AP Macro Unit 2 Review
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Unemployment
People who are not working, but actively seeking a job. Ex: Glenn did not work last week, however he tried to find a job, so he is considered unemployed.
unemployment rate
Percentage of population that is unemployed. Formula: number unemployed/total labor force
labor force
number of people in population who are employed and unemployed
eligible population
people deemed likely to be in labor force. Ex: anyone over 16 in US that is not incarcerated or in military.
Labor force participation rate
percentage of eligible population in labor force. Formula: number of labor force/total eligible population
full employment output
the amount of output that is produced in an economy when that economy is using all of its resources efficiently; the full employment output would be a combination of output that is on that country's PPC.
natural rate of unemployment
the unemployment rate that exists when an economy is producing the full employment output; when an economy is in a recession, the current unemployment rate is higher than the natural rate. During expansions, the current unemployment rate is less than the natural rate.
frictional unemployment
the component of the natural rate of unemployment that occurs because the job search process is not instantaneous; for example, after Rosita graduated from dental school, it took her a few weeks to find a job as a dentist. During this period she will be frictionally unemployed.
structural unemployment
unemployment that occurs as a result of a structural change in the economy, such as the development of a new technology or industry; this is a part of the natural rate of unemployment. For example, Negan finds a cure for all dental diseases, and as a result, Rosita loses her job as a dentist and is now structurally unemployed.
Cyclical unemployment
the unemployment associated with the recessions and expansions; this can have a positive or negative value. The current unemployment rate will depend on both the natural rate of unemployment and the amount of cyclical unemployment at the time. (cyclical unemployment= current rate of unemployment-natural rate of unemployment)
The current rate of unemployment in Burrland is 3%. Economists estimate that frictional unemployment is 5% and structural unemployment is 2%. What best describes the amount of cyclical unemployment in Burrland and current output in the economy?
Cyclical rate of unemployment is -4%: Output is greater than full employment rate (3%-7%=-4%)
When the cyclical economy is negative, ____
the economy is producing more than full employment output
How do you find the current rate of unemployment in a country
Natural rate of unemployment + cyclical rate. If an economy is producing below a full employment output, then structural, frictional, and cyclical unemployment will have a positive output.
The nation of Jacksonia specializes in producing high-quality cream cheese and fire trucks for export to other countries.
Which of the following best describes something that would decrease the natural rate of unemployment?
Improvements in fire truck production mean that more fire truck workers are needed. (This change in technology would cause a decrease in the natural rate of unemployment. Improvements in technology can either increase or decrease structural unemployment, depending on the nature of the improvement.)
Angelica is unsatisfied with how well her job as an urban planner pays and quits to find another job.
Which of the following best describes Angelica’s employment situation?
Frictionally unemployed
A decrease in the LFPR that occurs at the same time as a decrease in the unemployment rate can signal that
there are more discouraged workers
During recessions, cyclical unemployment
increases and drives up unemployment rate. During expansions it decreases and drives down unemployment rate.
inflation
a sustained increase in the overall price level in the economy, which reduces the purchasing power of a dollar
inflation rate
CPInew-CPIold/CPIold x100
equation for CPI in any year
cost of basket in year/ cost of basket in base year x100
deflation
a sustained decrease in the overall price level in the economy; deflation occurs if the inflation rate is negative.
disinflation
a slowing of the rate of inflation; for example if the rate of inflation is 5% in 2016 and 3% in 2017, there is still inflation in 2017.Prices are just not rising as fast as they were before.
aggregate price level
a single number that summarizes all prices in an economy; price indices are frequently used to represent the aggregate price level.
price index
a measure that calculates the changing cost of purchasing a particular (and unchanging) combination of goods (called a "market basket") each year; the consumer price index and the producer price index are examples.
market basket
the combination of goods that are used to calculate a price index; the goods stay the same from year to year.
real variables
variables that are adjusted for the rate of inflation that represent the true value of something (such as real interest, real income, or real GDP); for example if your boss gives you a 10% raise, but the purchasing power of your money has decreased by 8% because of inflation, your raise is really only worth 2%
nominal variables
variables such as wages, income, or interest that have not been adjusted for the rate of inflation; you can think of nominal variables as the "sticker price." The bank tells you they will pay you 3% interest, but the real interest rate that tells you what you are actually earning.
purchasing power
what can actually be bought with money; if you walk into a store with $10 and want to buy apples that cost $1 each, the purchasing power of your $10 is 10 apples; If the next day the price of apples increases to $2 you can only buy 5 apples, so the purchasing power of your $10 has decreased.
real interest rate
the interest rate earned that reflects the actual purchasing power of that interest; for example if a bank pays 3% interest, but there is 2% inflation, you really have only gained 1% interest because the purchasing power of your interest has decreased.
Which of the following is a valid criticism of the consumer price index (CPI)?
The CPI overstates the burden of inflation on households because households can substitute cheaper goods instead of more expensive goods when prices increase. (Substitution bias occurs in the CPI because when prices of goods increase, people look for cheaper alternatives and buy those cheaper alternatives. This switch means their cost of living might not increase. However, the CPI ignores the possibility of substitution and assumes that people will continue to buy the same, more expensive goods, overstating the increase in the cost of living)
unanticipated inflation
when the price level increases at a faster pace than expected; for example, if you think that the rate of inflation will be 5%, but it turns out to be 8%.
unanticipated disinflation
when the price level increases at a slower pace than anticipated; for example, if you think the rate of inflation will be 5%, but it turns out to be 2%.
unanticipated deflation
when the price level decreases when it was expected to increase; for example, if you think the rate of inflation will be 2%, but it turns out to be -2%.
wealth redistribution
when the real value of wealth is transferred from one agent to another; when inflation is higher than borrowers and lenders expected, wealth is transferred from lenders to borrowers.
bond
an asset that is a promise to pay a fixed amount at some point in the future; for example, the government sells Tony a bond for $100with the promise of paying him back $104 in one year, which allows Tony's savings to earn interest.
Who does inflation at fixed rates benefit? Who does deflation at fixed rates benefit?
Inflation benefits borrowers at fixed rates, however it hurts lenders. Deflation is the opposite. Deflation helps lenders but hurts borrowers.
nominal GDP
the market value of the final production of goods and services within a country in a given period using that year's prices (also called "current prices")
real GDP
nominal GDP adjusted for changes in the price level, using prices from a base year (constant prices) instead of "current prices" used in nominal GDP; ____ GDP adjusts the level of output for any price changes that may have occurred over time
GDP deflator
a price index used to adjust nominal GDP to find real GDP; the GDP deflator measures the average prices of all finished goods and services produced within a nation's borders over time.
Real GDP equation
nominal GDP/ GDP deflator over 100
Nominal GDP equation
real GDP x GDP deflator/100
In 2017 Spamland's real GDP was $50 billion and the GDP deflator was 120
What was Spamland's nominal GDP in 2017?
60 billion (50x 120/100)
Justinia is a country that produces three goods: guitars, physics books, and sandals.
Which of the following would definitely cause an increase in nominal GDP but not a change real GDP in Justinia?
The quantity of goods produced stays the same; prices increase
Real GDP measures how much is actually produced, which has not changed according to this statement. Nominal GDP is a measure of how much is spent on output, which according to this statement would have increased.
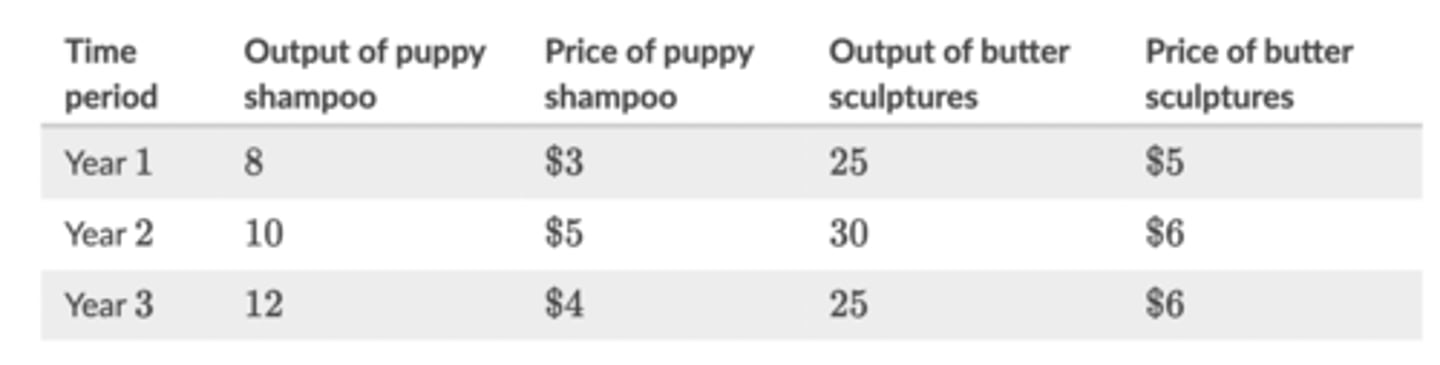
The country of Neverland produces two goods: puppy shampoo and butter sculptures. The table below shows the output and prices of the two goods over three years: (see chart)
What is Neverland's real gross domestic product (GDP) in Year 222, assuming Year 111 is the base year?
$180
Real GDP is calculated by multiplying the quantity of output in one year by the prices in a base year. Real GDP for year 2 is the quantities of the two goods from year 2 multiplied by the prices in year 1:
real GDP=(10×$3)+(30×$5)=$180real GDP=(10×$3)+(30×$5)=$180
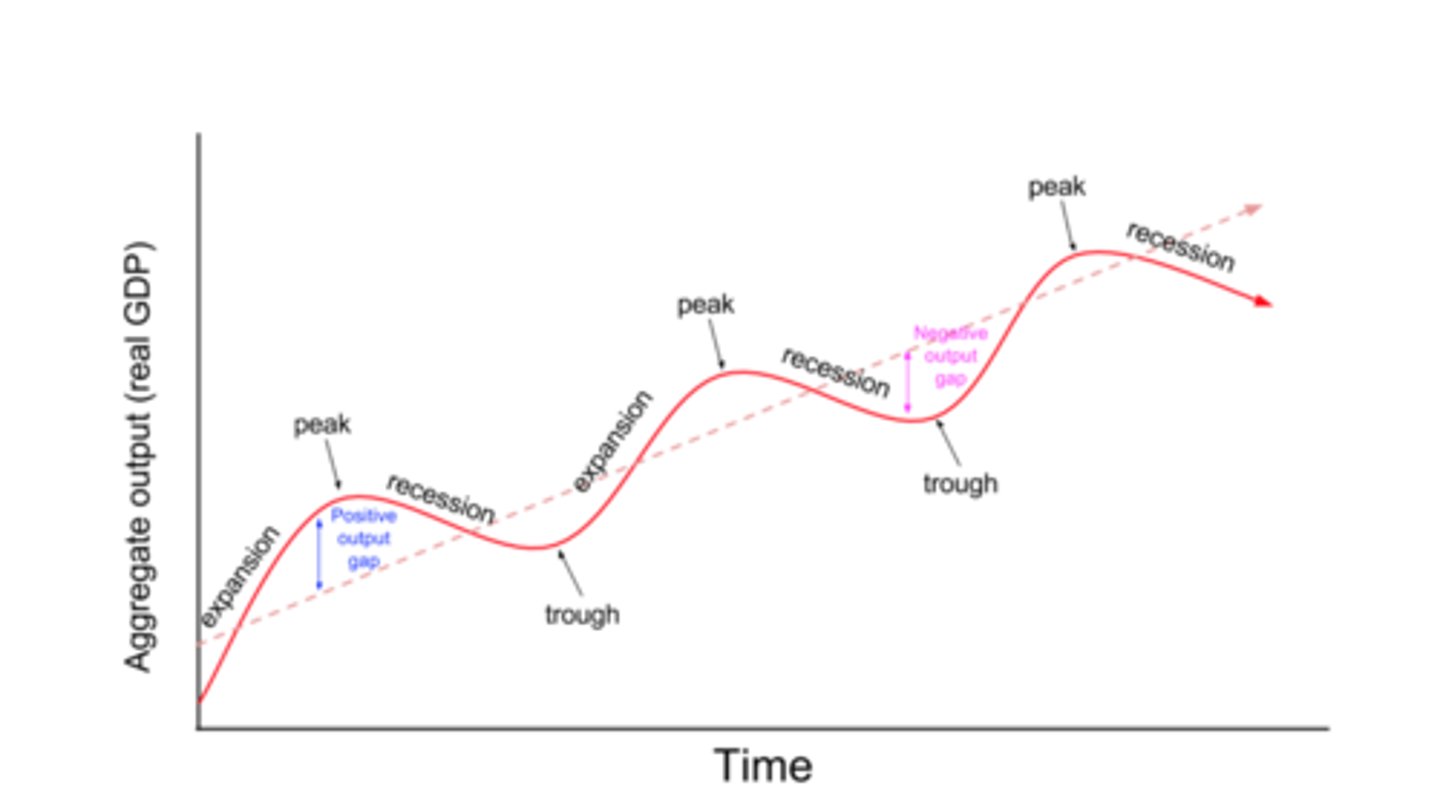
The phases of a business cycle
Expansion, Peak, Recession, Trough
Expansion
When real GDP is increasing and unemployment is decreasing
Peak
The turning point in the business cycle at which output stops increasing and starts decreasing
Recession
When output is decreasing and unemployment is increasing
Trough
The turning point at which a recession ends and output starts increasing again
aggregate demand
the total demand for a nation's output, including household consumption, government spending, business investment, and net exports
aggregate supply
the total supply of goods and services produced by a nation's businesses
positive output gap
the difference between actual output and potential output when an economy is producing more than full employment output; when there is a positive output gap, the rate of unemployment is less than the natural rate of unemployment and an economy is operating outside of its PPC.
negative output gap
the difference between actual output and potential output when an economy is producing less than full employment output; when there is a negative output gap, the rate of unemployment is greater than the natural rate of unemployment and an economy is operating inside its PPC.
potential output
the level of output an economy can achieve when it is producing at full employment; when an economy is producing at its potential output, it experiences only its natural rate of unemployment, no more and no less.
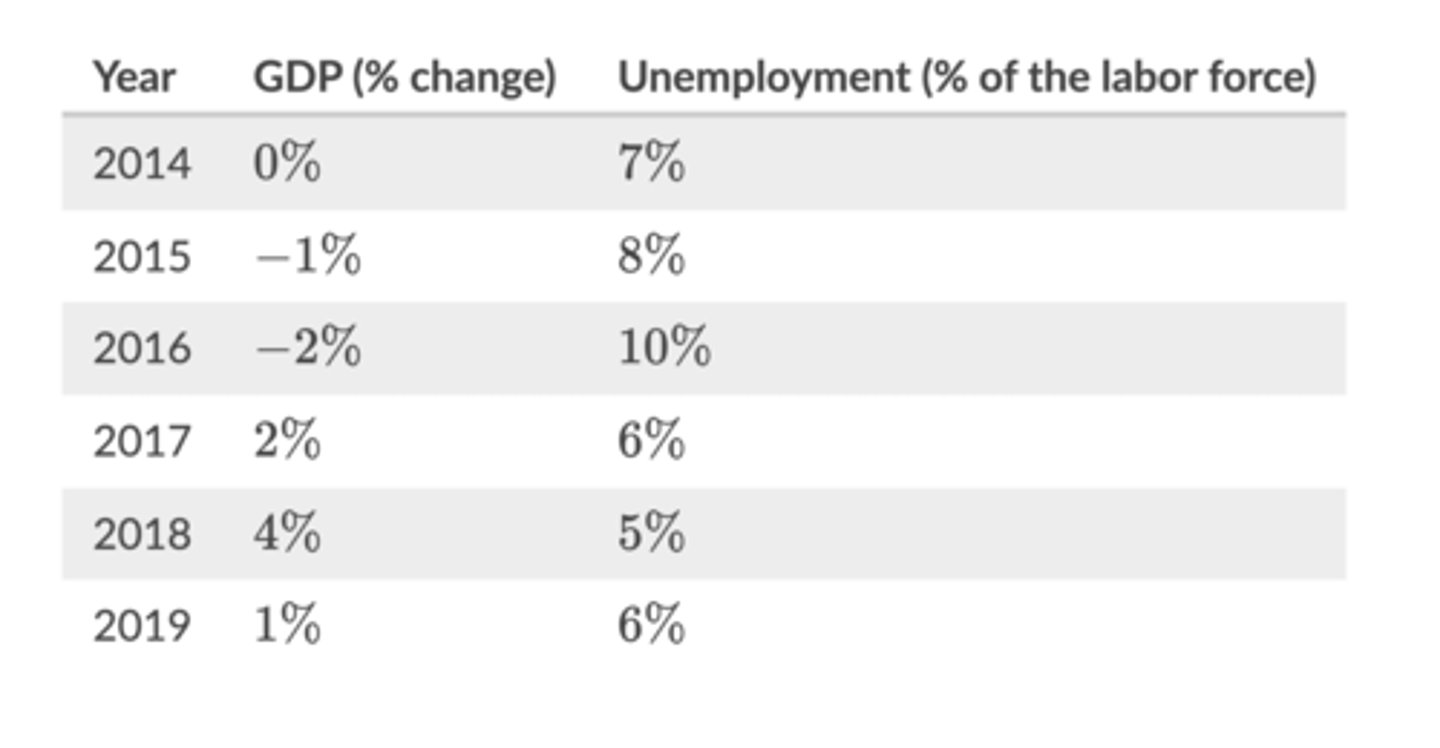
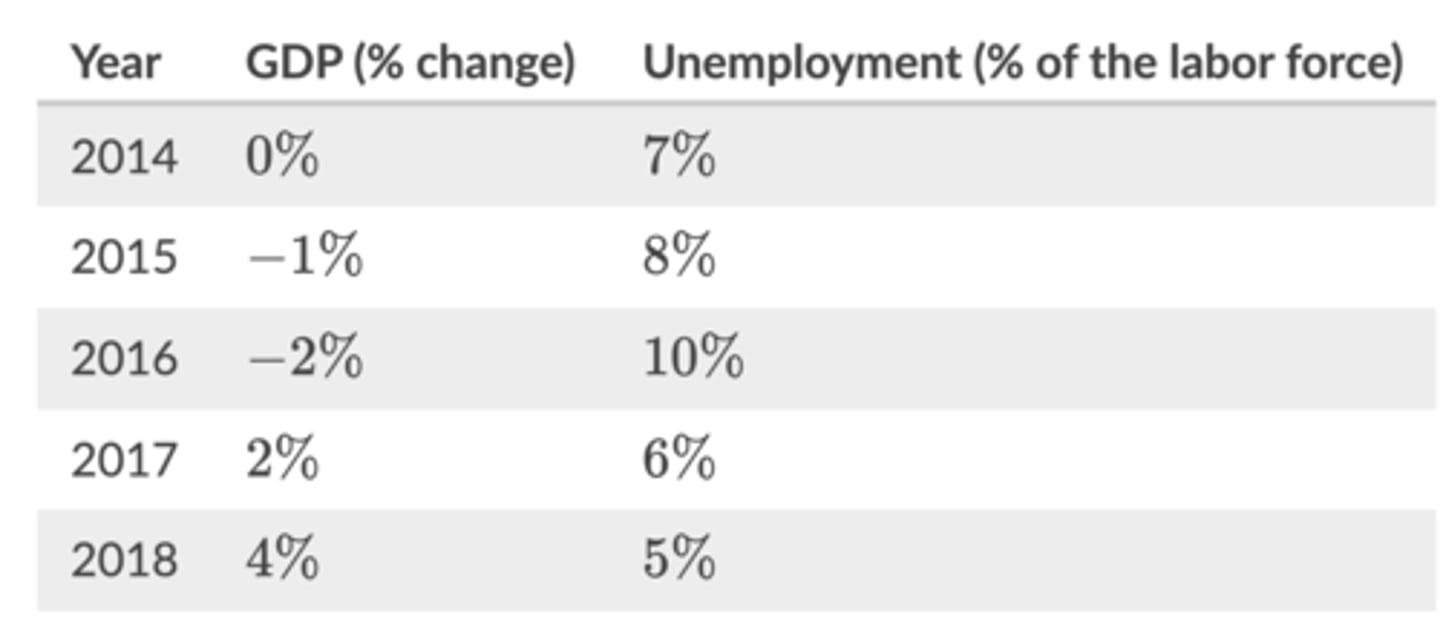
In which of the years was Libertyville most likely experiencing a trough in its business cycle?
2016
GDP fell in 2016 but increased in 2017, indicating that 2016 was the turning point at which Libertyville's two year recession ended and the economy entered the recovery/expansion phase of its business cycle.
what is occurring when an economy's actual output is above its full employment level of output?
a positive output gap
Assume Libertyville has a natural rate of unemployment of 6%and has averaged a GDP growth rate of 3% per year over the last 30 years.
Based on the data given in this table, during which years was Libertyville most likely to be in the expansion phase of the business cycle?
2017 and 2018
An expansion is the phase of the business cycle when aggregate output (GDP) increases and unemployment decreases. In 2017 and 2018 both these changes were happening in Libertyville.
Economic data on the economy of the Nether are presented in the table below:
Which of the following is true based on the employment data in the table?
Current real GDP equals $300 million.
The natural rate of unemployment is the sum of structural and frictional unemployment: 4% + 6% = 10%. Since the current unemployment rate equals the natural rate of unemployment, the economy is currently producing its full employment output of $300 million GDP.