Physiology: Homeostasis
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Homeostasis
a condition of equilibrium or balance in the body’s internal environment
maintained by the body’s regulatory processes
To maintain homeostasis a control system must
detect deviations from normal in the internal environment that need to be held within limits
integrate this information with other relevant information
make appropriate adjustments to restore a factor to its desired value
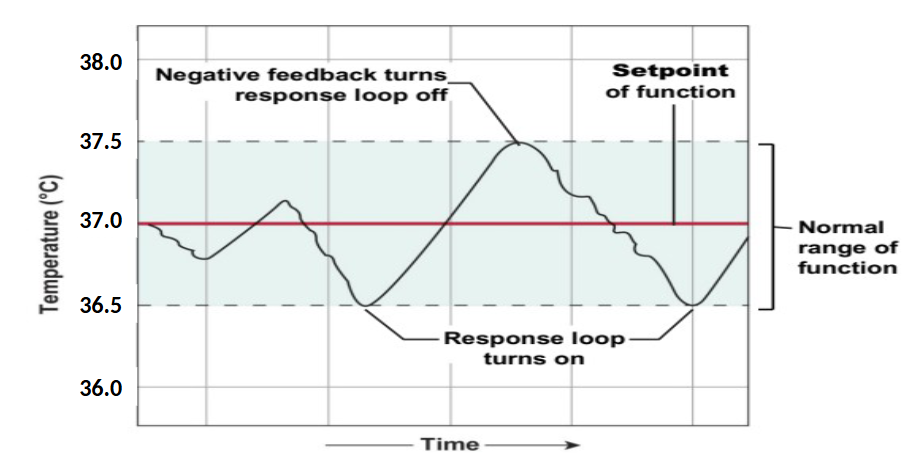
Set point
the normal range for a given system and will be monitored by the control contre for that particular system (ex: hypothalamus monitoring body temp)
Intrinsic controls
local controls that are inherent in the organ
Extrinsic controls
regulatory mechanisms initiated outside an organ
accomplished by nervous and endocrine systems
Feedback loops
responses make after a change
negative and positive
Feedforward loops
responses made in anticipation of a change
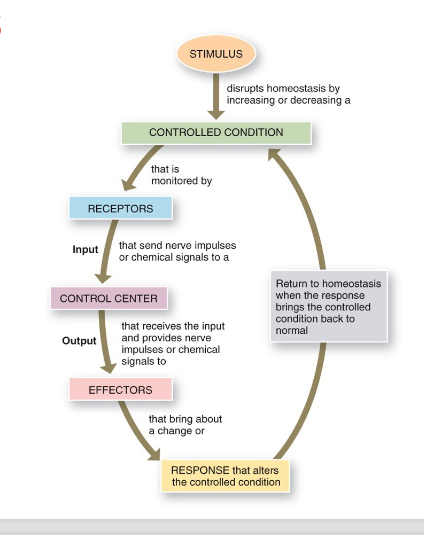
Basic components of a feedback loop
Negative Feedback loop
primary type of homeostatic control
opposes initial change
Components of the negative feedback loop
Sensor: monitors magnitude of a controlled variable
Control center: compares sensor’s input with a set point
Effector: makes a response to produce a desired effect
Main goal of the negative feedback loop
keeping internal environment stable
ex: body temp, nutrients/wastes, O2/CO2 levels, pH, water/electrolytes, blood volume, blood pressure
Example of the negative feedback loop
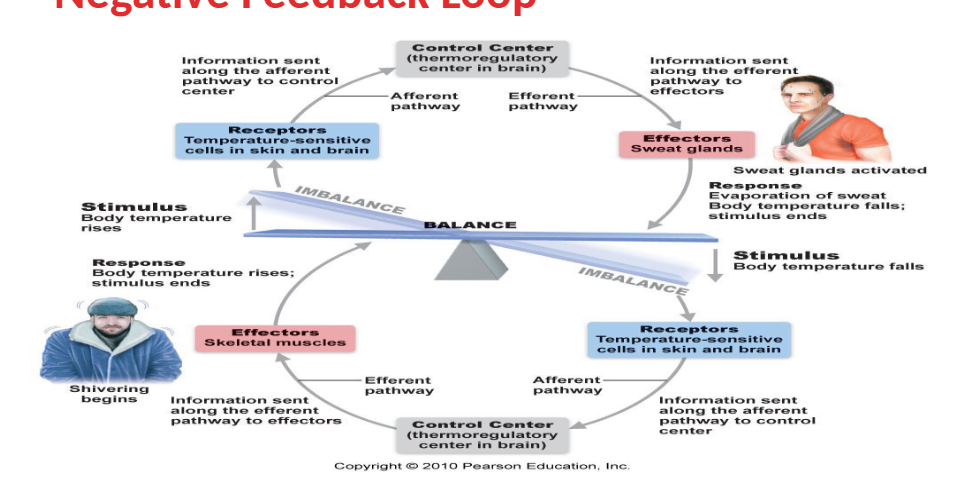
Negative feedback loop set point and response loop example
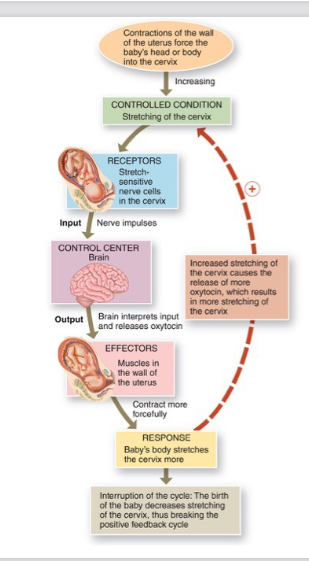
Positive feedback loop
amplifies an initial change and therefore does not truly contribute to homeostasis
does not occur very often
abnormal changes move the body farther away from homeostatic balance and potentially toward death
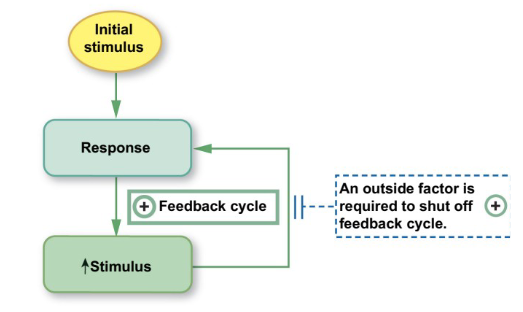
Example of positive feedback loop
contractions during labour
Homeostatic imbalances
disruptions of homeostasis can lead to disease and death
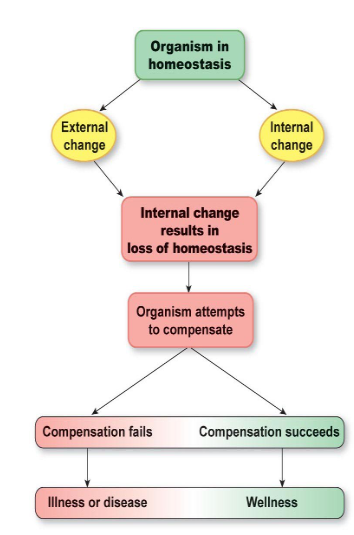
Disorder
a general term for any derangement of abnormality of function
Disease
a more specific term for an illness characterized by a recognizable set of signs and symptoms
Aging and homeostasis
aging is a normal process characterized by a progressive decline in the body’s ability to restore homeostasis
ex: blood pressure, diabetes
Feedforward Mechanisms and Anticipation
although not as commonly used in the body, there are mechanisms which are activated before a change in a variable actually occurs
these mechanisms attempt to anticipate changes before they occur rather than responding to a change after it has occurred
ex: saliva production prior to eating (prepare for the breakdown of carbohydrates), central command makes changes prior to exercise