A-Level Business Studies key content part 3
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what is an autocratic leader
leader makes a decision without consultation
what is a democratic leader
consults his team but makes the final decision
what is a laissez-faire leader (to leave alone)
leader allows his teams to makes decisions
what is a paternalistic leader
acts in a fatherly way towards the workforce- making decisions based on needs and wants of business/ workforce
what is a bureaucratic leader
works to rules and regulations “by the book”, culture is led by the rules
what is level 1
Manager makes decision, announces it, expects compliance.
what is level 2
Manager decides, persuades team, seeks commitment.
what is level 3
Manager presents decision, invites questions and feedback.
what is level 4
Manager presents tentative decision, considers suggestions seriously.
what is level 5
Manager presents problem, accepts group decision as final.
what is level 6
Manager outlines boundaries, subordinates decide independently.
what is level 7
Full freedom, subordinates define problem and make decisions.
what does scientific decision making state
managers need to maximise reward and minimise risks
what decisions do managers need to make right
people
money
materials needed
machinery
risk and reward of finances
reward: could make more money than anticipated
risk: lose money or not make as much as expected
risk and reward of reputation
reward: could enhance reputation of business + investment
risk: could ruin business’s reputation
risk and rewards effect on people
reward: could attract good staff in future
risk: could lose good staff
decisions are either…
strategic or tactical
strategic decisions have which qualities
more resources
long term
difficult to reduce
mainly given to managers/superiors
tactical decisions have what qualities
less resources
short term
easier to reverse
taken by middle and junior management
decision making is based on which 3 assumptions
data
experience
hunch/gut feeling
benefits of scientific decision making
clear direction, based on logic, easier to back up, decisions can be changed
when is intuition used in business
by small business owners, more experienced=better judgement, can lead to creative solutions
when are hunches/gut feelings used in business
too much data to be collected, time consuming, data could be flawed
what are decisions trees used for
sales forecasting, investment appraisal, business objectives
what are decision trees
mathematical models used to help managers make decisions by using estimates and probabilities
what is expected value
what you believe that probability is
how do you work out the financial value of an outcome
estimated financial effect x probability
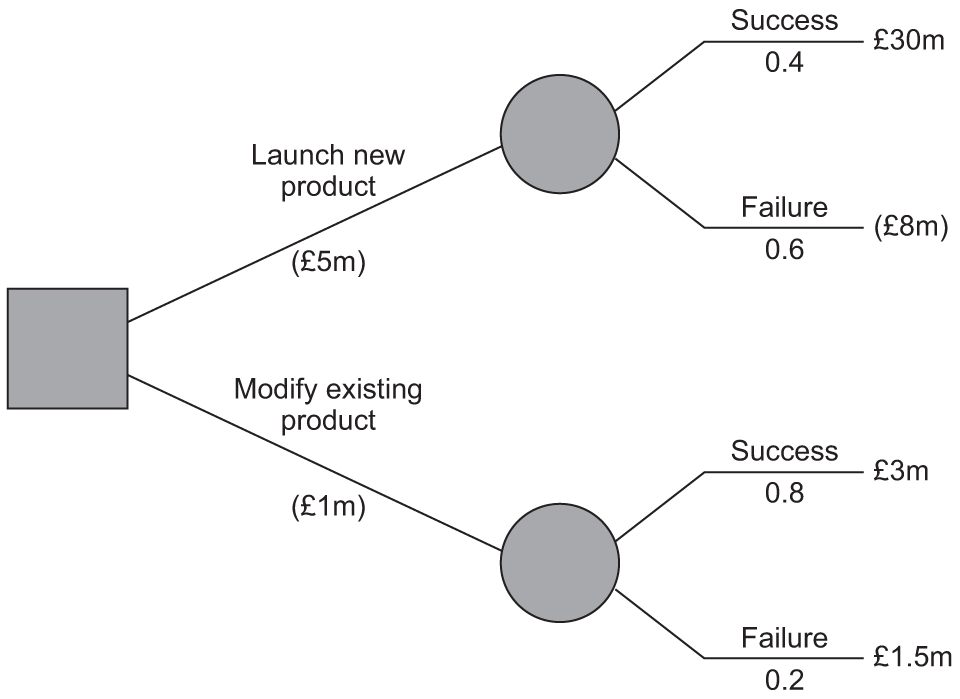
calculate the expected value of launching a new product and it being successful
0.4 x £30 million = £9 million
what is net gain
value gained from making a decision