2.1.1 Atomic structure and isotopes
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is the definition of relative isotopic mass?
The mass of an atom of an isotope compared with 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
What is the definition of isotopes?
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons and so, different masses.
What is the definition of relative atomic mass?
The weighted mean mass of an atom of an element compared with 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
What does it mean by ‘the weighted mean mass’ in relative atomic mass?
It takes account the abundance of different isotopes for an element, giving a more accurate average of atomic mass.
What is the relative mass and relative charge of a proton?
Relative mass = 1
Relative charge = +1
What is the relative mass and relative charge of a neutron?
Relative mass = 1
Relative charge = 0
What is the relative mass and relative charge of a electron?
Relative mass = 1/1836
Relative charge = -1
What are the uses of mass spectrometry?
To find the relative isotopic masses and the relative abundances of the isotope
(abundance tells us how common each isotope is)
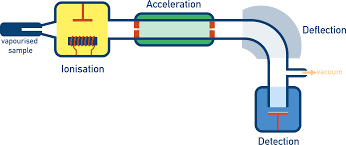
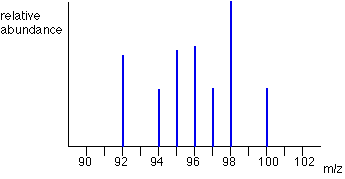
How do you interpret the mass spectra to find the relative atomic mass?
The symbol m/z means mass/charge.
The 3 key characteristics:
The number of peaks shows how many isotopes there are.
The m/z value of each peak shows the isotope mass (because the charge of the ion is +1, so everything divided by 1 is that number).
The height of each peak shows the relative abundance of that isotope.
What is the formula to find the relative atomic mass (RAM) ?
The sum of (each relative isotopic mass x its abundance) divided by the total abundance (usually 100)
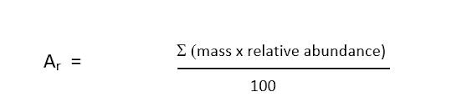
What is the definition of relative molecular mass (Mr) ?
The weighted mean mass of a molecule of a compound compared with 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
Used for simple covalent substances
What is the definition of relative formula mass?
The weighted mean mass of the formula unit of a compound compared with 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
used for ionic substances
Why is the carbon-12 isotope chosen as the international standard?
Because it can be obtained in an isotopically pure state and is unreactive.