Combined LJM TBL 3
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
What is the role of a fixator muscle?
Stabilises the origin of the prime mover
Which of the following muscles is a synergist in elbow flexion?
Brachialis
Which muscle functions as a fixator during elbow joint motion?
Subscapularis
What is true of synergist muscles?
They share a similar function as part of a muscle group
Which is an example of a synergist group for knee joint flexion?
Biceps femoris, semimembranosus, and semitendinosus
hat best describes a muscle acting as an agonist?
The muscle generating the net torque for movement
What is the functional role of the antagonist muscle?
Controls and modulates the agonist’s action
What is the primary mechanism of increased muscle size due to resistance training?
Hypertrophy through increased contractile protein volume
What term describes the increase in the volume of contractile proteins per muscle fibre?
Hypertrophy
Which of the following statements best defines hyperplasia?
Increase in the number of muscle fibres
What occurs in skeletal muscle following prolonged immobilisation?
Atrophy
What is the recommended clinical strategy following injury to reduce muscle atrophy?
Passive mobilisation followed by gradual loading
Which connective tissue layer surrounds individual muscle fibres?
Endomysium
In ageing muscle, what happens to the connective tissue volume?
It increases and contributes to muscle stiffness
What is a major functional outcome of reduced contractile proteins in ageing muscle?
Reduced strength generation
Muscle stiffness in ageing is largely due to:
Increase in collagen-rich connective tissue
Which change most directly leads to reduced flexibility in aged skeletal muscle?
Combined reduction in strength and increased stiffness
Fine motor control diminishes with age primarily due to:
Loss and reorganisation of motor neurones
When muscle fibres are reinnervated by surviving motor neurones, what is the typical result?
Recovery of force but reduced fine control
A motor unit is best described as:
A group of muscle fibres and their innervating neuron
Which of the following is not a direct consequence of muscle atrophy?
Increase in myofibrillar density
What is the key benefit of regular, diverse exercise as described in the lecture?
It maintains functional capacity over time
What best explains the mechanism of strength loss in ageing muscle?
Reduction in sarcomere number and crossbridges
Which component is primarily responsible for the mechanical stiffness of muscle?
Collagen-based connective tissue
What is the primary function of the muscle spindle?
To detect changes in muscle length and initiate contraction
Which sensory neuron is associated with the muscle spindle?
1a afferent neuron
What is the role of gamma motor neurons in muscle spindle function?
Maintain intrafusal fibre tension for sensitivity
What initiates the stretch reflex in the patellar tendon test?
Passive stretch of the quadriceps femoris muscle
During the stretch reflex, which muscle group is inhibited?
Antagonist muscle group
What is the function of the Golgi tendon organ in reflex activity?
Inhibit host muscle activity during high tension
What type of sensory neuron is associated with the Golgi tendon organ?
1b afferent
Where is the Golgi tendon organ located?
Near the muscle-tendon junction
What characterizes the flexor withdrawal reflex?
Polysynaptic pathway with unilateral flexion and contralateral extension
Which sensory input triggers the flexor withdrawal reflex?
Nociceptive signal from a pain receptor
What is the result of flexor withdrawal on the opposite limb?
Activation of extensors and inhibition of flexors
What is the purpose of activating the extensors in the opposite limb during the withdrawal reflex?
To maintain postural stability
What are the extrafusal fibres innervated by
Alpha Motor Neurons
What are the ends of the intrafusal fibres innervated by
Gamma motor neurons
What best describes lactose?
A disaccharide made from galactose and glucose
What structural feature distinguishes oleic acid from palmitic acid?
Presence of a double bond causing a bend
Which amino acid has the simplest side chain (R group)?
Glycine
Why must ATP be continuously regenerated in cells?
Because its availability is limited in cells
Which of the following is unique to muscle cells for ATP regeneration?
Creatine phosphate system
What is the role of creatine kinase in ATP production from creatine phosphate?
It removes a phosphate from creatine phosphate and adds it to ADP
When is creatine phosphate re-synthesized in the muscle?
During recovery or inactivity
Which enzyme catalyzes the first step of glycolysis?
Hexokinase
What is the net ATP gain from anaerobic glycolysis per molecule of glucose?
2 ATP
Which enzyme is responsible for splitting fructose 1,6-bisphosphate into two three-carbon molecules?
Aldolase
The molecule dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is eventually converted into:
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
What is the role of genetics in glycolysis?
Genes encode enzymes that catalyze each step of glycolysis
Which statement best describes the speed and efficiency of ATP production by the creatine phosphate system?
Fast and complete due to an efficient enzyme
How long can the creatine phosphate system alone provide energy to muscles?
10–15 seconds
Which of the following contributes to muscle soreness and fatigue?
Lactic acid accumulation
What is the total duration of energy that can be supplied by stored ATP, creatine phosphate, and anaerobic glycolysis together?
About 1 minute
What is the primary reason anaerobic metabolism is useful during intense, short-term activities?
It generates ATP faster than aerobic metabolism
Which intermediate is NOT produced during glycolysis?
Acetyl-CoA
What happens to lactate after it is produced in skeletal muscle?
It diffuses into blood and is used by liver, heart, and kidneys
Which structure within the mitochondrion increases surface area for ATP production?
Cristae
Where does the citric acid (Krebs) cycle take place within the mitochondrion?
Matrix
What is the correct sequence for pyruvate metabolism in aerobic respiration?
Pyruvate → Acetyl CoA → Citric acid cycle → NADH/FADH2
What is the immediate product when acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate?
Citrate
Which of the following is not a product of the citric acid cycle?
Pyruvate
What is the main role of the electron transport chain in the mitochondria?
To transfer electrons and pump protons for ATP synthesis
Where in the mitochondrion are the proteins of the electron transport chain located?
Inner membrane of cristae
What directly powers the ATP synthase enzyme to produce ATP?
Flow of protons through a membrane channel
What is the total ATP yield per glucose molecule via aerobic metabolism?
36–40 ATP
How do fatty acids enter the citric acid cycle?
After being converted to acetyl CoA
Which of the following statements about protein metabolism is correct?
Amino acids enter at various points in aerobic metabolism
What compound is regenerated at the end of the citric acid cycle to restart the process?
Oxaloacetate
Which of the following best explains why aerobic metabolism produces more ATP than anaerobic metabolism?
It includes both citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation
What happens to NAD+ and FAD after they release electrons in the electron transport chain?
They return to the citric acid cycle to collect more electrons
Which structure ensures action potentials reach the interior of the muscle fibre?
T tubules
What receptor detects voltage change in the T tubule membrane?
Dihydropyridine (DHP) receptor
How is calcium moved back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum during relaxation?
Calcium ATPase (SERCA) pumps
Which molecule helps buffer calcium concentration inside the SR?
Calsequestrin
What allows the myosin head to detach from actin during the cross-bridge cycle?
ATP binding to the myosin head
What triggers the power stroke during muscle contraction?
Release of phosphate from the myosin head
What repositions the myosin head after detachment from actin?
Hydrolysis of ATP into ADP and phosphate
What causes the calcium channels in the SR to close during relaxation?
Repolarisation and return of DHP receptor to resting state
What maintains low intracellular sodium levels at rest in the muscle fibre?
Sodium ATPase pumps
Which of the following best describes a concentric muscle contraction?
Muscle shortens when its contractile force exceeds opposing resistance
In an eccentric contraction, which of the following is true?
Muscle is stretched as its contractile effort is less than opposing resistance
What is the primary characteristic of an isometric contraction?
Muscle length remains constant despite active force generation
During a controlled lowering of a dumbbell at the elbow, the biceps brachii is:
In an eccentric contraction, actively lengthening against gravity
Which contraction type is demonstrated when holding the knee at a fixed angle against gravity?
Isometric contraction of the biceps femoris
When stepping up, the hip and knee extensors primarily perform:
Concentric contractions to generate upward force
During stepping down, the gluteal and quadriceps muscles experience:
Eccentric contractions as they resist gravitational descent
According to the force-velocity relationship, a muscle:
Generates less force at higher shortening velocities
Which of the following correctly matches force capability with contraction type?
Eccentric – force increases with rapid but small stretches
n the combined force-velocity graph, where is the maximum active force observed?
At zero velocity, corresponding to isometric contraction
Which muscle action functions as a braking system during movement?
Eccentric contraction of extensors during limb lowering
What is the approximate safe range of muscle length change during contraction?
Approximately 10% of muscle’s resting length
Which of the following statements about eccentric contractions is correct?
Muscle generates more resistive force with rapid lengthening
When lifting a dumbbell during an elbow flexion exercise, the triceps brachii is likely:
Relaxed and passively lengthened
Which condition would result in near-zero force production?
Rapid concentric contraction at maximum shortening velocity
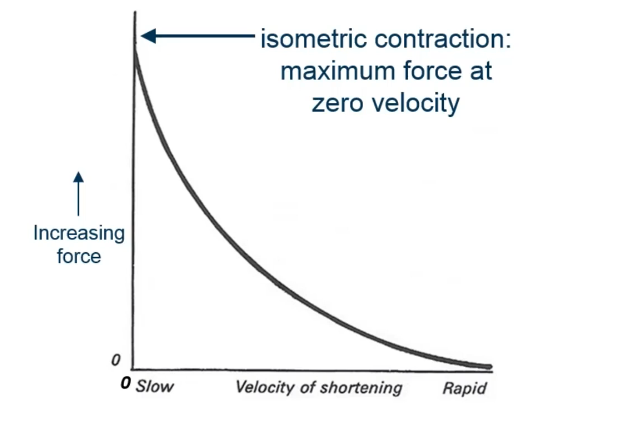
What type of contraction
Concentric
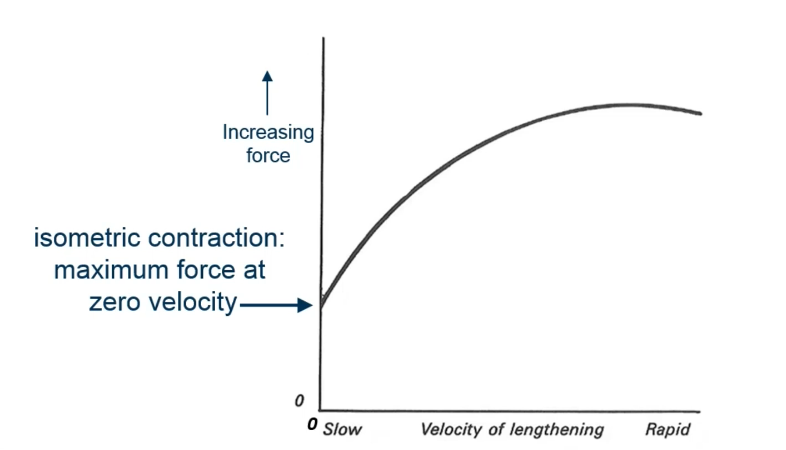
What type of contraction
Essentric
In the twitch myogram, which phase involves the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Latent period