GCSE AQA Geography - Section C: River Landscapes in the UK
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
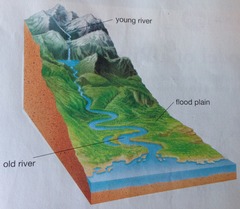
What is a long river profile?
A line representing the river from its source (where it starts) to its mouth (where it meets the sea). It shows how the river changes over its course
2
New cards
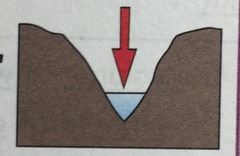
Explain the key points on the upper course of a river
- steep gradient
- V-shaped valley, steep sides, narrow, shallow channel
- V-shaped valley, steep sides, narrow, shallow channel
3
New cards
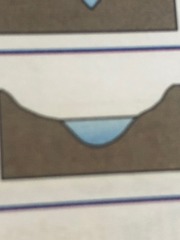
Explain the key points on the middle course of a river
- medium gradient
- gently sloping valley sides, wider, deeper channel
- gently sloping valley sides, wider, deeper channel
4
New cards
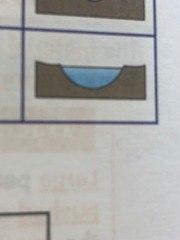
Explain the key points on the lower course of a river
- gentle gradient
- very wide, almost flat valley, very wide, deep channel
- very wide, almost flat valley, very wide, deep channel
5
New cards
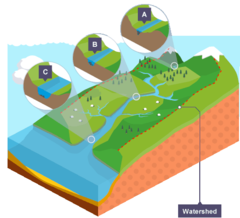
What does the cross river profile show?
A cross profile shows a cross-section of a river's channel and valley at a certain point along the river's course.
6
New cards
What is the course?
The path of a river as it flows downhill
7
New cards
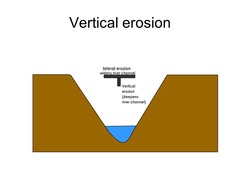
What is vertical erosion?
- deepens valley, V-shaped
- dominant in upper course
- high turbulence causes intense downward erosion
- dominant in upper course
- high turbulence causes intense downward erosion
8
New cards
What is lateral erosion?
- widens valley + channel during meander formation
- dominant in lower + middle course
- dominant in lower + middle course

9
New cards
How can a cross profile of a river change?
It can change through lateral or vertical erosion
10
New cards
What are the four processes of erosion in rivers?
Hydraulic action, Abrasion, Attrition and Solution
11
New cards
The faster the river is flowing...
the more erosion happening
12
New cards
What is hydraulic action?
The force of the water breaks rock particles away from the river channel
13
New cards
What is abrasion?
Eroded rocks picked up by the river scrape and rub against the channel, wearing it away.
14
New cards
What is attrition?
Eroded rocks picked up by river smash into each other and break into smaller fragments. Their edges also get rounded off as they rub together.
15
New cards
What is solution?
River water dissolves some types of rocks e.g. chalk + limestone
16
New cards
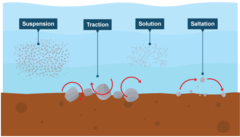
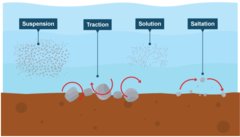
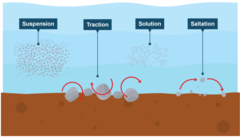
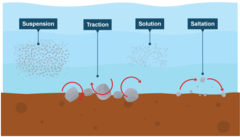
How can rivers transport eroded material?
traction, suspension, solution, saltation
17
New cards
What is traction?
Large particles like boulders are pushed along the river bed by the force of the water
18
New cards
What is suspension?
Small particles like silt and clay are carried along by the water
19
New cards
What is saltation?
Pebble sized particles are bounced along the river bed by the force of the water
20
New cards
What is solution? (transport)
Soluble materials (e.g. limestone) dissolve in the water and are carried along
21
New cards
What is deposition?
the process in which sediment moved by erosion is dropped and comes to rest
22
New cards
When does deposition occur?
When a river loses velocity and energy
23
New cards
Why could a river slow down and deposit material?
- volume of water falls
- eroded material increases
- water is shallower (e.g. inside of bend)
- river reaches its mouth
- eroded material increases
- water is shallower (e.g. inside of bend)
- river reaches its mouth
24
New cards
How material is transported depends on...
- velocity of water
- size of particles
- size of particles
25
New cards
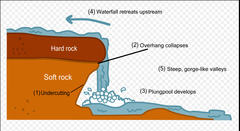
Explain the formation of waterfalls and gorges
1. forms over an area of hard rock then soft rock below
2. softer rock erodes by H.A and abrasion more than the hard rock, creating a 'step' in the river
3. water flows over step eroding more of softer rock
4. steep drop is created, called the waterfall (e.g. High Force waterfall on the River Tees, County Durham)
5. hard rock undercut by erosion, unsupported + collapses
6. collapsed rock swirls around foot of waterfall where they erode softer rock by abrasion creating deep plunge pool
7. undercutting causes more collapses, waterfall retreats leaving a steep-sided gorge
2. softer rock erodes by H.A and abrasion more than the hard rock, creating a 'step' in the river
3. water flows over step eroding more of softer rock
4. steep drop is created, called the waterfall (e.g. High Force waterfall on the River Tees, County Durham)
5. hard rock undercut by erosion, unsupported + collapses
6. collapsed rock swirls around foot of waterfall where they erode softer rock by abrasion creating deep plunge pool
7. undercutting causes more collapses, waterfall retreats leaving a steep-sided gorge
26
New cards
What does fluvial mean?
river
27
New cards
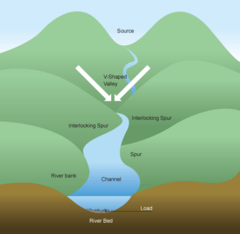
What are interlocking spurs?
Hillsides that interlock with each other as the river winds around them
28
New cards
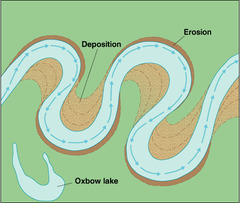
How are meanders formed?
1. faster current on outside bend as river channel is deeper
2. erosion takes place on outside bend, forming river cliffs
3. slower current on inside bend as river is shallower
4. deposited eroded material in inside bend, forming slip-off slopes
2. erosion takes place on outside bend, forming river cliffs
3. slower current on inside bend as river is shallower
4. deposited eroded material in inside bend, forming slip-off slopes
29
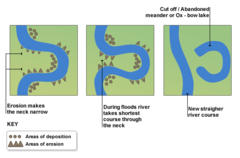
New cards
How are oxbow lakes formed?
1. erosion causes outside bends to get closer until narrow neck is created
3. flooding makes river breaks through neck
4. river flows along the shortest course, through neck
5. deposition cuts of meander forming ox-bow lake
e.g. River Calder, near Castleford, West Yorkshire
3. flooding makes river breaks through neck
4. river flows along the shortest course, through neck
5. deposition cuts of meander forming ox-bow lake
e.g. River Calder, near Castleford, West Yorkshire
30
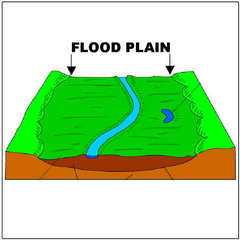
New cards
How do flood plains form?
1. during floods, water slows down + loses energy and deposits transported material building floodplain
2. meanders widen as they move across floodplains laterally
3. over time, meanders move downstream
2. meanders widen as they move across floodplains laterally
3. over time, meanders move downstream
31
New cards
What is a flood plain?
Area of low-lying ground adjacent to river
32
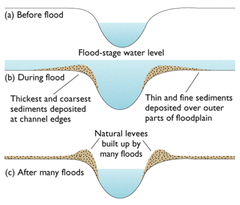
New cards
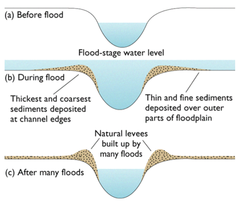
How do levees form?
1. during floods, eroded material deposited over flood plain
2. heaviest material deposited closest to the river channel as it gets dropped first when the river slows down and loses energy
3. gradually, deposited material builds up, creating levees along edges of channel
e.g. River Trent, Nottinghamshire
2. heaviest material deposited closest to the river channel as it gets dropped first when the river slows down and loses energy
3. gradually, deposited material builds up, creating levees along edges of channel
e.g. River Trent, Nottinghamshire
33
New cards
What are levees?
Natural embankments along the edges of a river channel
34
New cards
What are estuaries?
regions where fresh water and salt water mix
35
New cards
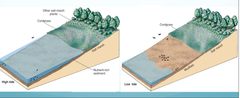
How do mudflats form?
1. water floods over river banks carrying silt + sand on valley floor
2. tide reaches highest point and waves moves slowly with little energy depositing sediment
3. mud builds up creating large mudflats
4. at low tide, wide + muddy banks are exposed
2. tide reaches highest point and waves moves slowly with little energy depositing sediment
3. mud builds up creating large mudflats
4. at low tide, wide + muddy banks are exposed
36
New cards
What are contour lines?
They are the orange lines over a map; they tell you:
- height of land (in metres) by the numbers marked on them
- steepness of the land by how close together they are (closer the lines= steeper slope)
- height of land (in metres) by the numbers marked on them
- steepness of the land by how close together they are (closer the lines= steeper slope)
37
New cards
How do maps contain evidence for upper course rivers?
- waterfalls are marked on maps but the symbol for cliffs are black, blocky lines and the close contour lines are evidence for an upper course waterfall
- the height gives it away
- river crosses a lot of contour lines in a short distance showing it's steep
- the river is narrow (thin blue line)
- the height gives it away
- river crosses a lot of contour lines in a short distance showing it's steep
- the river is narrow (thin blue line)
38
New cards
How do maps contain evidence for lower course rivers?
- nearby land is low
- river doesn't cross any contour lines so it's gently sloping
- river meanders across a large flat area
- rivers wide (thick blue line)
- river has large meanders + ox-bow lake may have formed
- river doesn't cross any contour lines so it's gently sloping
- river meanders across a large flat area
- rivers wide (thick blue line)
- river has large meanders + ox-bow lake may have formed
39
New cards
What is the river discharge?
The volume of water that flows in a river per second
40
New cards
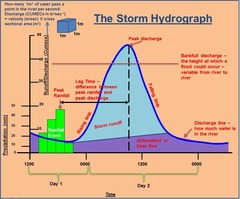
What are hydrographs?
They show how the discharge at a certain point in a river changes over time in relation to rainfall.
peak discharge: highest discharge in the period of time you're looking at
lag time: the delay between peak rainfall and peak discharge
rising limb: increase in river discharge as rainwater flows into the river
falling limb: decrease in river discharge as river returns to its normal speed
peak discharge: highest discharge in the period of time you're looking at
lag time: the delay between peak rainfall and peak discharge
rising limb: increase in river discharge as rainwater flows into the river
falling limb: decrease in river discharge as river returns to its normal speed
41
New cards
Why does lag time occur?
- surface runoff (flows quickly overland)
- infiltration (soaks into ground and runs underground)
- infiltration (soaks into ground and runs underground)
42
New cards
What are the causes of flooding?
- heavy rainfall
- geology (rock type)
- prolonged rainfall
- relief (changes in land height)
- land use
- geology (rock type)
- prolonged rainfall
- relief (changes in land height)
- land use
43
New cards
How does heavy rainfall cause flooding?
Heavy rainfall means water arrives too quickly to infiltrate, so there's a lot of surface runoff, increasing discharge
44
New cards
How does geology cause flooding?
impermeable rocks do not allow infiltration and increase surface runoff e.g. granite/shale
45
New cards
How does prolonged rainfall cause flooding?
Prolonged rainfall saturates soil and any further rainfall cannot infiltrate, increasing runoff into river channels
46
New cards
How does relief cause flooding?
steep-sided valley -> water reaches channel faster as it flows quicker on steeper slopes increasing discharge causing a flood
47
New cards
How does land use cause flooding?
1. buildings and roads are made from impermeable materials increasing surface runoff; man-made drains transport runoff to rivers increasing discharge
2. cutting down trees increases the volume of water that enters the river channel as trees intercept water on their leaves which evaporates
2. cutting down trees increases the volume of water that enters the river channel as trees intercept water on their leaves which evaporates
48
New cards
What are the hard engineering methods for reducing flooding + effects of flooding?
- dams and reservoirs
- channel straightening
- embankments
- flood relief channels
- channel straightening
- embankments
- flood relief channels
49
New cards
What are the soft engineering methods for reducing flooding + effects of flooding?
- flood warnings + preparation
- flood plain zoning
- planting trees
- river restoration
- flood plain zoning
- planting trees
- river restoration
50
New cards
What are dams & reservoirs, its benefits and cons?
What are they?
- dams are barriers built across the river, usually in the upper course + a reservoir is formed behind the dam
Benefits
- stores water (e.g. after heavy rain) controlling water flow preventing flooding downstream
- generates HEP
Cons
- expensive to build
- farmland downstream becomes less fertile as material is deposited in the dam
- dams are barriers built across the river, usually in the upper course + a reservoir is formed behind the dam
Benefits
- stores water (e.g. after heavy rain) controlling water flow preventing flooding downstream
- generates HEP
Cons
- expensive to build
- farmland downstream becomes less fertile as material is deposited in the dam
51
New cards
What is channel straightening, its benefits and cons?
What is it?
- meanders are removed by building straighter + artificial channels
Benefits
- water leaves area quicker rather than building up, lowers flood risk
Cons
- flooding may happen downstream instead
- faster-moving water may cause more erosion downstream
- meanders are removed by building straighter + artificial channels
Benefits
- water leaves area quicker rather than building up, lowers flood risk
Cons
- flooding may happen downstream instead
- faster-moving water may cause more erosion downstream
52
New cards
What are embankments, its benefits and cons?
What are they?
- raised walls built along river banks
Benefits
- river holds more water lowering flooding
Cons
- expensive
- risk of flooding if water flows above embankments
- raised walls built along river banks
Benefits
- river holds more water lowering flooding
Cons
- expensive
- risk of flooding if water flows above embankments
53
New cards
What are flood relief channels, its benefits and cons?
What are they?
- channels built to divert water around built-up areas or to divert excess water if river level gets to high
Benefits
- gates control water release
Cons
- increased discharge where the relief channel rejoins the river which could cause flooding in that area
- channels built to divert water around built-up areas or to divert excess water if river level gets to high
Benefits
- gates control water release
Cons
- increased discharge where the relief channel rejoins the river which could cause flooding in that area
54
New cards
What are flood warnings + preparation, its benefits and cons?
What are they?
- E.A issues flood warnings through various media/buildings are modified to minimise flood damage/residents can prepare sand bags and flood boards prior to floods
Benefits
- give people time to move possessions upstairs
- evacuation
Cons
- warnings don't prevent floods
- modifying buildings is expensive
- E.A issues flood warnings through various media/buildings are modified to minimise flood damage/residents can prepare sand bags and flood boards prior to floods
Benefits
- give people time to move possessions upstairs
- evacuation
Cons
- warnings don't prevent floods
- modifying buildings is expensive
55
New cards
What is flood plain zoning, its benefits and cons?
What is it?
- restrictions prevent building on part of a flood plain that are likely to be affected by floods
Benefits
- reduced flood risk, less impermeable surfaces
- no buildings to damage
Cons
- expansion of an urban area is difficult is there isn't any other suitable building sites
- can't help in areas with existing buildings
- restrictions prevent building on part of a flood plain that are likely to be affected by floods
Benefits
- reduced flood risk, less impermeable surfaces
- no buildings to damage
Cons
- expansion of an urban area is difficult is there isn't any other suitable building sites
- can't help in areas with existing buildings
56
New cards
What is tree planting, its benefits and cons?
What is it?
- planting trees in river valleys increases interception of rainwater + lag time
Benefits
- discharge and flood risk decrease
- vegetation reduces soil erosion in valleys providing habitats for wildlife
Cons
- less land available for farming
- planting trees in river valleys increases interception of rainwater + lag time
Benefits
- discharge and flood risk decrease
- vegetation reduces soil erosion in valleys providing habitats for wildlife
Cons
- less land available for farming
57
New cards
What is river restoration?, its benefits and cons?
What is it?
- making the river more natural
Benefits
- improves wildlife habitats
- little maintenance
Cons
- local flood risk can increase, especially if nothing is done to prevent major flooding
- making the river more natural
Benefits
- improves wildlife habitats
- little maintenance
Cons
- local flood risk can increase, especially if nothing is done to prevent major flooding