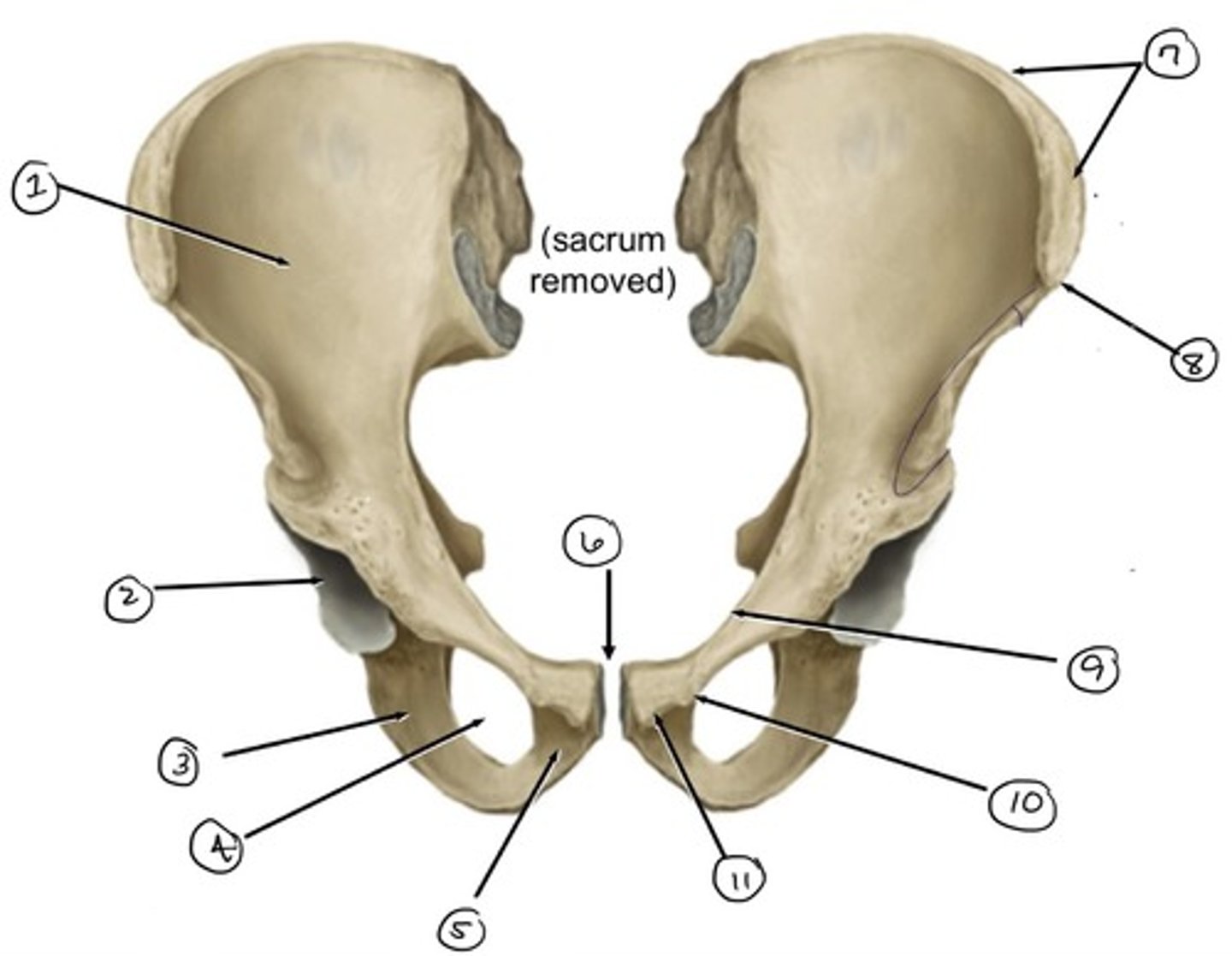
ischium
what is 3

acetabulum
what is 2
obturator foramen
what is 4
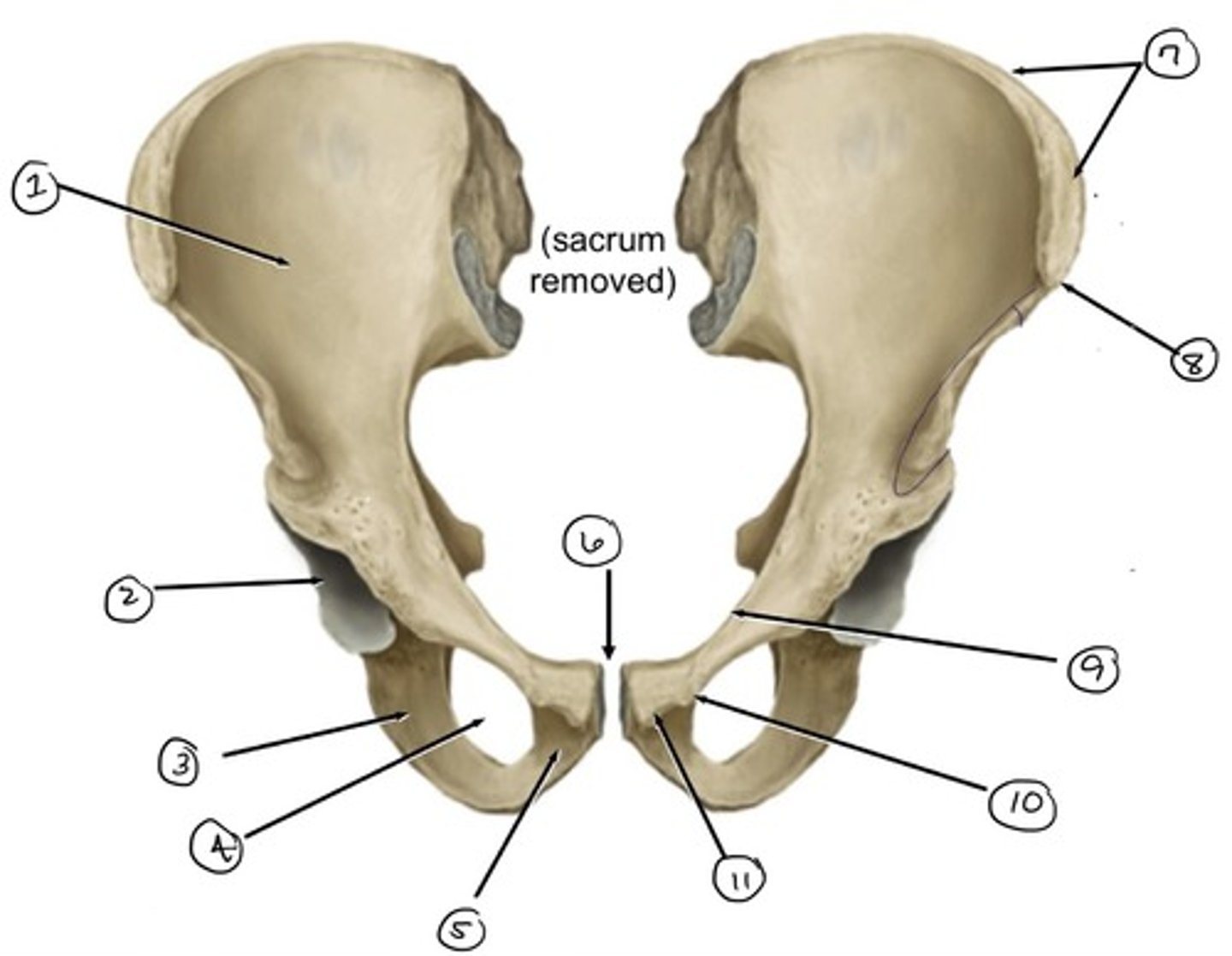
pubis
what is 5

pubic symphysis (location of)
what is 6
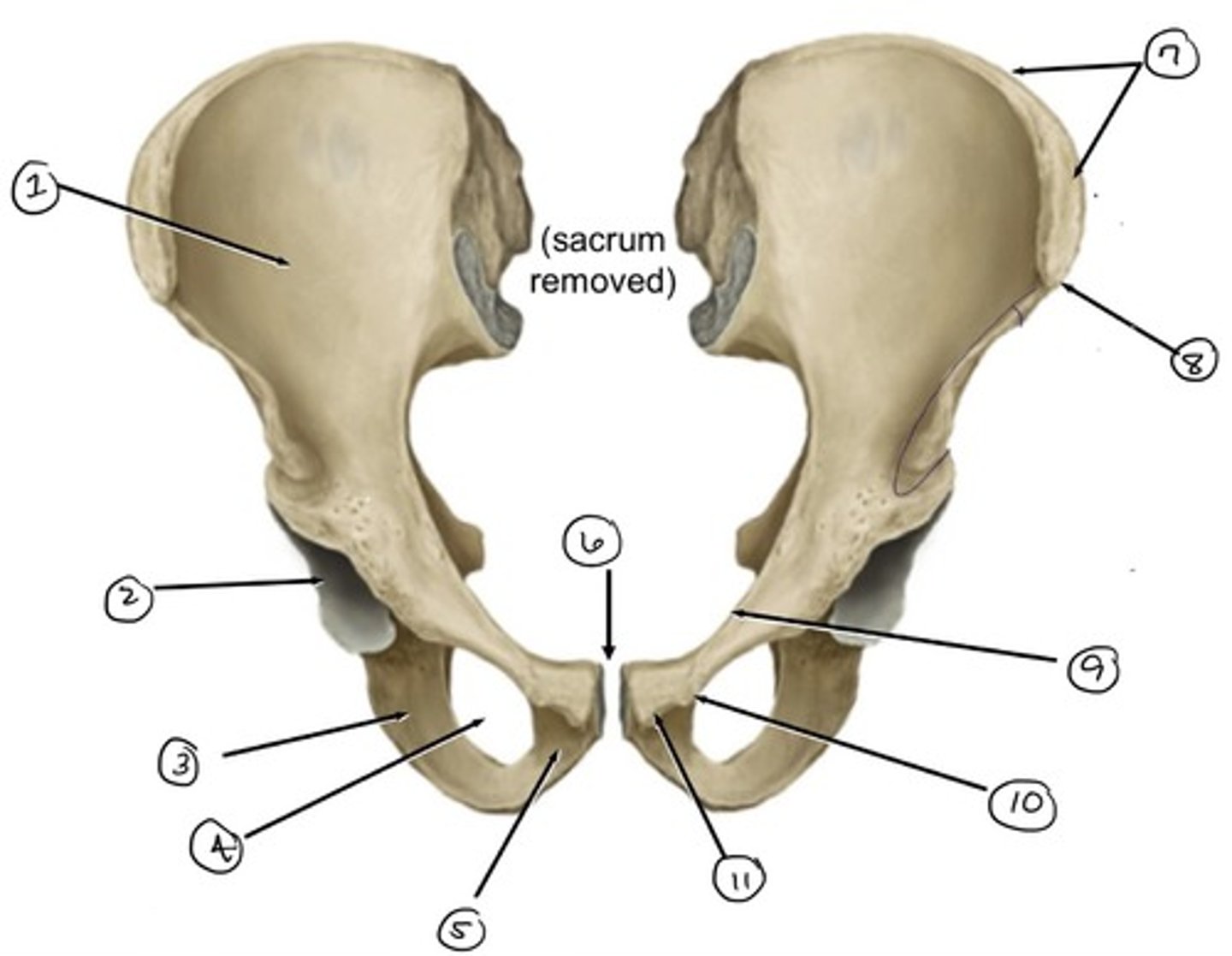
iliac crest
what is 7
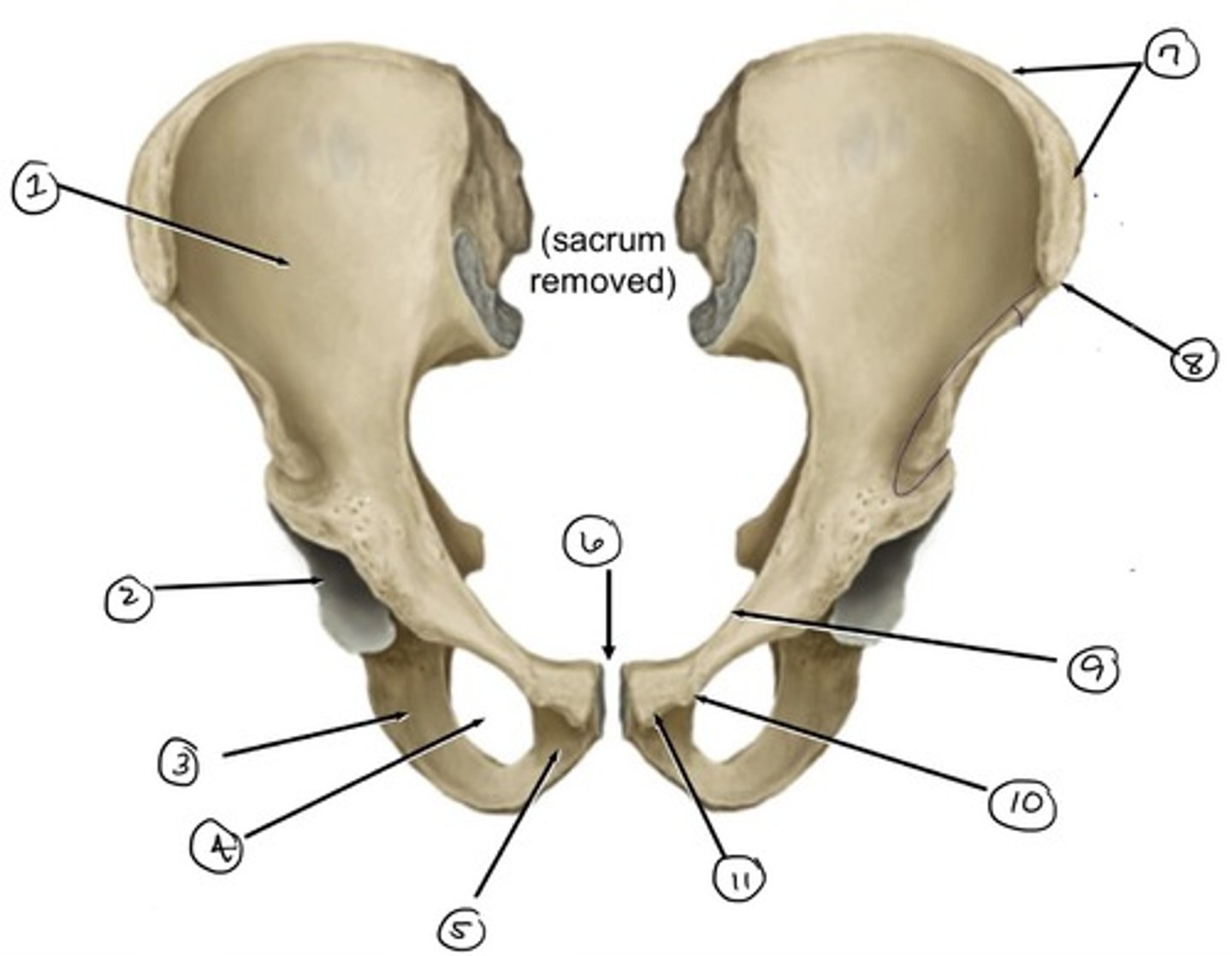
anterior superior iliac spine
what is 8

pecten pubis
what is 9

pubic tubercle
what is 10
pubic crest
what is 11
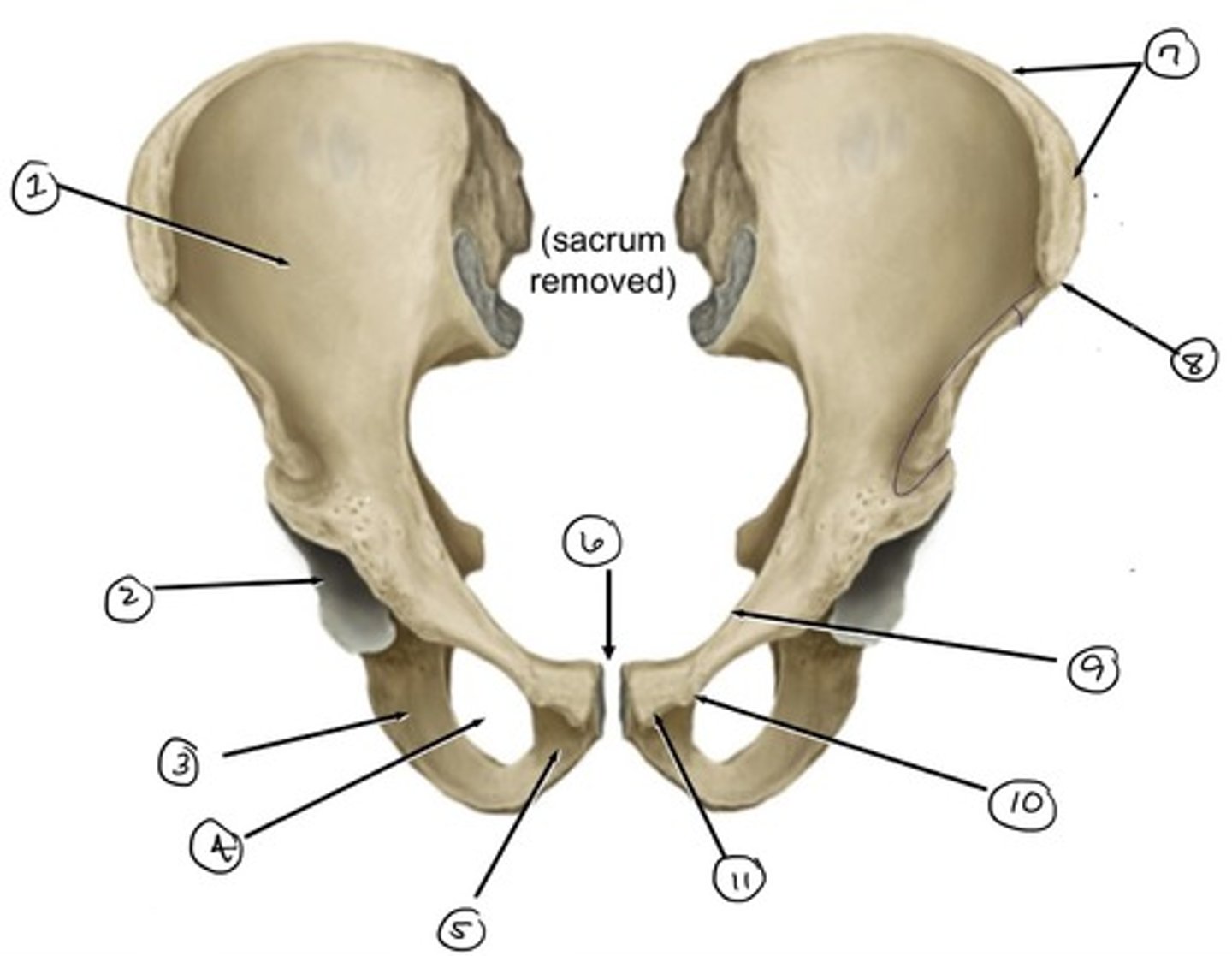
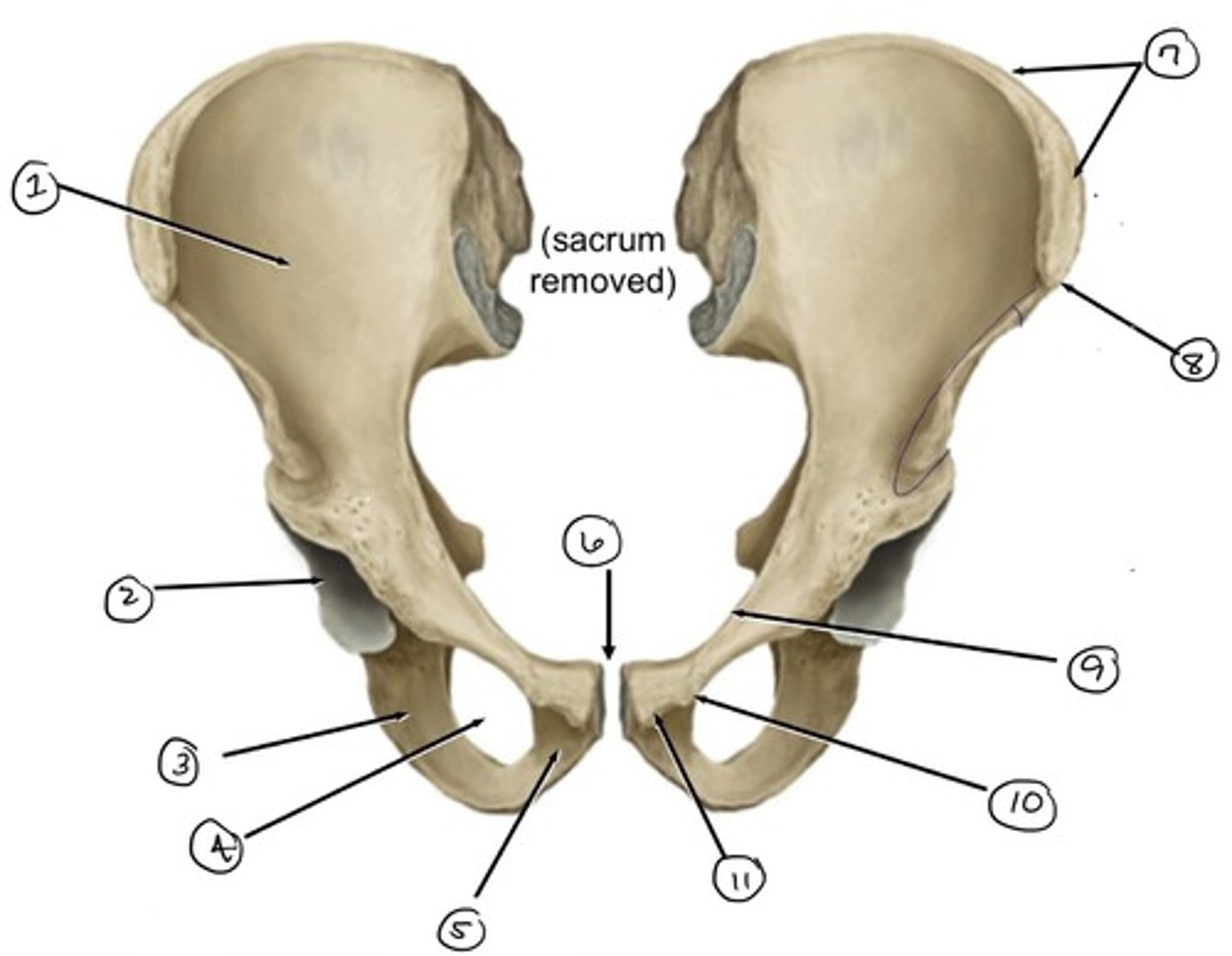
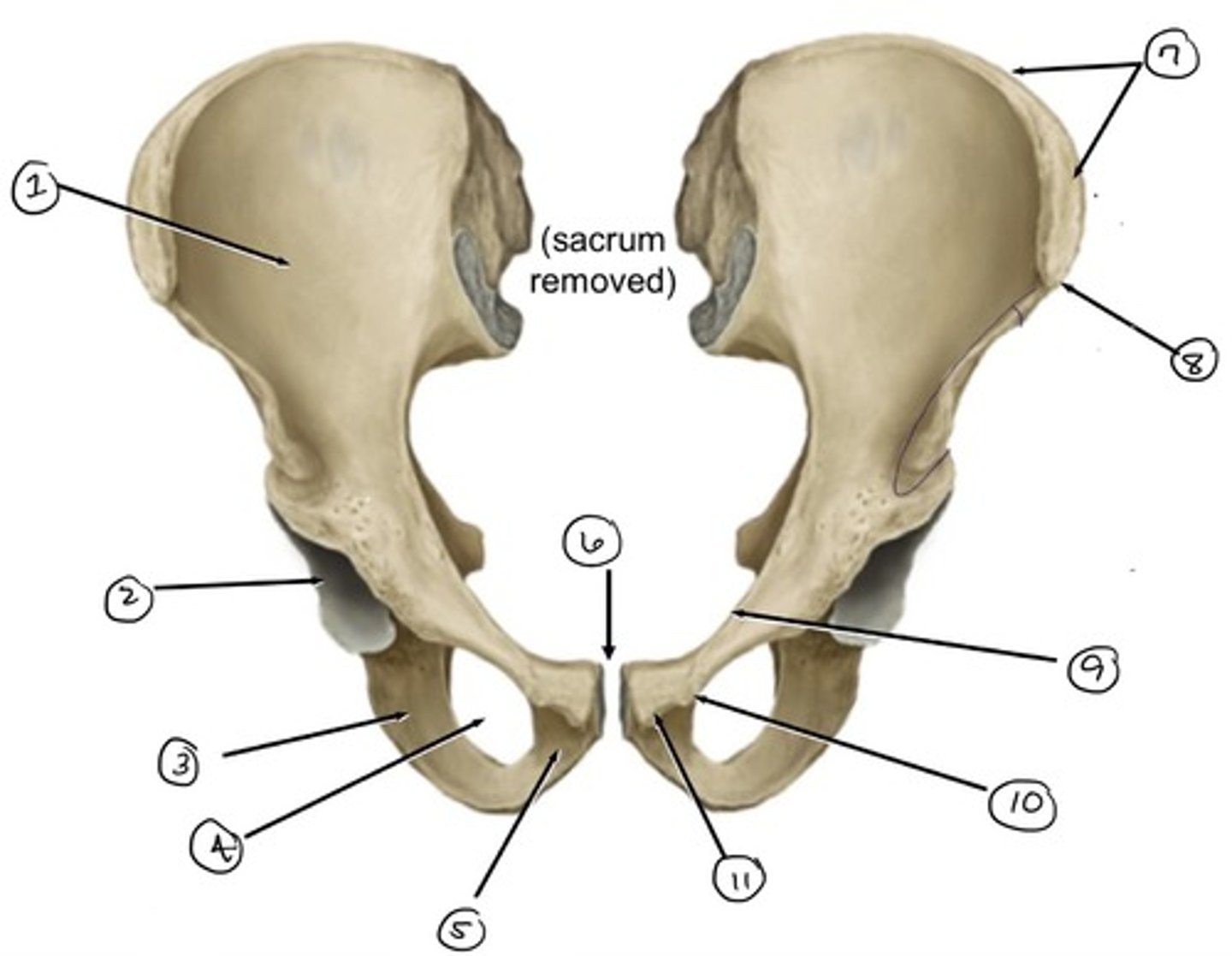
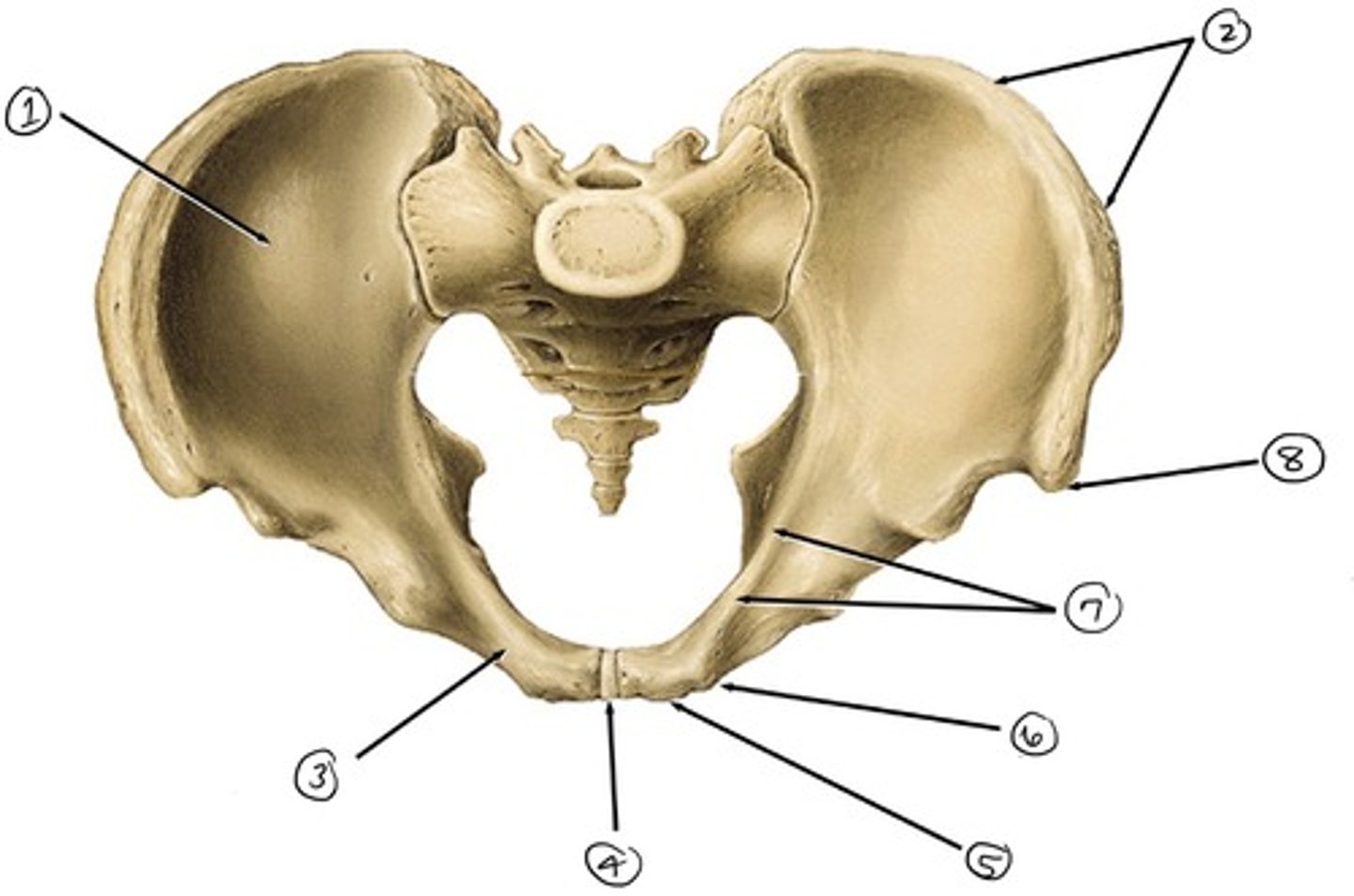
ilium
what is 1

iliac crest
what is 2

pubis
what is 3
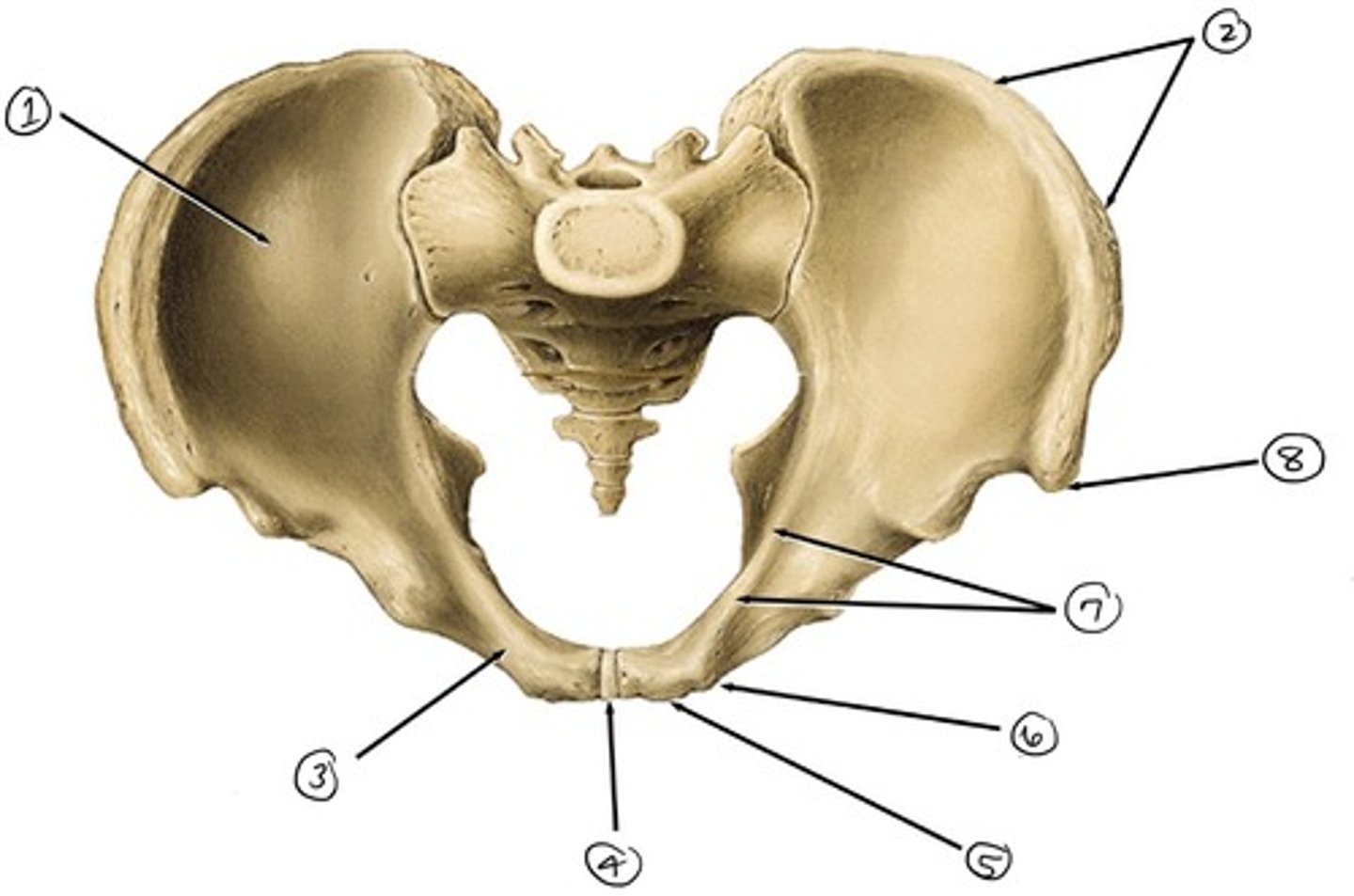
pubic symphysis
what is 4

pubic crest
what ss 5
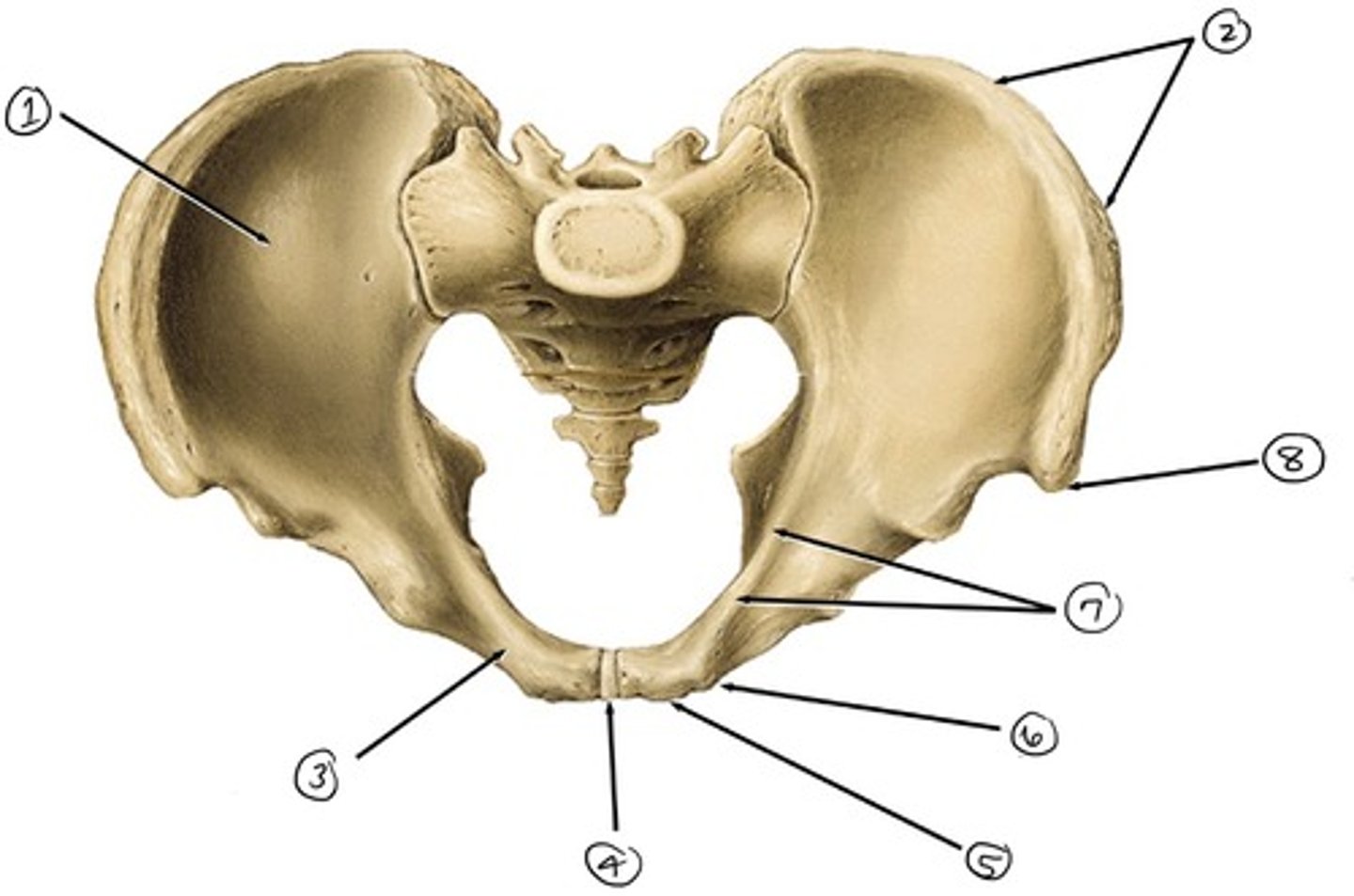
pubic tubercle
what is 6

pecten pubis
what is 7
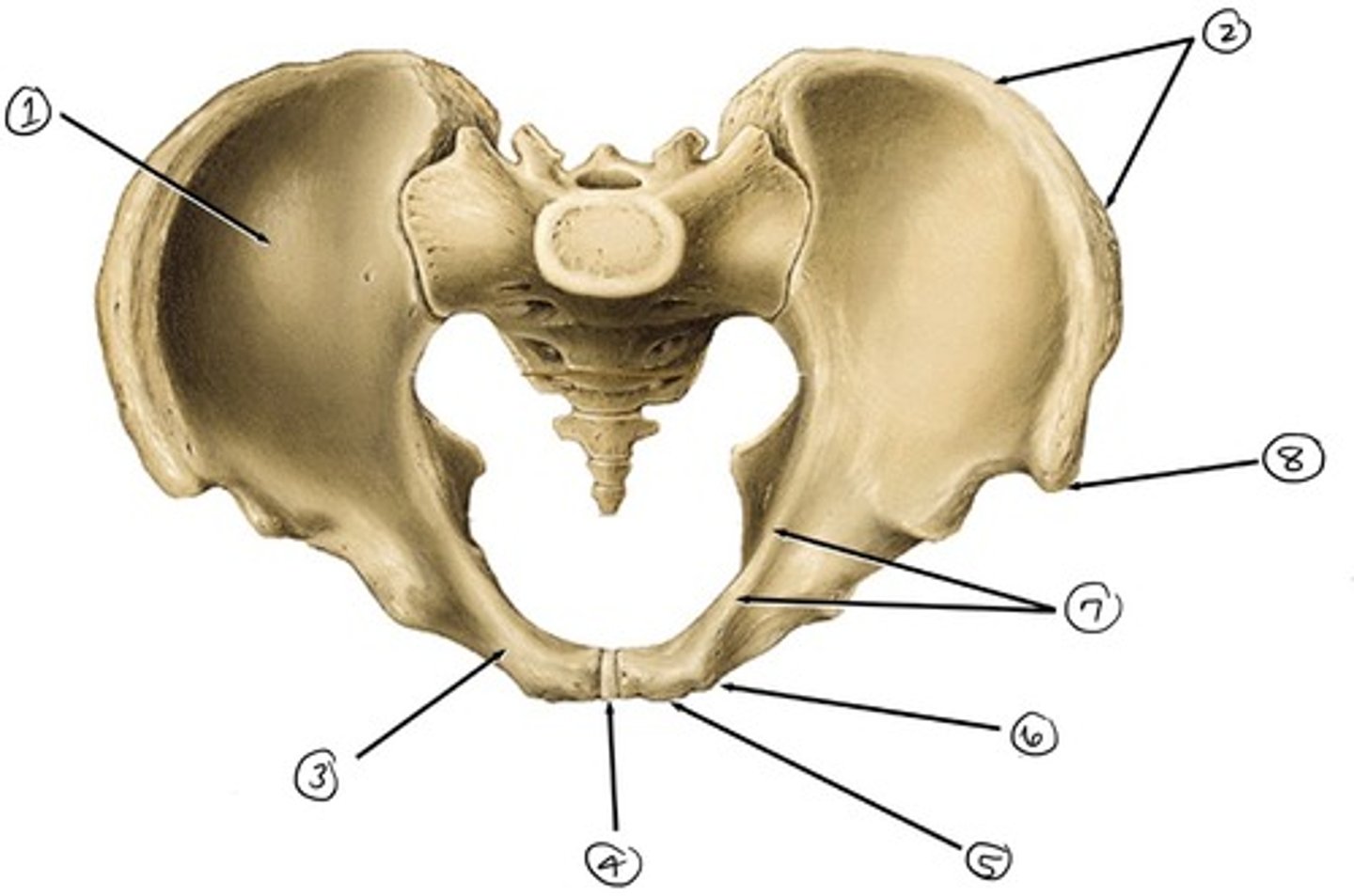
anterior superior iliac spine
what is 8
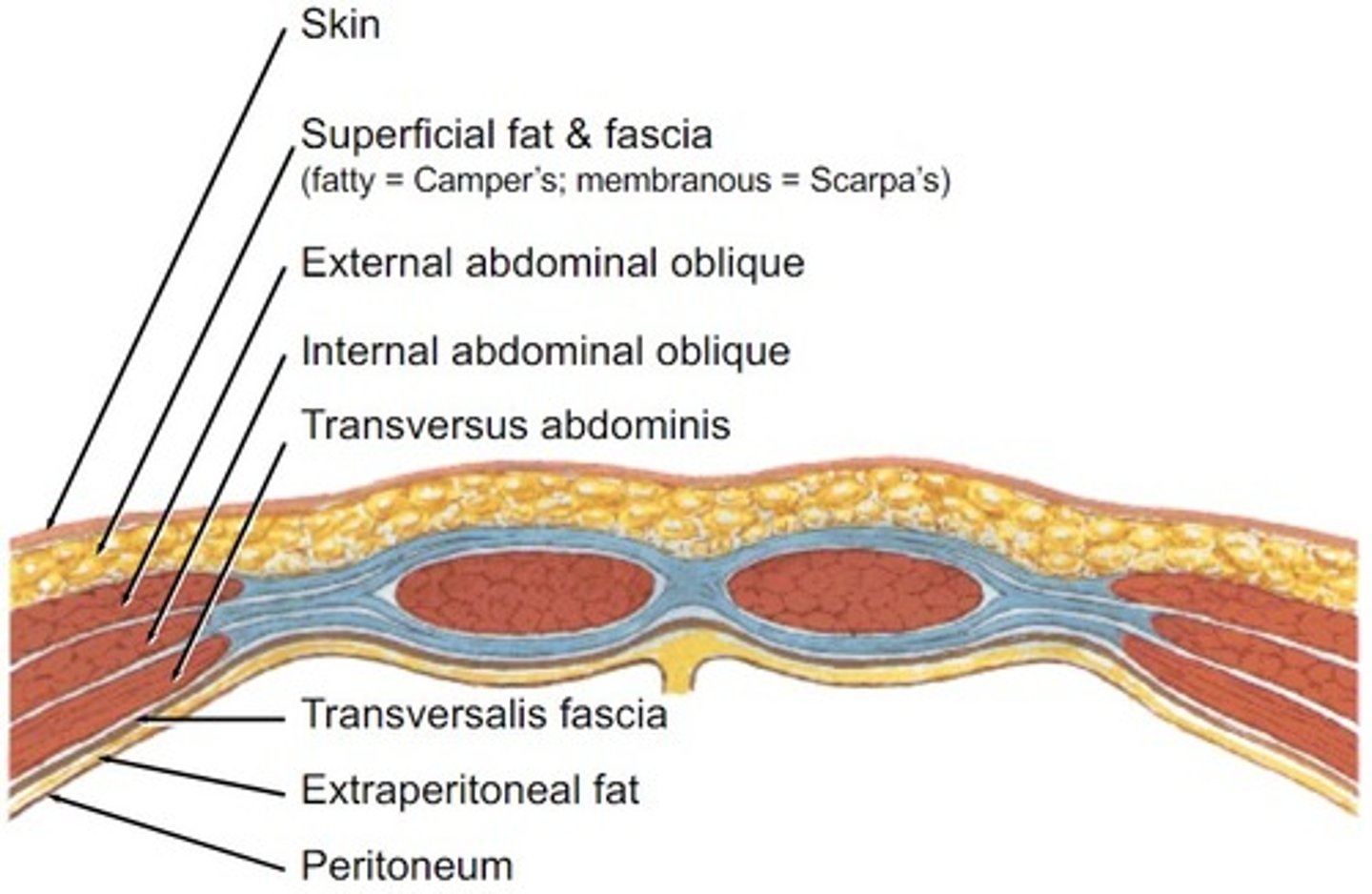
Camper's Fascia (camping out on the outskirts of town)
The superficial fatty layer of the abdomen
Scarpa's fascia
the deep membranous layer of the abdomen, continuous layer of superficial fascia of the scrotum and penis (dartos)
external abdominal oblique
the outermost layer of the anterolateral abdominal wall; contralaterally rotates trunk (unilateral); flexes trunk (bilateral)
T7-T11 intercostal nerves, subcostal nerve (T12), and L1
what is the innervation of the external abdominal oblique?
Origin: superficial surface of lower ribs; insertion: iliac crest, linea alba, pubic tubercle
what is the origin and insertion of the external abdominal oblique?

external abdominal oblique aponeurosis
The external abdominal oblique is connected to the linea alba by the _______________________
superficial inguinal ring
site for passage of spermatic cord in male and round ligaments of the uterus in female
inguinal ligament
ligament extending from pubic bone to anterior superior iliac spine, lower edge of external oblique aponeurosis
Intercrural fibers
fibers of the external oblique aponeurosis that form the top of the superficial inguinal ring
lateral crus
lateral margin of superficial inguinal ring; attaches to pubic tubercle
medial crus
medial margin of superficial inguinal ring; attaches to pubic symphysis
internal abdominal oblique
the middle layer of the anterolateral abdominal wall; ipsilaterally rotate trunk (unilateral); flex trunk (bilateral)
T7-T11 intercostal nerves, subcostal nerve (T12), and L1
what is the innervation of the internal abdominal oblique?
origin: thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, inguinal ligament; insertion: inferior border of lower ribs and intercostal margin, linea alba, pubic crest, pecten pubis
what is the origin and insertion of the internal abdominal oblique?
internal abdominal aponeurotic fibers
what internal abdominal oblique is connected to the linea alba by __________________________________
transversus abdominis
the innermost layer of the anterolateral abdominal wall, compresses abdomen and stabilizes trunk
T7-T11 intercostal nerves, subcostal nerve (T12), and L1
what is the innervation of transversus abdominis?
origin: internal aspects of lower 6 costal cartilages, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, and inguinal ligament; insertion: linea alba, pubic crest, pecten pubis
what is the origin and insertion of transversus abdominis?
aponeurotic fibers
transversus abdominis is connected to its insertion via __________________
rectus abdominis
muscle on the abdomen that flexes trunk and compresses viscera- sectioned by tendinous intersections
T7-T11 intercostal nerves, subcostal nerve (T12) [not T12]
what is the innervation of rectus abdominis?
origin: pubic symphysis, pubic crest; insertion: anterior aspect of xiphoid process, anterior aspects of costal cartilages 5-7
what is the origin and insertion of rectus abdominis?
increases
contraction of abdominopelvic muscles ____________ stability of core
Valsalva
the ________________ maneuver entails increasing abdominal pressure by holding a deep breath while contracting the abdominal muscles. the depressed diaphragm increases abdominal pressure and helps push out organ contents during childbirth, urination and defecation.
Superior; the posterior rectus sheath is present
Is the picture a representation of the abdominal wall superior or inferior to the arcuate line? How do you know?
inferior ; there is no posterior rectus sheath inferior to the arcuate line
Is the picture a representation of the abdominal wall superior or inferior to the arcuate line?

rectus abdominis
what is 1
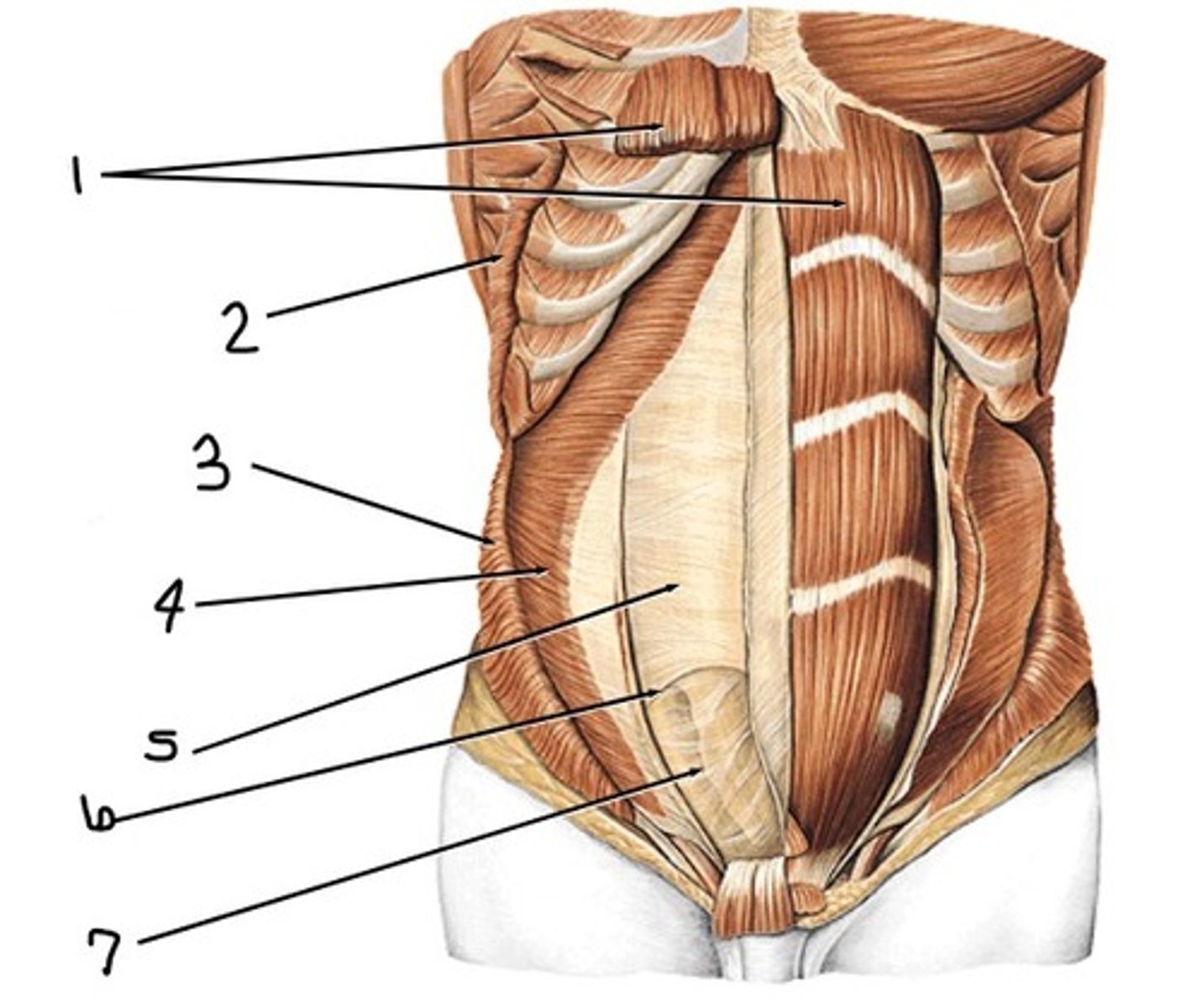
external abdominal oblique (cut away)
what would have been at 2 (notice the origin at the superficial surface of lower ribs)
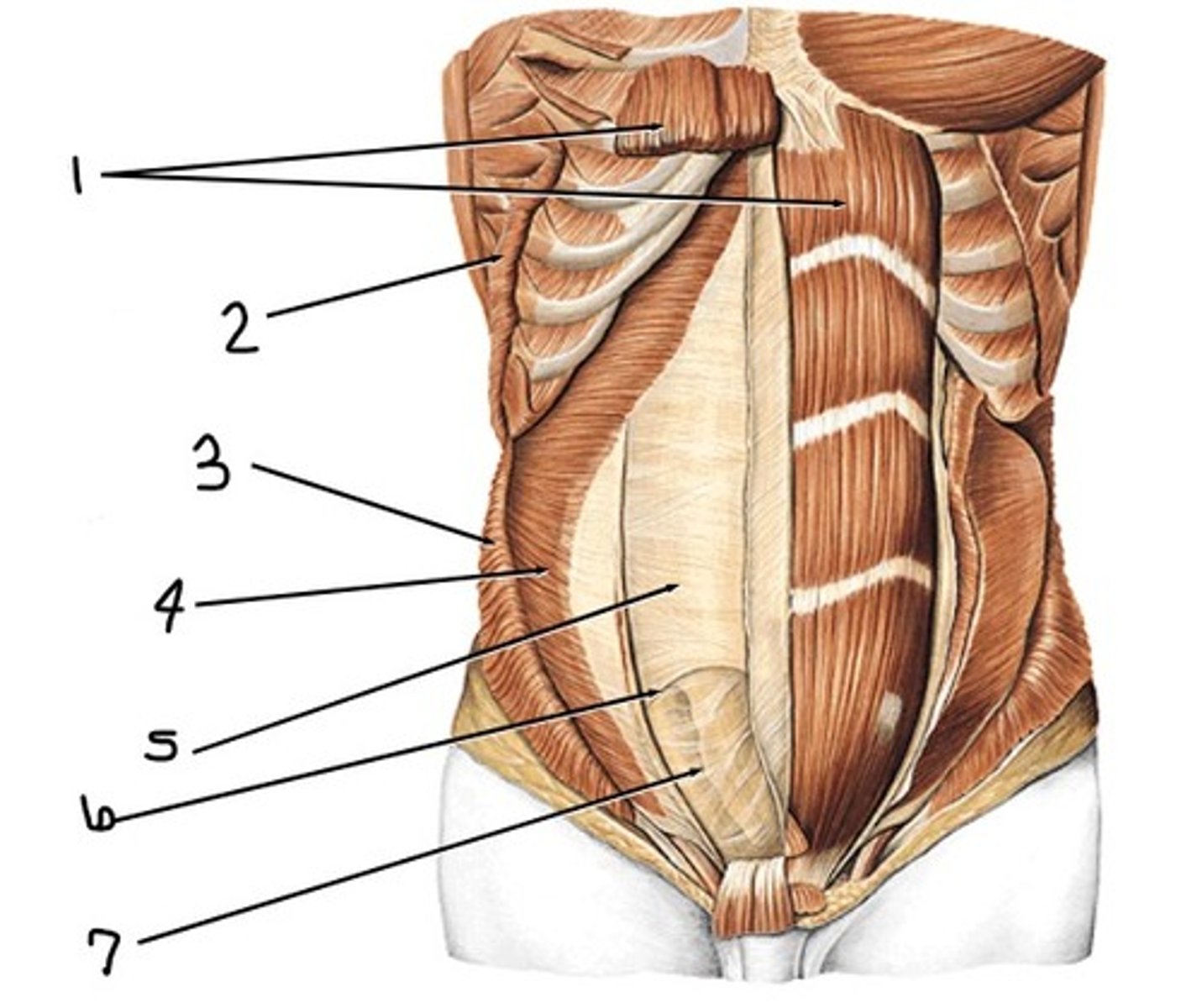
internal abdominal oblique (cut away)
what would have been at 3 (notice the insertion at inferior border of lower ribs and intercostal margin, pubic crest, and pecten pubis)
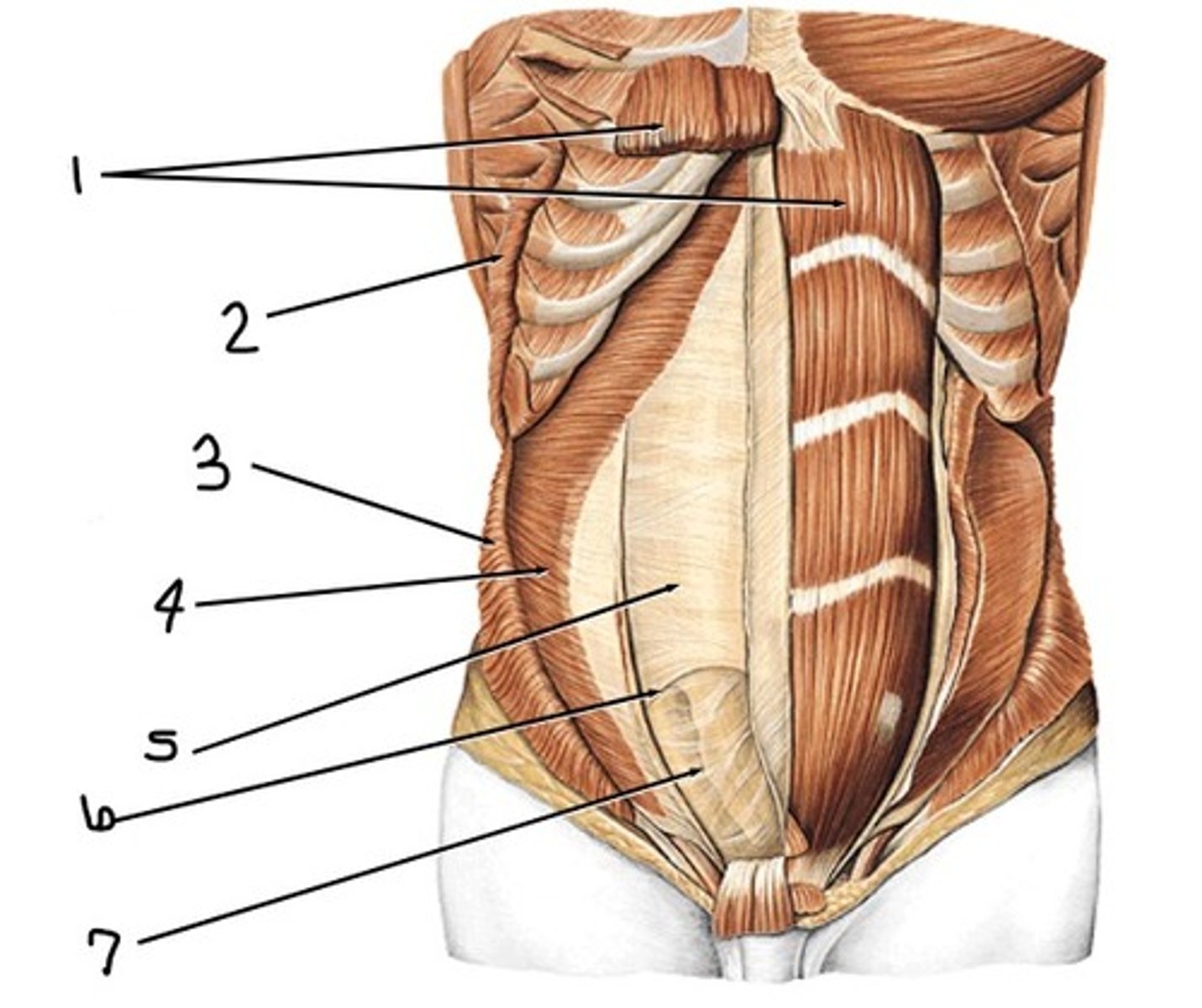
transervsus abdominis
what is 4

posterior rectus sheath
what is 5
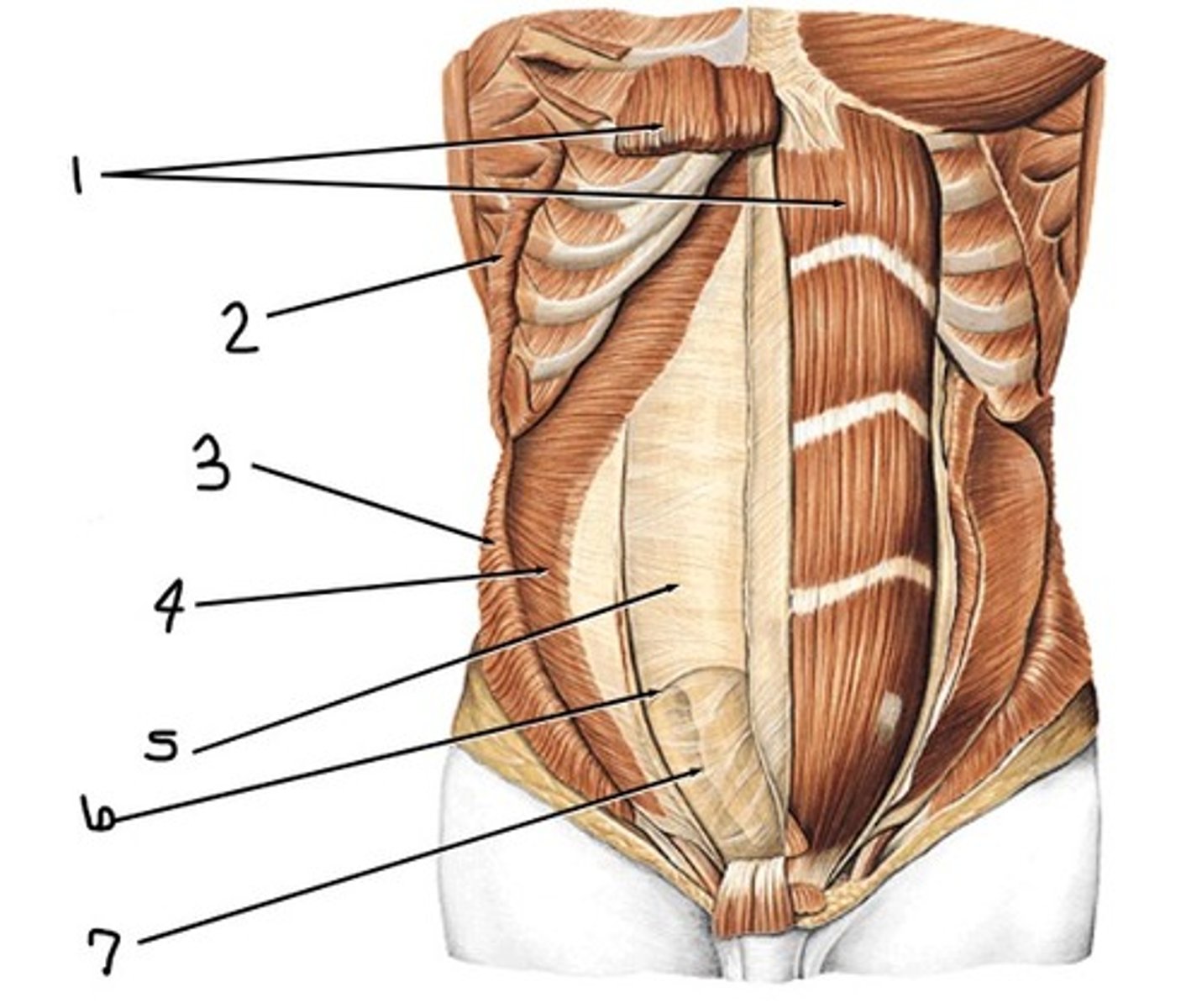
arcuate line
what is 6

transversalis fascia
what is 7

superior epigastric artery and vein and inferior epigastric artery and vein
what vessels are in the rectus sheath?
internal thoracic artery and vein
where do the superior epigastric artery and vein originate?
external iliac artery and vein
where do the inferior epigastric artery and vein originate?
median umbilical fold
what is 1

medial umbilical fold
what is 2
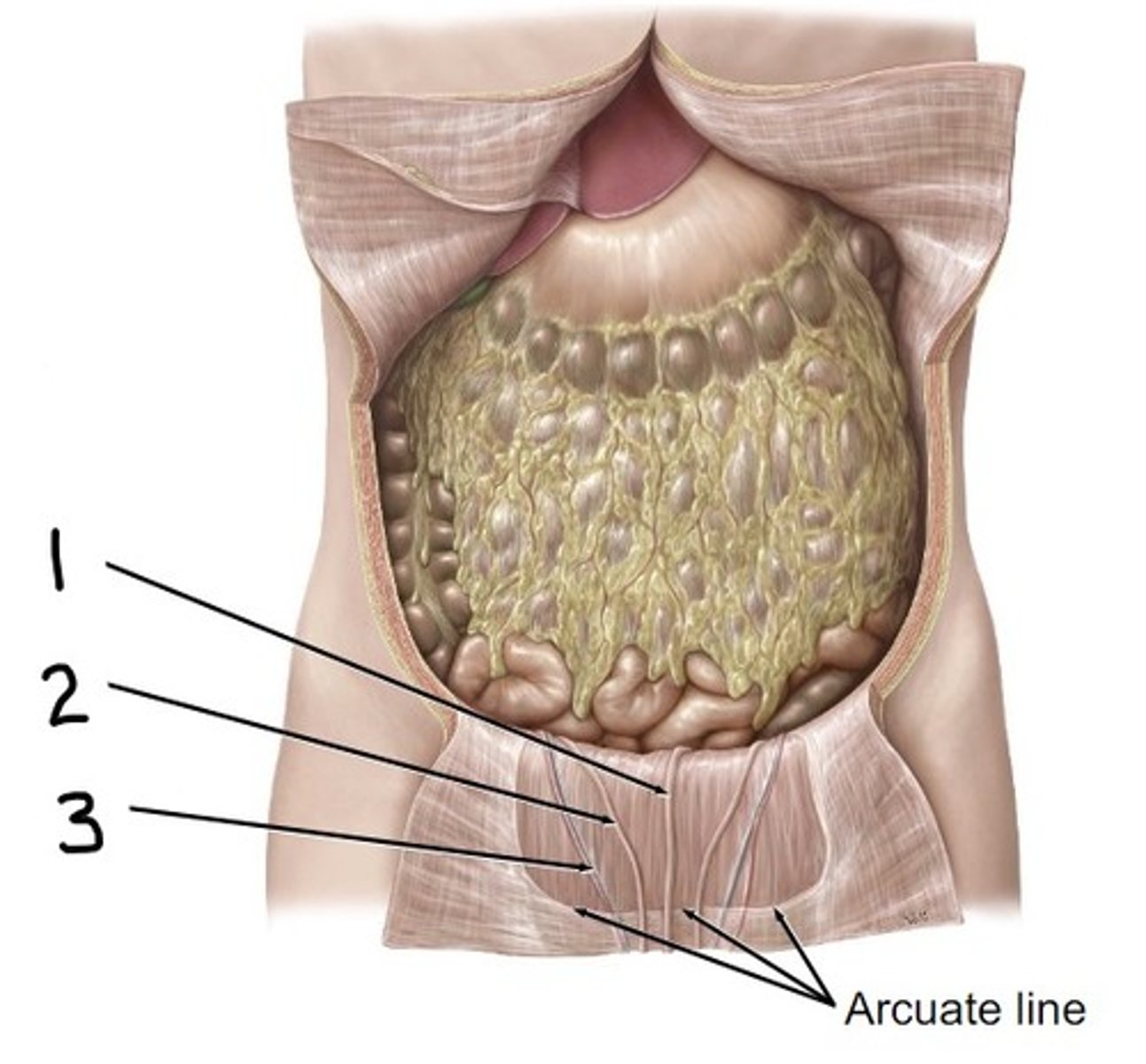
lateral umbilical fold
what is 3

lateral umbilical fold
what is 1

medial umbilical fold
what is 2

median umbilical fold
what is 3
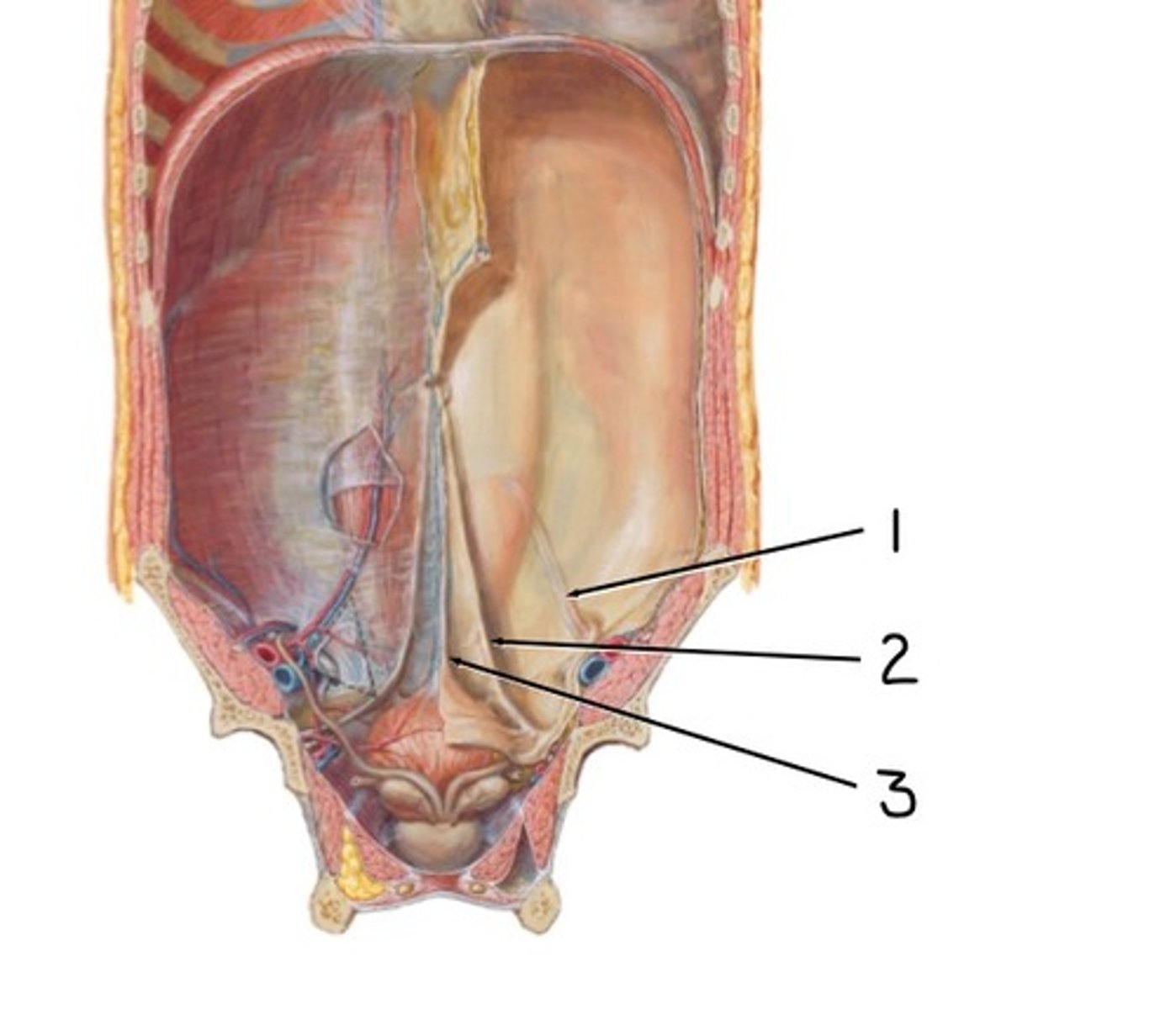
Gubernaculum
Aids the descent of testes and ovaries
aponeurosis of external oblique
what make sup the anterior "wall" of the inguinal canal?
medial half of inguinal ligament
what makes up the "floor" of the inguinal canal?
internal oblique & transversus abdominis muscle
what makes up the "roof" of the inguinal canal?
Tranversalis fascia (this is the weakest part)
what makes up the posterior "wall" of the inguinal canal?
collapses; anteriorly
contraction of the abdominal wall muscles __________ the roof of the inguinal canal, increasing the intra-abdominal pressure compressing the canal __________
True
True or False: failure to "close" the canal can lead to herniation of abdominal viscera
deep inguinal ring
what is 1
Inguinal Triangle of Hesselbach
what is 2
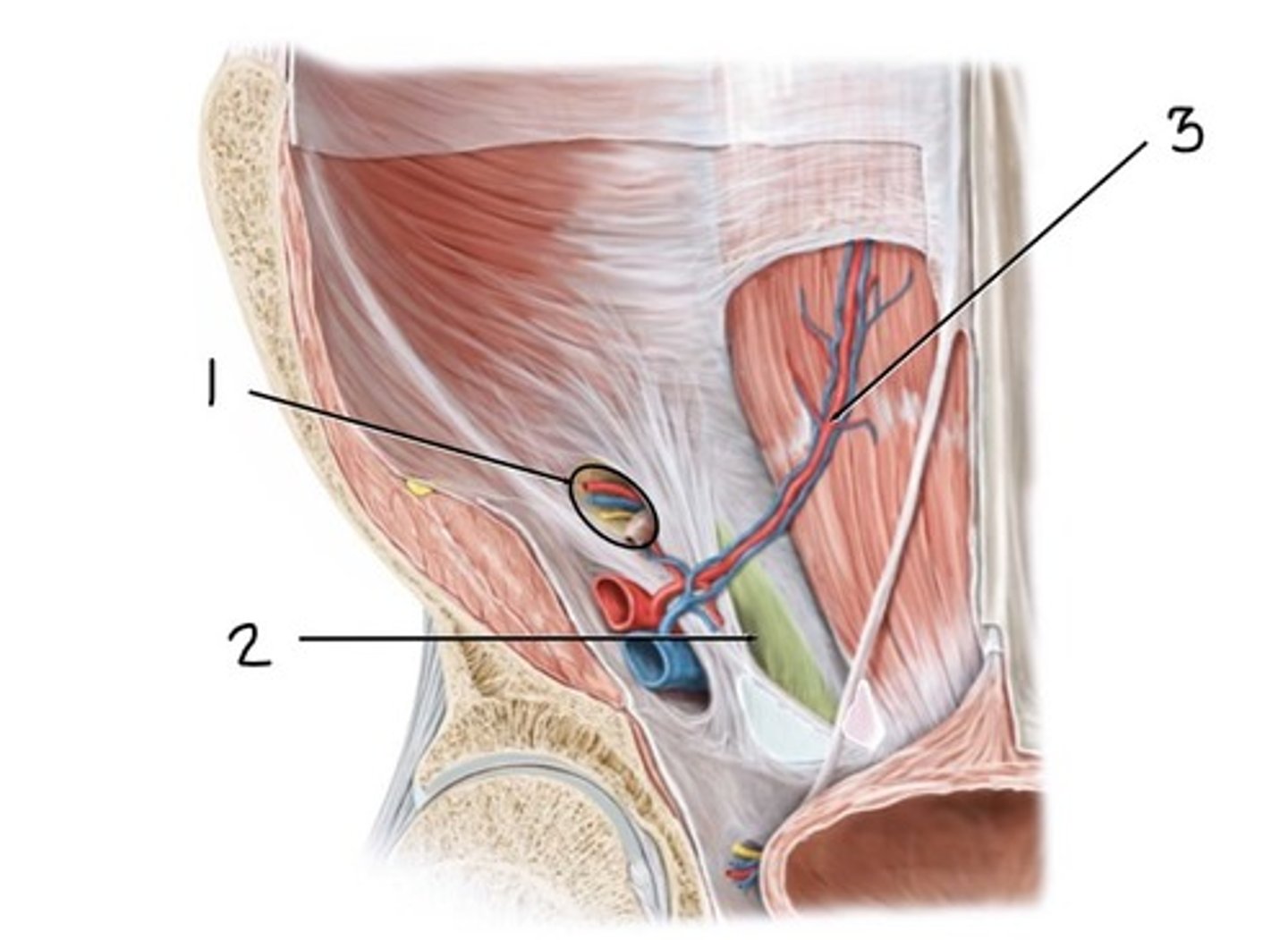
inferior epigastric artery and vein
what is 3

the deep inguinal ring
where do indirect inguinal hernias exit the abdominal cavity?
entire canal
indirect inguinal hernias typically traverse the _________
lateral
indirect inguinal hernias usually occur _________ to the inferior epigastric artery and vein
congenital (often early in life)
indirect inguinal hernias are _______________________
the Inguinal triangle (posterior wall of inguinal canal)
where do direct inguinal hernias exit the abdominal cavity?
medial
direct inguinal hernias usually occur ____________ to the inferior epigastric artery and vein
acquired (often in old age)
direct inguinal hernias are ________________
shortens; descend
in male inguinal development, the gubernaculum ____________, causing testes to __________________ through anterior abdominal wall
shortens; uterus
in female inguinal development, the gubernaculum __________, but is interrupted by the developing _____________________
true
true or false: as the testis and spermatic cord travel through the inguinal canal, they are enveloped by thin layers derived from the abdominal wall
tranversalis fascia: internal spermatic fascia
transversus abdominis: no contribution
internal oblique: cremaster muscle (and fascia)
external oblique: external spermatic fascia
as the testes descend through the inguinal ring, they pick up layers of the muscles they pass. Recall what these these layers become. (Transversalis fascia, transversus abdominis, internal oblique, and external oblique)
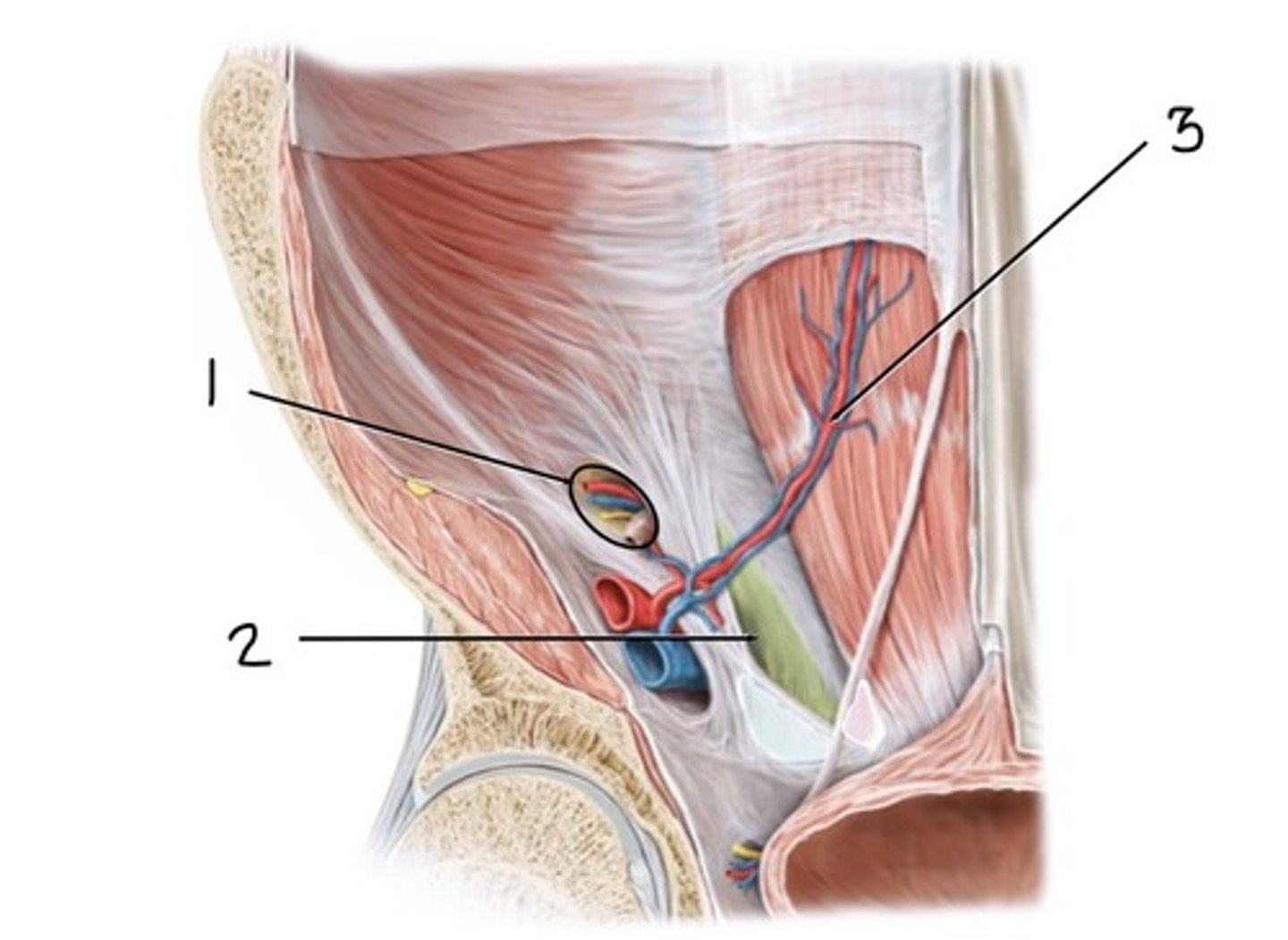
ductus (vas) deferens, testicular artery, pampiniform plexus of veins, lymphatics, genital branch of genitofemoral nerve (L1-L2)
what are the contents of the spermatic cord?
testicular artery
what is 1

ductus deferens
what is 2
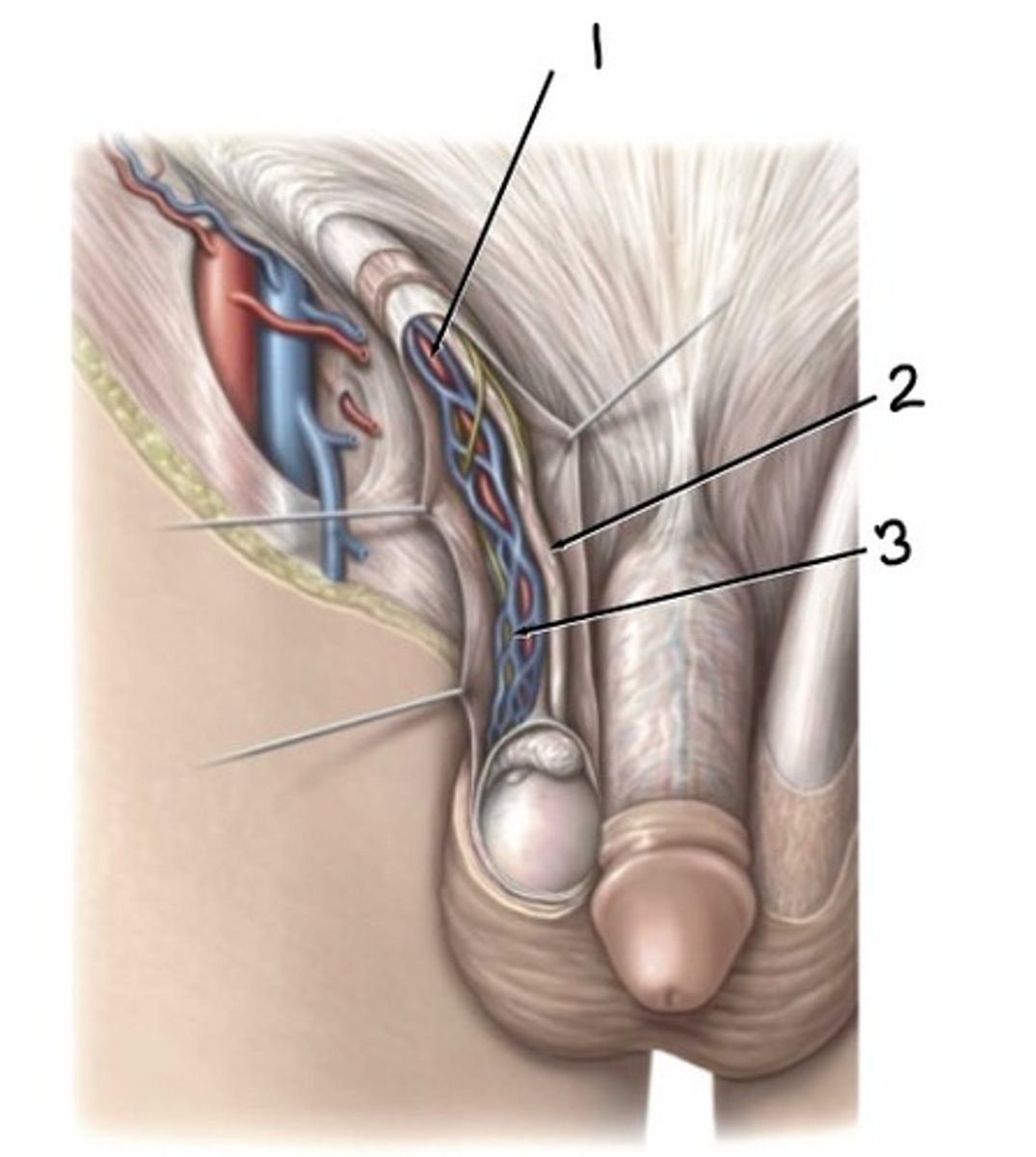
pampiniform plexus
what 3

dartos
The ____________ fascia and muscle is continuous with Scarpa's fascia, thickens scrotal wall and helps draw testes closer to body for heat regulation
L1-L2
the genitofemoral nerve is innervated by SC levels ___________
superficial inguinal
the lymphatics of the scrotum drain into _______________________________ lymph nodes
tunica vaginalis
covering, particularly of a tubular structure; the sheath of the testis and epididymis
processus vaginalis
The tunica vaginalis is a remnant of this embryological structure
parietal tunica vaginalis, and visceral tunica vaginalis
tunica vaginalis is made up of two layers:
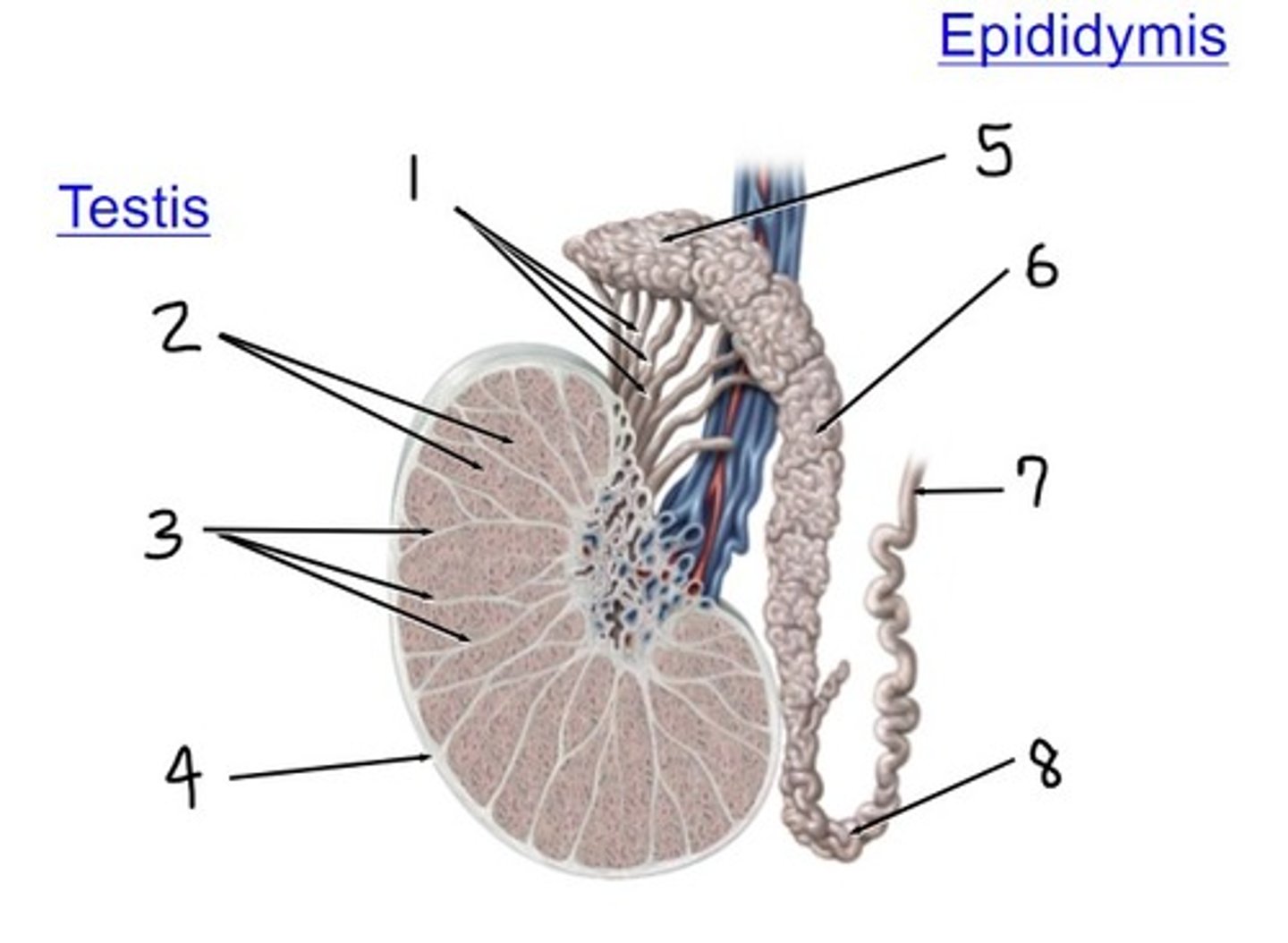
efferent ductules
what is 1
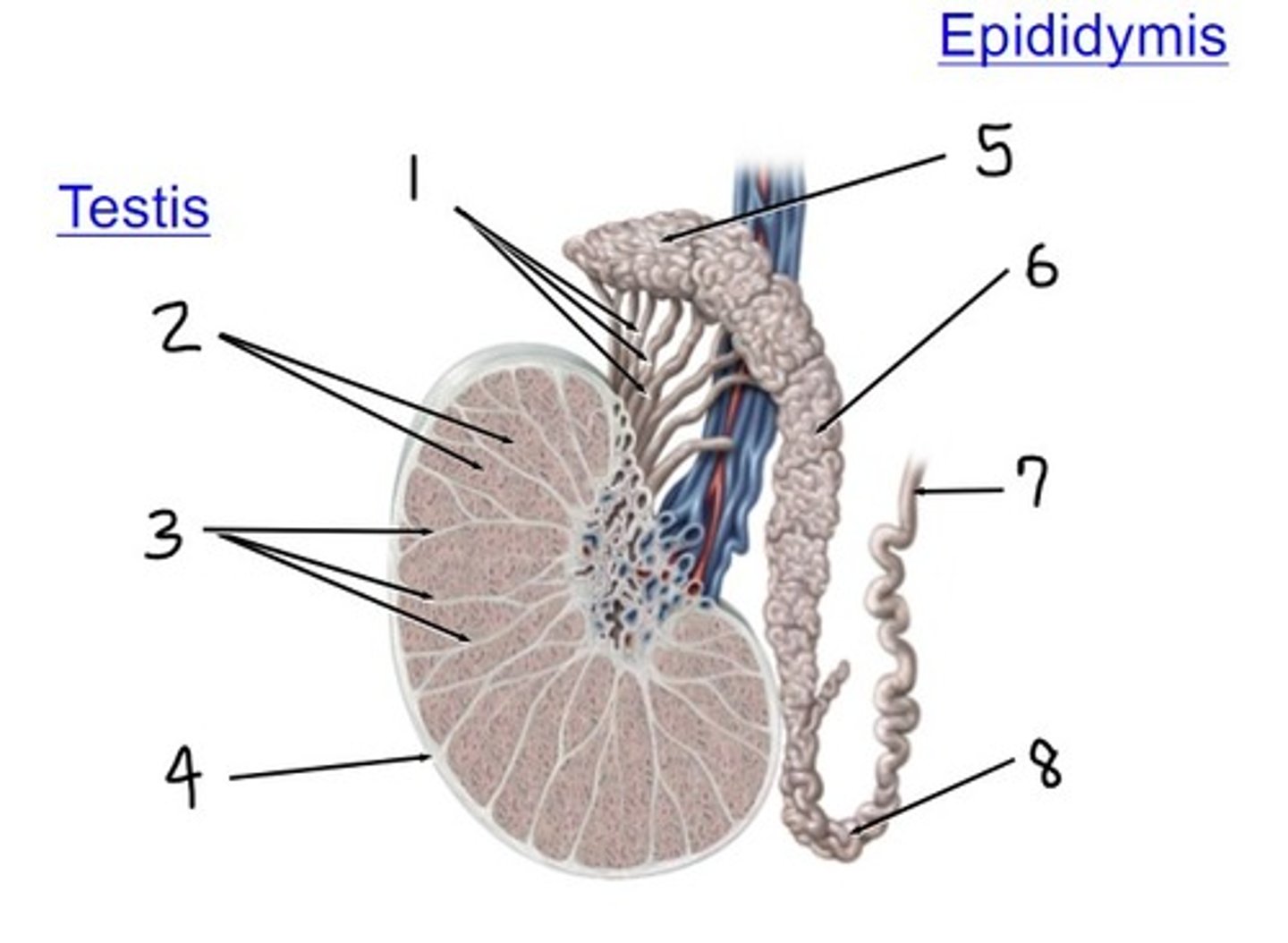
lobules
what is 2
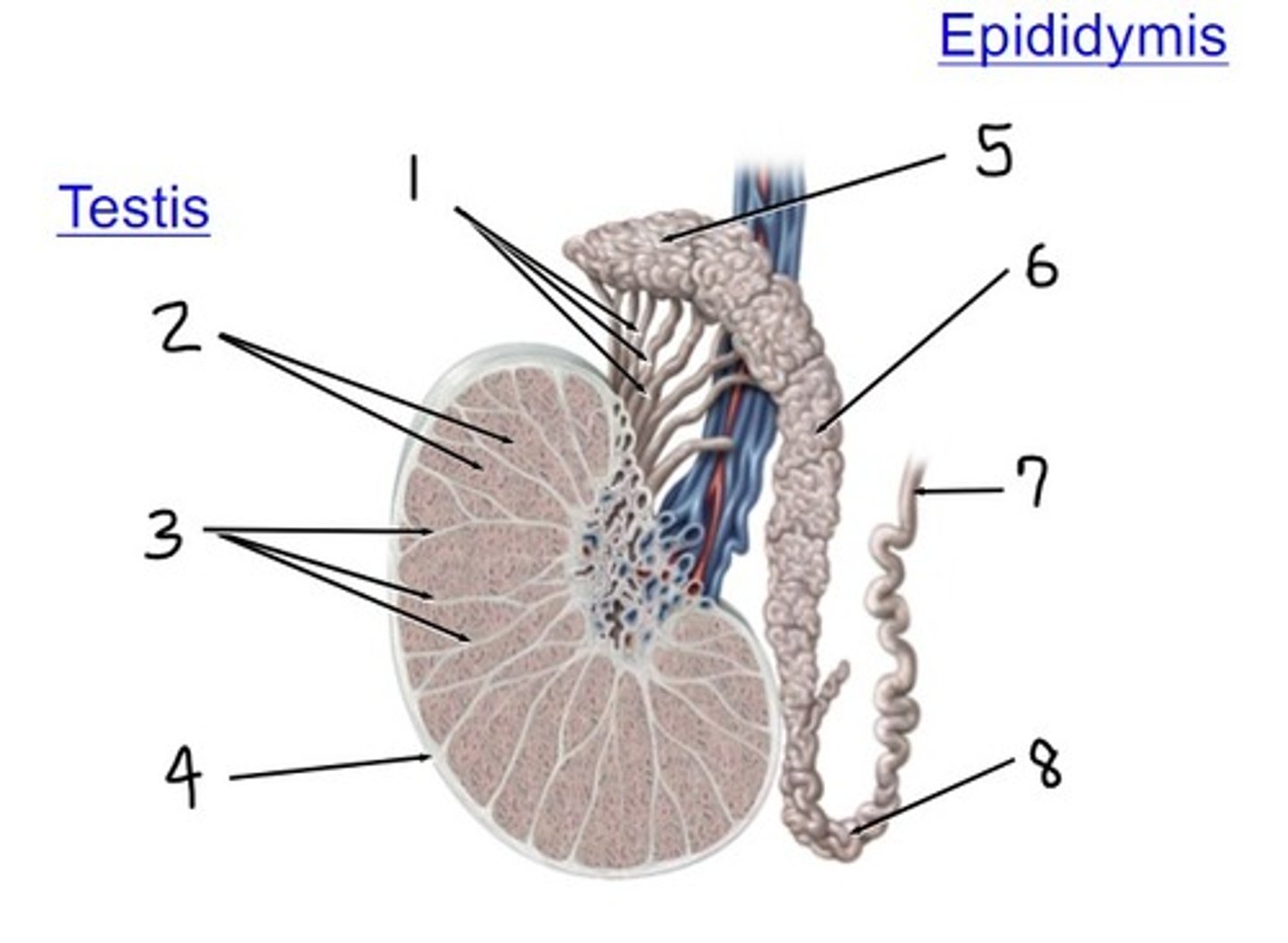
septa
what is 3
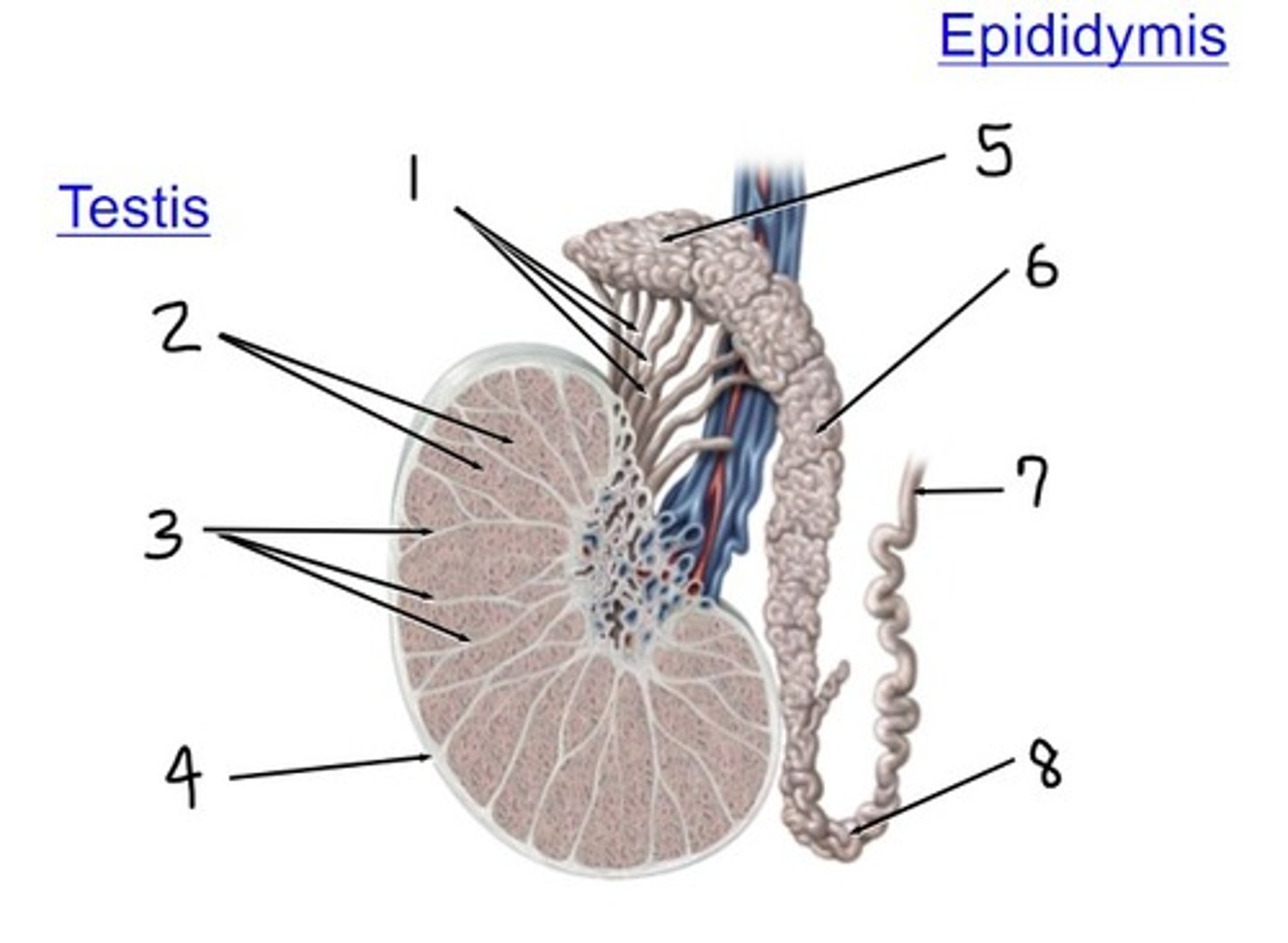
tunica albuginea
what is 4

head
what is 5

body
what is 6
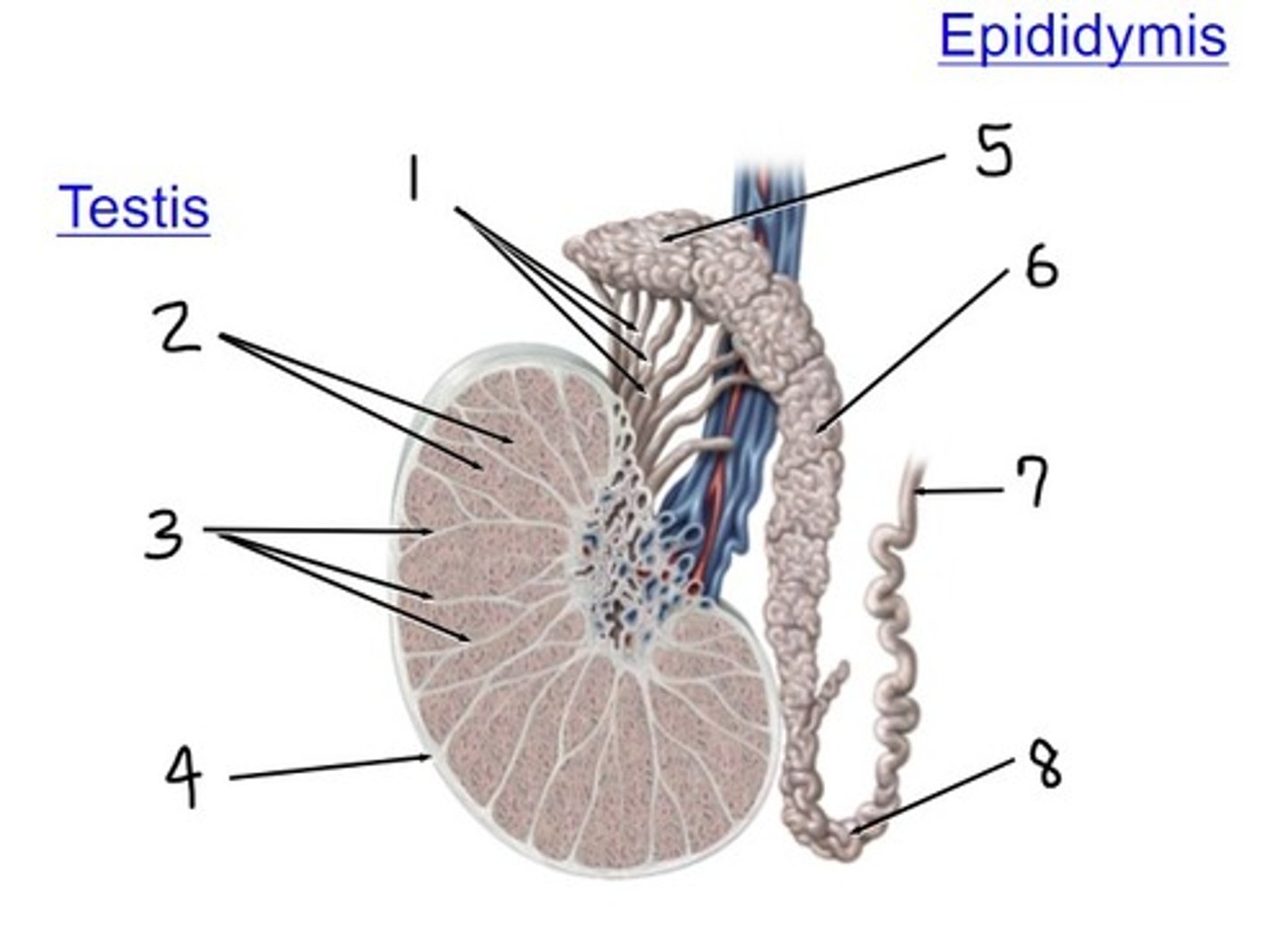
ductus (vas) deferens
what is 7

tail
what is 8