E.3 Radioactive Decay
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
conversions from kg to joules
E = mc²
conversion from u to joules
E = mc²
1 u = 1.661×10-10 kg
binding energy
The energy required to separate an atomic nucleus completely into its constituent protons and neutrons.
Nucleus has a smaller mass than Nucleons separated
mass defect
the difference in mass between the mass of an object and the sum of the masses of its constituent particles
binding energy
what is keeping the nucleus together
electric repulsion of protons strains the nucleus, but the residual strong force holds the nucleus together
to graph
y = force between nucleons (+ = repulsive, - = attractive_)
x = nucleon separation
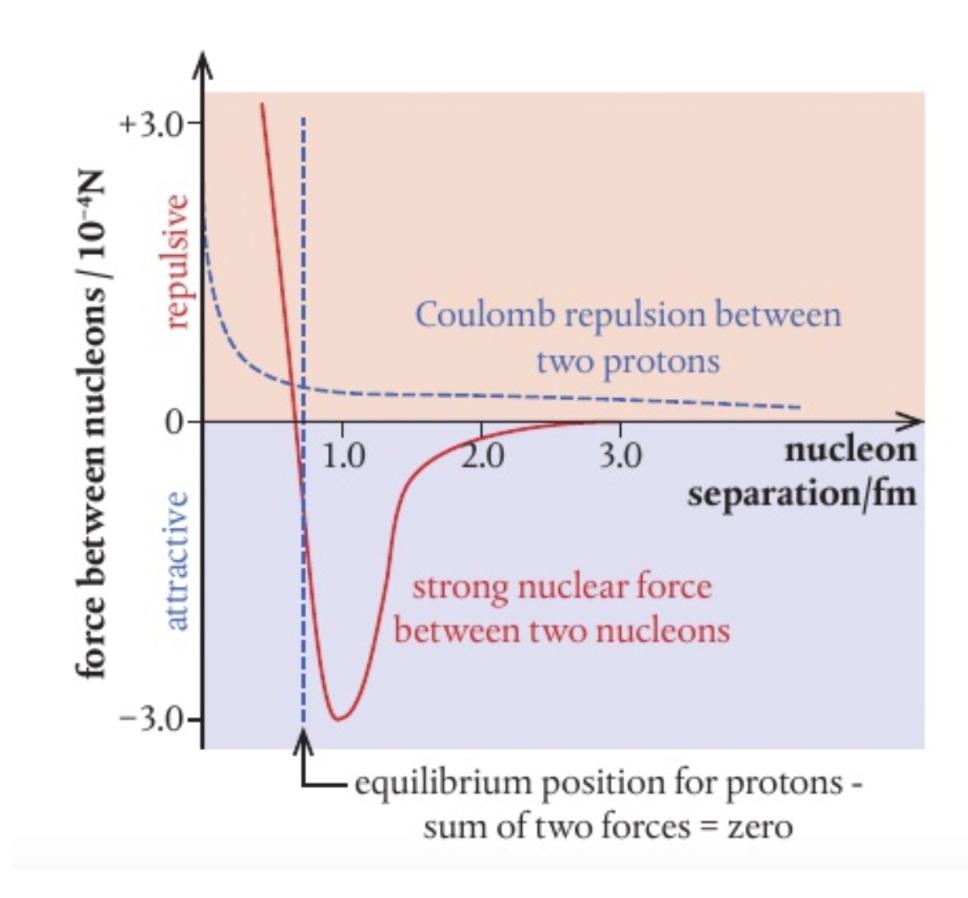
evidence of strong force
protons’ positive charge thus from Coulomb’s law repel each other, electrostatic force. however, neutrons allow for stability. This stability indicates the presence of strong force, binding protons, and neutrons to overcome electrostatic repulsion
The mass deficit can be converted into binding energy from E = mc², showing the energy required to keep the nucleus together. The binding enegry per nucleon shows the strong force
if strong force did not exist nuclei of more than one proton would not exist electrostatic repulsion would exceed gravitational force
when does binding energy per nucleon peak
iron -56
strong force versus electrostatic repulsion
since the strong force is from short range, it does not act across the whole nuclei, which electrostatic force does.
Thus nuclei with greater nucleons require more neutrons than protons for stability. This is because neutrons provide equal amounts of strong force and additional spacing reducing electric force
Line of stability
neutron number, against the proton number graph. the line of stability reveals that for stable atoms more protons required at larger nucleus’s
Binding energy versus nucleons graph
Beyond 60 nucleons, Coulomb repulsion grows for heavier nuclei, but nuclear attraction remains the same
Binding energy from atomic mass units
multiply by MeV (931.5) rather than E = mc² which is joules, u is eV