Mr. Bastin - Cnidarians
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Taxonomy
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Cnidaria (from Greek "nettle"
Cnidarian Basics (includes, live with anyone, feeding, where they live)
-most marine
-includes hydras, jellyfish, sea anemones, coral
-some colonial
-carnivorous w/ stinging tentacles
Structure
-simplest animals to have body symmetry + specialized tissues
-radial symmetry (can respond to stimuli from all directions
-central opening surrounded by tentacles (functions as bot mouth/anus)
Life cycle
sperm/egg
zygote
larva
polyp
budding polyp
young madusa
adult madusa
2 tissue layers (diploblastic)
-both the polyp and medusa have
-epiderm(is): outer layer of cells
-gastroderm(is): inner layer of cells lining gastrovascular cavity
-mesoglea: layer between
Feeding
Cnidocytes sting and capture prey + defend
nematocysts shoot poison barbs
-pulls paralyzed prey through mouth/anus into gastrovascular for digestion
-wastes expelled through mouth/anus
Response
-simple nerve net but lacks brain
-nerve net = loosely organized network of cells
-eyespots detect light
Movement
-microfilaments and gastrovascular cavity
>enables body to change shape
>allows medusa to move by jet propulsion
Reproduction
-both asexual and sexual
Asexual: polyps clone by budding
-swell to form new polyp
-seperate to form tiny medusas
-polyps also clone by splitting
Sexual:
-individuals usually male + female
-external fertilization in water (sperm and egg released by parents) (usually Medusa)
-zygote becomes free swimming larva
-larva attaches to hard surface to form polyps
-polyps form medusas
Class Hydrozoa
Hydra, Obelia
-solitary polyps
-lack medusa stage
Class Scyphozoa
-jellyfishes (cup animals)
-medusa most prominent stage
-sting for feeding + defense (painful to fatal)
Class Anthrozoa
-sea anemones and corals
-only occur as polyps (lack a medusa stage)
-solitary polyps
-capture prey with nematocysts
-fight for space with other anemones
Corals:
colonial polyps
larva settle onto hard surface
>produce colony by budding
]>cement to adjacent polyps
>over time, build up rocklike formations called coral reefs
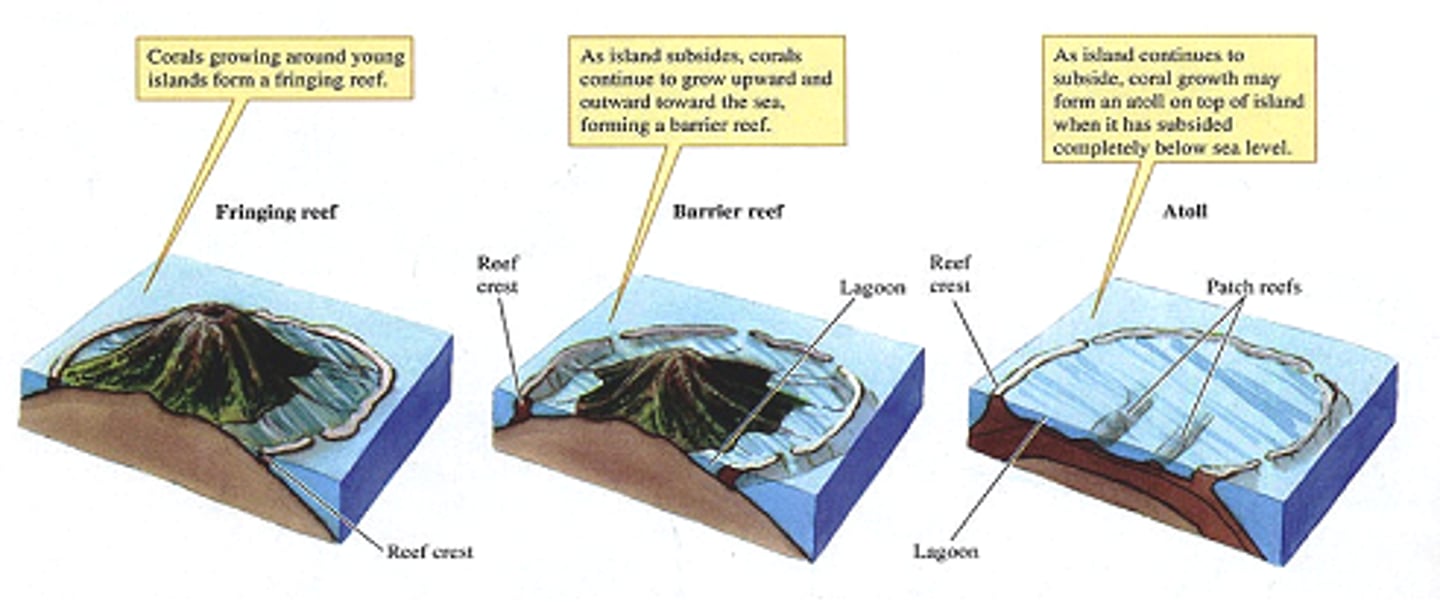
Types of reefs
Fringing: near coastline and around islands/continents
Barrier: parallel to coastline but are separated by deeper, wider lagoons
Atolls: rings of coral that create protected lagoons
Corals rely on symbiotic zooxanthellae for?
-its a type of algae
-provides oxygen
-aids in CaCo3 (calcium carbonate) production
Threats to coral reefs
-Siltation
Ocean warming
results in coral bleaching (coral loses color without zooxanthellae)