Day 5 Plant Reproduction
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Label the plant life cycle diagram
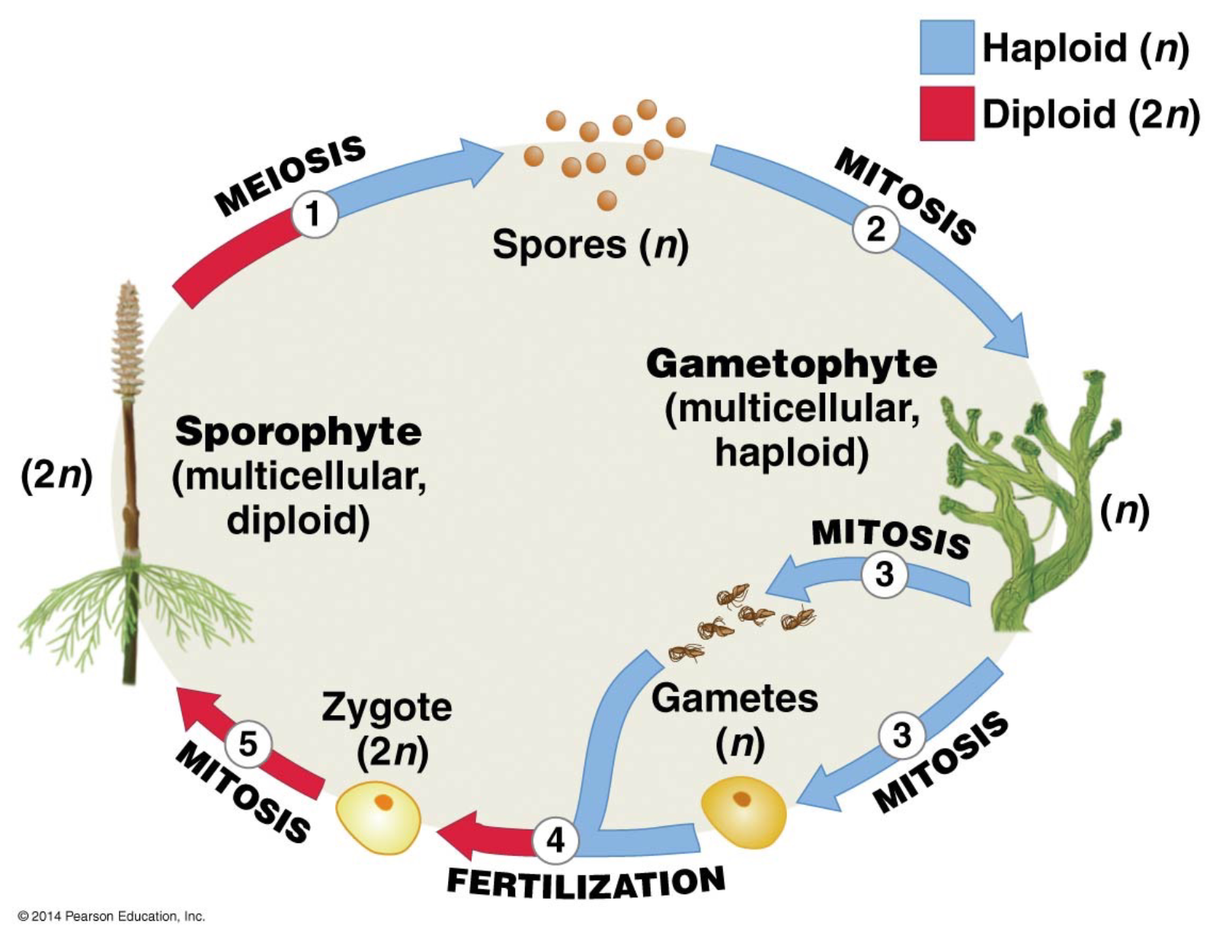
Sporophytes: ploidy, what they produce and how
2n
produce spores (n) via meiosis
What do the spores grow into and by what process
they grow into gametophytes via mitosis
Gametophytes: ploidy, what they produce and by what process
n
produce gametes (n) via mitosis
What do the gametes create and by what process
create a zygote via fusion/fertilization
What does the zygote grow into and by what process
grows into sporophyte via mitosis
Example of gametophyte dominant
moss
Example of sporophyte dominant
flowering plant
Sexual reproduction in angiosperm reproduction
sporophyte-dominated alternation of generations with gametes and fertilization
Asexual reproduction in angiosperm reproduction
clonal copies of parent plant created by mitotically driven growth
Asexual reproduction in plants
many different mechanisms
many plants use it
Angiosperm reproduction vis sexual mode
sexual reproduction in plants requires flowers
flowers host gametophytes in angiosperm life cycle
flowers often use nectar to attract animals to carry pollen
Label the flower structures/parts
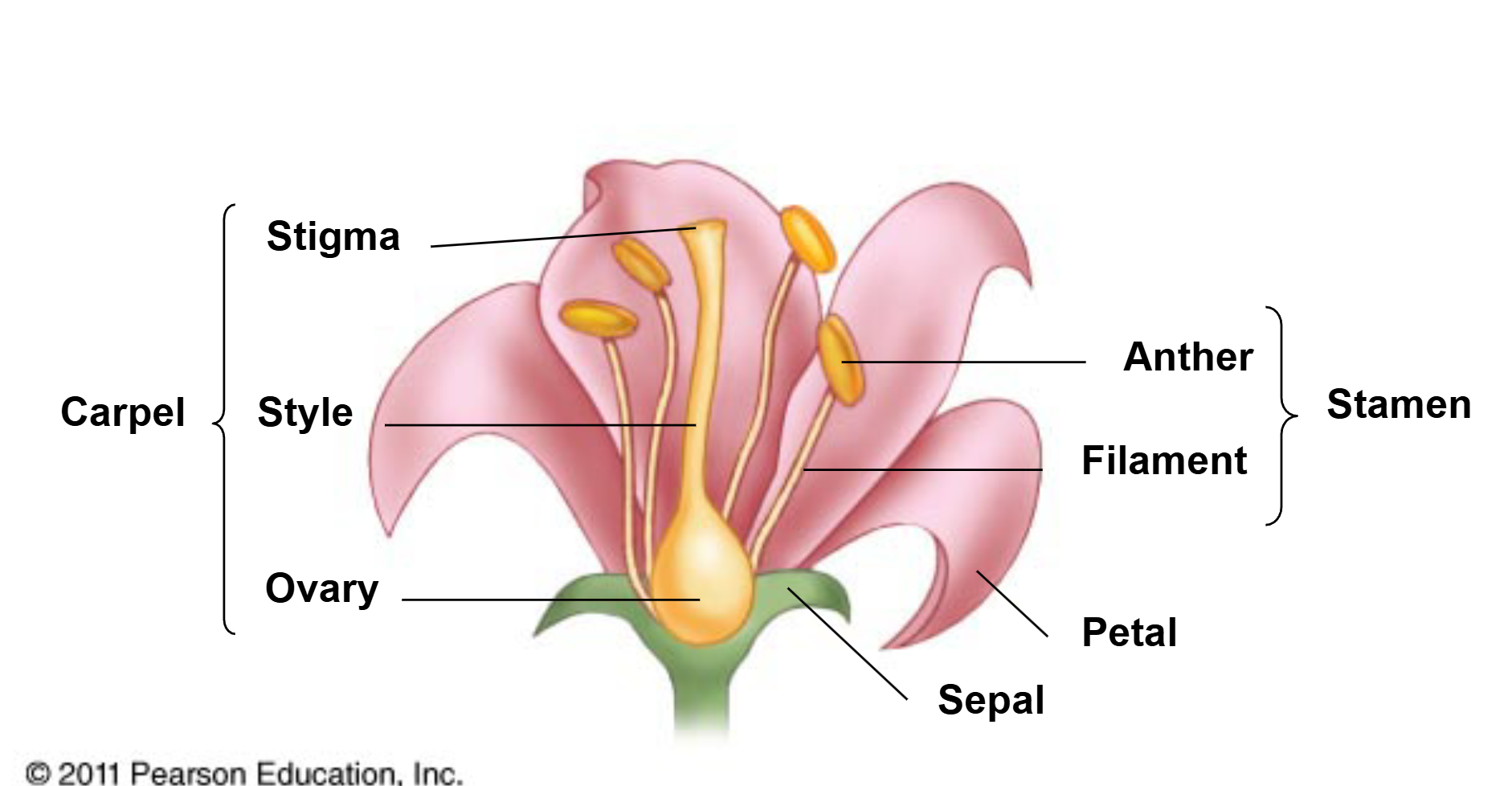
What is the stamen
male part/structures of the flower
What does the stamen consist of and their roles
anthers - produce pollen
filaments - elevate/hold up anther
What is the carpel
the female part/structures of a plant
What does the carpel consist of and their role
stigma - receives pollen
style - elevates/holds up the stigma
ovary - contains ovules
Facts of the carpel in flowers
defining feature of angiosperm
not found in any other plant
Type of sexes/sex combos in flowers
bisexual
unisexual
What does it mean when a flower is bisexual
they are perfect because they have both stamen and carpel
What does it mean when a flower is unisexual
the flower has only stamen or only carpel
Types of plants with unisexual flowers
monoecious - male and female flowers on same plant
dioecious - male and female flowers on different plants
Label angiosperm life cycle
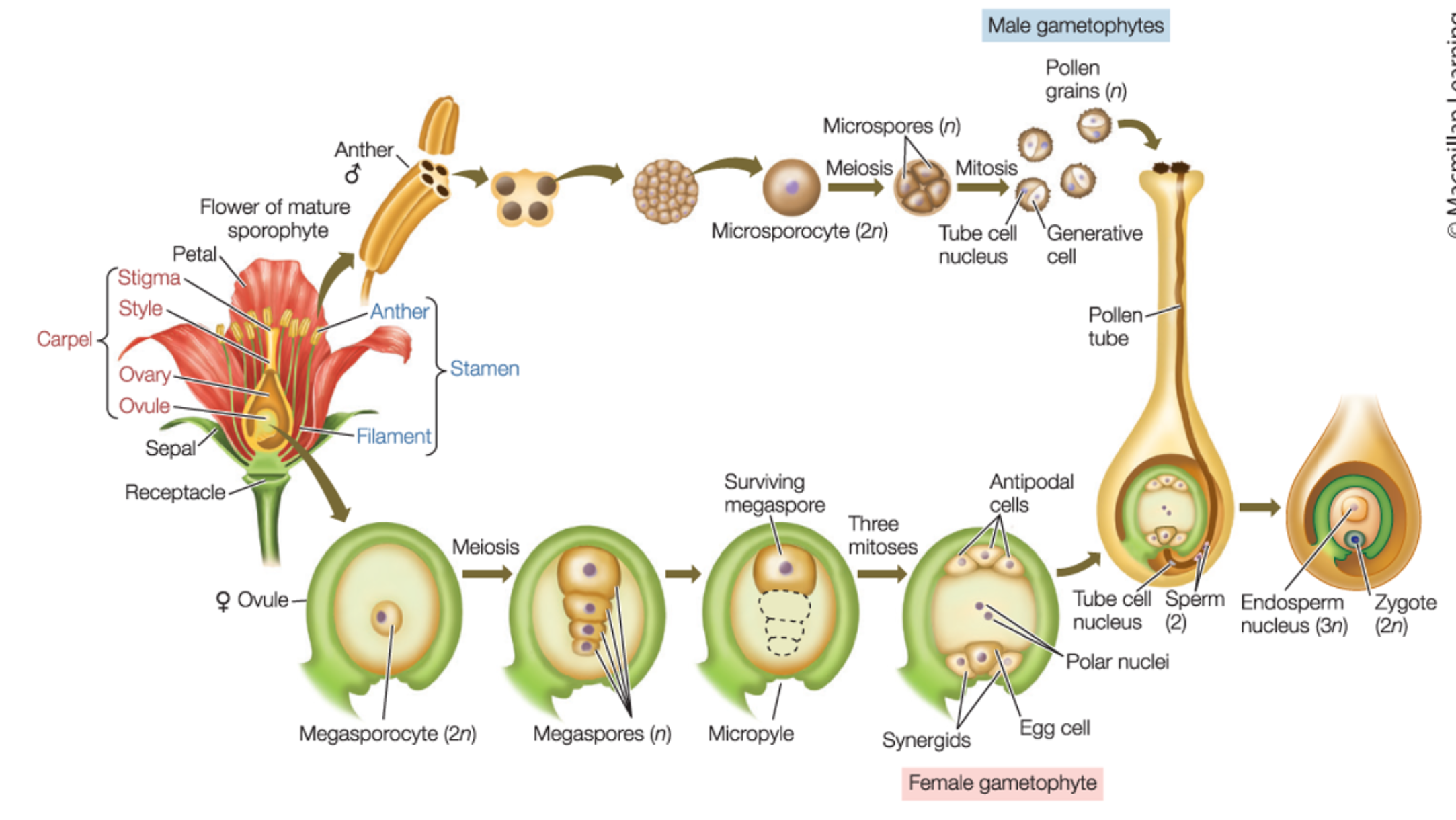
How is pollen developed
(2n) microsporocytes for (n) micropores via meiosis
microspores grow into pollen - 2 cell male gametophytes via mitosis
(tube cell and generative cell)
What are the 2 male gametophytes produced when microspores grow into pollen
tube cell
generative cell
Draw/label pollen development
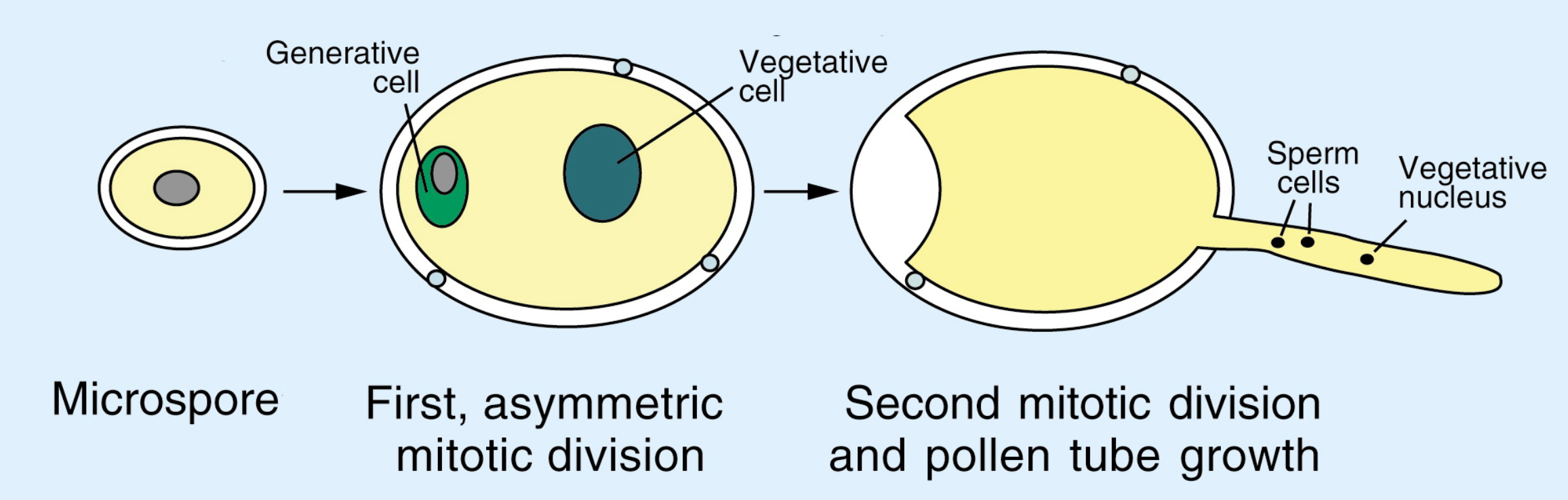
What is the cell wall of pollen grains made out of
sporopollenin
Role/benefits of sporopollenin
prevents desiccation
almost indestructible by microorganisms
insoluble in most solvents
leaves great pollen fossils
How female gametophytes formed
(2n) megasporocytes form (n) megaspores via meiosis
megaspores grow into a 7-cell female gametophyte via mitosis
(includes egg and central wall with 2 nuclei)
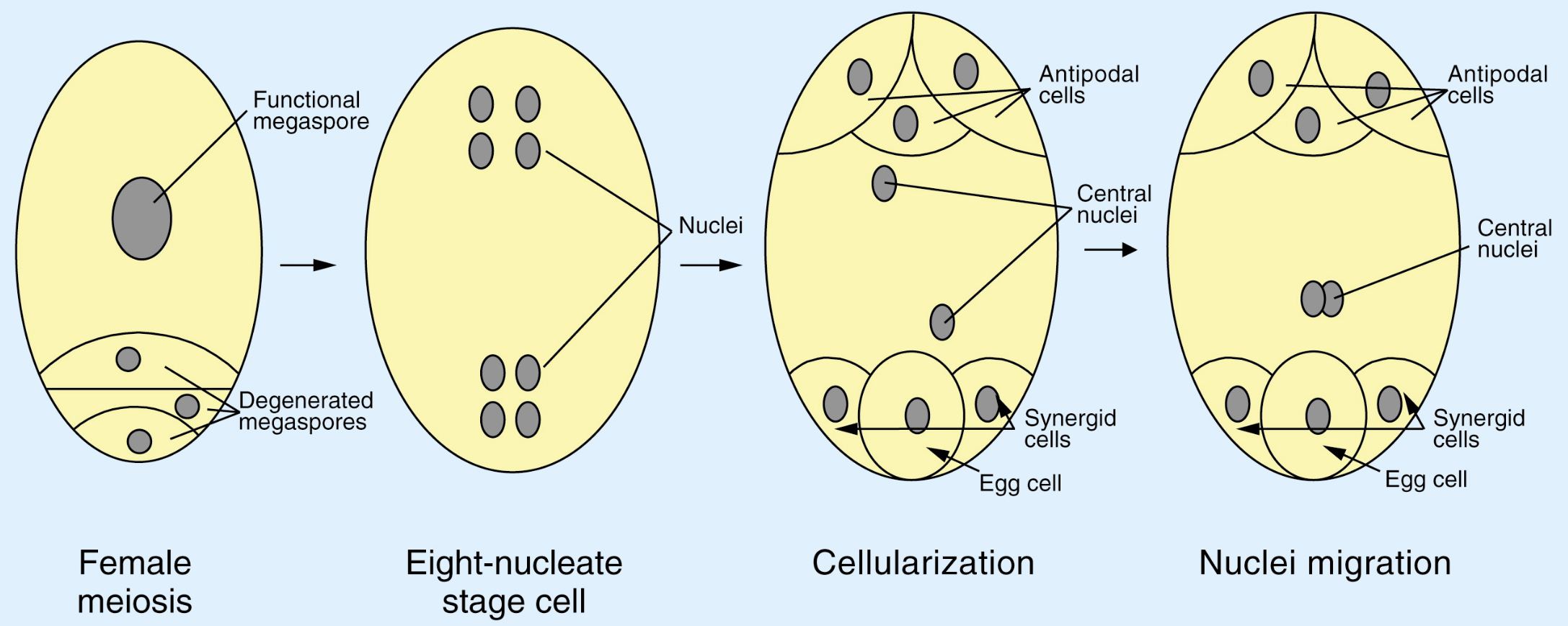
What are the 7-cell female gametophyte that megaspores grow into
egg
central wall with 2 nuclei
Purpose of the pollen tube
grows down into the style towards the female gametophyte
What is pollen competition
as pollen tubes grow through the style, they compete with each other
only the fastest (most fit) will fertilize eggs
What is pollen competition an example of
a form of male-male competition
What is self-incompatibility
reactions to reduce inbreeding
How do flowers reduce inbreeding
pistil can arrest growth of pollen tubes of likely close relatives
How does the pistil arrest pollen tube growth
S gene has many different alleles within a population, so sharing same S allele suggests kinship
pollen tube (n) carries one allele and pistil (2n) carries two
if pollen tube chares an S allele with the pistil, then pollen tube growth is arrested
Steps of fertilization in flowers
the two sperm nuclei are released into the female gametophyte
one sperm fertilizes the egg to form a (2n) zygote
the other sperm “fertilizes” the central cell and forms an (3n) endosperm
What is double fertilization
the second sperm nuclei fertilize the central wall: fusing with polar nuclei to form (3n) endosperm
Benefits of endosperm
triploid endosperm may increase nutritive stores
Steps of fruit development
the ovules develop into the seeds (one per zygote)
the ovary becomes the fruit
the remaining flower parts die back
Whats a monocotyledon
type of angiosperm and is characterized by haing a single seed leaf, or cotyledon
Examples of monocotyledons
true grasses
orchids
corn seed
Whats a dicotyledons
type of angiosperm and is characterized by having two embryonic leaves, or cotyledon
Examples of dicotyledons
common garden plants
tress
been seed
Whats germination
many seeds require physical “abuse” to germinate
Scarification occurs when seed coats are
abraded by soil particles over time
heated by fire
exposed to digestive action
broken down by mircrobes
What is scarification
weakening or altering the coat of a seed to encourage germination
What are pollination syndromes
are flower traits that evolve to facilitate pollination
different modes of pollination favor different structures, colors, scents
Co-evolution between flowers and pollinators
they evolve together, but to maximize their individual fitness, not to help the other organism
plants evolve to maximize pollen transfer for minimum reward output
pollinators evolve to obtain as much reward as possible
What is nectar
a sugar solution produced by plants to attract pollinators
Where do flowers hold nectar
in nectaries
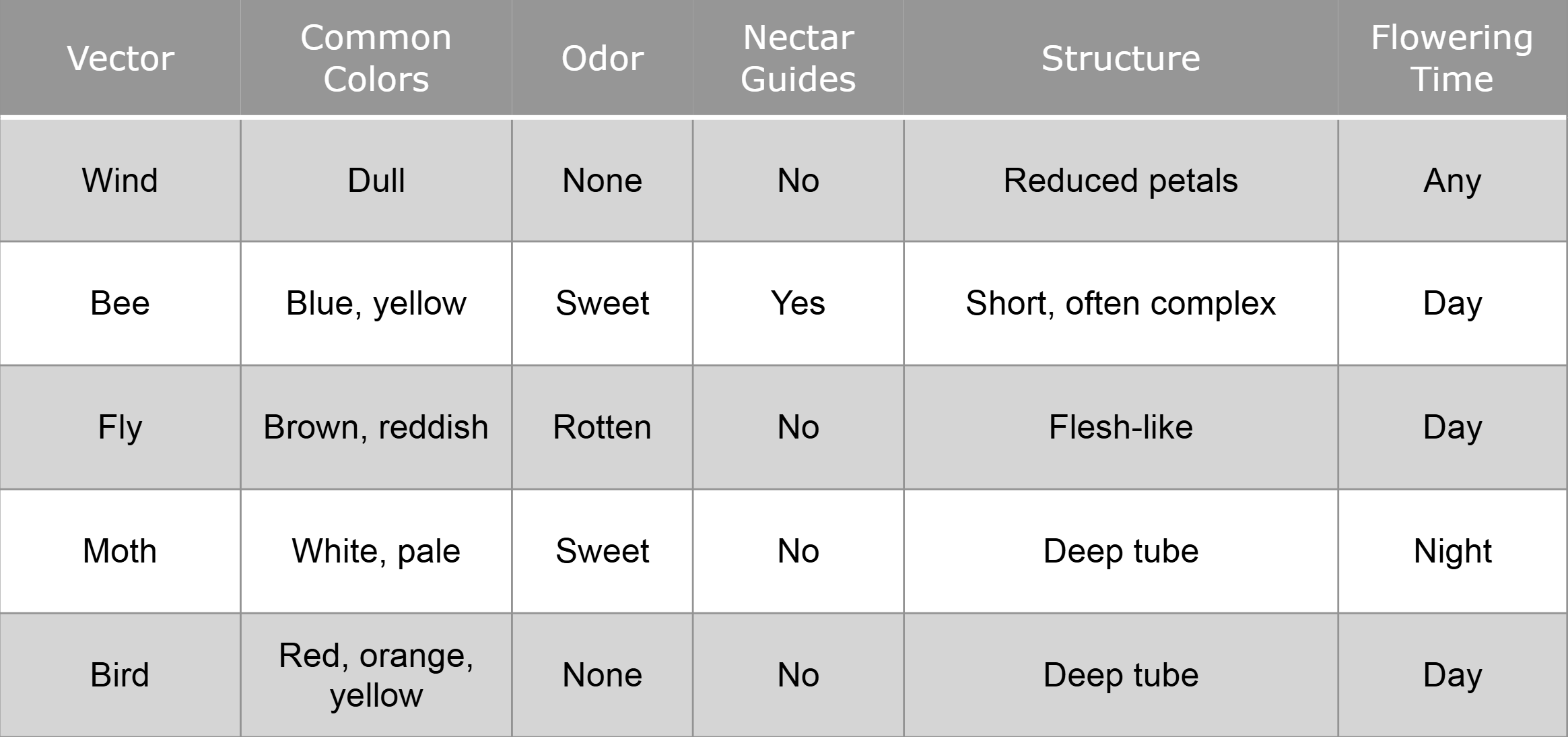
Bee pollination
flower parts visible
often colored, but not red
has nectar guides
sweet floral odor
What are nectar guides
help bees find nectaries
some are visible only in UV range
Fly pollination
flowers resemble carrion
reddish to purple-brown color
strong foul odor
no nectar guides
Moth pollination
open at night
usually white
strong/sweet odor
lots of nectar
Hummingbird pollination
flowers produced nectar, hidden in long floral tube
often red, orange, or yellow
no odor
often lack landing platforms
Wind pollination
don’t need to attract pollinators
petals, sepals reduced
lots of pollen produced
pollen is lightweight, non-sticky
stigma is large, often feathery
Complete table of the summary of pollinator syndromes