Chemistry Test -- Matter, Density Percent Error, Atoms, Temperature Conversions
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
matter, density, atoms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
what is chemistry?
study of matter, its composition, its structure, its properties, and its reactions
what is matter? is air matter?
anything that has mass and takes up space
yes because it takes up space and has mass
what is a pure substance?
matter that always has the same composition
uniform composition and fixed properties
elements and compounds
what are elements?
cannot be broken down
substances made up of one type of atom
contains one type of atom
1st letter capital and 2nd letter lowercase
what are compounds?
substances made of 2 or more elements that are chemically bonded
can be broken down into simpler substances and will not have those characteristics
properties of a compound are different than the properties of the elements that make up
what are mixtures?
combinations of substances that are not chemically bonded together
retain some properties of individual substances
composition is not fixed
what are the two types of mixtures?
homogenous and heterogenous
what is an example of a homogenous mixture? explain.
solution
particle are too small to settle out, to be trapped by filter, to scatter light
what are 2 examples of a heterogenous mixture? explain.
suspension
separates into layers over time
particle are trapped by filters and can scatter light
oil and water, dirt and water, orange juice
colloid
particles never settle out
scatter light = Tyndall effect
gel, fog
how do you find density?
D = m/v
solids —> g/cm³
liquids —> g/mL
round to sig fig
how do you find volume with formula and water displacement?
volume found by multiplying height, width, and length
subtract amount of water by how much it rose
what is the formula for percent error?
percent error = (experimental value - accepted value) / (accept value) * 100
review the scientists and their experiments.
review !!
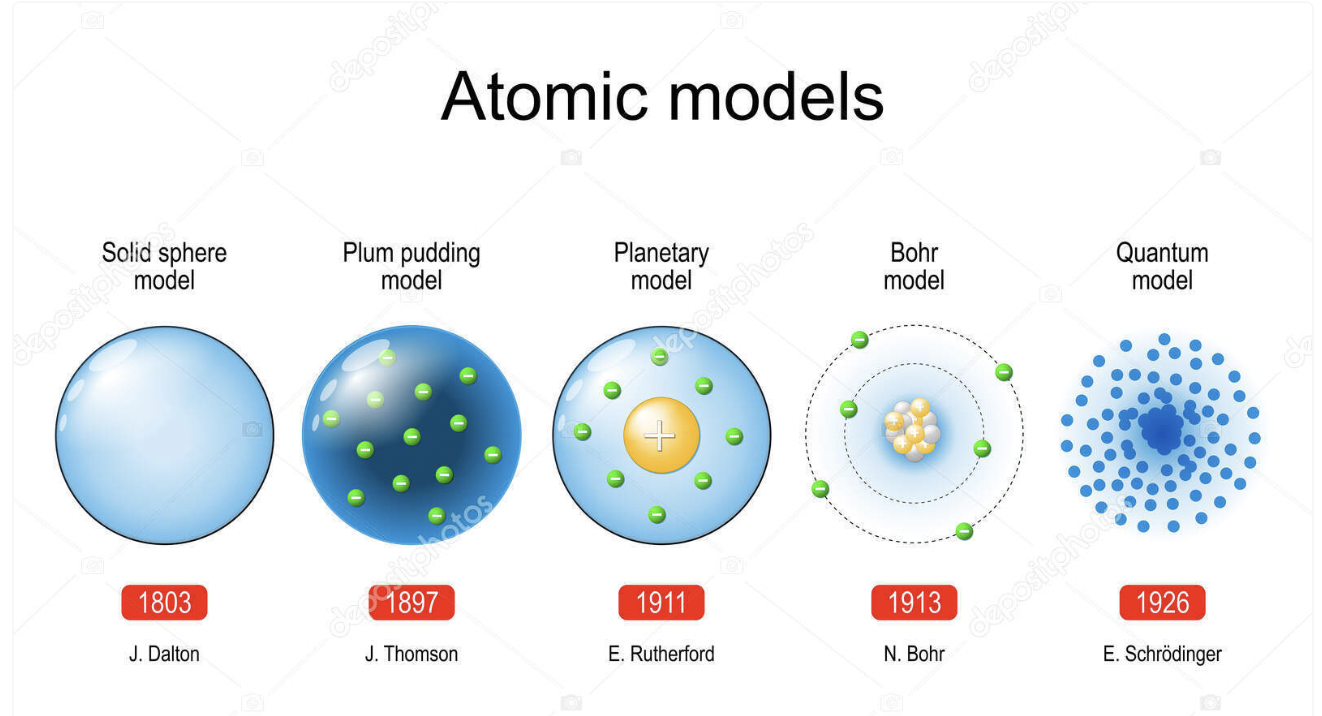
know this
what is the atomic number?
# of protons in each atom of a given element
unique to each elements and does not change
tells # of electrons for the elements if the element is neutral
protons = ___ or ___
electrons or mass number
what is an isotope?
amount of protons and electrons are constant in all neutral atoms of an element, but the # of neutrons can vary
atoms of the same element that have different # of neutrons
what are ions?
typically in an atom, the electron can change the # of protons and neutron do not change especially in chemical reactions
gained or lost electron therefore they have a charge
cation: lost (+)
anion: gained (-)
what is a Bohr model?
focused on electron
count # of electrons and place in energy levels
what changes in an atom and what stays the same for chemical reactions?
the electrons in the outer shells of atoms are rearranged
the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus stays the same
what is unique for each element? what is the most common isotope for each element? why does an element have a positive or negative charge?
it has a specific number of protons in its nucleus, called its atomic number
most common isotope of an element is the one that has the most stable nucleus
an element gets a positive charge if it loses electrons or a negative charge if it gains electrons
how do you calculate average atomic mass?
(mass * percent) + (mass * percent) …
what are the conversion formulas for Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin?
F = (C * 1.8) + 32
C = (F - 32)/1.8
K = C + 273.15
identify the masses of various subatomic particles and tell where the atom gets most of its weight/mass.
almost all of an atom’s weight comes from the protons and neutrons in the nucleus
what is the difference between accuracy and precision?
accuracy is how close a measurement is to the actual value
precision is how close together a group of measurements are
how is science and philosophy different?
science uses experiments and observations to test ideas about the natural world
philosophy uses reasoning and logic to explore questions about existence, knowledge, and meaning.