Alkenes
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Why is there no rotation about the C=C double bond?
Due to the pi orbitals, which hold the carbons in place
Are alkenes more or less reactive than alkanes? Why?
More reactive - due to high electron density of double bond and the fact that the pi-bond is slightly easier to break
What IM forces do alkenes have?
Only VdW forces due to non-polar bonds
Are alkenes soluble in water? Why?
No as they are non-polar
Name the 4 kinds of isomers alkenes can have?
Chain isomerism
Position isomerism
Functional group isomerism
E/Z isomerism
What’s the trend for mp and bp in alkenes?
Mp and bp increases with chain length as VdW forces are stronger
What shape are double bonds?
Planar
What is an electrophile?
An electron deficient species which accepts a pair of electrons
What is the most stable type of carbocation intermediate? Why?
Carbocations that are bonded to the most other carbon atoms as these have a positive inductive effect
What’s the positive inductive effect?
When atoms push electron density towards an electron deficient centre (eg a carbocation) in order to stabilise it
What are major and minor products?
Major products are formed in greater proportion as they are formed via the most stable pathway (involves the more stable carbon cation intermediate)
Minor products are formed in a smaller amount via a less stable carbocation
Major products will be formed from which kind of carbocations?
Secondary or tertiary (the most stable available)
Why are minor products formed less readily?
Primary carbocations require more energy to produce as they are less stable. If we need to put more energy in to make it, it’s less likely to form.
What 3 reagents can be used for the electrophilic addition of alkenes?
HBr
Br2
H2SO4
What conditions are needed for the electrophilic addition of a halogen molecule to an alkene?
Room temperature
Organic solvent
Draw a mechanism for the reaction between bromine and ethene
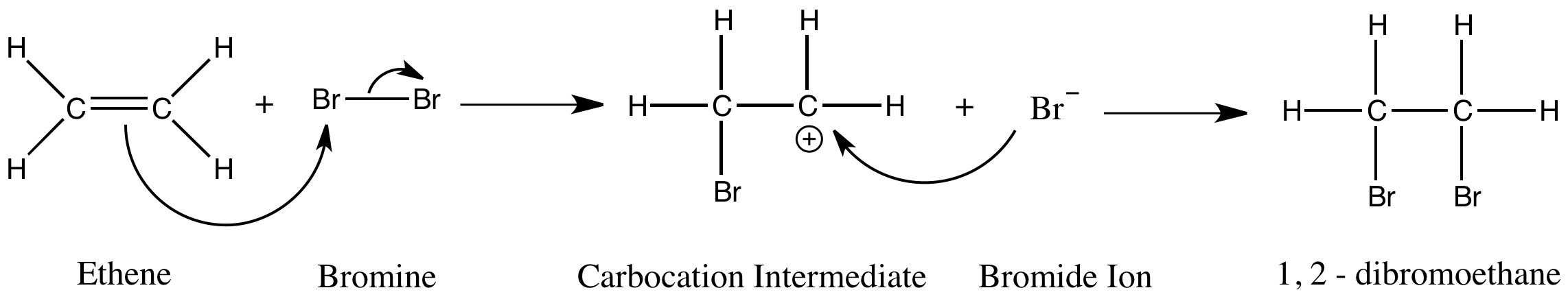
How does a molecule with a non-polar bond react as if it is an electrophile?
The C=C double bond in an alkene has high electron density.
When a halogen molecule approaches this region of negative charge, the electrons in the halogen bond are repelled.
This causes the halogen molecule to be polarised and induces a dipole.
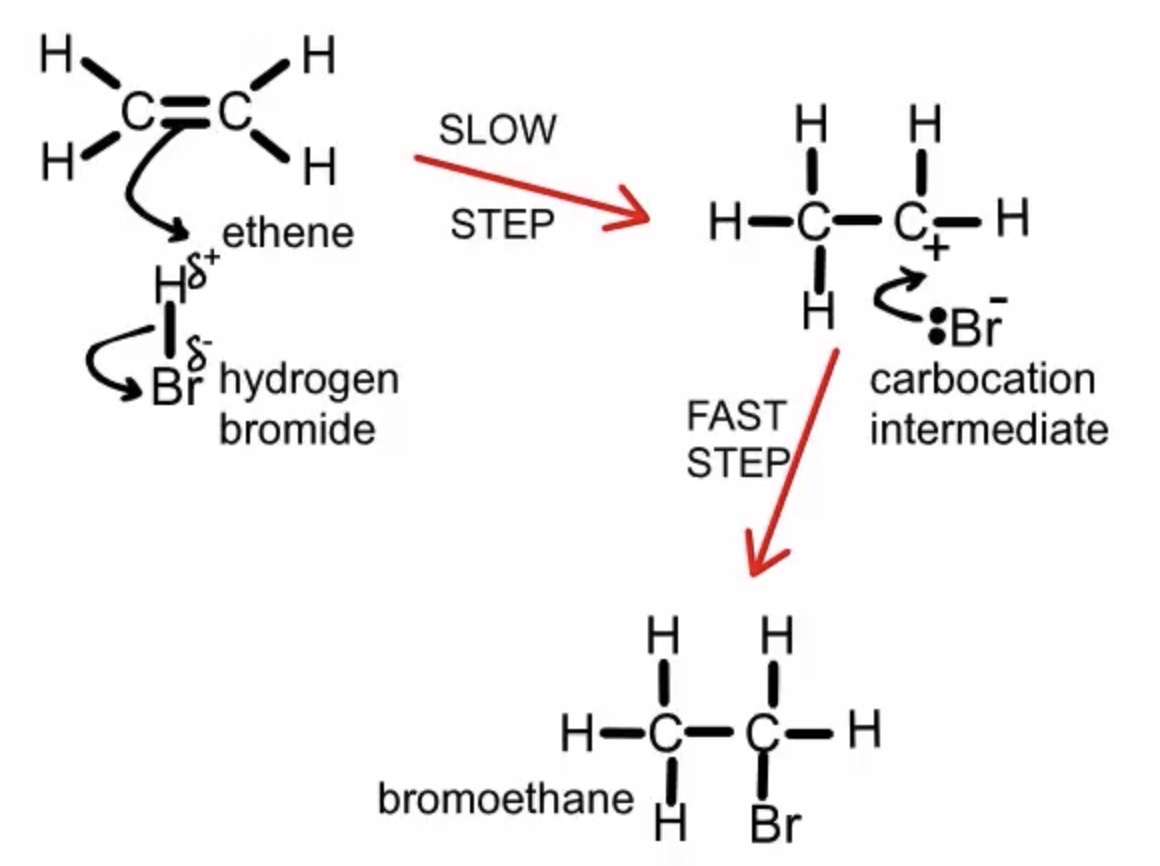
What conditions are needed for the electrophilic addition of a hydrogen halide to an alkene?
Room temperature
No catalyst
Draw a mechanism for the reaction of HBr and ethene
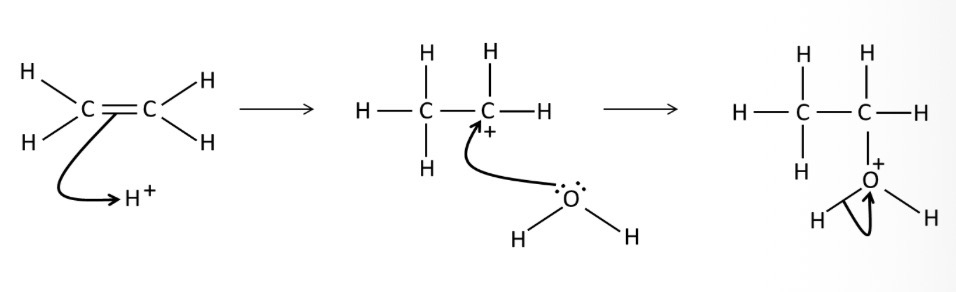
What conditions are needed for the electrophilic addition of H2O to an alkene?
Acid catalyst (H3PO4)
300 degrees C
60-70 atm
What is formed when water reacts with an alkene in the presence of phosphoric acid?
An alcohol
Draw a mechanism for the addition of water to ethene
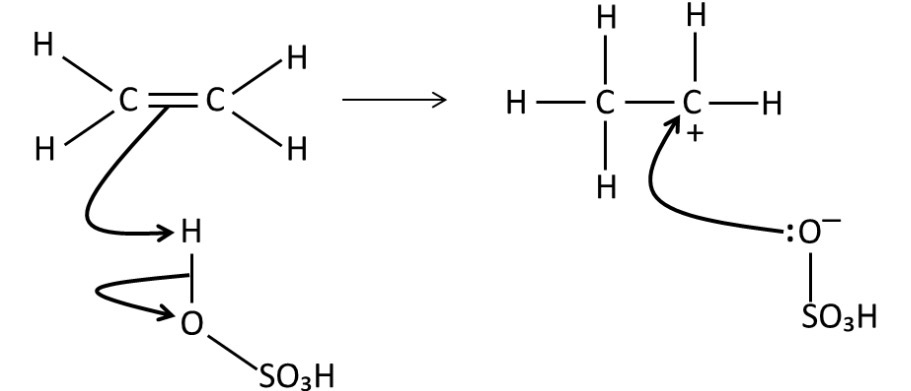
Draw a mechanism for the reaction of sulfuric acid with ethene
What is an addition polymer?
Many monomers bonded together via the rearrangement of bonds without the loss of any atom or molecule
How do you draw the repeating unit of a polymer?
Break C=C bond
Extend the bonds on either side
Enclose the structure in square brackets
Do not include small n outside the bracket if showing a repeating unit - only if showing a polymer
What are 3 properties of addition polymers?
Non-biodegradable - due to stability of strong C-C bonds
Inert - no polar group
Solid and tough - lots of VdWs forces
What are 3 problems associated with polymer waste?
Non-biodegradable - persist in the environment
Landfill use - take up space
Combustion - release CO2 and other toxic gases
Give 4 solutions to tackle polymer waste
Recycle - melt and remould polymers
Feedstock recycling - break polymer into monomer for reuse
Burn to generate heat/electricity
Design biodegradable polymers
What are plasticisers?
Small molecules that get between polymer chains to force them apart and allow them to slide over one another, making them more flexible
What is PVC?
Polyvinylchloride (polychloroethene)
How do the physical properties of PVC change due to a plasticiser? What applications does this lead to?
PVC without a plasticiser → rigid, used for drainpipes
PVC with a plasticiser → flexible, used for aprons
Why do things containing mainly C-C and C-H bonds not decompose easily?
Bonds are non-polar so are not attacked by enzymes or water
Strong covalent bonds need lots of energy to break
What are the 2 types of polyethene?
How are they made?
What are their properties?
What are their uses?
High density polyethene (HDPE)
- made using low temp + pressure, Ziegler-Natta catalyst
- strong and high m.p.
- crates, buckets, bottles
Low density polyethene (LDPE)
- made using high temp + pressure
- flexible/stretchy
- plastic bags, electric insulation
What are the 2 types of recycling polymers?
Mechanical recycling
Feedstock recycling
What is a problem with recycling?
Repeated heating/melting and remoulding can damage chains and degrade plastics properties so not as useful