T4.3:Carbon Cycling
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
lithosphere
atmosphere
hydrosphere
* This concentration gradient ensures that carbon dioxide will passively diffuse into the autotrophic organism as required
* In aquatic producers, CO2 can usually diffuse directly into the autotroph; whereas in terrestrial plants, diffusion occurs at stomata
* \
(net carbon assimuplation=0)
which will then dissociate to form *hydrogen carbonate* ions and hydrogen ions (HCO3– + H+)
these will be absorbed by autotrophs to form organic compounds
\-living animals can combine the hydrogen carbonate ions with calcium to form calcium carbonate eg. top form shells
\
\
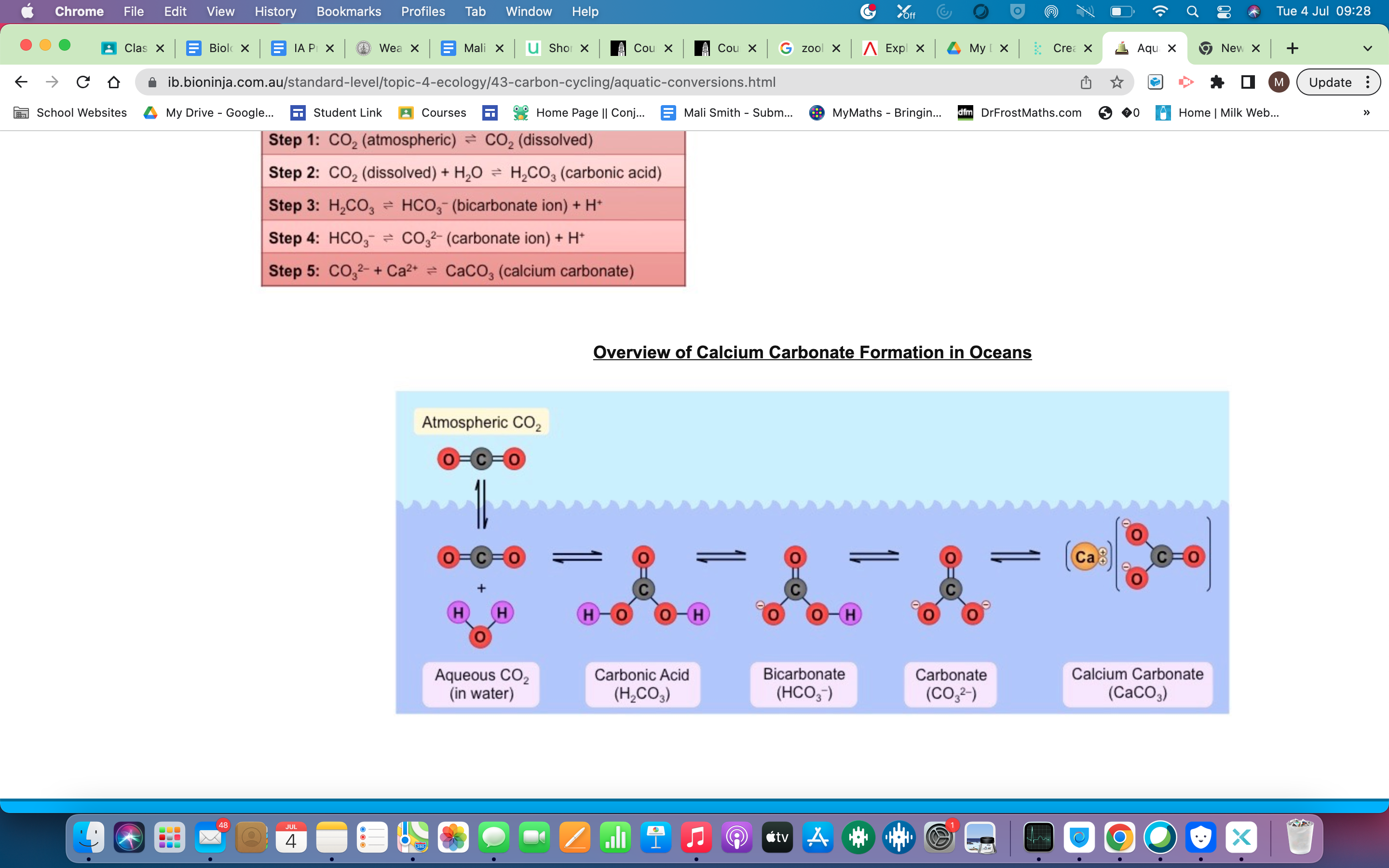
* Marine sediments (e.g. in the mud of lake beds)
* Digestive tract of ruminant animals (e.g. cows, sheep, goats)
acidogenesis (monomers to alcohols)
acetogenesis (alcohols to acetate)
methanogenesis (acetate to methane)
\
methanogenic archaeans
break down peat in anaerobic conditions to produce methane
anaerobic respiration produces organic acids resulting in acidic conditions which saprotrophic b+f cannot function effectively preventing decomposition
\
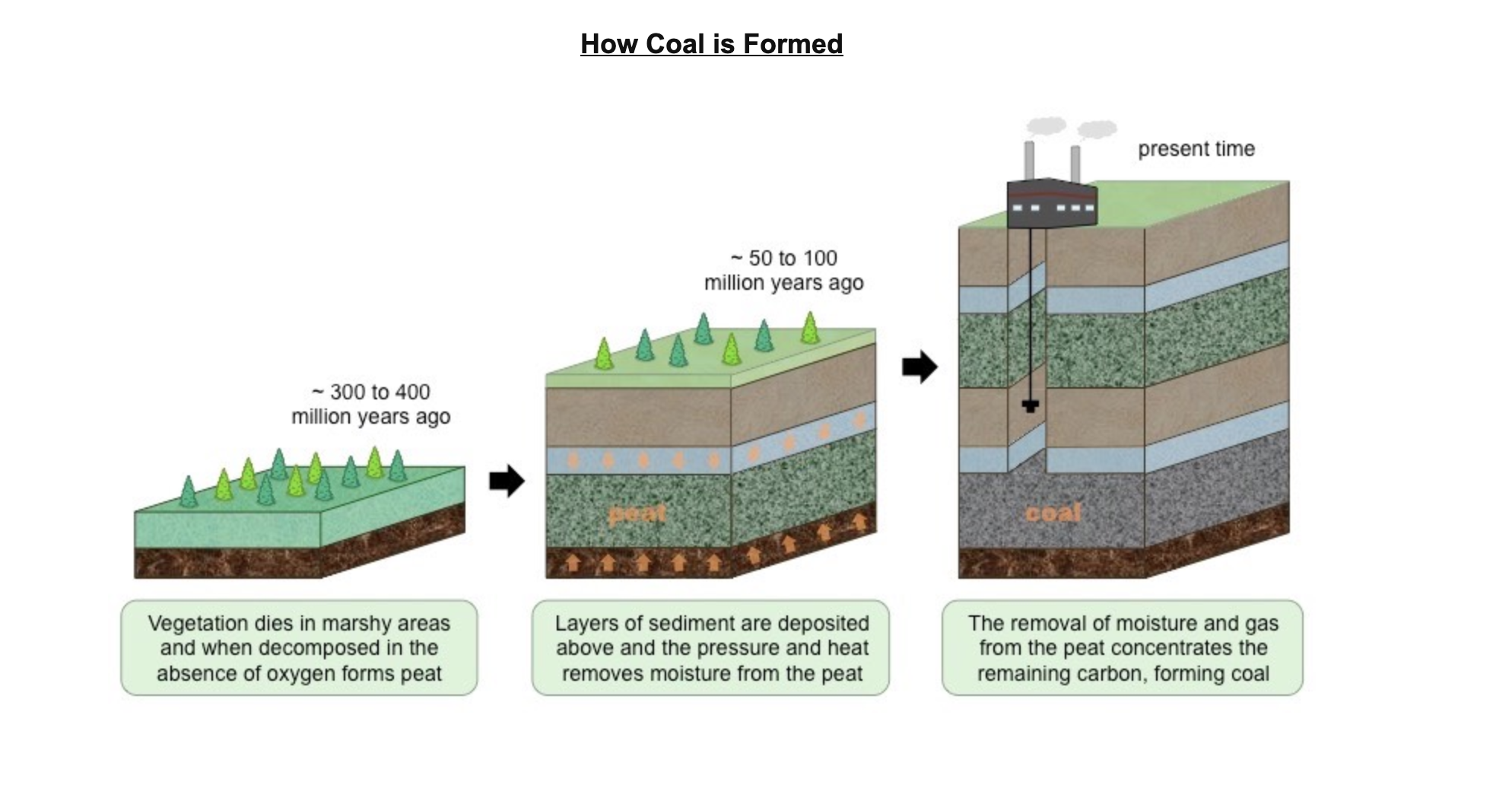
* Sediments (e.g. clay and mud) are deposited on top of the organic matter, creating anoxic conditions that prevent decomposition (partial decomposition)
* As a result of the burial and compaction, the organic material becomes heated and hydrocarbons are formed
* The hydrocarbons form **oil** and **gas**, which are forced out of the source rock and accumulate in porous rocks (e.g. sandstone)
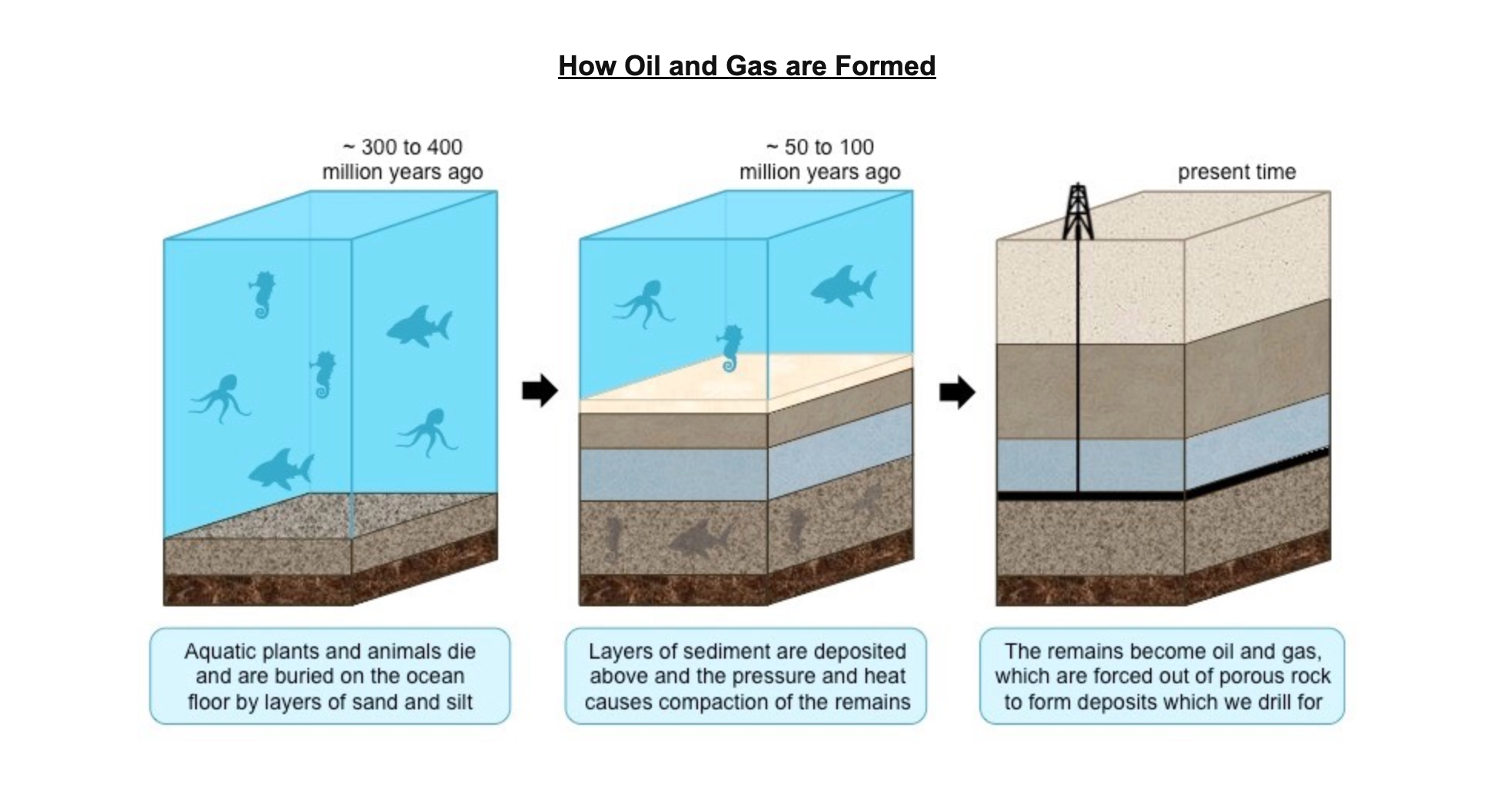
* These hydrocarbons can be extracted and purified to produce an alternative fuel source (e.g. bioethanol and biodiesel)
* Provided new raw materials are provided and waste products are removed, this source of energy is renewable
measured in gigatons
* *Respiration* – releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere when organic compounds are digested in living organisms
* *Decomposition* – releases carbon products into the air or sediment when organic matter is recycled after death of an organism
* *Gaseous dissolution* – the exchange of carbon gases between the ocean and atmosphere
* *Lithification* – the compaction of carbon-containing sediments into fossils and rocks within the Earth’s crust (e.g. limestone)
* *Combustion* – releases carbon gases when organic hydrocarbons (coal, oil and gas) are burned as a fuel source
\
\
how does climate change affect carbon fluxes
Rates of photosynthesis will likely by higher in summer seasons, as there is more direct sunlight and longer days
Oceanic temperatures also determine how much carbon is stored (lower stored in higher temps) as dissolved CO2 or as hydrogen bicarbonate ions
Climate events like El Nino and La Nina will change the rate of carbon flux between ocean and atmosphere
Melting of polar ice caps will result in the decomposition of frozen detritus
* Volcanic eruptions can release carbon compounds from the Earth’s crust into the atmosphere
* Increased numbers of ruminant livestock (e.g. cows) will produce higher levels of methane
* The burning of fossil fuels will release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere
* Global CO2 trends will conform to northern hemisphere patterns as it contains more of the planet’s land mass (i.e. more trees)
* CO2 levels are steadily increasing year on year since the industrial revolution (due to increased burn
explain hopw increased levels of atmospheric co2 contribute to global warming
short wave/UV radiation from the sun passes through the atmosphere/reaches the Earth’s surface;
which warms the (surface of the) Earth;
long wavelength/infra-red radiated from the (warmed) Earth’s surface;
carbon dioxide absorbs/traps long wavelength/infra-red radiation;
more heat trapped in/less heat escapes from atmosphere with more carbon dioxide;