Bio OpenStax ch4-6
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Cells
____ are the units of structure & function
Theory of Biogenesis
the principle that states “All cells arise from pre-existing cells” is called?
Cells
All ____ have these 4 components
Plasma Membrane
Cytoplasm
DNA
Ribosomes
Cells & Cell Products
all living things are made up of ____ & ______
Water
Cytoplasm is a mostly made of?
DNA
What thing’s function is to code for proteins?
the Plasma Membrane
What is another name for the phospholipid bilayer?
Plant cells
Do plant cells or animals cells have cell walls? (only one has em btw)
Animal call does NOT use cellulose
Which cell type does NOT have/use cellulose?
Animal cell
Plant cell
Eukaryotic cell
Prokaryotic cells
These cells have:
1 chromosome, NO NUCLUES and no membrane bound organelles. These cells DO HAVE CELL WALLS THO
(Trick question) they can ALL have cell walls (some types of eukaryotes like animal cells don’t but shhhh the genre as a whole can have em)
Which cell type CANNOT have a cell wall?
Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes
Plant Cells
Fungi Cells
Eukaryotes are bigger 💅
Which cell is bigger than the other?
Prokaryotic cells vs Eukaryotic cells
Plant cells & Fungi cells
In Eukaryotes, cell walls are only found in which cells?
Nucleoid
In a Prokaryote, it’s chromosome is singular, circle shaped, and in a “jumble” called a _____.
Prokaryotic
Which type of cell has no membrane bound organelles (hint think broadly not specific)
Eukaryotic
Which type of cells HAS organelles bound in a membrane?
Eukaryotic
Which type of cell has 1 or more chromosomes found in a nucleus, and has cell walls found only in plant and fungi cells?
Fluid Mosaic Model
What is the principle called describing the cell membrane, which states that a variety of particles move thru/around the membrane?
Phospholipid Bilayer
What is the cell membrane called, specifically in reference to what it’s made out of?
Proteins + other molecules
The cell membrane is made of what things?
Cellulose
IN PLANTS:
What is the cell wall made of?
Chitin
IN FUNGI ANNND ARTHROPODS
What is the cell wall made of?
To provide strength, rigidity, and maintain turgor pressure
In plants, what is the purpose/function of having cellulose make up the cell wall?
The Nucleus 🥳
What is the largest organelle (in most cells 💀)
Nuclear Envelope
The ____ refers to the 2 membranes (basically a quad bilayer🤯) that surround the nucleus
Nuclear Pores
These shits are proteins that perforate the Nuclear Envelope and regulate traffic 🚧
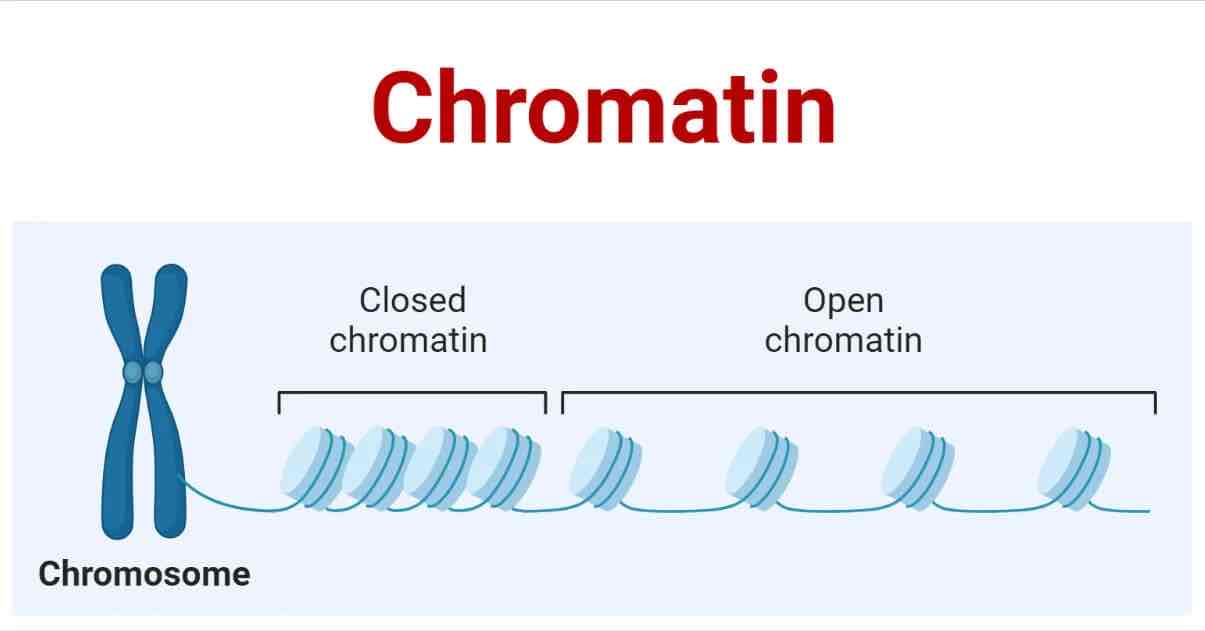
Chromatin
-Fine😮💨, thread-like matter that r made/composed of DNA & Protein
Nucleoli
-these guys r masses where Ribosomes🥵 are produced
Ribosomes🥵
-Small granules/clusters of proteins & RNA
-Functions: interpret genetic code & synthesize polypeptides
-(translate DNA to usable proteins/amino acids)
Ribosomes
Which organelle interprets genetic code and synthesizes polypeptides?
Ribosomes🥵
Which organelle translates DNA into usable proteins
Proteins🤭
What (small/particle?) thing “builds just about everything”?
MITOCHONDRIAAAAAA
Which organelle synthesizes ATP?
Mitochondria
Which organelle gets it DNA from ur mom😳
Lysosomes and Peroxisomes
Which 2 organelles are just packets of digestive substances?
Peroxisomes
Which organelle oxidizes fatty acids and amino acids with H2O2?
(it’s also a packet of digestive substances)
Lysosomes
Which organelles breaks down proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, cell parts?
(it’s also a packet of digestive substances)
lipids
Lysosomes break down proteins, polysaccharides, ____, nucleic acids, cell parts.
polysaccharides
Lysosomes break down proteins, _____, lipids, nucleic acids, cell parts.
nucleic acids
Lysosomes break down proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, _____, cell parts.
cell parts
Lysosomes break down proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, _____.
proteins
Lysosomes break down _____, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, cell parts.
fatty acids
Peroxisomes oxidize _____ and amino acids with H2O2.
oxidize
Peroxisomes _____ fatty acids and amino acids with H2O2.
Amino Acids
Peroxisomes oxidize fatty acids and ____ with H2O2.
H2O2
Peroxisomes oxidize fatty acids and amino acids with what?
Vacuoles
Which organelle contain water and dissolved materials?
Vacuoles
Which organelle (in plants) can provide Turgor to plants?
Vacuoles (dw too much abt this one tho cuz spell check usually shows up on tests 🤫🤫)
Is it spelled Vacoules or Vacuoles?
(yes Lounsberry will mark us off on this if it’s wrong 💀💀)
Protists
In which of the 5 family/class/groups do Vacuoles function to pump out excess water?
Plants (Vacuoles also provide turgor but that would’ve been a dead giveaway)
In which of the 5 class/family/groups do Vacuoles function to store nutrients?
Turgor= Pressure from fluids against the cell wall, BASICALLY rigidness/stiffness.
If not enough turgor, the plant can wilt :(
What is turgor in plants? (provided by Vacuoles & Cellulose 🤓) and what can happen if there’s not enough turgor pressure in a plant?
Vacuoles
In Protists, which organelle pumps out excess water?
Vacuoles (also provides turgor)
In Plants, which organelle stores nutrients?
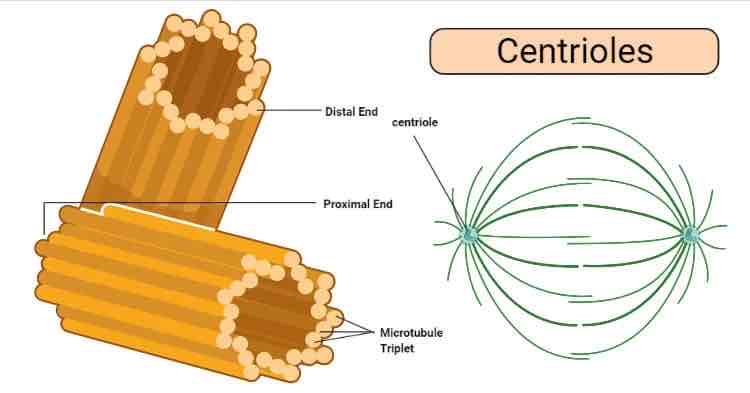
Centriole
Which organelle is a short assembly of microtubules that “play a role” in cell division?
-they also form the basal body of a flagellum/cillium?
that Membrane bound organelles share 😚😚connections 🥰💫🧚 w each other (either psyhsichally or w vesicles)
What does the words “Endomembrane System” refer to/mean?
Vacuoles = storage(ish) ONLY also NOT in animal cells
Vesicles = storage, AND transportation
What is the difference between a Vacuole and a Vesicle 💀💀
FALSE (only found in plants/protists, not animals)
True or false:
Vacuoles are found in animal AND plant cells
True (VACUOLES are the ones not found in animals)
True or False:
Vesicles are found in plant AND animal cells
Vacuoles
The Endomembrane system refers to connections between these organelles:
ER, Nuclear Envelope, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosomes, and ______
Lysosomes
The Endomembrane system refers to connections between these organelles:
ER, Nuclear Envelope, Golgi Apparatus, ____, Vacuoles
Golgi Apparatus
The Endomembrane system refers to connections between these organelles:
ER, Nuclear Envelope,_____, Lysosomes, Vacuoles
Nuclear Envelope
The Endomembrane system refers to connections between these organelles:
ER, _______, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosomes, Vacuoles
ER
The Endomembrane system refers to connections between these organelles:
____, Nuclear Envelope, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosomes, Vacuoles
ER
Which organelle is made of interconnected😏 channels that produce molecules?
ROUGH ER
Which organelle is made of flattened sacs COVERED w ribosomes😛?
SMOOTH🦵 ER
Which organelle is made of tubular channels with NO RIBOSOMES😖?
Smooth ER
Which ER type produces lipids 😳😳
ROUGH ER
Which ER type produces proteins, and membrane? 😳😳
Rough ER
Which ER type uses transport vesicles?
Rough ER
Which ER type has Ribosomes😛
Golgi Apparatus/Complex
Which organelle’s functions are storage, modification, packing of materials to be secreted(cell products)?
Golgi Apparatus/Complex
Which organelle has Vesicles budding off of it?
Chloroplasts
Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis?
Chloroplasts
Which organelle contains stroma fluid and chlorophyll, and gramma?
Grana or singular form “granum”
What are the stacks of discs found in Chloroplasts that are “power packs for photosynthesis” called?
Cytoskeleton
What is this called:
“a microscopic network of protein filaments and tubules in the cytoplasm of many living cells, giving them shape and coherence”?
The Cytoskeleton 🫳🎤
Protein filaments/cylinders, Microtubules, Intermediate, and Microfilaments are all components of what 🎤🤏
AND CAN PROVIDE MOVEMENT
Movement
Protein filaments/cylinders, Microtubules, Intermediate, and Microfilaments are all components of the Cytoskeleton and can provide ______
On top 🔝 of Microtubules
Where do walking proteins walk in relation to the Cytoskeleton
Cilia and Flagella
The Basal Bodies of ___ and ____ are made of Microtubules
Microtubules
The Basal Bodies of Cilia and Flagella are made of what?
Cell Junctions
What is the term for the place where cells come together 🥵 and which functions include resisting stress, communication, and moving shit?
Cell Junction
The functions of this type of cell meeting are to resist stress, communicate, and move shit.
Tight Junction
What type of cell meeting is described as “proteins that encircle an epithelial cell near its apex (seals off intercellular space)”?
Tight Junctions
What type of cell junction is watertight, but not mechanically resistant to stress?
Desmosomes
What type of cell junction is described as “a patch-like intercellular junction that MECHANICALLY links 2 cells together to keep the cells from pulling apart”?
Desmosomes
What type of cell junction mechanically links cells?
Hemidesmosome
What type of cell junction could be described as “Basement membrane anchors”?
Gap Junction
What type of cell junction is described as “rings of proteins allow solutes to pass directly between cells”?
Active transport
What type of transport requires energy?
Passive Transport
Which type of transport is diffusion?
Facilitated Transport
What type of transport uses carrier proteins?
Osmosis
What term best describes this situation:
Water follows the solutes
Hypertonic
What is it called when there are more solutes in the blood OUTSIDE a red blood cell?
Cell can shrivel up and die :,)
In a Hypertonic cell, which occurs when there are more solutes outside the cell than inside, what can happen to the cell?
Hypertonic
Which cell “condition” refers to a cell shriveling up because of more solutes outside than inside the cell?
Hypotonic
What cell “condition” occurs when there are too little solutes outside a red blood cell? (less solutes outside cell, too much solutes inside cell)
Water flows into the cell, can inflate and explode 💀
What can happen to a Hypotonic cell, which occurs because of less solutes outside of the cell (too many solutes inside the cell)?
Hypotonic
What cell “condition” refers to a red blood cell inflating and potentially exploding (bc the outside has too little solutes)?