GI 3: Secretion
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
GI Secretion
the production and release of fluids/substances into the lumen of the GI tract
- by mucosal cells and/or accessory GI organs
- Overall functions of secretory glands in GI Digestive enzymes
- Mucus for lubrication and protection
Gastrointestinal Secretion Volumes
>7 L of fluid is secreted into the GI tract each day
- not including approximately 2 L of daily fluid intake in the diet
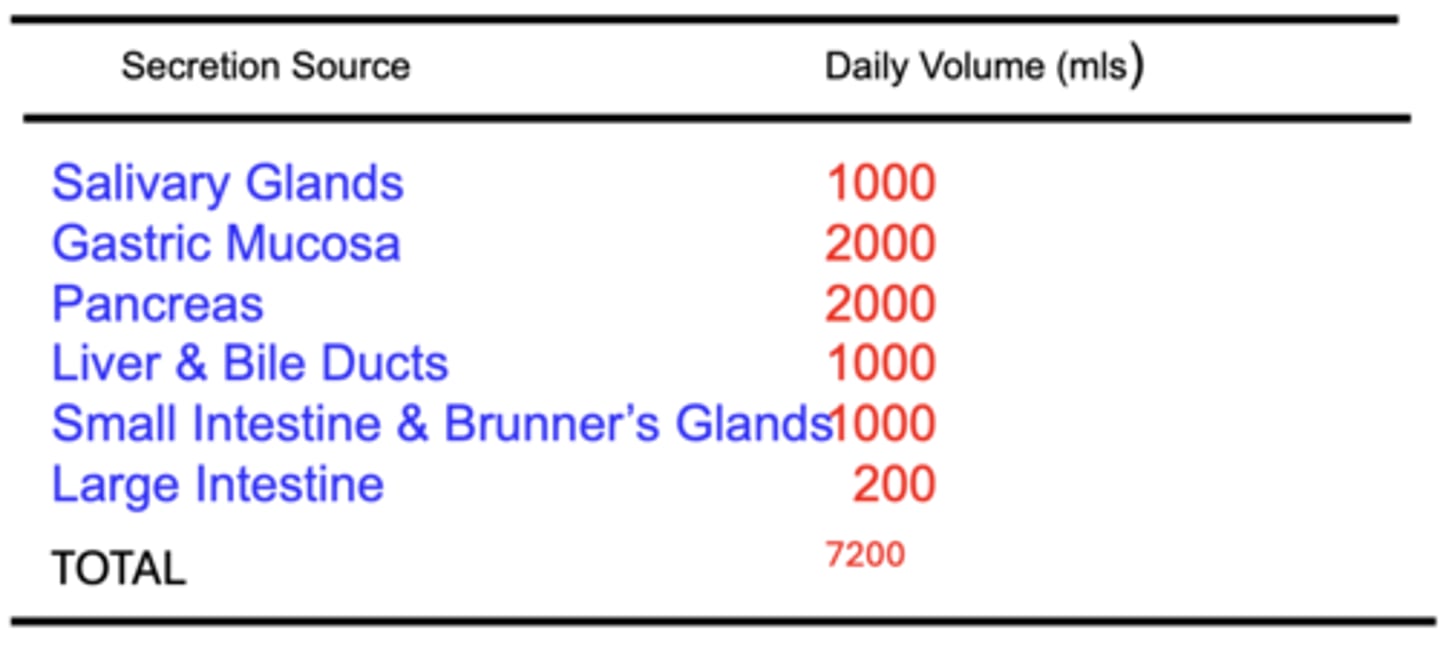
Fluid secreted into the GI tract is mainly composed of?
Water, Mucus & Ions
- important Hormones & Enzymes also contribute functionally to GI secretions
Secretions along the GI tract are highly Variable in Composition, depending on?
1. Mucosal Cell Type within the segment
- APUD, Parietal, Chief, Goblet, etc.
2. Accessory Organs
- Salivary Gland, Pancreas, Liver
Gastrointestinal Secretion Composition
• Water
• Mucus
• Ions
• Enzymes
• Hormones
types of GI secretory glands
1. Goblet cells
2. Brunner's Glands
3. Tubular Glands
4. Crypts of Lieberkuhn
5. APUD cells
6. Accessory glands
Goblet cells
− Single-celled glands lining the GI mucosa
− Found everywhere in GI, but abundance is largest in the colon
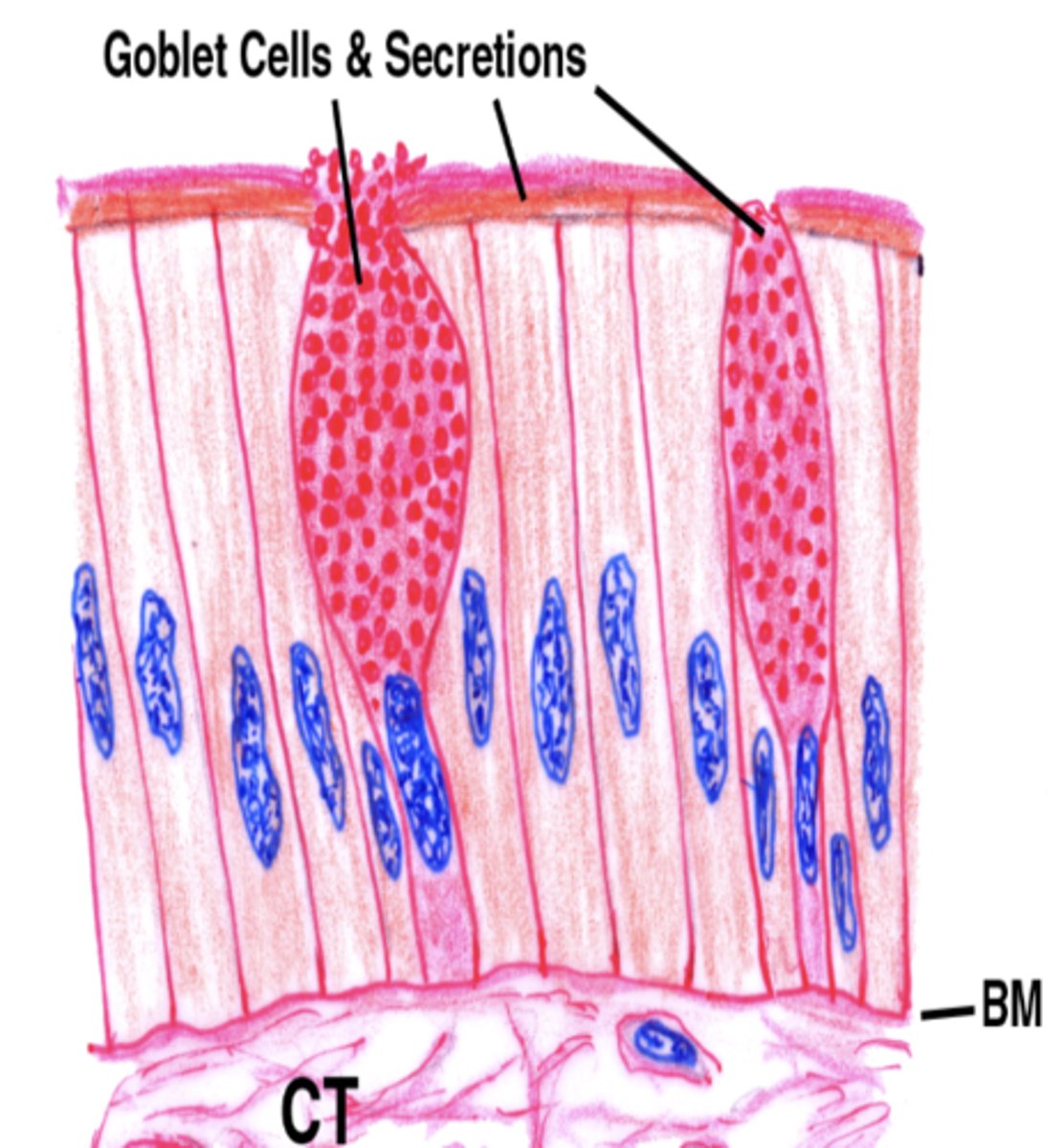
Goblet cells Function
secrete mucus
- onto the mucosa
- lubricates and protects surface from abrasion and chemical digestion
Brunner's Glands
− Compounds glands
- located near the proximal duodenum
Brunner's Glands Function
secrete alkaline mucus
- neutralizes gastric acid → protects the mucosa
Tubular Glands
Location: stomach and duodenum
cells:
- parietal cells
- chief cells
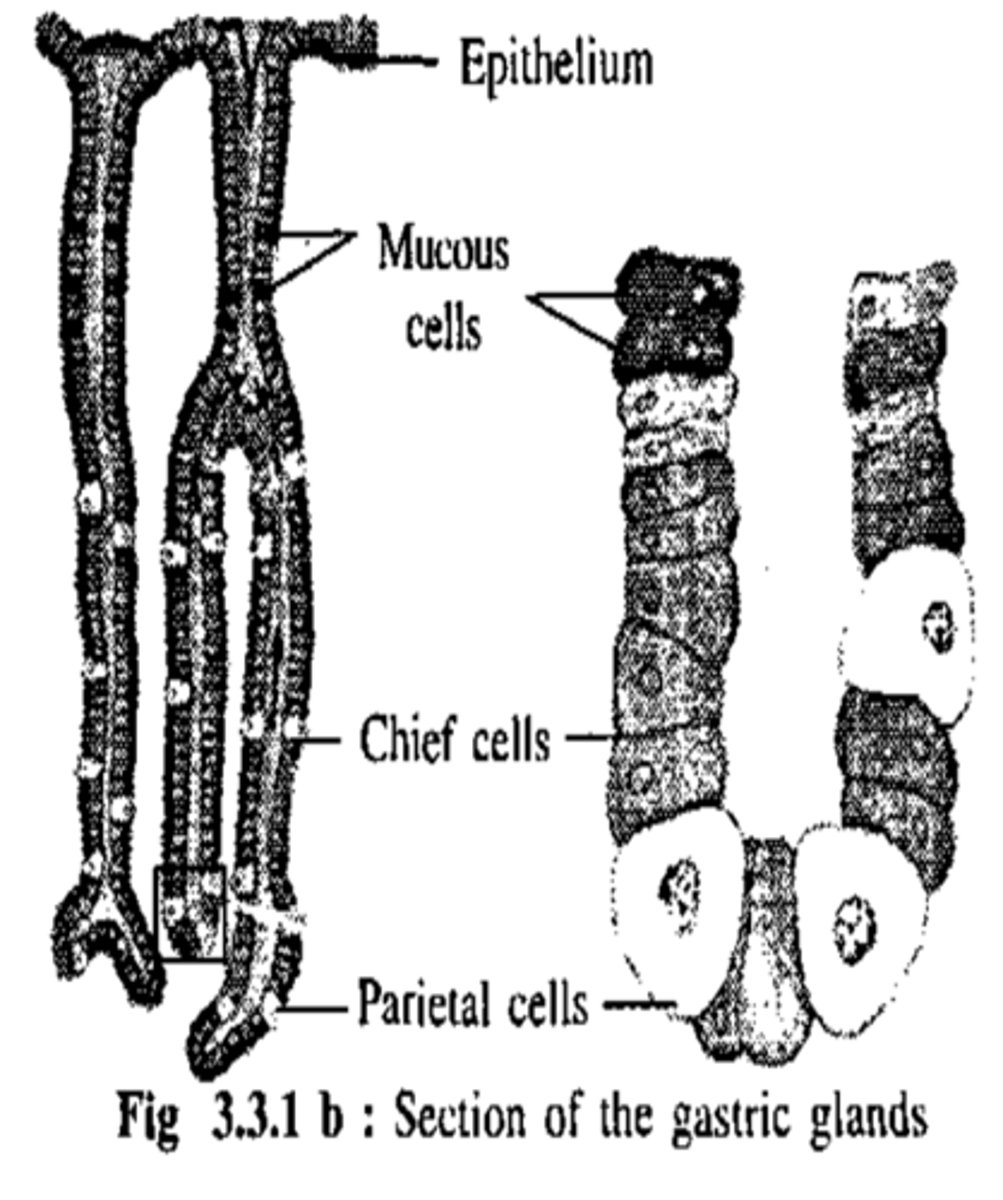
Tubular Glands Function
protein digestion and GI immunity
1. parietal cells: acid secreting
- Digestion + Immunity
2. chief cells: pepsinogen secreting
- Protein Digestion
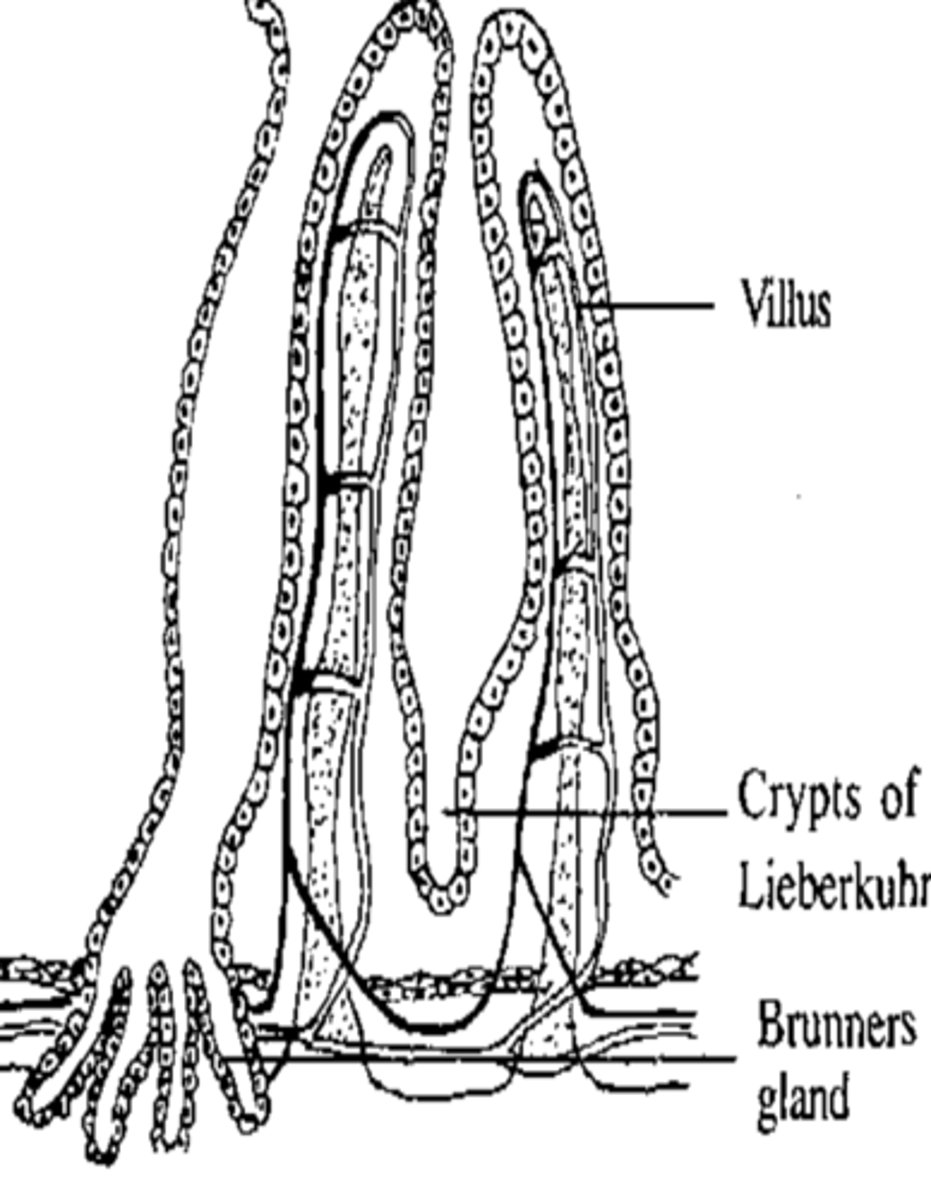
Crypts of Lieberkuhn
− Deep pits/invaginations formed by mucosal folds
- mainly in small intestine
− Contain villi for absorption
- Contains several types of secretory cells, including Goblet cells and enterocytes
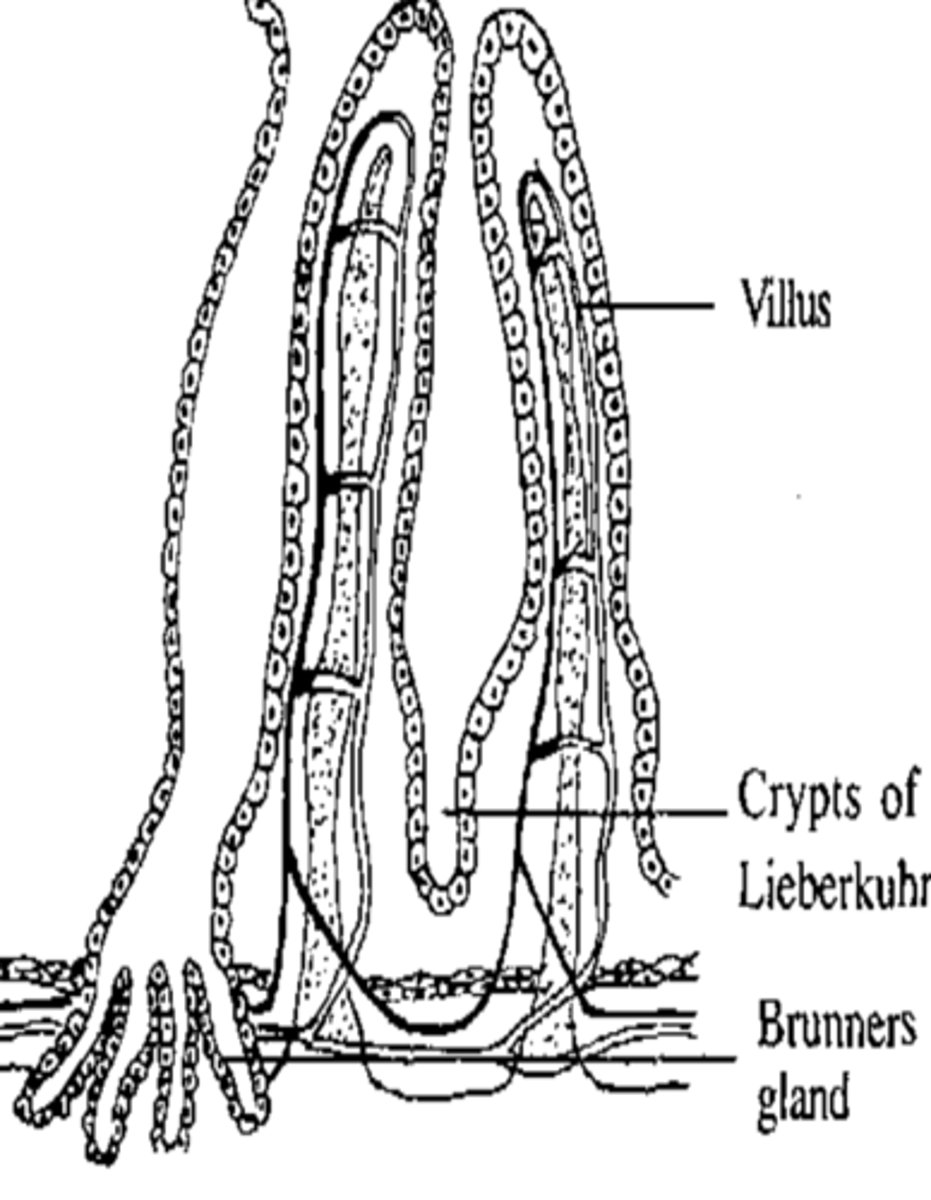
Crypts of Lieberkuhn Function
Goblet cells and enterocytes secrete:
- digestive enzymes
- H2O
- ions
- Mucus
facilitate lubrication, digestion and absorption
APUD cells
− Single-cell mucosal endocrine glands
- mainly small intestine
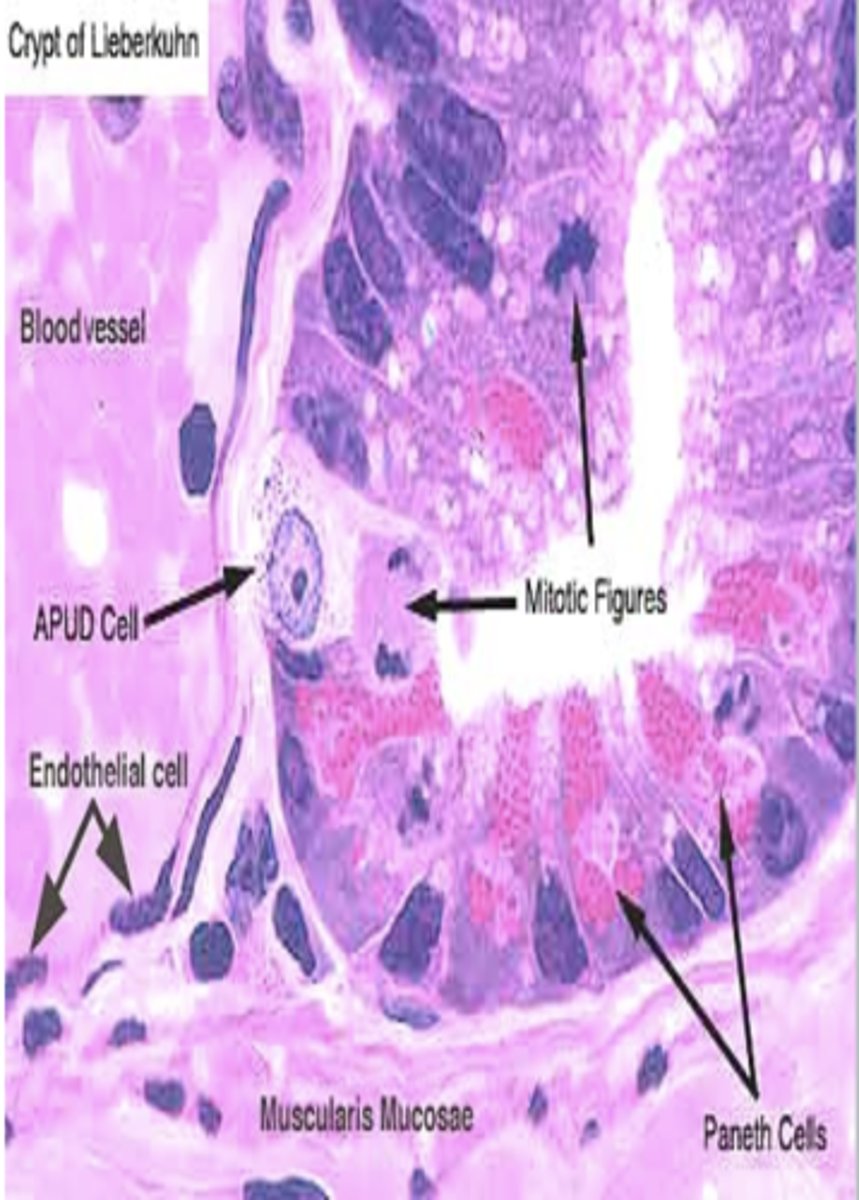
APUD cells Function
Secrete various GI hormones
- endocrine regulation of GI functions
Accessory glands
- Salivary Glands
- Pancreas
- Liver
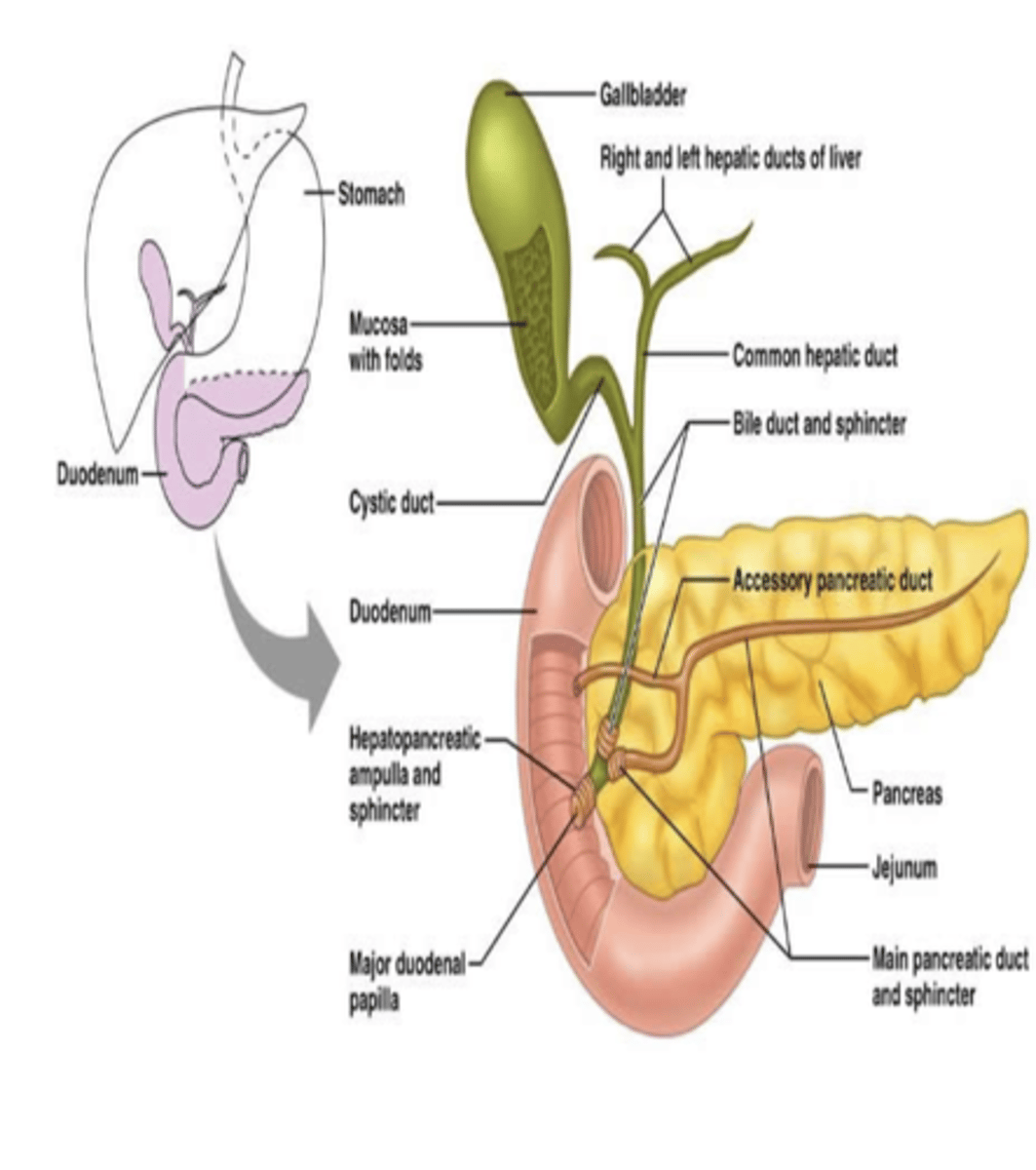
Salivary Gland Function
Secretes saliva
- Lubrication/Protection
Pancreas Function
Secretes Enzymes + HCO3-
- Digestion and Acid Neutralization
Liver Function
secretes bile
- Fat Digest./Absorption
Apud (enteroendocrine) cells are best described as:
A. Exocrine glands releasing mucus
B. Endocrine cells secreting GI hormones into the bloodstream
C. Neurons releasing VIP and GRP
D. Hepatic cells detoxifying blood
B. Endocrine cells secreting GI hormones into the bloodstream
Which of the following glands primarily secretes digestive enzymes and bicarbonate?
A. Salivary glands
B. Pancreas
C. Brunner's glands
D. Crypts of Lieberkühn
B. Pancreas
Basic mechanism of stimulation of secretion
1. Contact of food
A. Direct stimulation of glandular epithelium
B. Activation of enteric nervous system
2. Autonomic stimulation
A. Parasympathetic
3. Hormonal regulation