Circulatory and Respiratory Systems in Vertebrates
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
187 Terms
ReViTaLise
Mnemonic for blood flow from right ventricle to lungs.
Right Ventricle
Pumps blood to lungs via pulmonary arteries.
Left Ventricle
Pumps oxygen-rich blood to body via aorta.
Unicellular Organisms
Exchange materials directly with environment via diffusion.
Diffusion
Net movement of substances across plasma membrane.
Gastrovascular Cavity
Distributes substances and aids digestion in Cnidarians.
Circulatory System Components
Includes fluid, vessels, and muscular pump (heart).
Circulatory Fluid
Fluid that circulates through the circulatory system.
Open Circulatory System
Haemolymph bathes body cells as interstitial fluid.
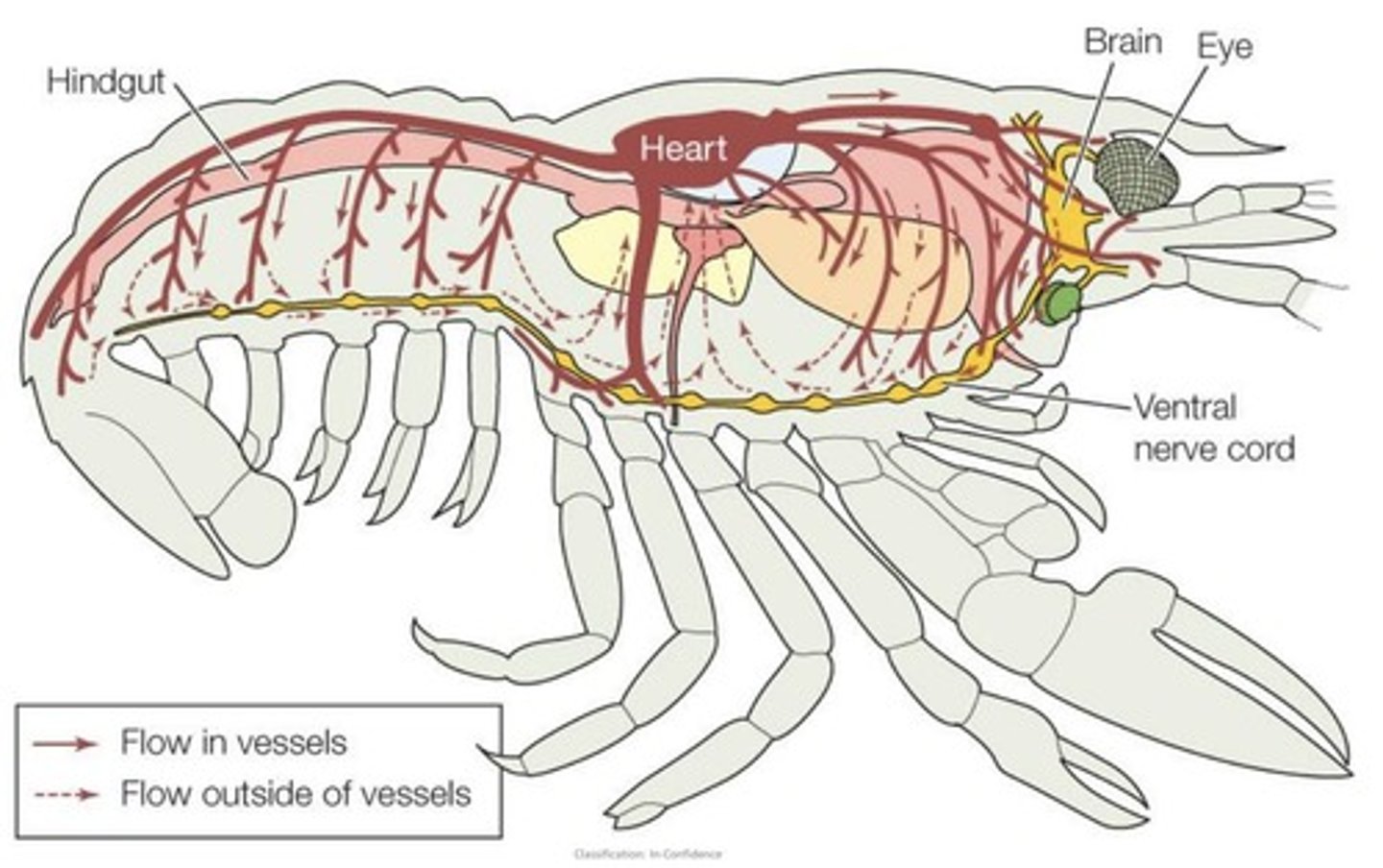
Closed Circulatory System
Blood confined to vessels, distinct from interstitial fluid.
Cardiovascular System
Heart and blood vessels in vertebrates.
Arteries
Carry blood away from the heart.
Arterioles
Smaller vessels branching from arteries.
Capillaries
Microscopic vessels with thin, porous walls.
Capillary Beds
Networks of capillaries infiltrating tissues.
Venules
Small vessels that converge into veins.
Veins
Carry blood back to the heart.
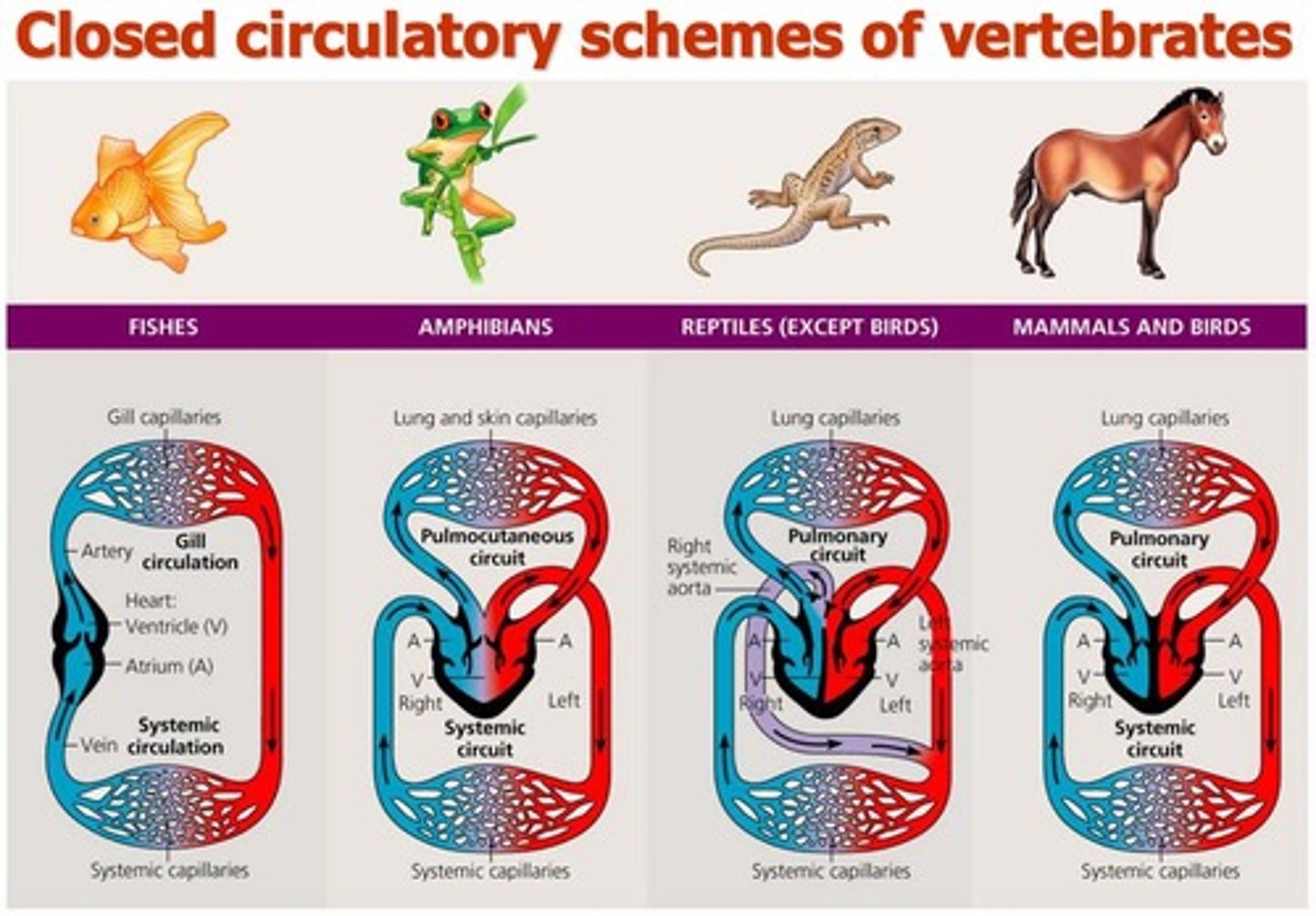
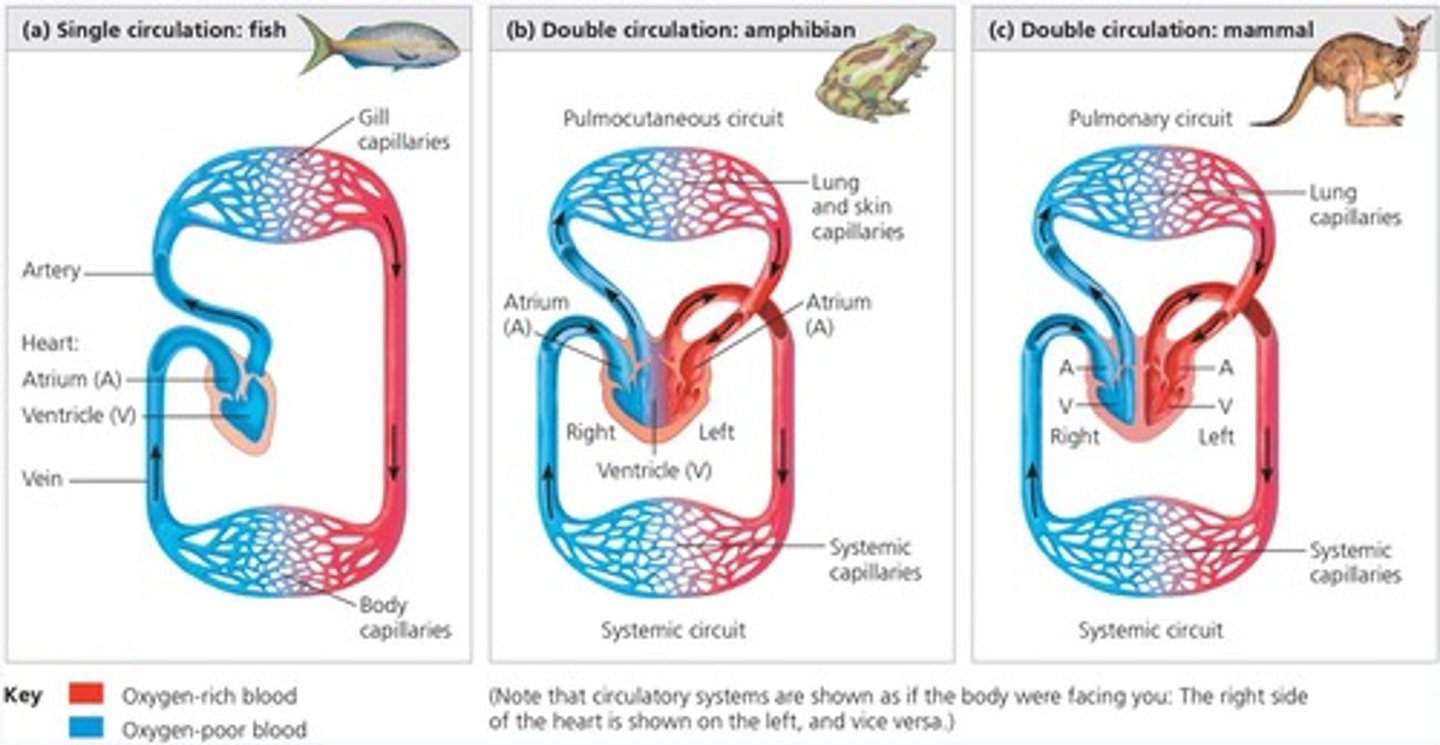
Single Circulation
Blood passes through two capillary beds before returning.
Double Circulation
Two circuits of blood flow in amphibians, reptiles, mammals.
Pulmonary Circuit
Right heart pumps oxygen-poor blood to gas exchange tissues.
Intermittent Breathers
Amphibians that breathe periodically, using skin for gas exchange.
Atrioventricular (AV) Valve
Valves between atria and ventricles.
Semilunar Valves
Valves at exits of heart to pulmonary artery and aorta.
Heart Murmur
Abnormal sound from blood squirting backwards through defective valve.
Sinoatrial (SA) Node
Pacemaker cells in right atrium setting heart contraction rate.
Endothelium
Single layer lining blood vessels, minimizing fluid flow resistance.
Lumen
Central cavity of blood vessels.
Capillary Diameter
Slightly greater than that of a red blood cell.
Smooth Muscle
Muscle tissue regulating vessel diameter.
Elastic Fibres
Fibres allowing vessel stretching and recoiling.
Collagen
Protein providing strength to vessel walls.
Ventricular Contraction
Heart muscle contraction generating blood pressure.
Diastole
Heart phase when ventricles relax.
Diastolic Pressure
Blood pressure during heart relaxation.
Vasoconstriction
Narrowing of arterioles increasing blood pressure.
Vasodilation
Widening of arterioles decreasing blood pressure.
Precapillary Sphincters
Muscle rings regulating blood flow to capillaries.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells transporting oxygen.
Leucocytes
White blood cells involved in defense.
Platelets
Cell fragments aiding in blood clotting.
Sickle-Cell Disease
Condition causing abnormal hemoglobin shape.
Atherosclerosis
Hardening of arteries due to fatty deposits.
Gas Exchange
O2 uptake and CO2 discharge process.
Partial Pressure
Pressure exerted by a specific gas.
Ventilation
Movement of respiratory medium over exchange surfaces.
Atmospheric Pressure
Pressure exerted by the atmosphere at sea level.
PO2
Partial pressure of oxygen in gas mixtures.
Gill ventilation
Movement of gills or water for breathing.
Alveoli
Air sacs in lungs for gas exchange.
Parabronchi
Channels in bird lungs for air flow.
Negative pressure breathing
Air pulled into lungs by diaphragm.
Medulla oblongata
Brain region regulating breathing rhythm.
Respiratory pigments
Proteins binding O2 for transport in blood.
Isoosmotic
Two solutions with equal osmolarity.
Hyperosmotic
Solution with higher solute concentration.
Hypoosmotic
Solution with lower solute concentration.
Osmoconformer
Animal isoosmotic with its environment.
Osmoregulator
Animal controlling internal osmolarity independently.
Stenohaline
Animals intolerant to osmolarity changes.
Euryhaline
Animals surviving large osmolarity fluctuations.
Marine bony fishes
Fish losing water, balancing by drinking seawater.
Shark osmoregulation
Sharks maintain lower salt concentration than seawater.
Trimethylamine oxide (TMAO)
Organic molecule aiding shark osmoregulation.
Freshwater animals
Must be hyperosmotic to survive in water.
Dilute urine
Excretion method for freshwater animals.
Euryhaline fish examples
Salmon and long-finned eel adapt to environments.
Gas exchange surface in birds
Air flows unidirectionally over lung surfaces.
Breathing control centers
Neural circuits in medulla for rhythm regulation.
Water balance in osmoregulators
Discharge or intake water based on environment.
Osmoregulation in salmon
Changes between freshwater and saltwater environments.
Cortisol
Steroid hormone aiding in salt secretion during migration.
Osmoregulation
Maintaining water and salt balance in organisms.
Metabolic Rate
Osmoregulation accounts for 5% of fishes' resting rate.
Ammonia Excretion
Common in aquatic species needing large water access.
Urea Excretion
Less toxic nitrogenous waste, requires energy to produce.
Uric Acid Excretion
Primary waste for insects, snails, and reptiles.
Protonephridia
Excretory system in Platyhelminthes with dead-end tubules.
Aerobic Respiration
Process of using oxygen to produce energy.
Cellular Metabolism
O2 consumption in mitochondria producing ATP and CO2.
Diffusion Rate
Rate of oxygen movement expressed as Ko2 .A . ΔP/d.
Cutaneous Diffusion
Gas exchange through skin, seen in flatworms.
Circulatory System
Transport system for gases between respiratory organs.
Oxygen Content in Air
Air at 20°C contains 260 mg/L of oxygen.
Oxygen Content in Water
Freshwater at 20°C contains 9.1 mg/L of oxygen.
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Larger animals have smaller ratios affecting respiration.
Gills
Thin outgrowths for gas exchange in aquatic animals.
External Gills
Gills ventilated externally and perfused with blood.
Internal Gills
Gills located inside the body for gas exchange.
High Altitude Adaptation
Frogs use gills and circulatory systems for oxygen.
Energy Cost of Urea
Energy required to convert ammonia into urea.
Salt-Secreting Cells
Specialized cells increased by cortisol during migration.
Passive Ventilation
Ventilation without energy expenditure, relies on natural processes.
Active Ventilation
Ventilation requiring energy to move air or water.
Lugworms
Burrowing polychaetes with afferent and efferent vessels.
Water 'Lungs'
Cavity ventilated by tidal movement of water.
Tidal Ventilation
Air enters and exits lungs through same pathway.
Energetic Cost of Ventilation
Ventilation requires significant energy expenditure.
Molluscs
Organisms with internal gills ventilated by cilia.
Crayfish Gill Bailer
Pumps water unidirectionally over enclosed gills.
Diffusion Factors in Crustaceans
Includes surface area and thin cuticle for gas exchange.