Lab 6: Blood Typing and Heart Anatomy Overview
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Plasma
Liquid component of blood, ~55% volume.
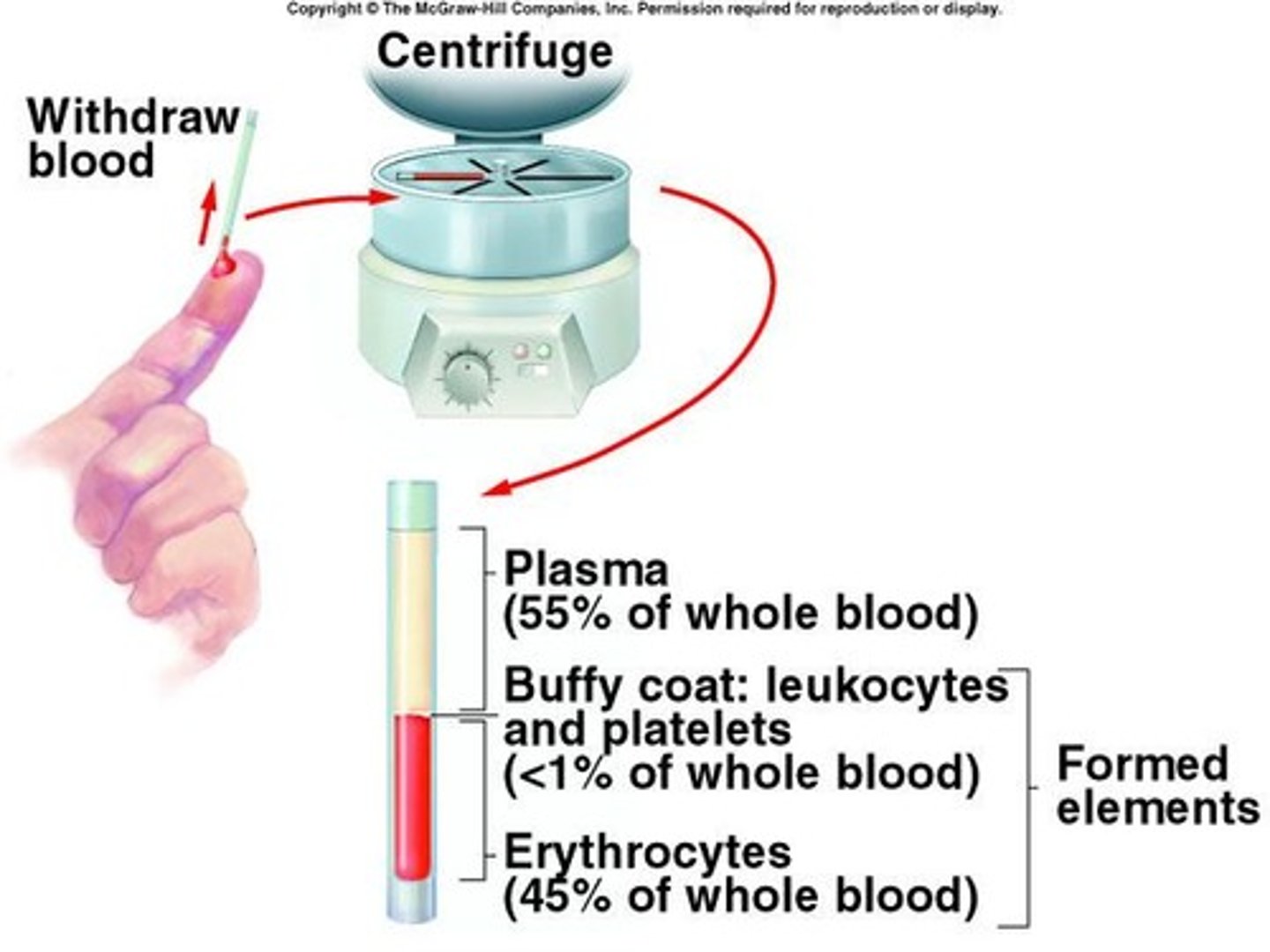
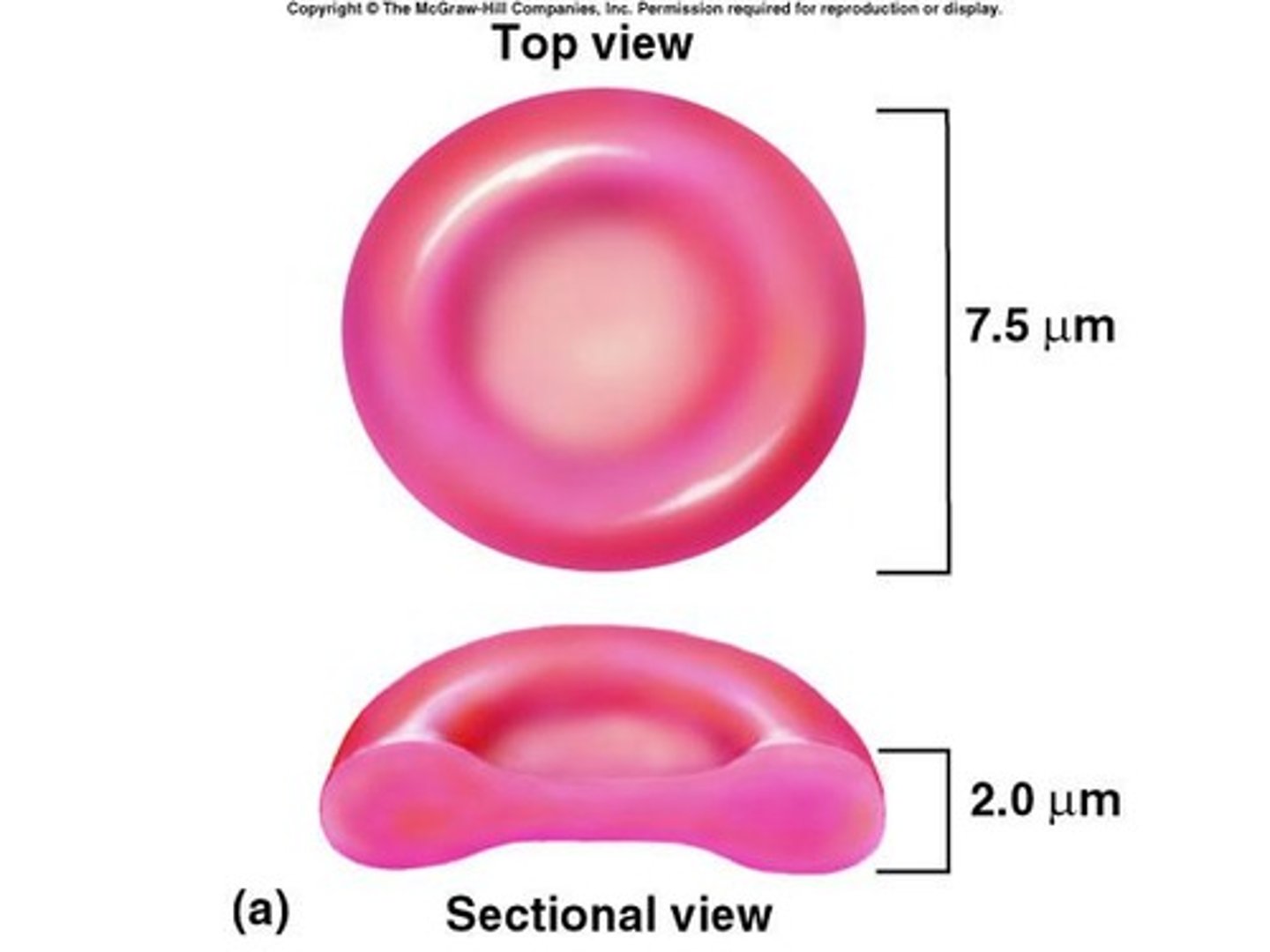
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells, transport O2 and CO2.
Leukocytes
White blood cells, involved in immunity.
Thrombocytes
Platelets, aid in blood clotting.
Differential WBC Count
Counts types of white blood cells in blood.
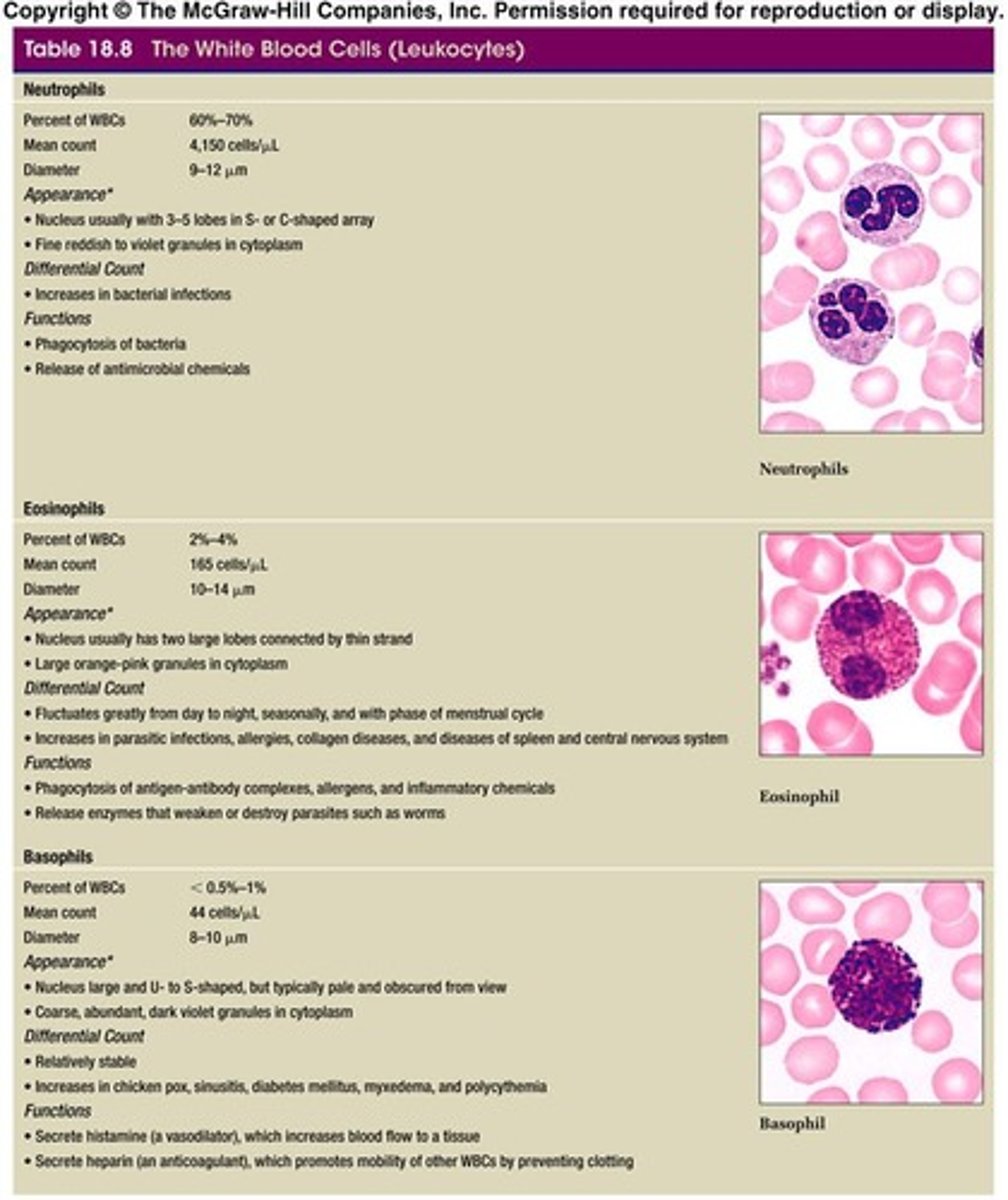
Neutrophils
Most abundant WBC, responds to bacterial infections.
Lymphocytes
WBCs involved in immune memory and response.
Eosinophils
WBCs that respond to parasitic infections and allergies.
Basophils
WBCs involved in allergic reactions and chemical poisoning.
Monocytes
Largest WBC, cleans up after infections.
Megakaryocyte
Bone marrow cell that produces platelets.
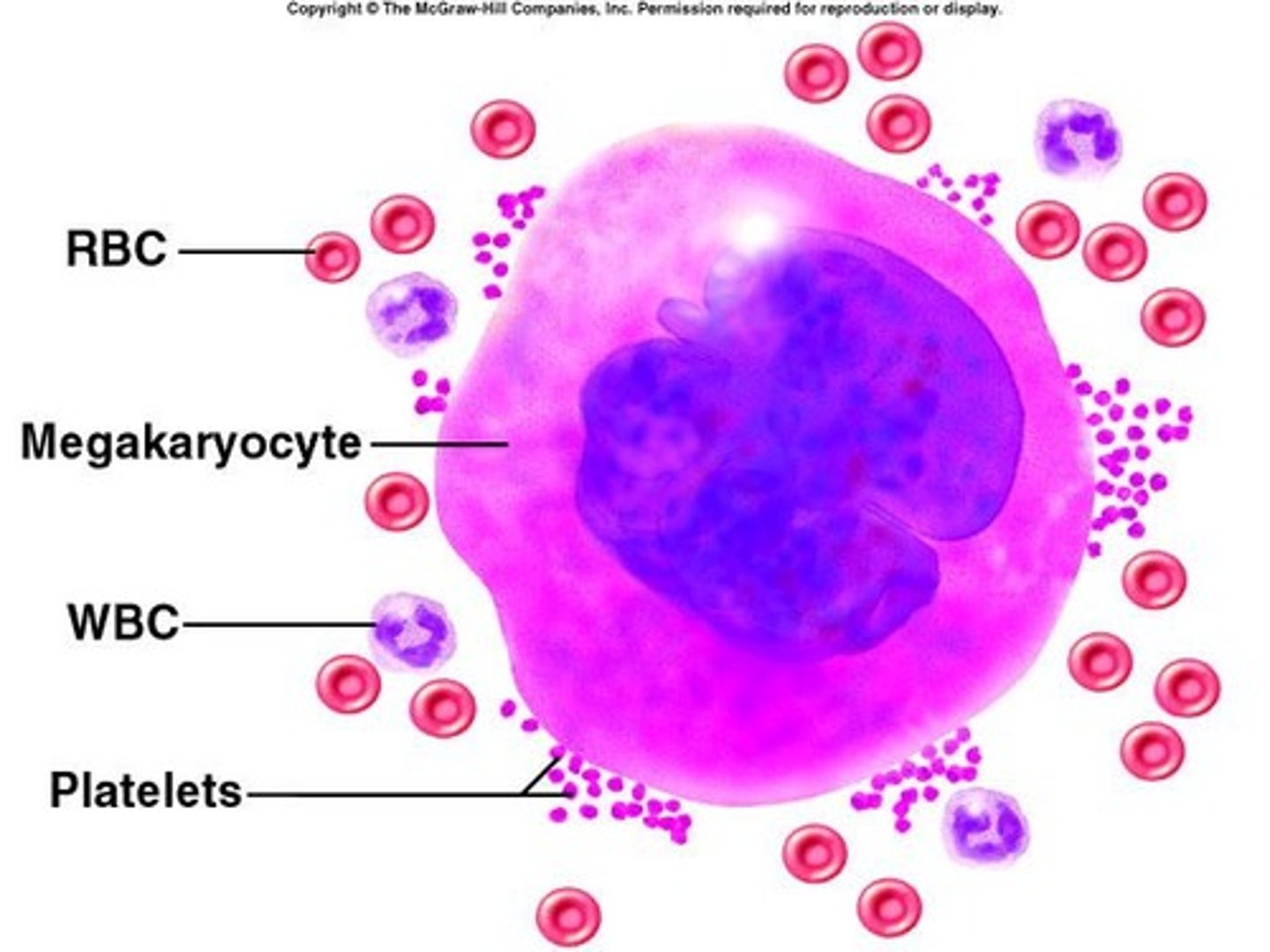
Platelet Count
Normal range: 130,000 to 400,000 platelets/µL.
Gas Transport
Function of RBCs, primarily O2 transport.
WBC Average Count
Normal range: 7000-8000 WBCs/µL.
RBC Lifespan
Survive approximately 90-120 days.
Vasospasm
Contraction of blood vessels to reduce blood loss.
Chemotaxis
Movement of WBCs towards sites of inflammation.
Granulocytes
WBCs with granules in their cytoplasm.
Agranulocytes
WBCs without visible granules.
Wright's Stain
Staining technique for identifying blood cells.
Immature WBCs
Young white blood cells seen in blood smears.
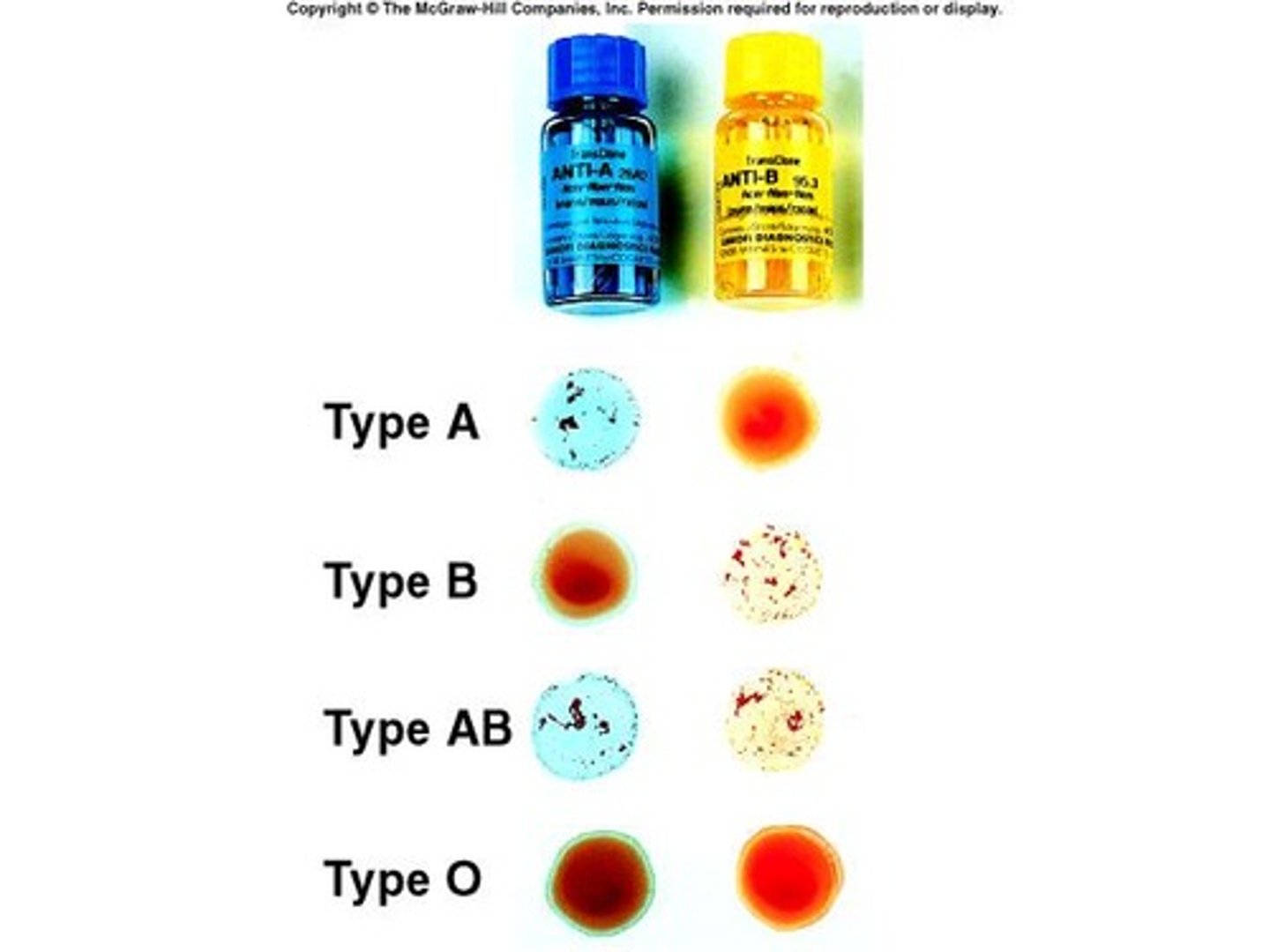
Blood Typing
Determining blood group based on antigens.
Cardiac Pathway
Route blood takes through the heart.
RBC antigens
Agglutinogens that identify blood types.
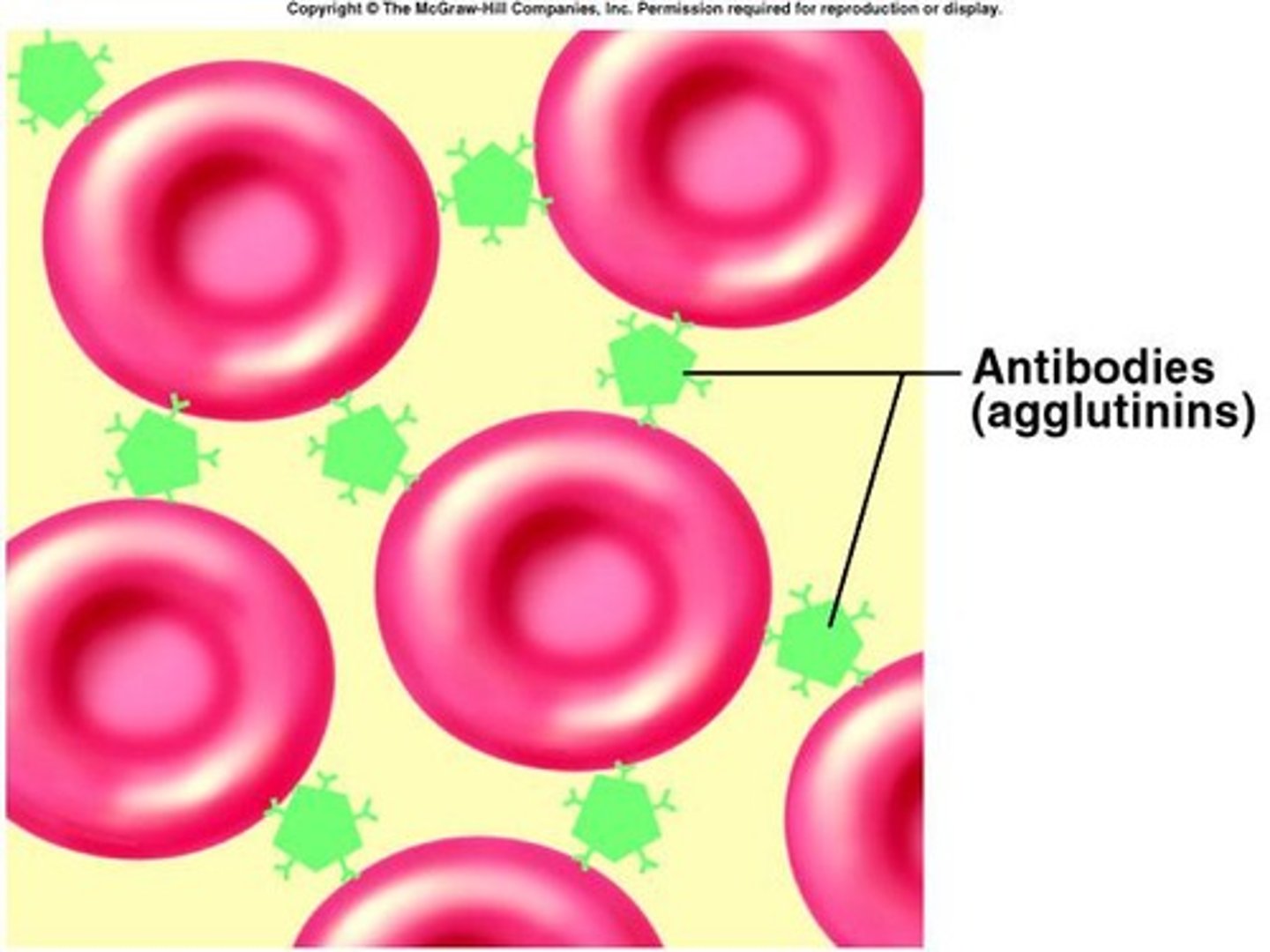
Agglutinogens
Markers on RBCs that determine blood type.
Agglutinins
Antibodies that attack foreign RBCs.
Anti-A
Antibody that targets A antigens.
Anti-B
Antibody that targets B antigens.
Anti-D
Antibody that targets Rh factor.
Blood type A
Has A antigens, produces anti-B antibodies.
Blood type B
Has B antigens, produces anti-A antibodies.
Blood type AB
Has both A and B antigens, no antibodies.
Blood type O
Has no antigens, produces both anti-A and anti-B.
Universal recipient
Blood type AB, accepts all blood types.
Universal donor
Blood type O, can donate to all types.
Agglutination
Clumping of RBCs due to antibody-antigen interaction.
Rh factor
Presence of D antigen on RBCs.
Rh positive
Blood type with Rh antigen present.
Rh negative
Blood type without Rh antigen present.
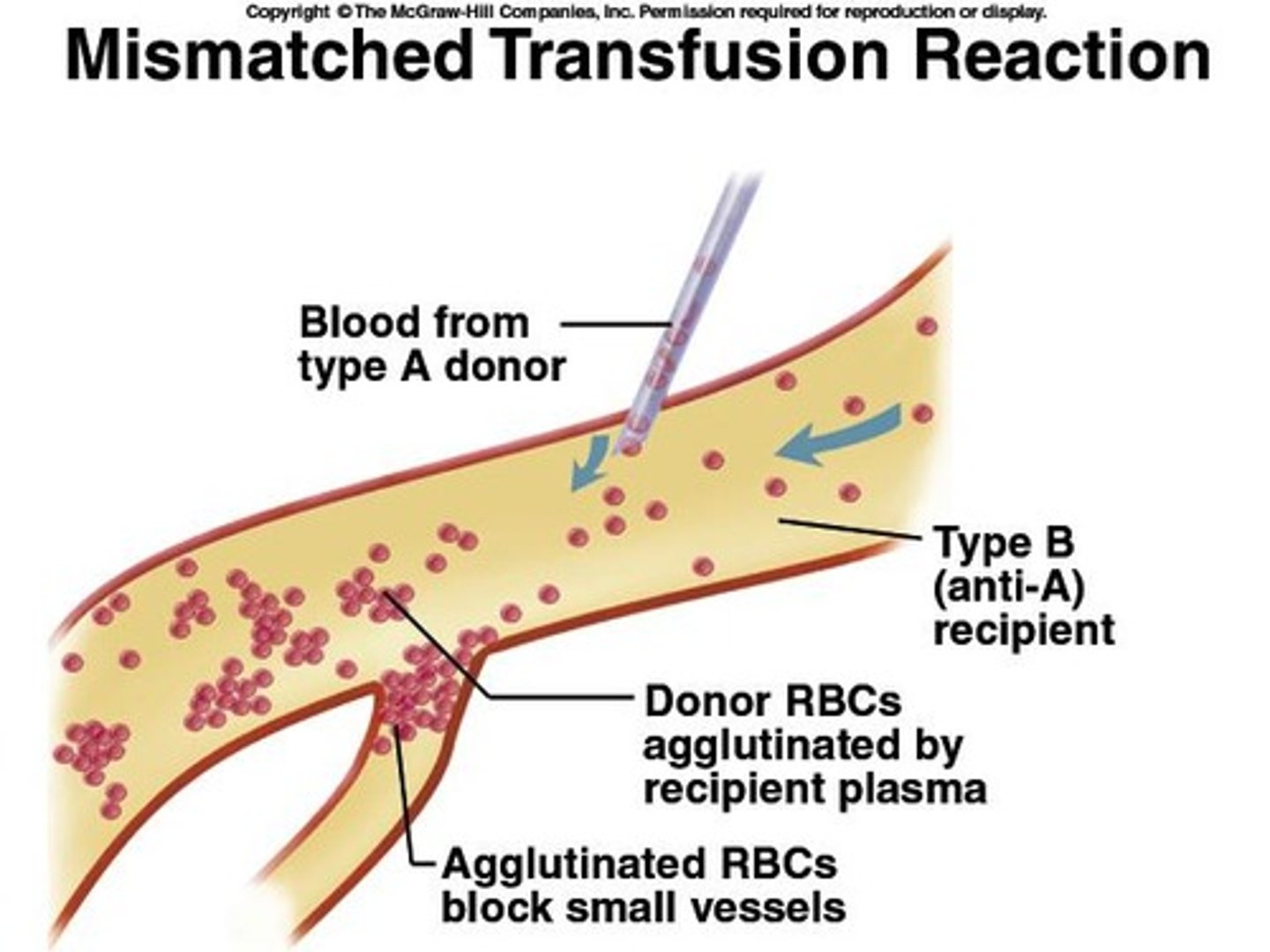
Mismatched transfusion reaction
Clumping blocks vessels, can cause death.
Antibody production
Begins 2-8 months after birth.
Maximum antibody concentration
Occurs around 10 years of age.
Dilution effect
Dilutes antibodies in blood during transfusions.
Blood typing practice
Testing blood with specific antibodies for typing.
Caution in blood handling
Use gloves, dispose of sharps properly.
Hemolytic Newborn Disease
Condition from Rh- mother with Rh+ fetus.
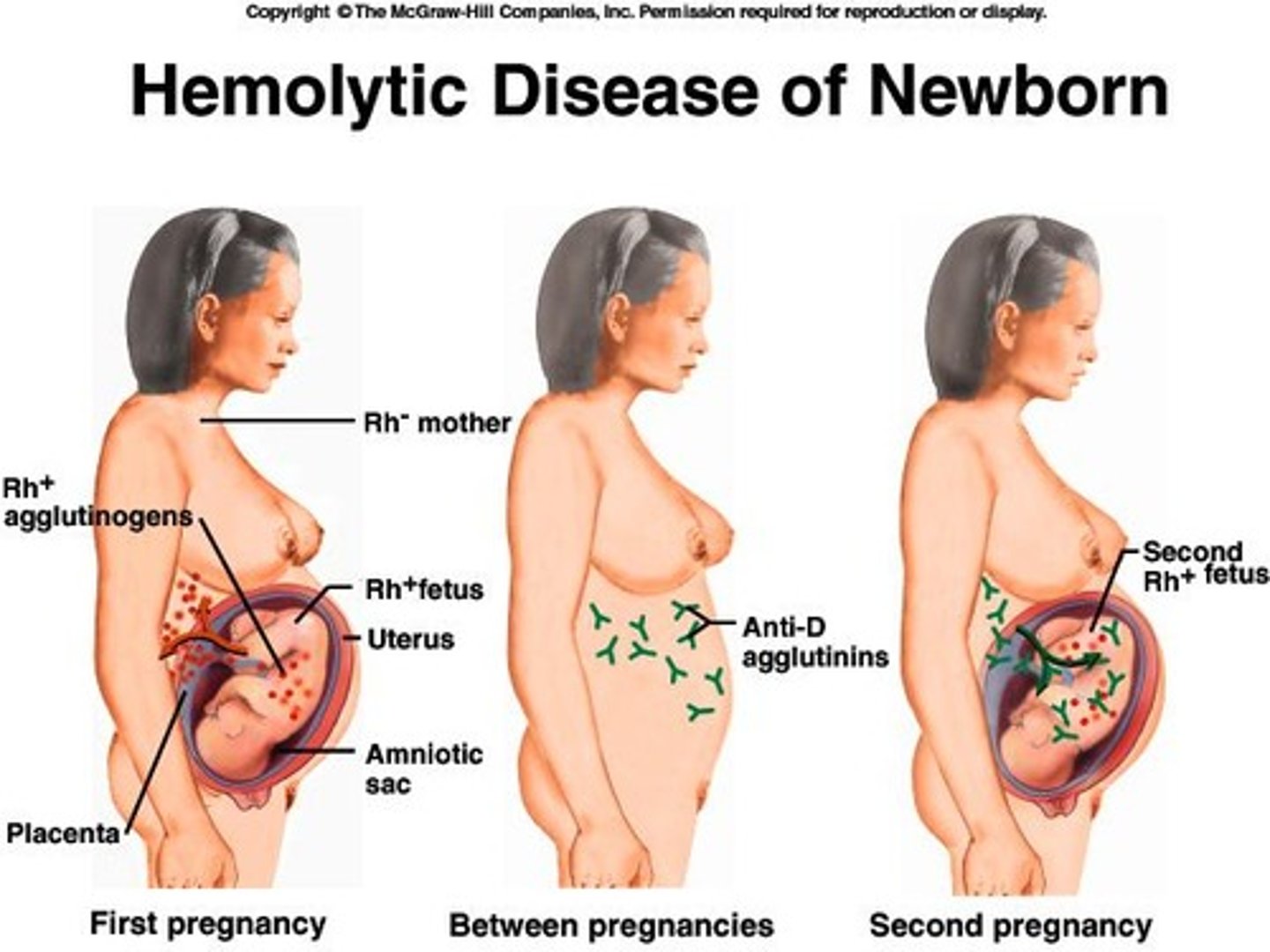
RhoGAM
Prevents antibody formation in Rh- mothers.
Erythroblastosis fetalis
Severe anemia in Rh+ newborns from maternal antibodies.
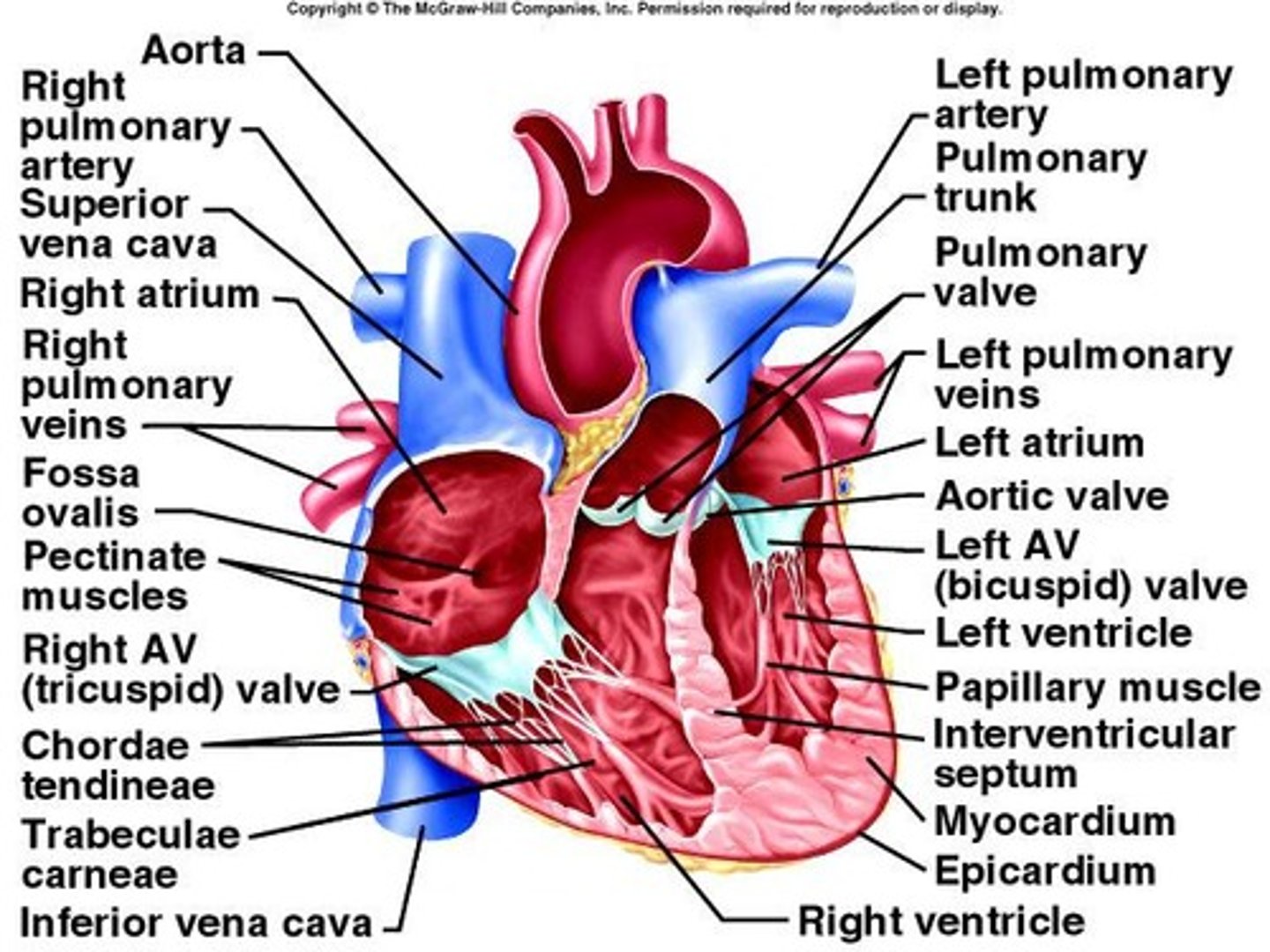
Cardiovascular system
Heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Pulmonary circuit
Carries blood from heart to lungs.
Systemic circuit
Supplies blood to body organs.
Cardiac circuit
Supplies blood to heart's vessels.
Pericardium
Membrane surrounding the heart.
Epicardium
Outer layer of the heart wall.
Myocardium
Thick muscular layer of the heart.
Endocardium
Inner lining of heart chambers.
Atrioventricular valves
Valves between atria and ventricles.
Tricuspid valve
Right AV valve with three cusps.
Mitral valve
Left AV valve with two cusps.
Semilunar valves
Control blood flow into great arteries.
Coronary arteries
Supply blood to heart muscle.
Coronary veins
Drain blood from heart muscle.
Pericardial cavity
Space between pericardium layers.
Serous fluid
Lubricates pericardial cavity for heart movement.
Heart chambers
Four chambers: atria and ventricles.
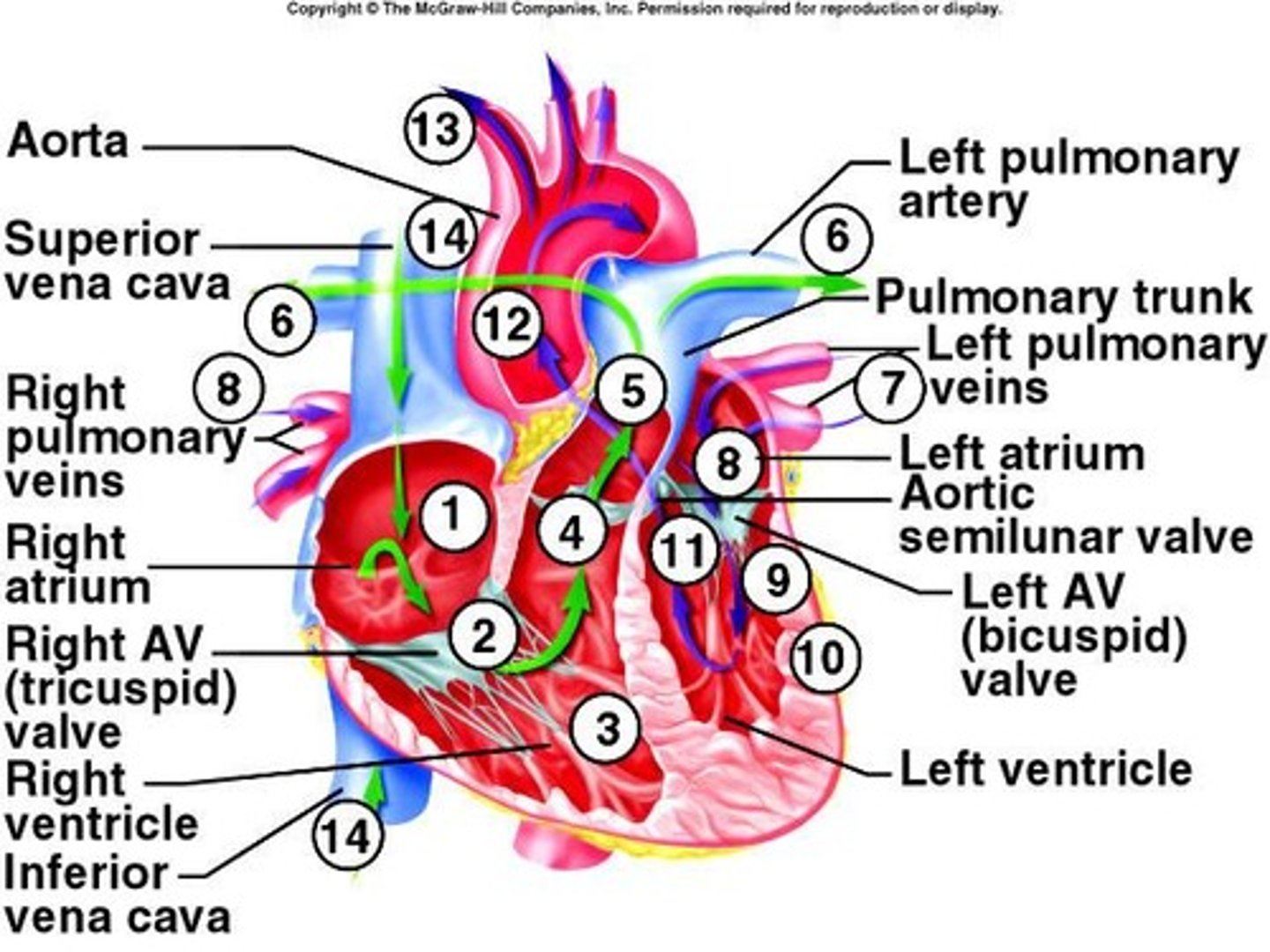
Heart valves
Ensure one-way blood flow through heart.
Cardiac pathway
Sequence of blood flow through heart.
Heart dissection
Lab procedure to study heart anatomy.