Week 6 - Memory Errors
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Schacter - seven sins of memory
transience
absentmindedness
blocking
misattribution
suggestibility
bias
persistence
transience
-decreasing accessibility of memories over time
Ebbinghaus - method (transience)
-participants asked to memorise nonsense trigrams
-see how long they could hold onto them for
Ebbinghaus - results (transience)
-after a short period of time there is a steep period of forgetting
-as we progress further, forgetting flattens and continues at a slower pace
-lose access to our memories as a function of time → Ebbinghaus’s curve
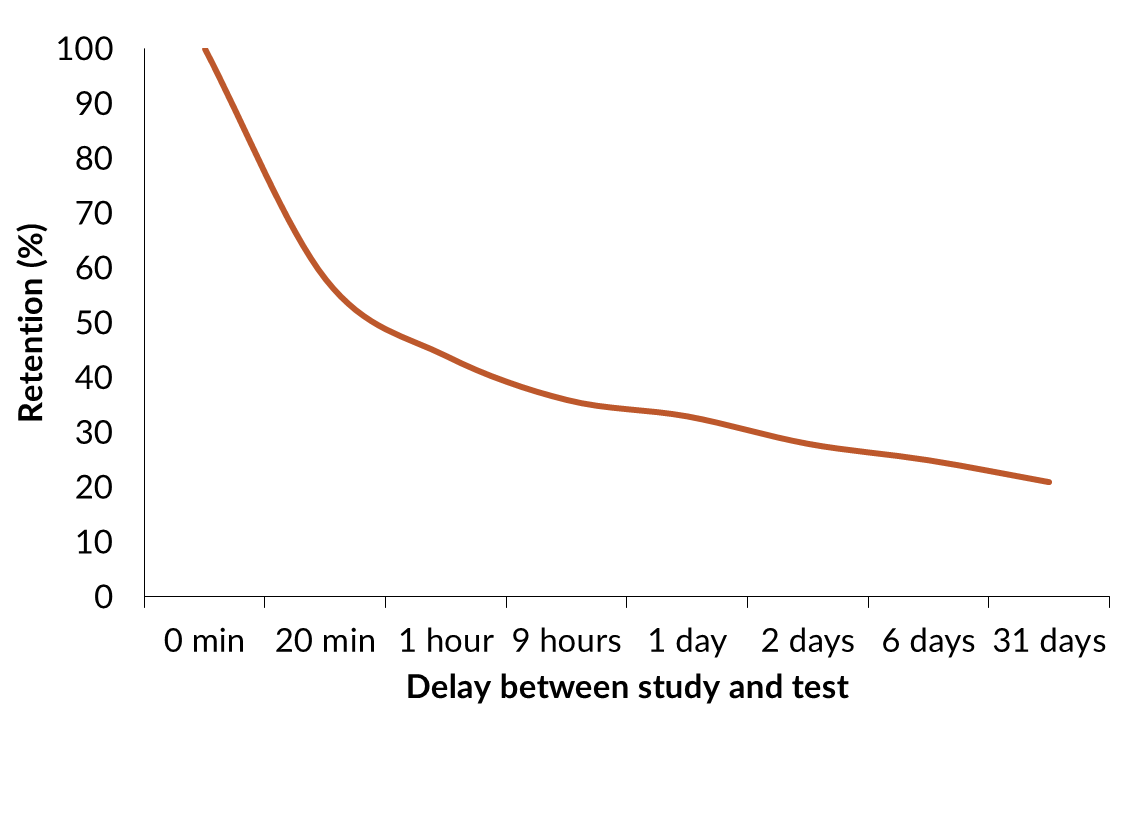
decay (reasons for transience)
-we forget due to the passage of time
interference (reasons for transience)
-forgetting due to competition between memories
Thorndike’s law of disuse (transience)
-the more time elapses without using a memory, the more the memory decays away until it is entirely forgotten
proactive interference (transience)
-older memories impair the retrieval of new memories
retroactive interference (transience)
-new memories impair retrieval of older memories
Brown-Peterson paradigm (transience)
participants learn a list of memoranda (trigrams)
complete a distracting task after learning memoranda to prevent rehearsal
asked to recall the memoranda
-the more time passes → the greater the forgetting
Keppel & Underwood - method (interference)
-testing for proactive interference
learn a list of 3 memoranda
complete a distracting task
asked to recall the first memoranda only
Keppel & Underwood - results (interference)
-found better memory with less proactive interference from old information
-memory preserved for first/oldest info, memory suffers for new info due to this interference
Jenkins & Dallenbach - method (interference)
-testing for retroactive interference
participants study trigrams
asked participants to either take a nap or stay awake → those who stayed awake would encode more memories whereas those who napped would not encode new memories
recall after 1, 2, 4, or 8 hours
Jenkins & Dallenbach - results (interference)
-better memory with less retroactive interference from new information
-those who stayed awake had worse recall over a period of time compared to asleep group
absentmindedness
-lapses of attention that affect memory and learning
Kane - method (absentmindedness)
-50 minutes stats lecture
-pre and post-lecture tests
-mind wandering probes during lecture → includes useful mind wandering and task-unrelated thoughts (TUTs)
Kane - results (absentmindedness)
-found lots of task-unrelated thoughts
-negative correlation between performance on stats test and TUTs
-TUTs positively correlated with multi-tasking habits → the more multitasking habits students reported, the more off-task mind wandering they experienced
-so multitasking habits had an indirect effect on learning outcomes through mind-wandering
blocking
-information is present but temporarily inaccessible
D’Angelo & Humphrey (blocking)
-’tip of the tongue phenomenon’
-induced tip of the tongue state by asking lots of questions about words not typically used in daily lexicon
-found that resolving the tip of the tongue state may prevent them from reoccurring later on
misattribution
-having a memory but attributing it to an incorrect source
source monitoring (misattribution)
-ability to check where our memories come from
-making an error in monitoring the sources of our memories we make a misattribution error
internal source (misattribution)
-memory came from us
external source (misattribution)
-have information about something but lost track of who told you the information
-taking in information but misattributing it to someone else
reality source (misattribution)
-misattributing sources when something that as happened to something that you haven’t experienced
cryptomnesia
-unconscious plagiarism
-think we are owner of idea when we actually sourced it from elsewhere
types of source information
-details to help identify sources of memory
perceptual details (types of source information)
-often higher for memories actually experienced than from other sources
contextual (types of source information)
-context in which memory was acquired is consistent with an expected source
affective (types of source information)
-emotional reaction in context of information
cognitive (types of source information)
-mental processing of the information
Deese-Roediger-McDermott (DRM) paradigm
-present participants with a list of similar words
-ask participants to recall the list
-then do a word recognition task
Roediger & McDermott (misattribution)
-people falsely recalled related concepts that were never presented
-resulted in false memories → remembering things that never happened
suggestibility
-implanted memories that never occurred
Loftus & Pickrell - method (suggestibility)
-generated a booklet of childhood stories containing:
3 true childhood memories
1 false memory (lost in a mall)
-then interviewed participants 1-2 weeks after generated booklet
-second interview another 1-2 weeks later
Loftus & Pickrell - results (suggestibility)
-about ¼ participants falsely ‘remembered’ having been lost in a mall
-shows false memories can be implanted via suggestion
Wade (suggestibility)
-showed doctored images of participants in a hot air balloon
-asked them about their experience
-half of the participants demonstrated false memories implanted via suggestion
-false “evidence” → contributes to formation of false memories
confabulation
-taking bits of information and developing that into a false memory
Zaragoza - method (suggestibility)
-watched 8 minutes of a film
-asked questions about the film - one question asks details about something that did not happen
-two conditions:
had to answer - if didn’t know were told to guess
discouraged from guessing
-recognition task 1 week later and recall task 4-6 weeks later
Zaragoza - results (suggestibility)
-participants who were forced to guess had higher rate of confabulated events at 1 week
-at 4-6 weeks participants recalled 20% of their forced confabulations as their own memories
-the effect was particularly strong for confabulations for which they received confirmatory feedback
Fazio - method (suggestibility)
-participants read a fiction story with or without misinformation
-asked short answer pre-knowledge test
-asked knowledge test after reading the story
Fazio - results (suggestibility)
misinformation effect → altering memories to conform to recently encountered but incorrect information
-more likely to answer using misleading information post-test if confidence was rated lower during pre-test
bias
-distorting memories of the past based on current knowledge and beliefs
Blank - method (bias)
-looked at participants’ prediction of election outcome before and after the election
-compared to participants’ recall of their prediction to the election outcome
Blank - results (bias)
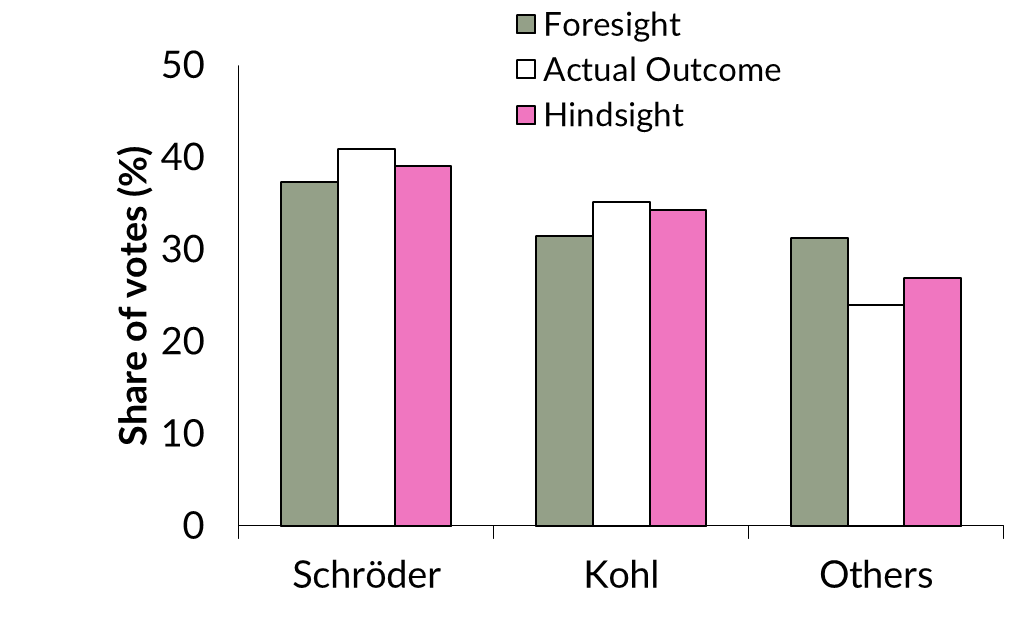
hindsight bias → misremember memories as being more similar to the current knowledge state
-hindsight outcomes closer to actual outcomes than their foresight predictions
persistence
-unwanted recollections that cannot be forgotten
amnesia
-a deficit in memory caused by brain damage, disease or psychological trauma
retrograde amnesia
-loss of ability to access memories prior to the event
anterograde amnesia
-loss of ability to store new memories after the event