NPTE (scorebuilders review, and Previous PEAT) musculosketal system
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Over 100 questions covering most of the musculoskeletal system for the boards exam. enjoy =)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Which joint receptor is MOST sensitive to high-frequency vibration and quick joint movements?
Pacinian corpuscles
A therapist applies sustained stretch to a patient's joint capsule. Which receptor is MOST involved in sensing this?
Ruffini endings
Which receptor is found in the ligaments, particularly near their bony attachment?
Golgi ligament endings
Which receptor is primarily responsible for detecting joint compression, especially in the knee joint?
Golgi-Mazzoni corpuscles
Which receptor is a non-specific detector of mechanical stress and pain, and is found in all joints?
Free nerve endings
A patient performs a side-lying hip abduction exercise. Which plane and axis does this motion primarily occur in?
Frontal plane, anteroposterior axis
A physical therapist observes a patient performing trunk rotation exercises on a stability ball. This movement occurs in which plane and around what axis?
Transverse plane, vertical axis
A patient is performing a forward lunge. Which plane is MOST active during this movement?
Sagittal
During shoulder abduction in standing, which plane and axis are primarily involved?
Frontal plane, anteroposterior axis
A therapist is assessing gait in a patient post-stroke. Which plane of movement is MOST challenged during step width control and lateral sway?
Frontal
A patient performs a 5-second maximal effort sprint during rehab. Which energy system is primarily used?
ATP-PCr (phosphagen)
Which energy system produces lactic acid as a byproduct?
Anaerobic glycolysis
During a 10-minute moderate-intensity cycling session, which energy system predominantly supplies ATP?
Aerobic
A patient complains of rapid fatigue during a 30-second high-intensity activity. What is the MOST likely cause?
Accumulation of lactic acid
Which energy system is considered the slowest but most efficient for ATP production?
Aerobic
During high-intensity exercise, lactic acid accumulates in the muscle cells. Which of the following is the PRIMARY effect of this accumulation on muscle function?
Decreased pH causing inhibition of enzyme activity
After repeated anaerobic sprints, a patient reports muscle burning and fatigue. Which energy system was MOST active?
Anaerobic glycolysis
Which of the following is an example of a fibrous joint classified as a gomphosis?
Tooth anchored in the maxilla
Which fibrous joint type allows for a small amount of movement, typically classified as an amphiarthrosis?
Syndesmosis
A patient has limited pronation and supination following a forearm fracture. Which fibrous joint was MOST likely involved?
Distal radioulnar syndesmosis
Which characteristic is shared by all fibrous joints?
Connection by dense connective tissue
A newborn’s skull has not yet fully ossified. What is the classification of the joints between the cranial bones?
Suture
Which of the following joints is an example of a symphysis?
Pubic symphysis
A joint connected by hyaline cartilage that eventually ossifies over time is best classified as a:
Synchondrosis
The intervertebral discs are structurally classified as:
Symphyses
A patient with SI joint dysfunction is also diagnosed with pubic symphysis instability. What type of tissue primarily connects this joint?
Fibrocartilage
Which ribs connect indirectly to the sternum via the costal cartilage of the rib above, allowing for more mobility during respiration?
Ribs 8–10 (False ribs)
Which ribs attach directly to the sternum via hyaline cartilage forming synchondrosis joints?
Ribs 1–7 (True ribs)
The joint formed between the first rib and the sternum is classified as:
Synchondrosis
Which type of cartilage primarily connects the true ribs to the sternum?
Hyaline cartilage
The flexible attachment of false ribs to the sternum primarily helps to:
Allow for expansion of the thoracic cavity during breathing
A physical therapist is treating a patient with knee osteoarthritis. Which of the following is the primary reason to continue low-impact exercise?
To increase synovial fluid production and cartilage nutrition
Which exercise is MOST appropriate to begin with for a patient with moderate knee osteoarthritis and joint pain?
Stationary cycling with moderate resistance
Articular cartilage receives most of its nutrition from:
Synovial fluid movement and diffusion
A sedentary, bed-bound patient with early-stage osteoarthritis is MOST at risk for:
Decreased cartilage thickness and joint stiffness
Which of the following physical therapy interventions would BEST reduce joint compression forces in a patient with mild knee OA?
Strengthening the quadriceps and gluteals
Which synovial joint is classified as a uniaxial pivot joint and allows rotation?
Proximal radioulnar joint
A physical therapist is assessing a joint that allows flexion/extension and abduction/adduction but not rotation. What type of joint is this?
Condyloid joint
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joint of the thumb is classified as a:
Saddle joint
Which sensory receptor is located in the musculotendinous junction and responds primarily to muscle tension?
Golgi tendon organ
During a rapid passive stretch of the hamstrings, which receptor is most likely to trigger a reflex contraction of the muscle?
Muscle spindle
A therapist is using prolonged stretching to improve hamstring flexibility. Which muscle receptor facilitates muscle relaxation during this technique?
Golgi tendon organ
Which of the following BEST explains the purpose of the autogenic inhibition reflex?
To reduce excessive tension in the muscle via GTO activation
Which receptor is MOST responsible for detecting the rate and magnitude of muscle stretch?
Muscle spindle
During passive range of motion of a patient’s shoulder, the therapist feels the patient’s muscles contract and tighten in response to the stretch. This protective muscle contraction is MOST likely mediated by which of the following?
Muscle spindle stretch reflex
Which muscle fiber type is characterized by high mitochondrial density, slow contraction speed, and high fatigue resistance?
Type I
A patient who is a long-distance runner most likely has a predominance of which muscle fiber type?
Type I
Which muscle fiber type generates the greatest amount of force but fatigues the fastest?
Type IIb (IIx)
Which muscle fiber type would be most involved in postural control?
Type I
Which joint allows most of the shoulder’s mobility?
Glenohumeral joint
During shoulder abduction, which muscle initiates the movement before the deltoid becomes dominant?
Supraspinatus
Which of the following muscles is NOT a prime mover for shoulder extension?
Anterior deltoid
What is the open-packed position of the glenohumeral joint?
55° abduction and 30° horizontal adduction
A patient lacks scapular upward rotation. Which muscle is MOST likely weak?
Serratus anterior
What is the closed-packed position of the glenohumeral joint?
Arm fully abducted and externally rotated
During horizontal abduction of the shoulder, which muscle is the primary mover?
Posterior deltoid
Which of the following does NOT contribute to shoulder internal rotation?
Infraspinatus
The acromioclavicular joint is best described as which type of joint?
Plane
A therapist performs a manual muscle testing on a patient and the patient demonstrates no palpable muscle contraction what grade would this be?
Grade zero
A therapist performs a manual muscle testing on a patient and the patient demonstrates a palpable muscle contraction with no movement what grade would this be?
Grade 1
A therapist performs a manual muscle testing on a patient and the patient demonstrates full ROM with gravity eliminated what grade would this be?
Grade 2
A therapist performs a manual muscle testing on a patient and the patient demonstrates full ROM against gravity what grade would this be?
Grade 3
A therapist performs a manual muscle testing on a patient and the patient demonstrates full ROM against gravity with moderate resistance what grade would this be?
Grade 4
A therapist performs a manual muscle testing on a patient and the patient demonstrates full ROM against gravity with max resistance what grade would this be?
Grade 5
A therapist passively flexes a patient’s elbow to the end range. What end feel should the therapist expect to feel?
Soft end feel
A therapist passively entends a patient’s elbow to the end range. What would be the expected end feel a therapist should expect?
Hard end feel
A therapist performs a passive movement on a patient’s shoulder, but is unable to finish the movement due to pain. What type of end feel would this be?
Empty end feel
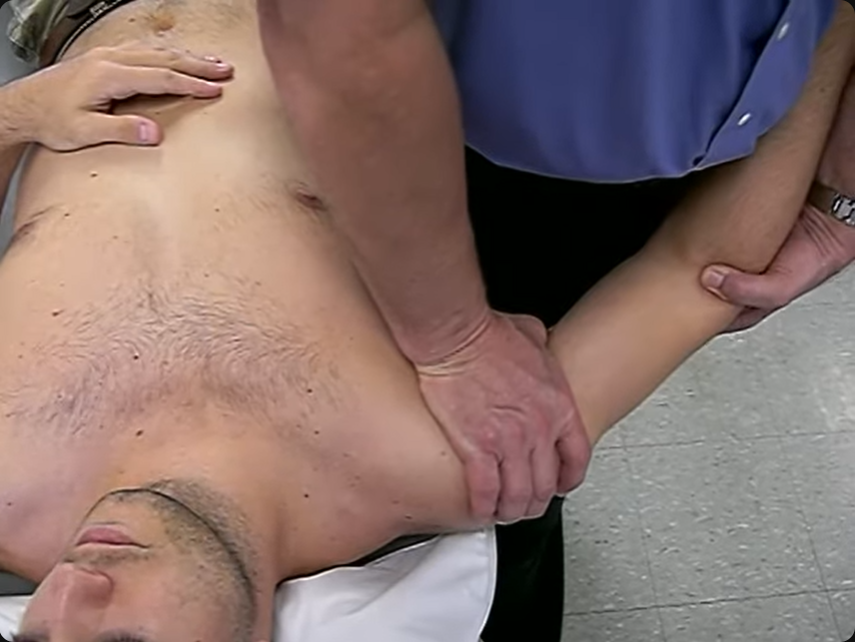
A therapist is about to perform a posterior glide on a patient’s shoulder. How should the therapist position the patient’s shoulder before performing the glide?
55 degrees if shoulder abduction and 30 degress of horizontal abduction
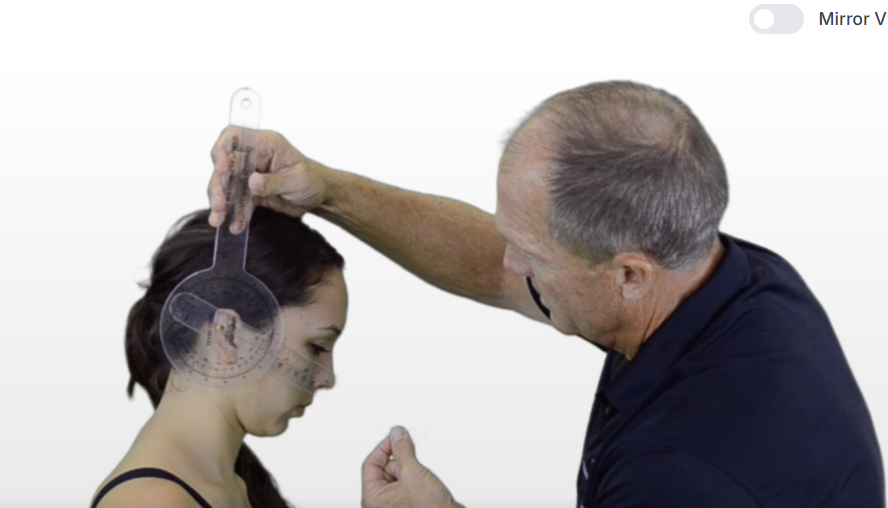

A therapist is preparing to use a goniometer to test for cervical flexion. What is the normal ROM for cervical flexion?
0-45
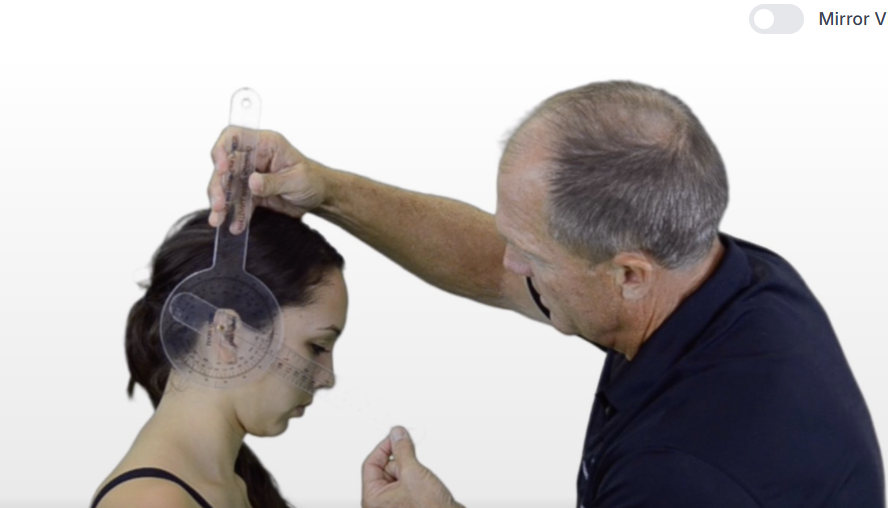

A therapist is preparing to use a goniometer to test for cervical flexion. Where should the therapist place the axis?
External Auditory Meatus
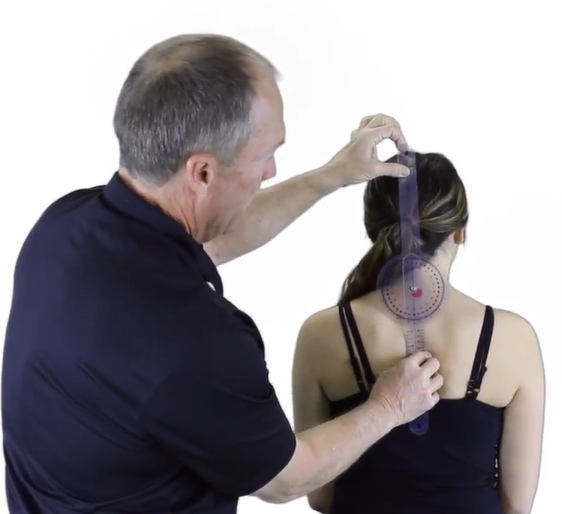
A therapist is preparing to use a goniometer to test for cervical lateral flexion. Where should the therapist place the axis?
Spinous Process of C7
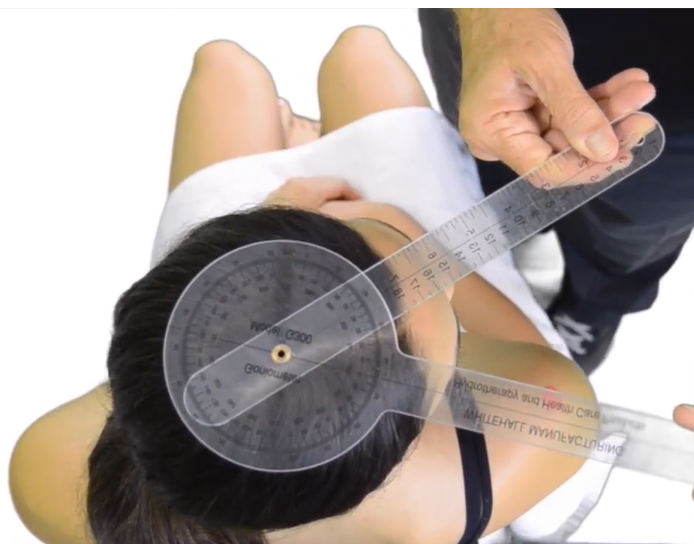
A therapist is preparing to use a goniometer to test for cervical rotation. Where should the therapist place the stationary arm?
Lateral border of acromion
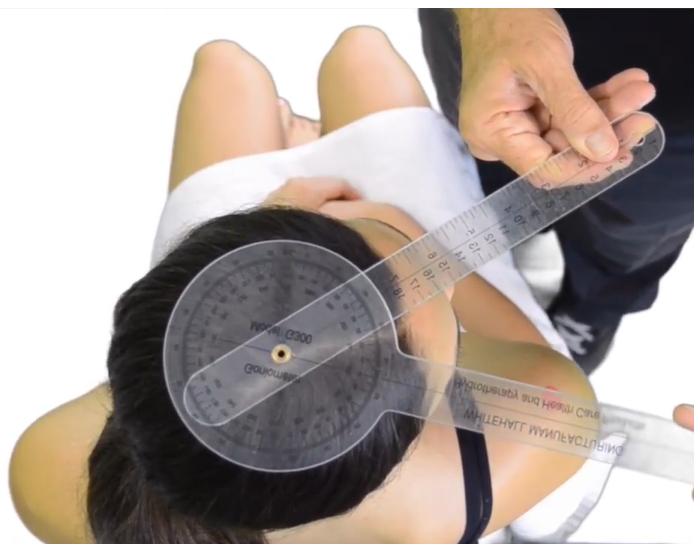
A therapist is preparing to use a goniometer to test for cervical rotation. What is the normal ROM for cervical flexion?
0-60
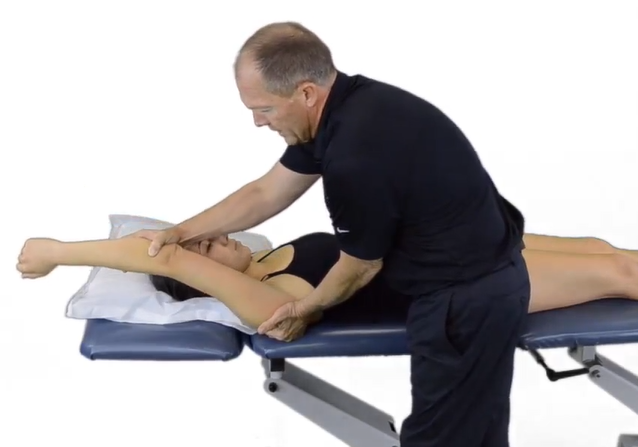
A therapist performs a passive shoulder flexion on a patient to her end range. What would be the expected end feel with minimal pain reported?
Firm end feel due to tight posterior capsule, muscle tension or ligaments
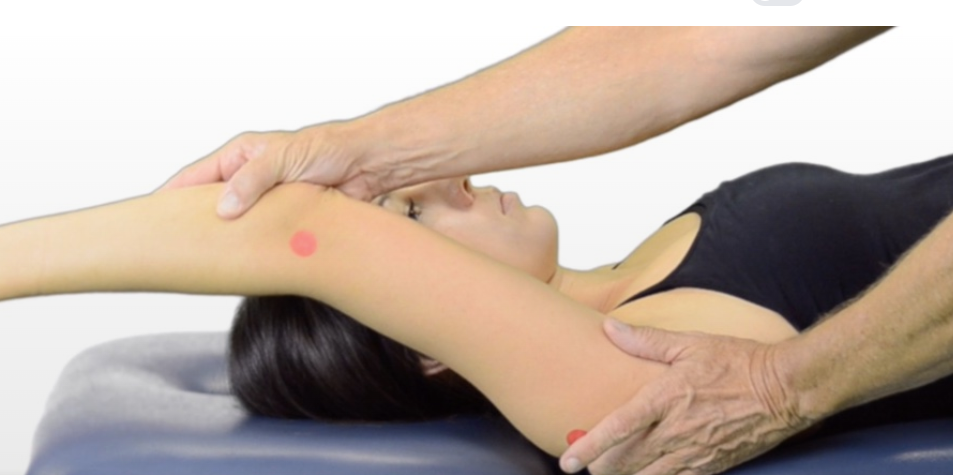
A therapist performs a goniometer on a patient’s shoulder and find obtain a range of 170 degress is this within nornal limits?
Yes normal ROM is 0-180
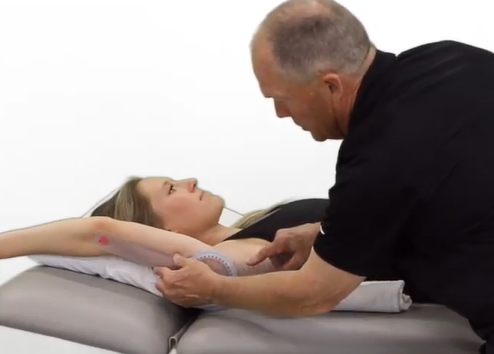
A therapist is about to perform a goniometer measurment to test the range of motion for shoulder flexion. Where should the stationary arm be placed?
Mid-axillary line
A therapist is about to perform a goniometer measurment to test the range of motion for shoulder abduction. Where should the axis be placed?
Anterior acromion
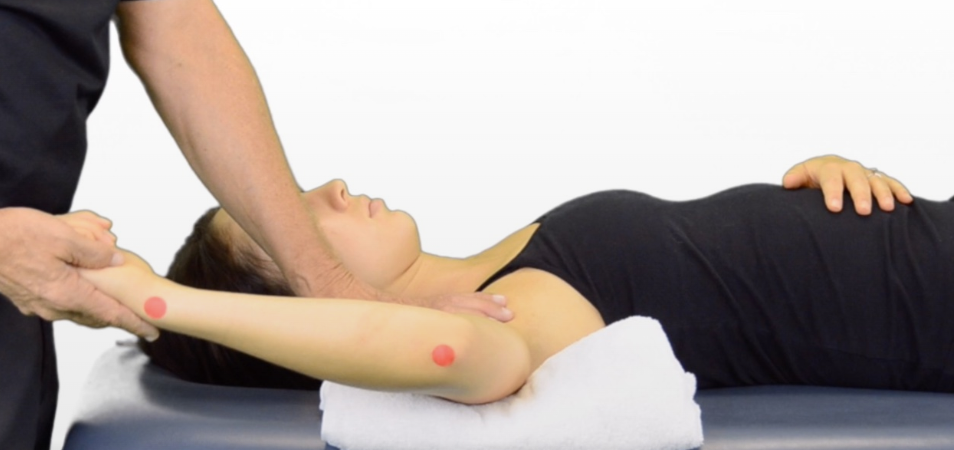
A therapist is testing the available range of motion for shoulder shoulder external (lateral) rotation. What is the normal range of motion for this area usually?
0-90
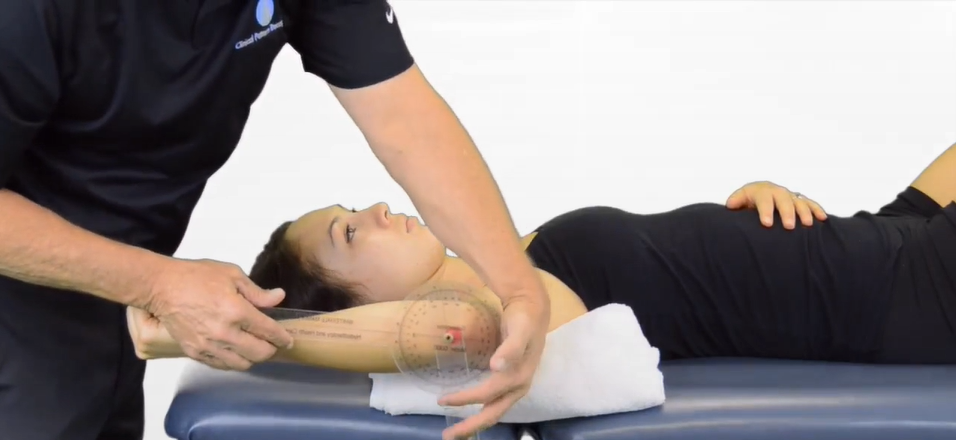
A therapist is about to perform a goniometer measurment to test the range of motion for shoulder external (lateral) rotation Where should the axis be placed?
Olecranon process
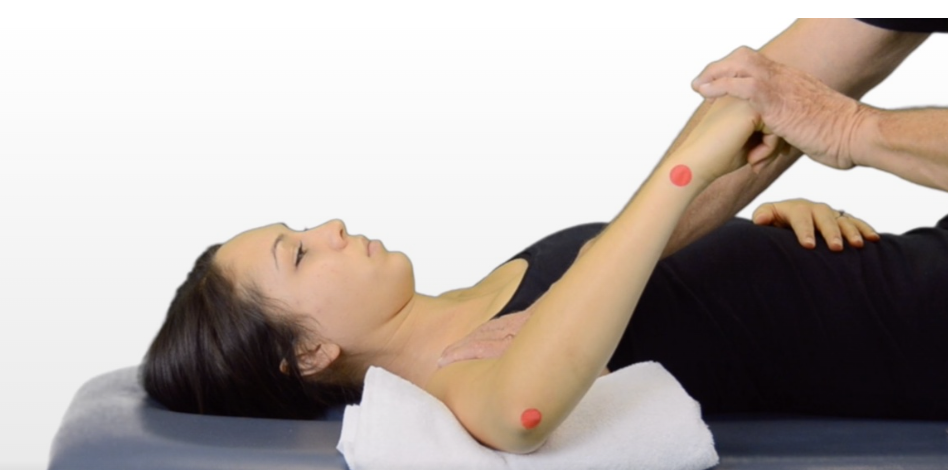
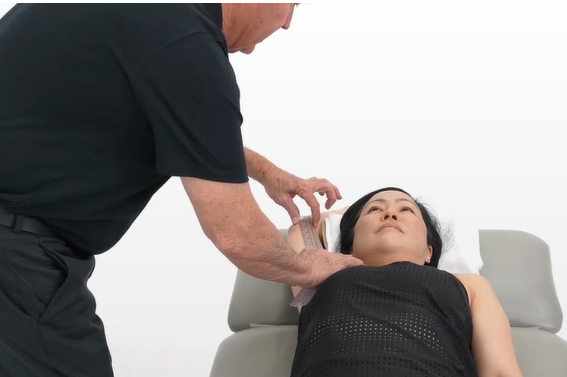
Review the picture, and answer the question. What is the therapist preparing to test?
shoulder interal rotation
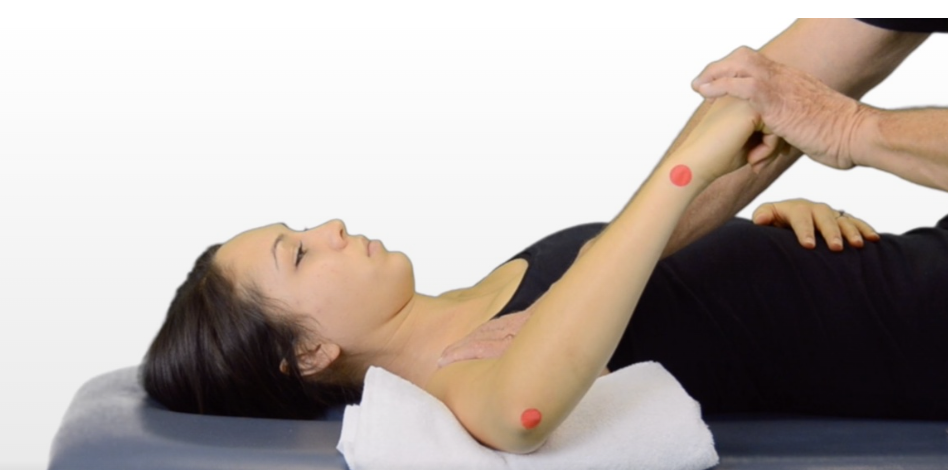
What is the normal ROM for shoulder Internal (medial) rotation?
0-70
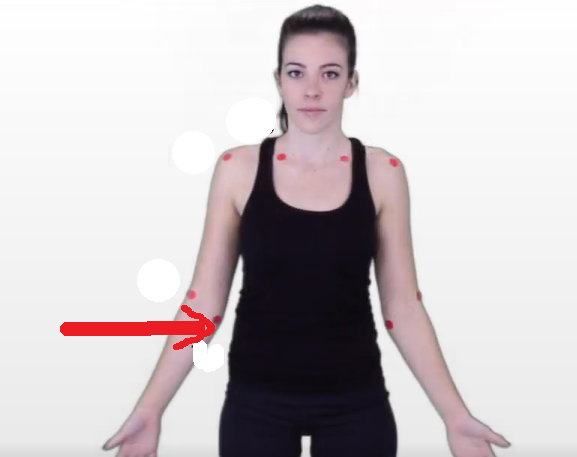

The dermatomal area where the arrow is pointing would indicate what level?
T1
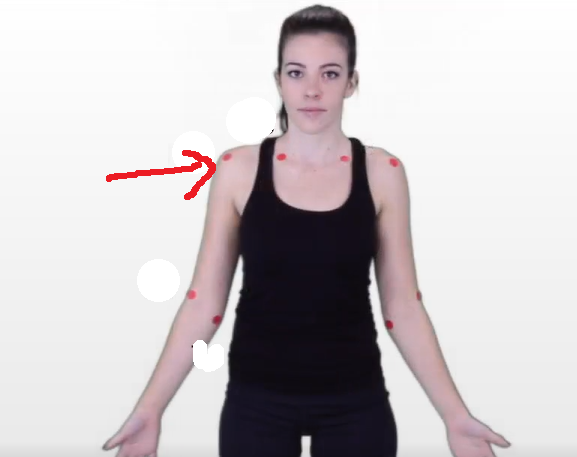

The dermatomal area where the arrow is pointing would indicate what level?
C4
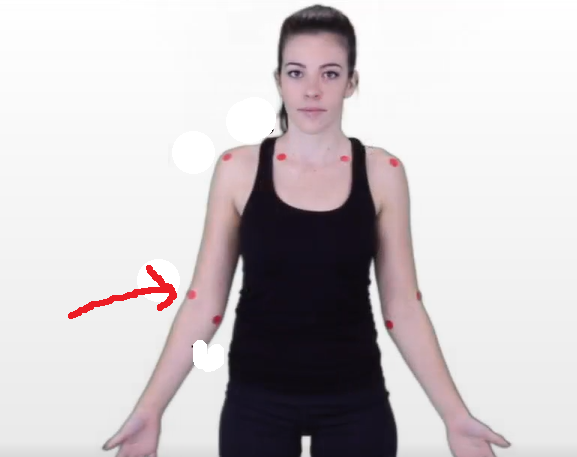

The dermatomal area where the arrow is pointing would indicate what level?
C5
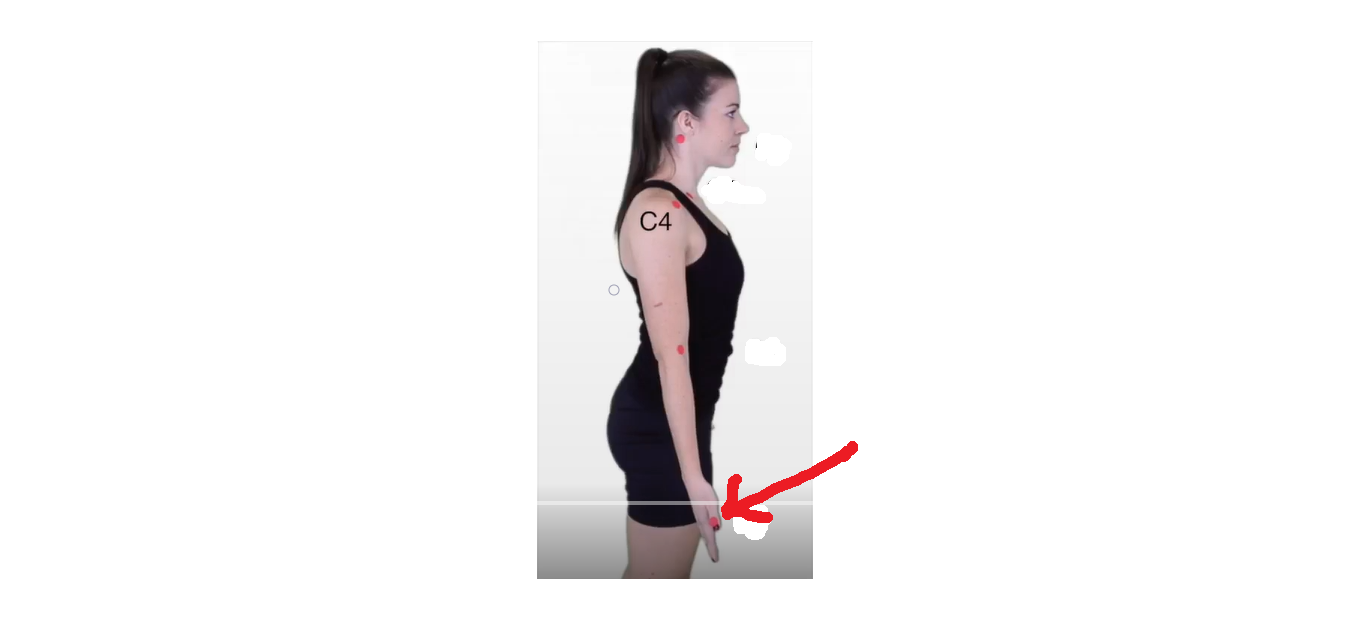
The dermatomal area where the arrow is pointing would indicate what level?
c6
A therapist takes a feather is touches a patient’s palmer distal phalanx middle finger, what dermatone level is he testing?
C7
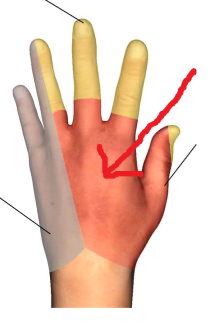
The area where the red arrow is pointing is what dermatomal nerve?
Radial nerve
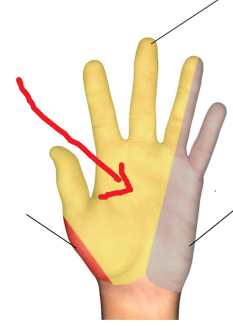
The area where the red arrow is pointing is what dermatomal nerve?
Median nerve
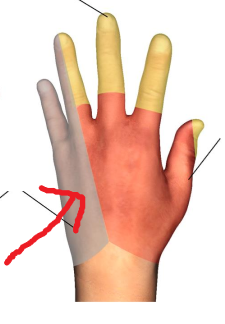
The area where the red arrow is pointing is what dermatomal nerve?
Ulnar nerve
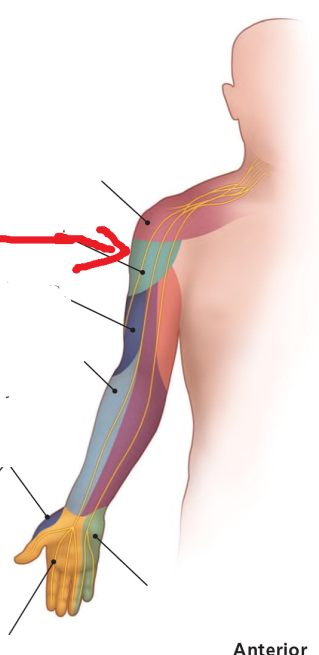
The area where the red arrow is pointing is what dermatomal nerve?
Axillary nerve
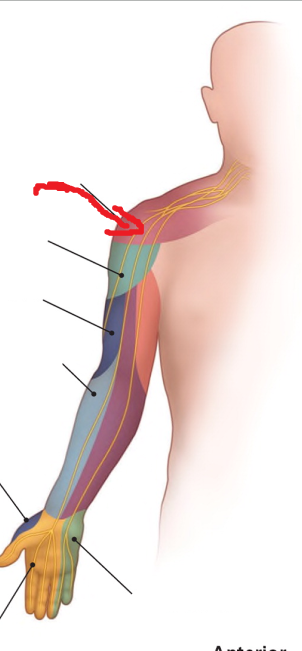
The area where the red arrow is pointing is what dermatomal nerve?
supraclavicular nerve
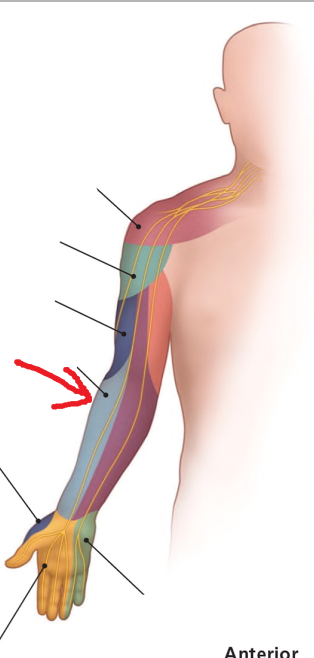
The area where the red arrow is pointing is what dermatomal nerve?
musculocutaneous nerve
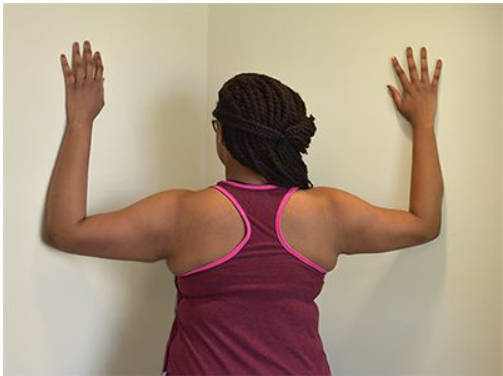
The exercise shown in the photograph is LEAST appropriate for a patient who has which of the following characteristics?
Anterior glenohumeral instability
For a patient who had a total shoulder arthroplasty 5 days ago, which of the following interventions would MOST effectively minimize joint adhesions?
Passive range of motion in a pain-free range
When assessing normal standing posture, where should the gravity line fall?
Anterior to the lateral malleolus
When assessing normal standing posture, where should the gravity line fall?
Slight posterior of hip joint
Which of the following orthotic irregularities is MOST likely to contribute to a patient exhibiting foot slap during the early stance phase of gait?
Inadequate dorsiflexion assist
A patient consistently catches the right toe box of the shoe while walking. Which of the following muscle groups MOST likely needs to be strengthened?
Dorsiflexion muscles
What standardized evaluation tool used to assess motor function, balance, and other physical abilities in individuals who have experienced a stroke?
Fugl-Meyer Assessment