UNIT 3: BIOENERGETICS
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Glycolysis
2 phases: 1st the energy investment phase glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of G3P using 2 ATP. In the energy payoff phase the 2 molecules of G3P forms a 2 pyruvate molecule which yields 4 ATP for a net gain of 2 ATP; occurs in the cytoplasm
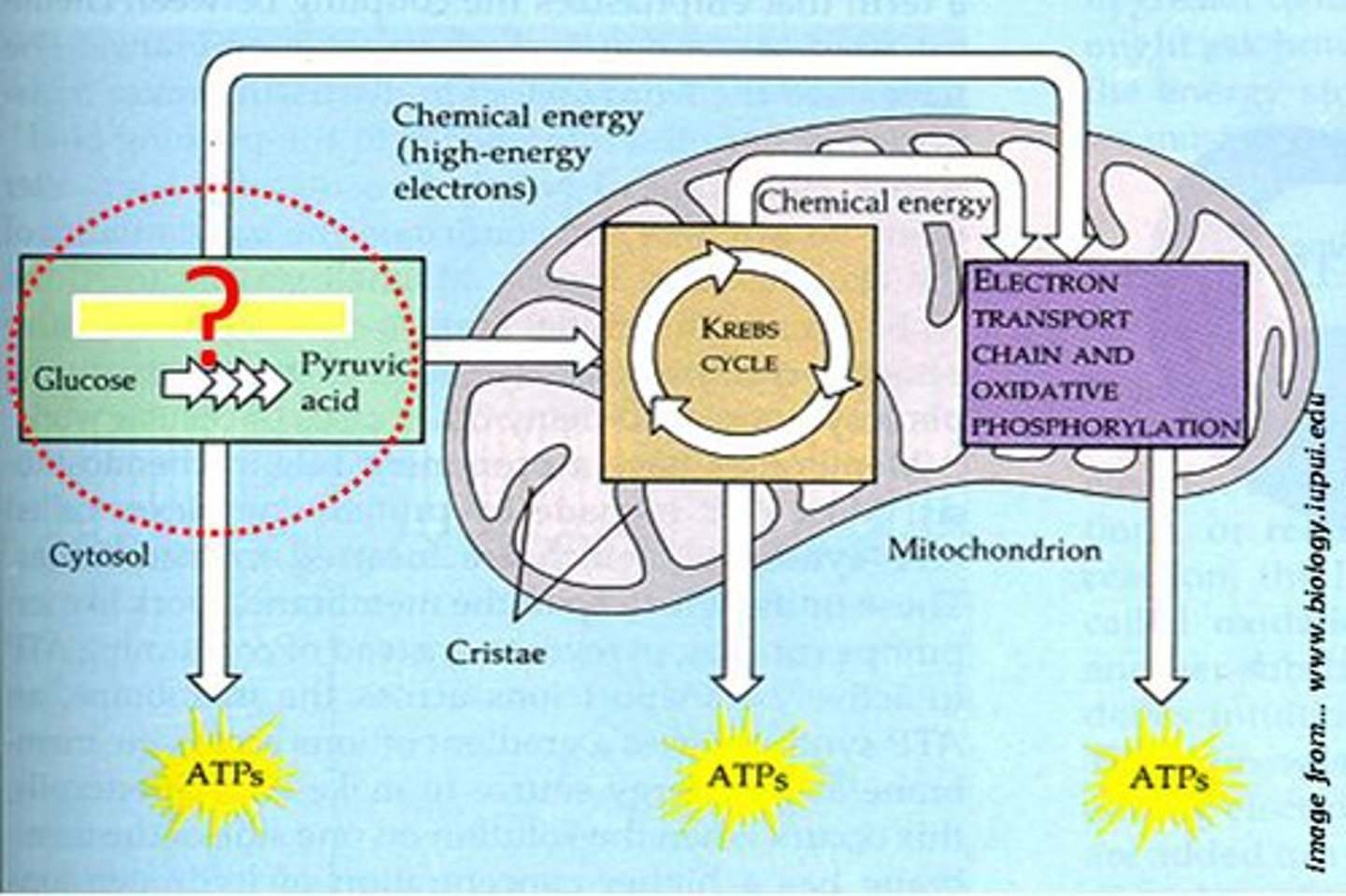
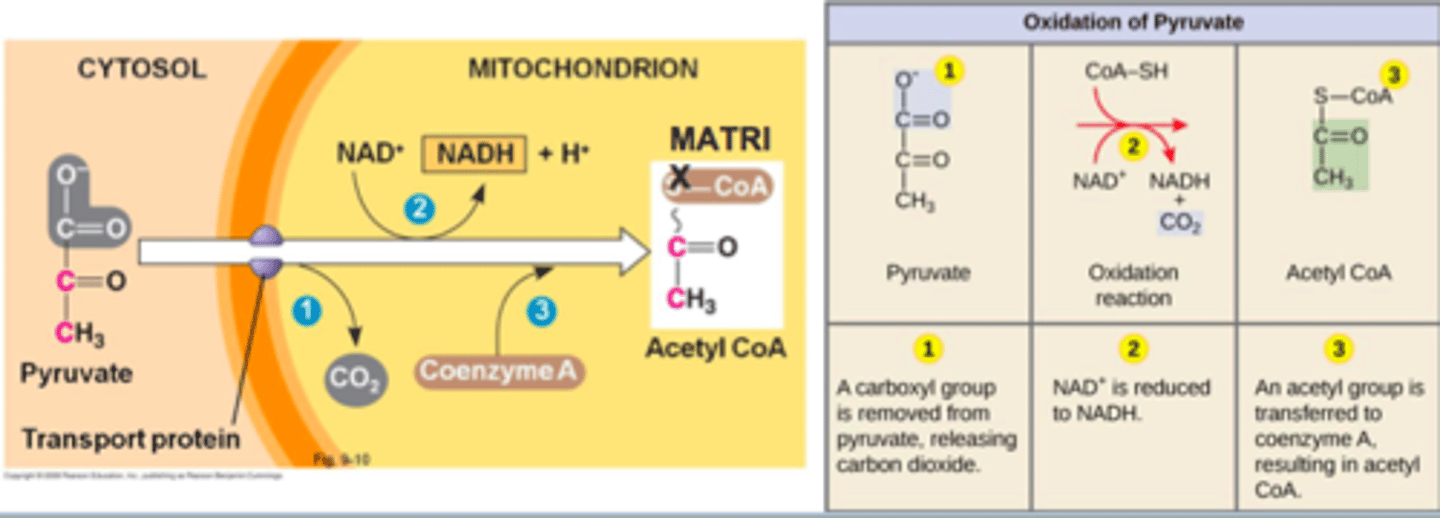
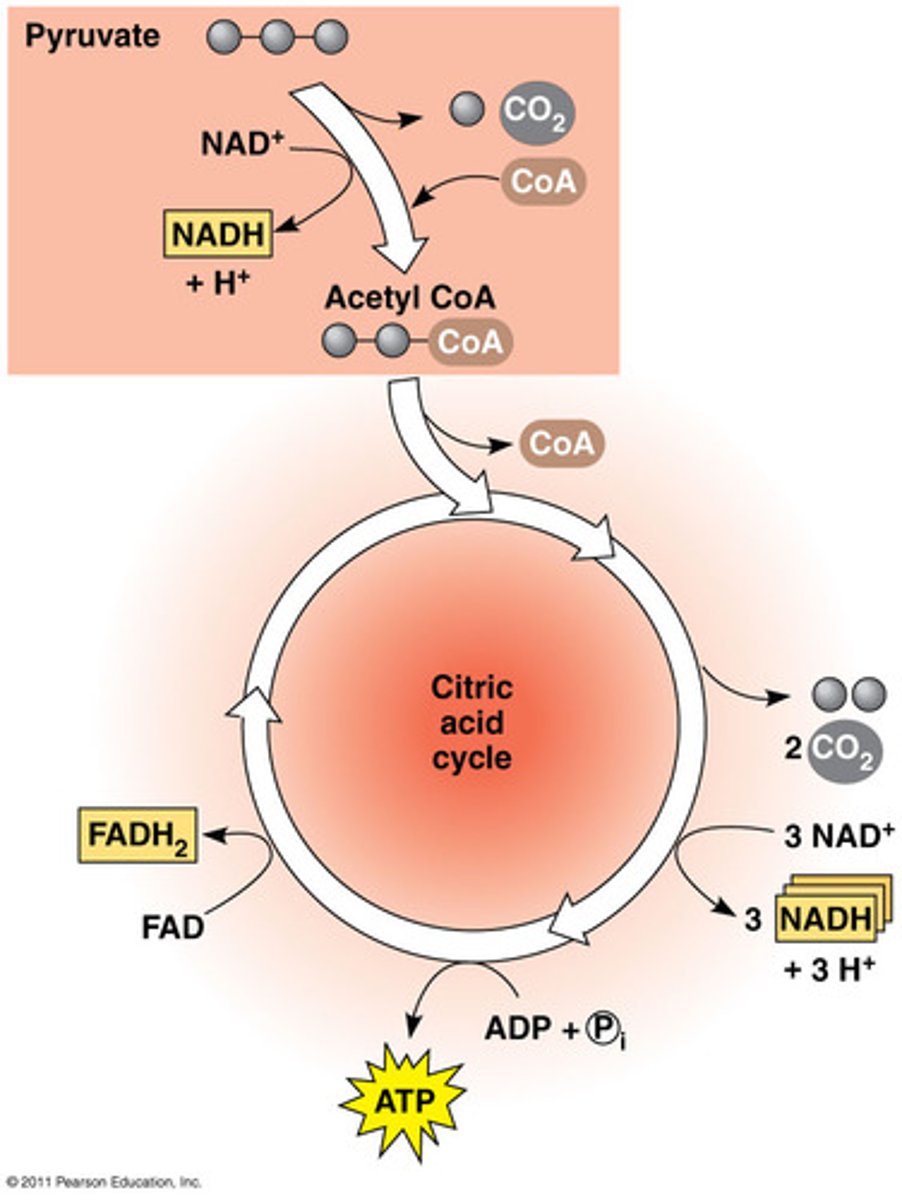
Pyruvate Conversion/ Link Reaction
The pyruvate molecules undergo modification where CO2 is removed from each molecule, NAD+ becomes reduced to create NADH. Creates Acetyl Coenzyme A
NADH and FADH2
Energy molecules produced during Krebs Cycle; provides H+ for ETC
Kreb's cycle
Produces 3-NADH, 1-FADH2, 1-ATP, & 2-CO2 with each turn
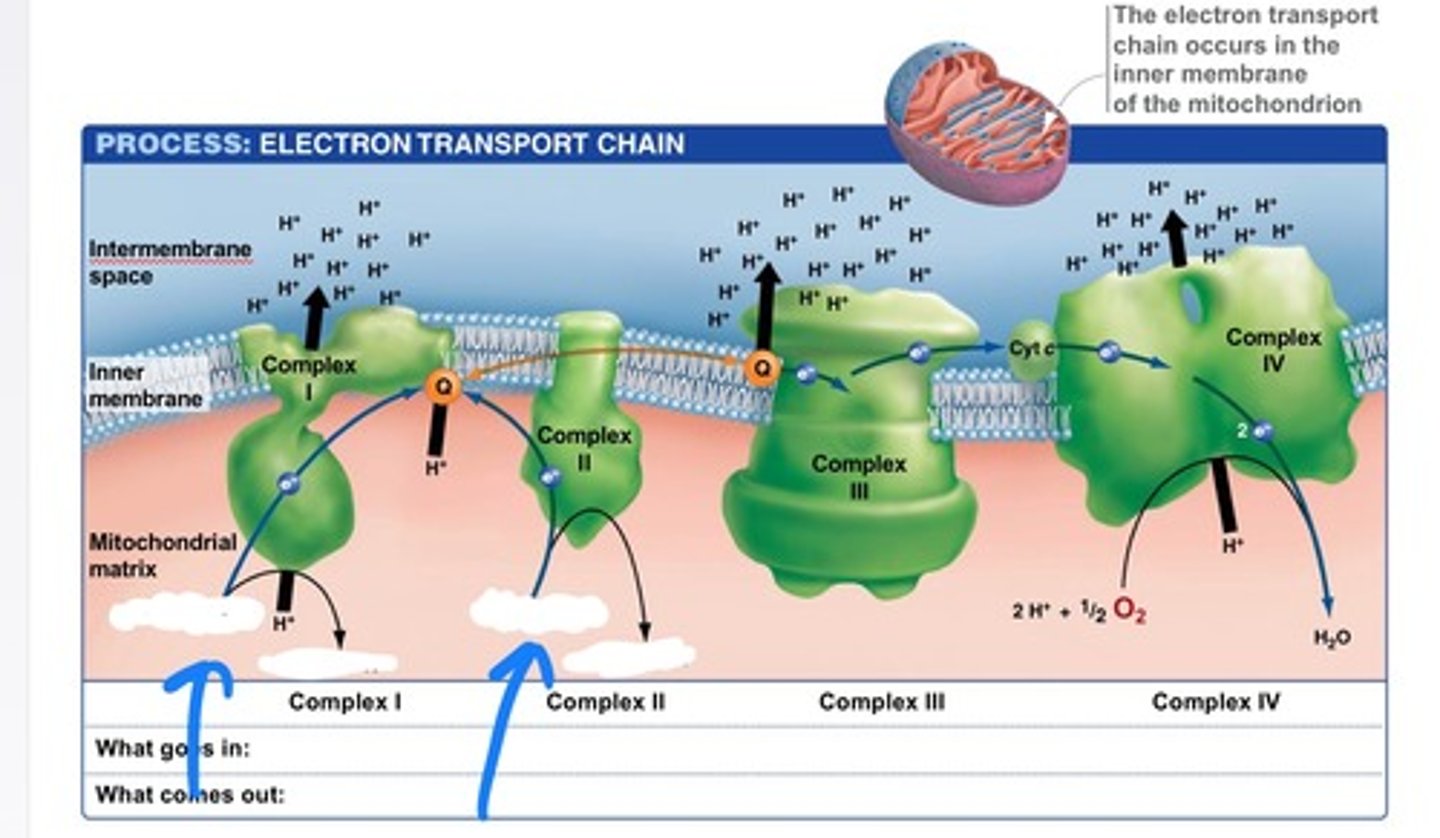
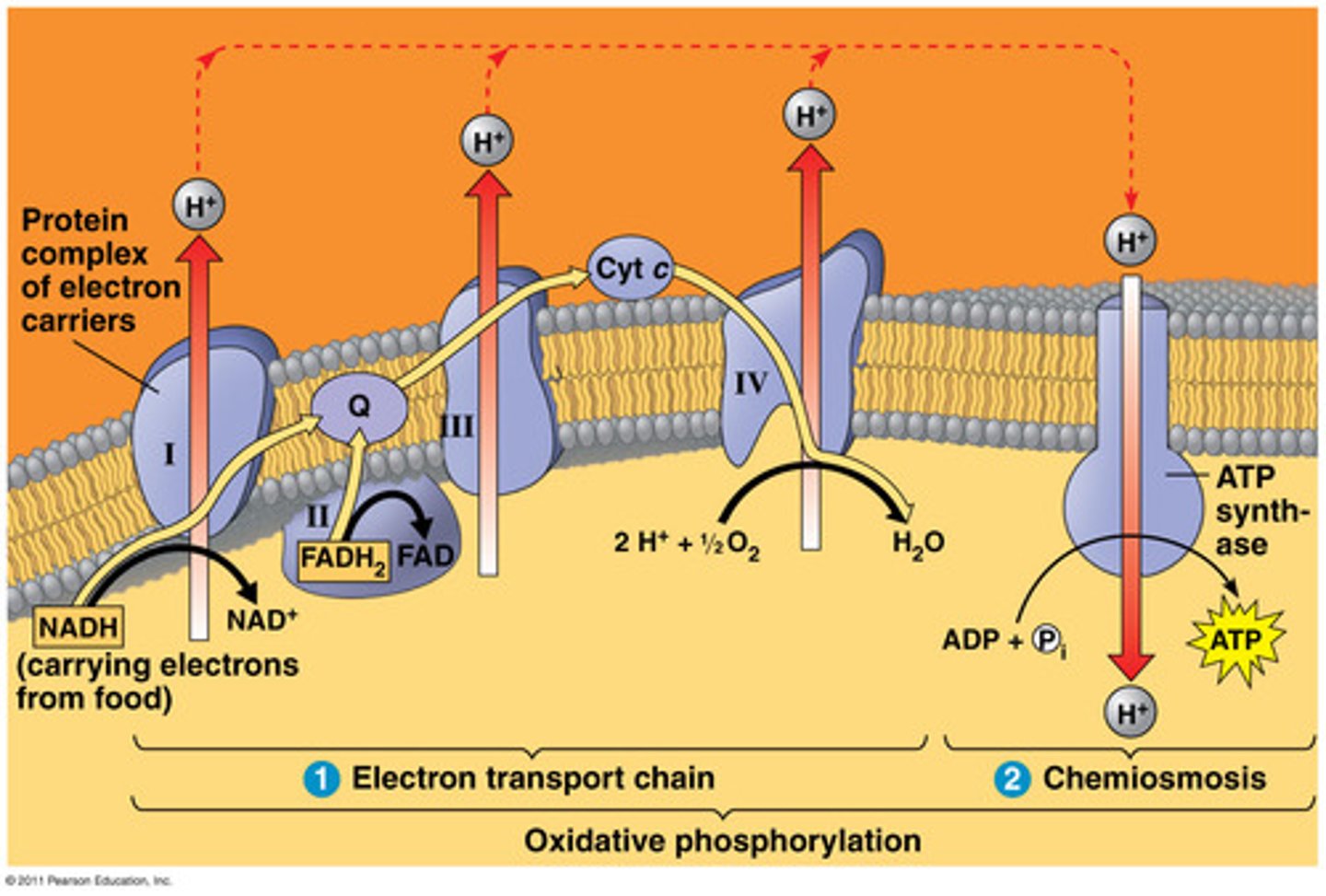
ETC
NADH and FADH2 loses its' electrons into the binding proteins on the innermembrane and the electrons travel through membrane proteins and as it goes through each protein hydrogen is pumped through and creates a concentration gradient
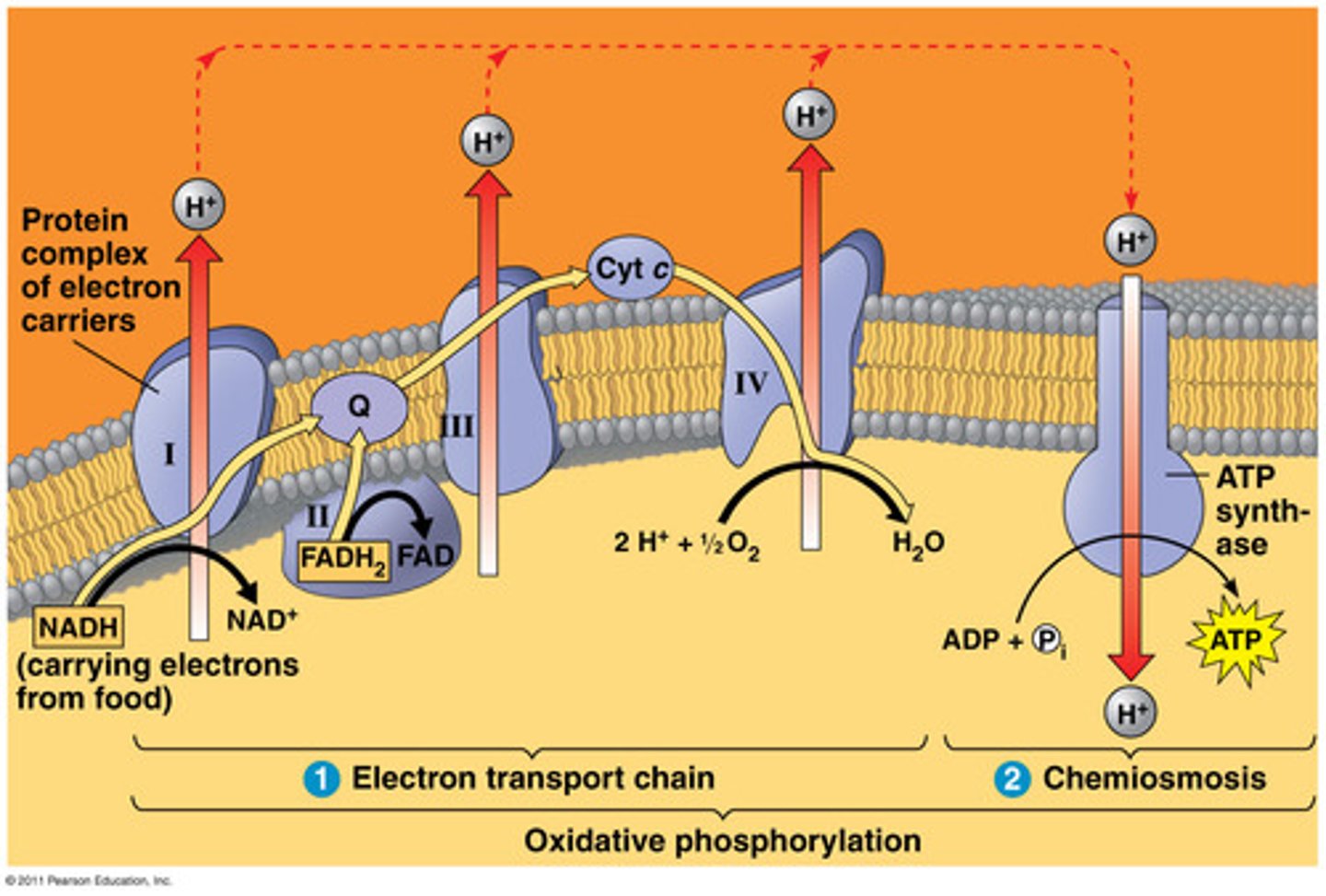
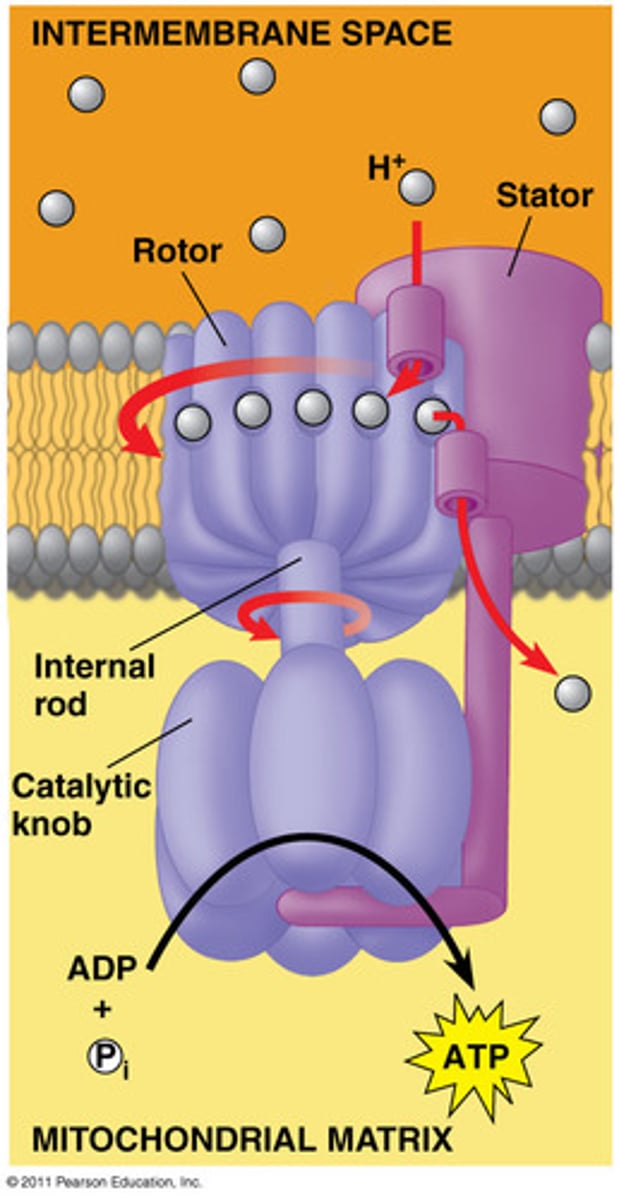
ATP Synthesis
The hydrogens now flow through ATP synthase and create ATP, at the end of the ETC oxygen gains the electrons from the ETC and binds with hydrogens in order to get water.
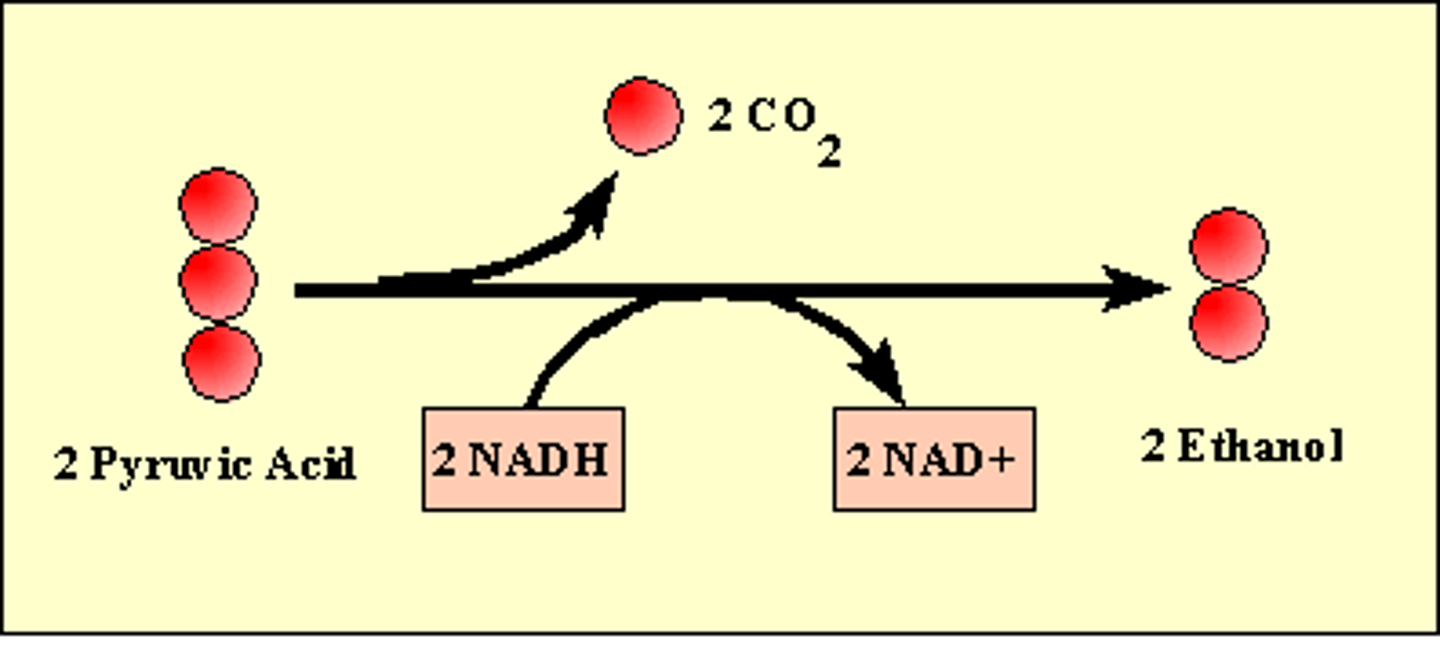
Alcohol Fermentation
Converts the two pyruvate molecules to 2 molecules of ethanol by cutting off CO2 and filling the open bonds with H from the electron carriers, this frees up the electron carrier and keeps glycolysis going
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Converts pyruvate into lactic acid by breaking off the ketone, the double bonded oxygen in the middle, and adding H. the H comes from the electron carrier keeping glycolysis going in the absence of oxygen.
oxidative phosphorylation
Part of the electron transport chain. A process occurring in the mitochondria that results in the formation of ATP from the flow of electrons across the inner membrane to bind with oxygen.
anaerobic respiration
Respiration that does not require oxygen
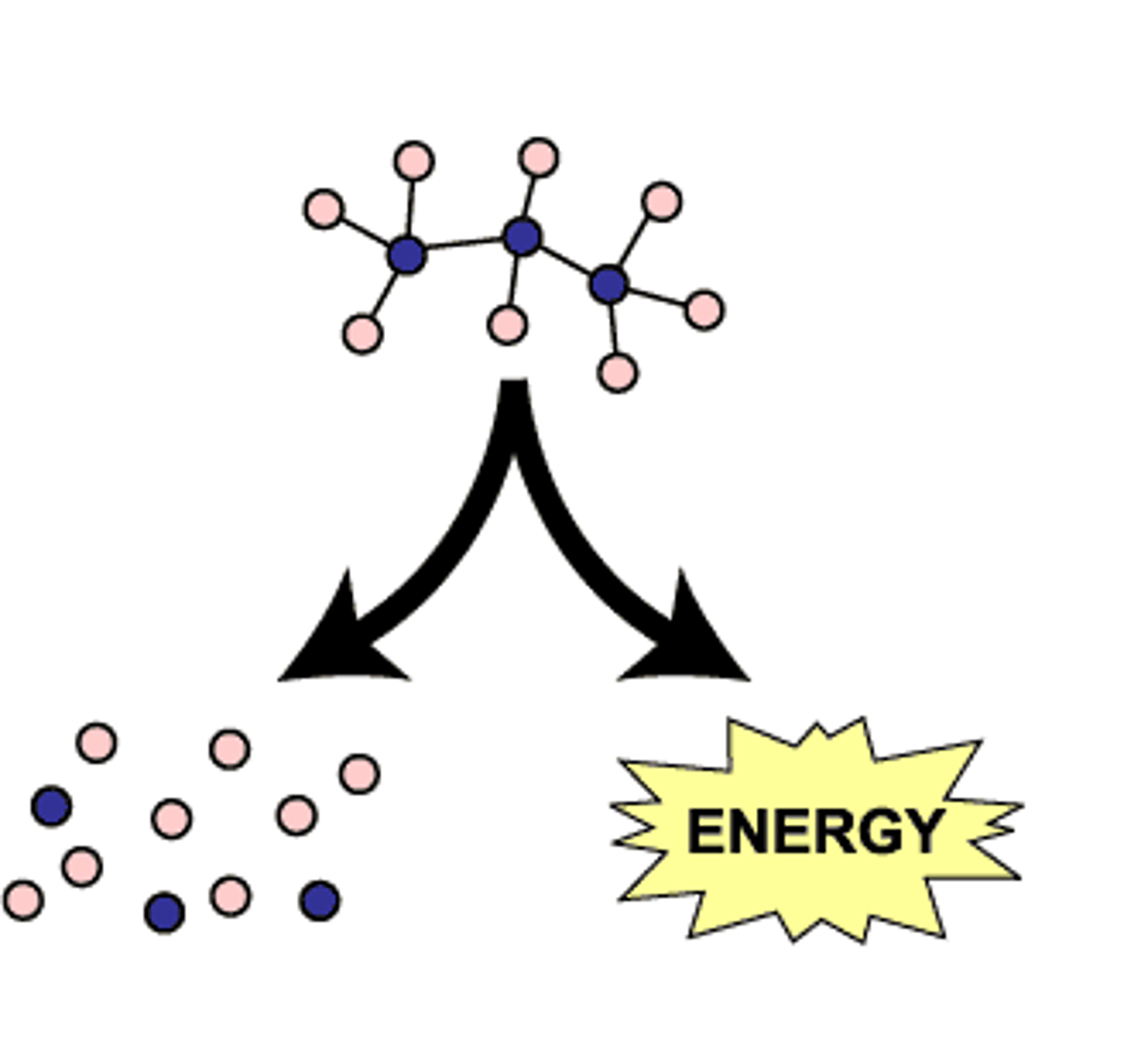
Catabolism
refers to the breaking down of a molecule, the reaction is exergonic which means that it releases energy.
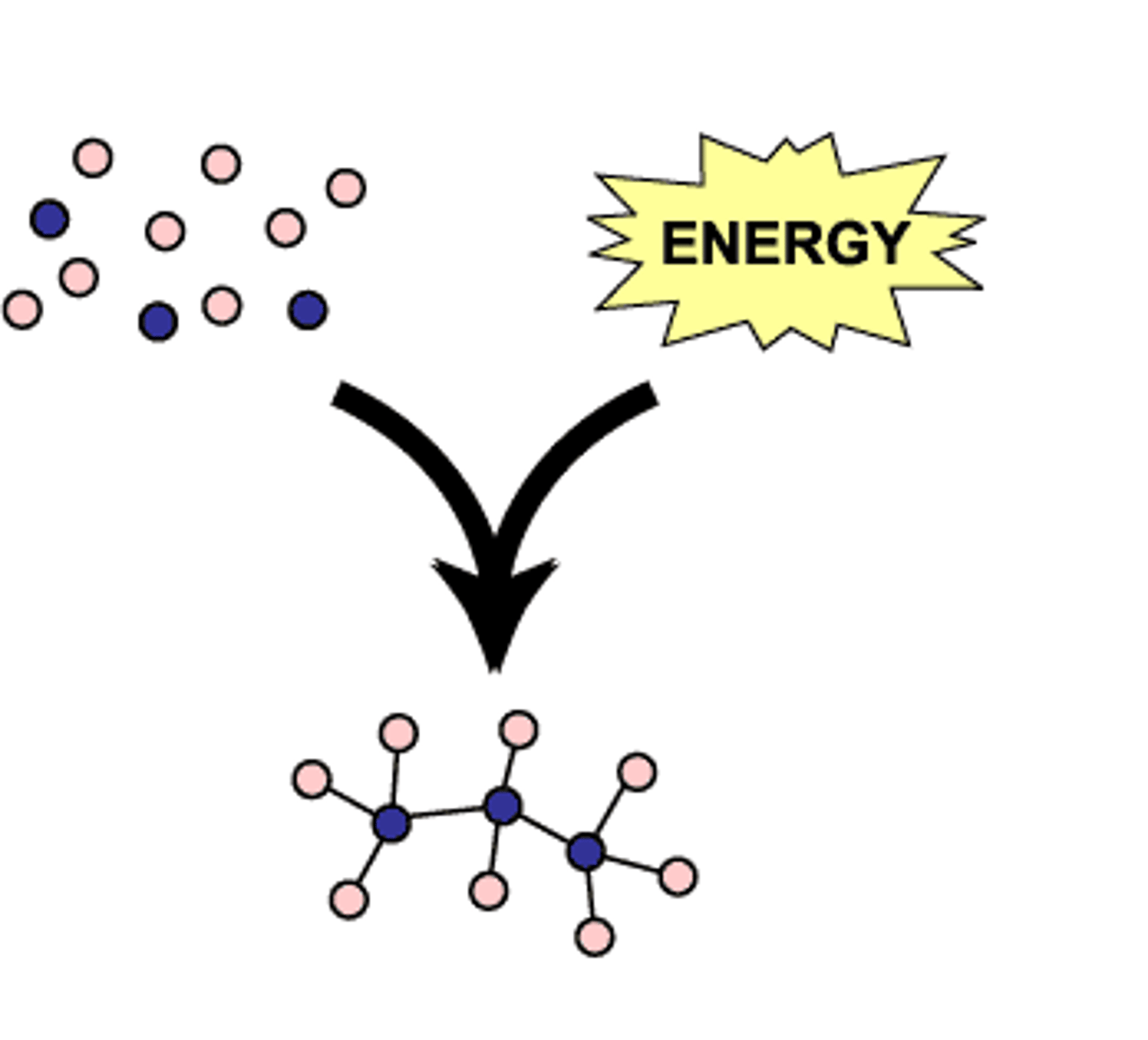
Anabolism
refers to the assembling of molecules, the reaction is endergonic meaning that it absorbs energy.
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed only transformed or transferred.
Second law of Thermodynamics
Every energy transfer increases the entropy of the universe

Adenosine tri-phosphate
Made from a Ribose sugar and the nitrogen base adenine, has 3 negative phosphate groups linked together making it highly unstable
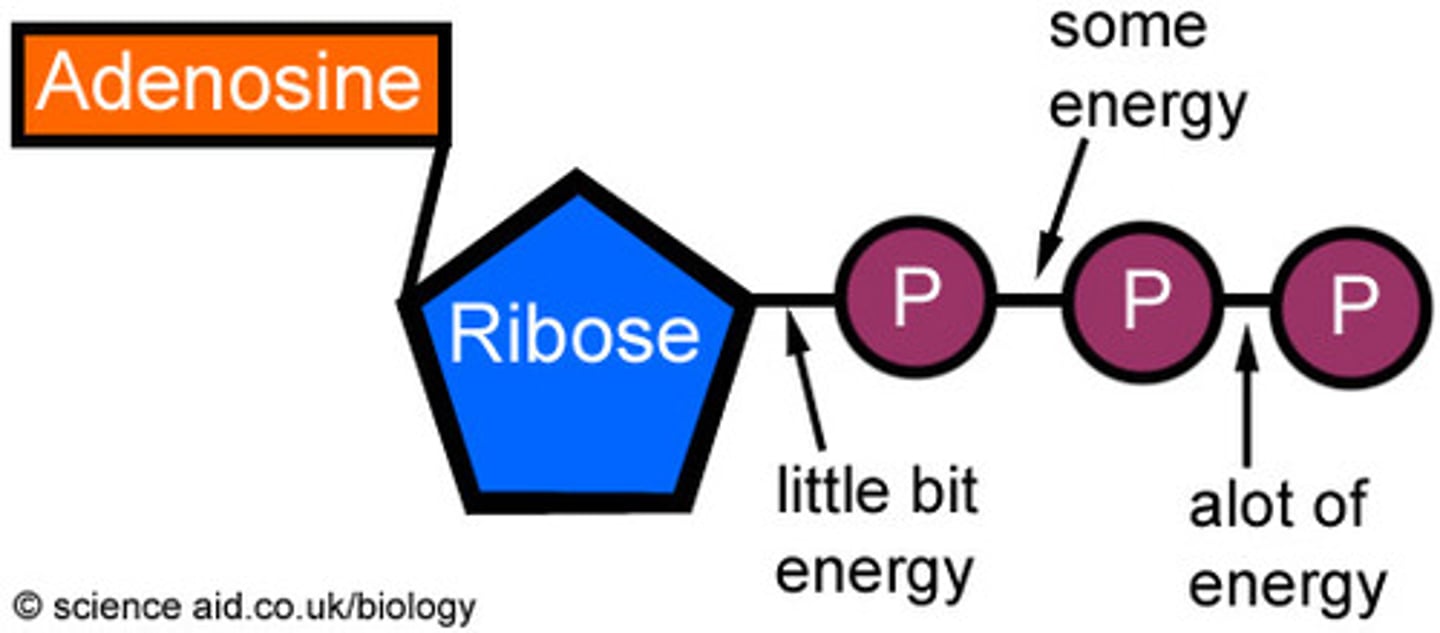
Phosphorylation
The attaching of an unstable phosphorus ion to another molecule to make it unstable thereby able to perform work.
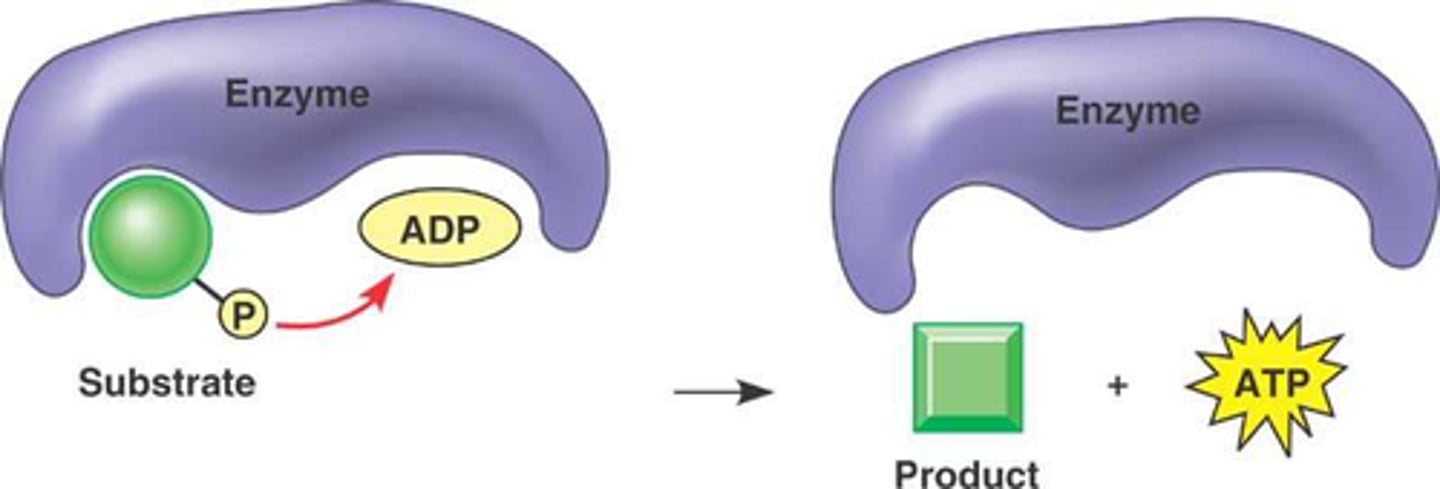
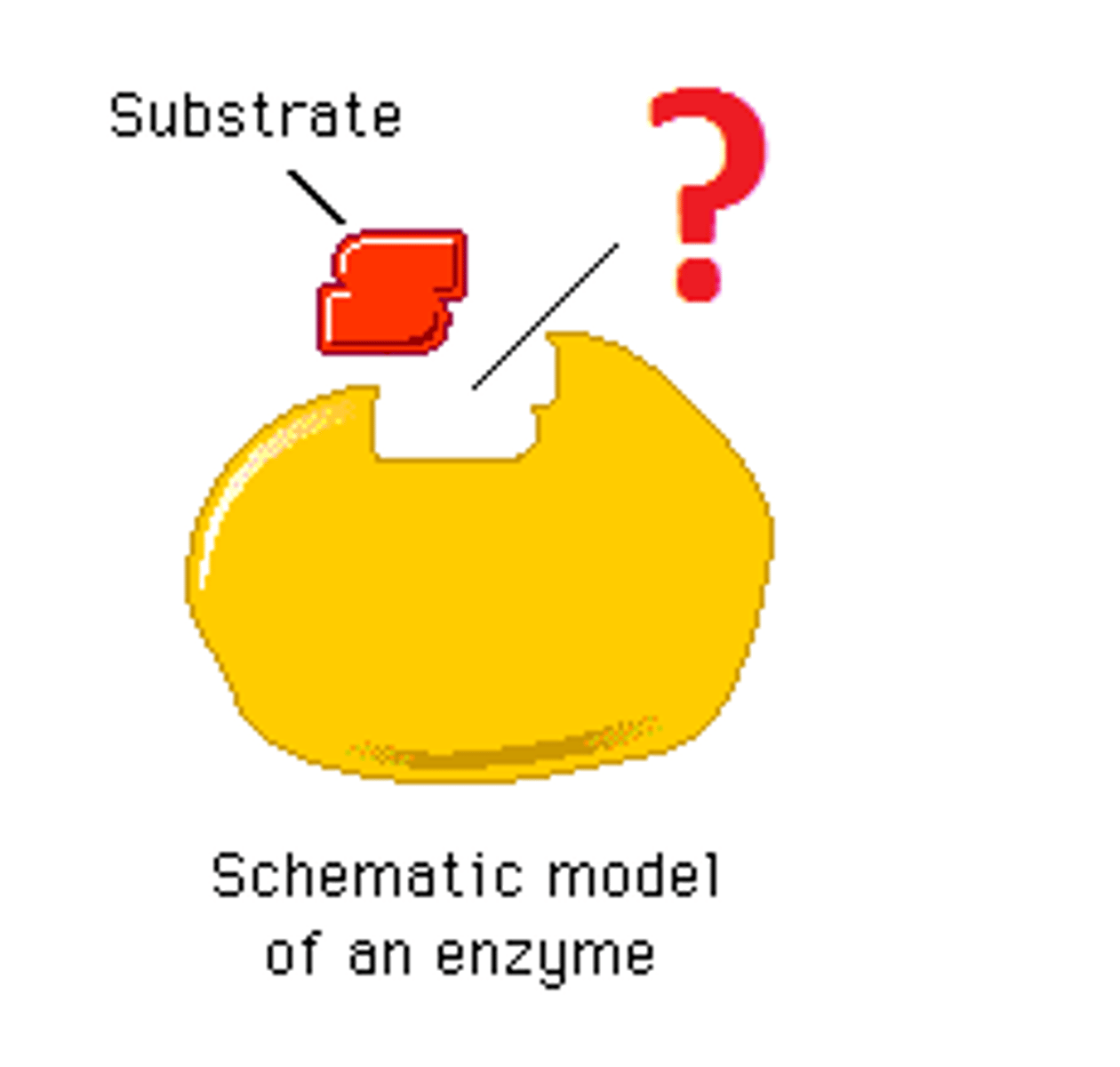
Enzymes
Biological catalysts, most are proteins that either speed up or control the rate of a reaction, they are NEVER consumed by the reaction, names ends with ase, and is very picky about what it receives (Induced fit).

Substrate
molecule that is affected by the enzyme.
Active site
location to where the chemical reaction is taking place between the enzyme and the substrate. The R-group of the Amino acid perform all the work for the reaction occurring in the active site.
Factors that can effect enzymes ability to work optimally
1). Temperature
2).PH or POH of an environment
3).Salt concentration
Inhibitors
molecules that negatively affect an enzymes ability to work optimally, by slowing down or stopping rates of reactions.
Competitive inhibitors
these molecules compete for the active site and slow down rate of reactions
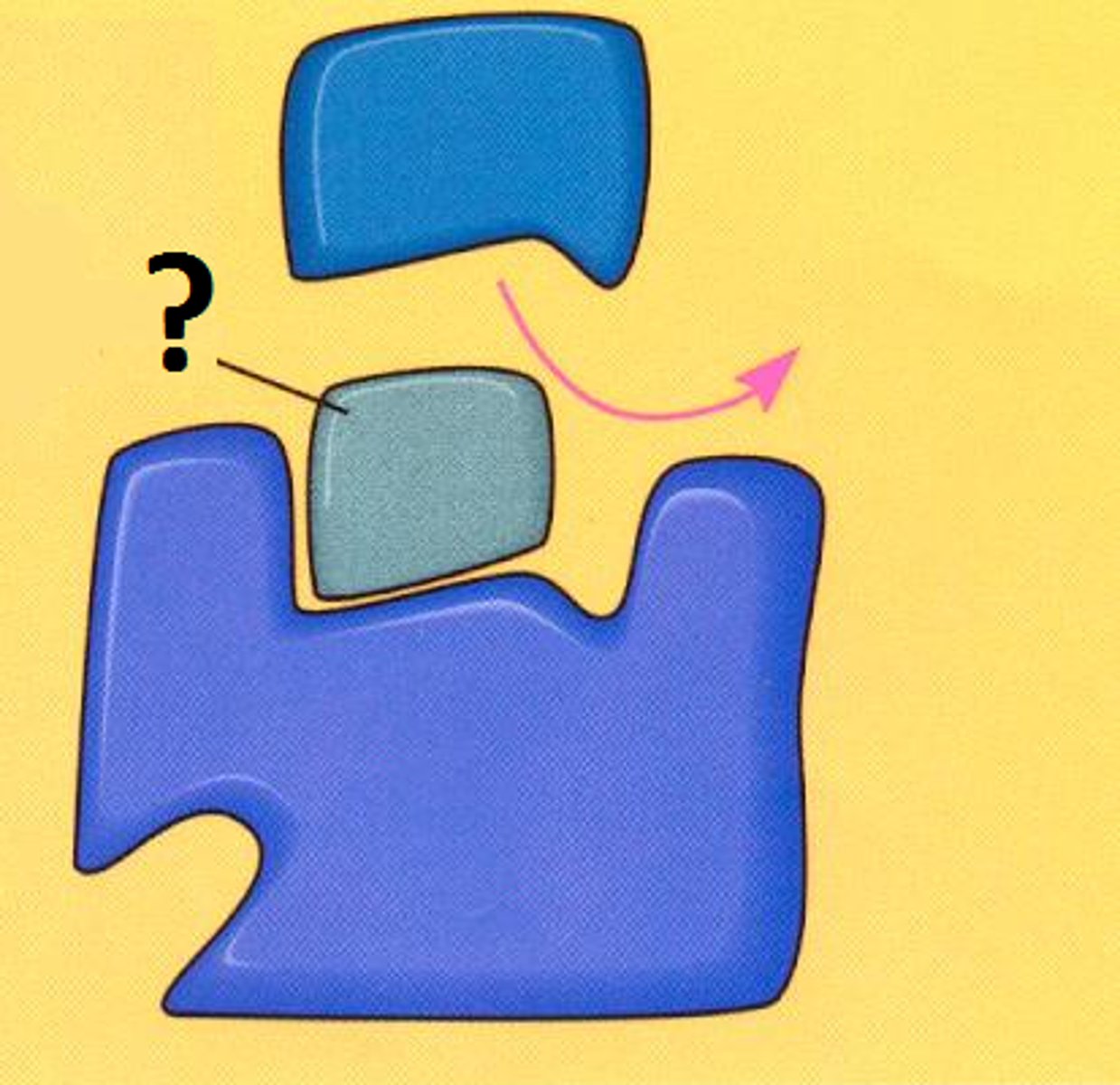
non-competitive inhibitors
these molecules attach somewhere other than the active site therefore causing the active site to change shape so that the substrate can no longer fit, these stop reaction rates completely
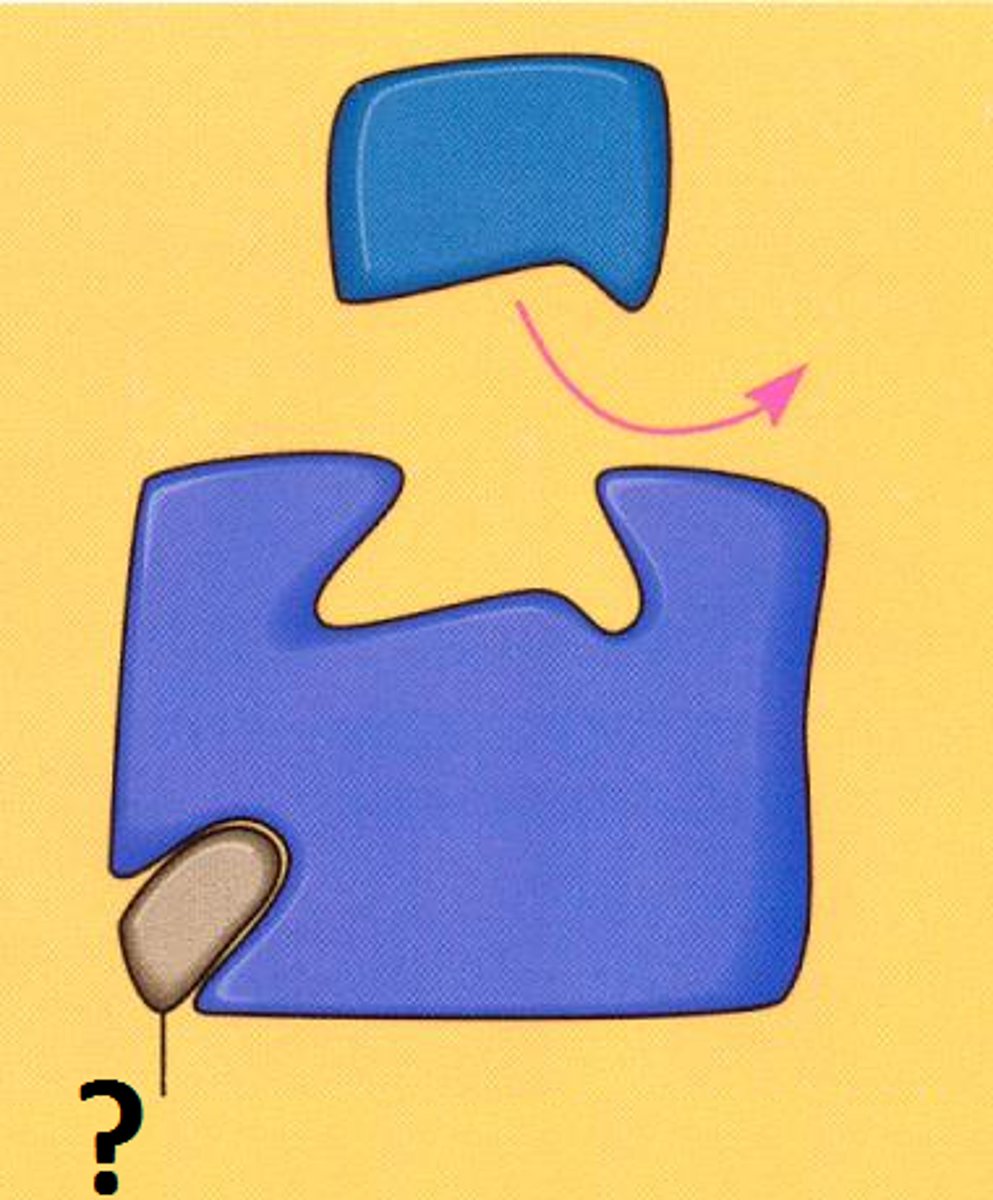
Allosteric site
Acts as an on/off switch for the enzyme, when a molecule binds to it the active site will either change shape causing the reaction to either cease of begin or block off the active site
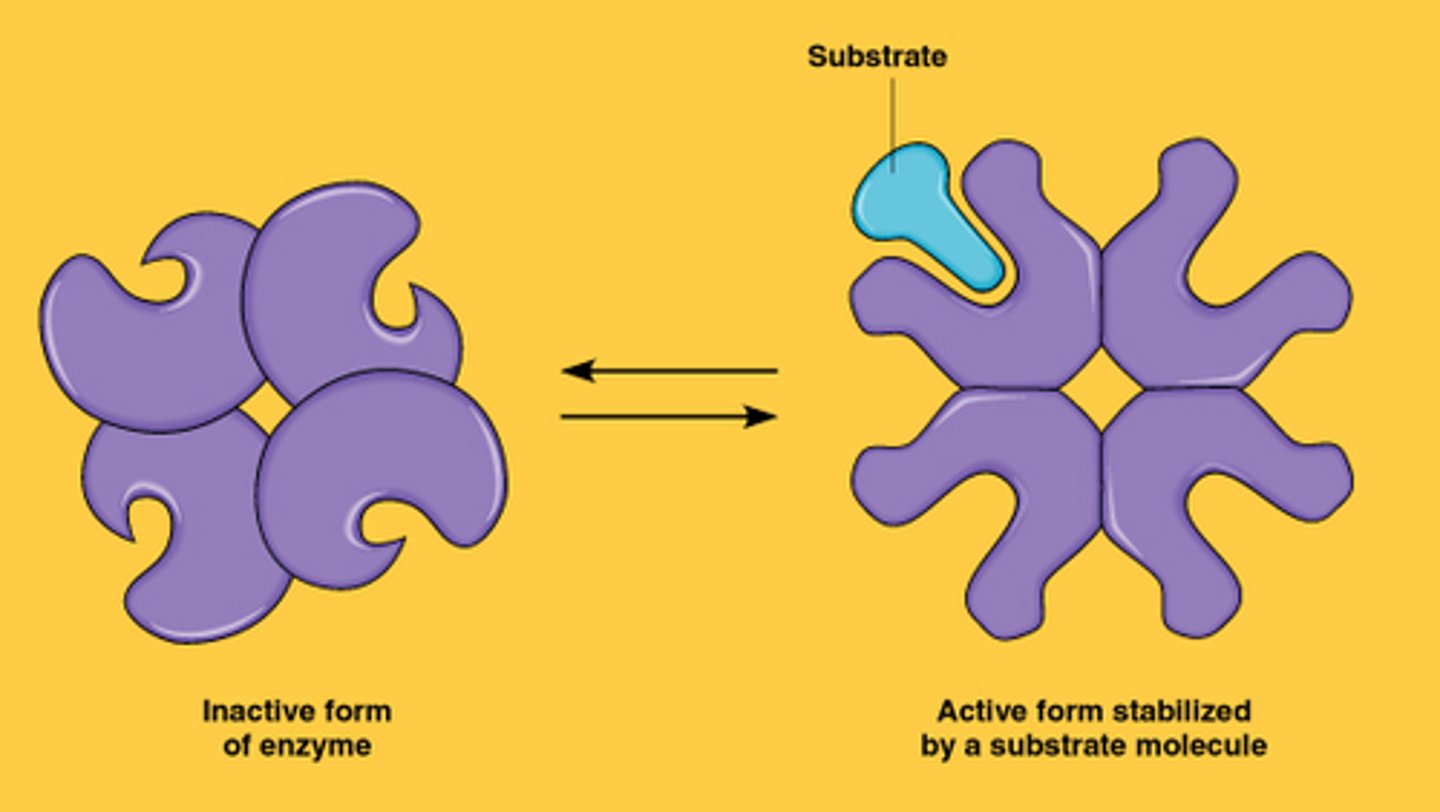
Cooperativity
one active site helps or cooperates with another active site on the same molecule.
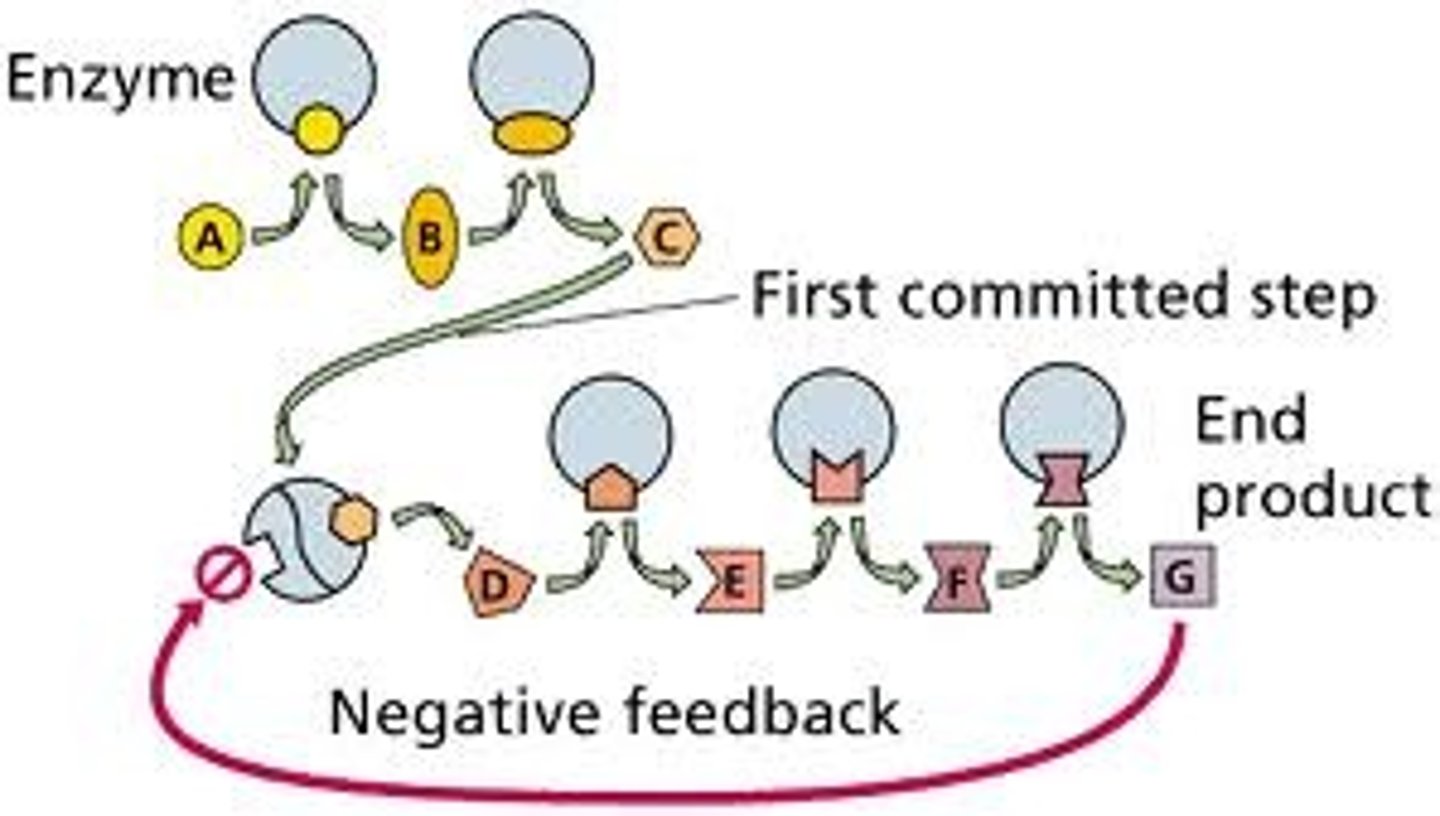
Feedback inhibition
Stops a process from occurring until conditions require more product ex. phosphofructokinase acts as an on/off switch for the process of glycolysis. When there is too much ATP in the cell the excess ATP and Citrate bind to the allosteric site of the enzyme and shut ATP production down.
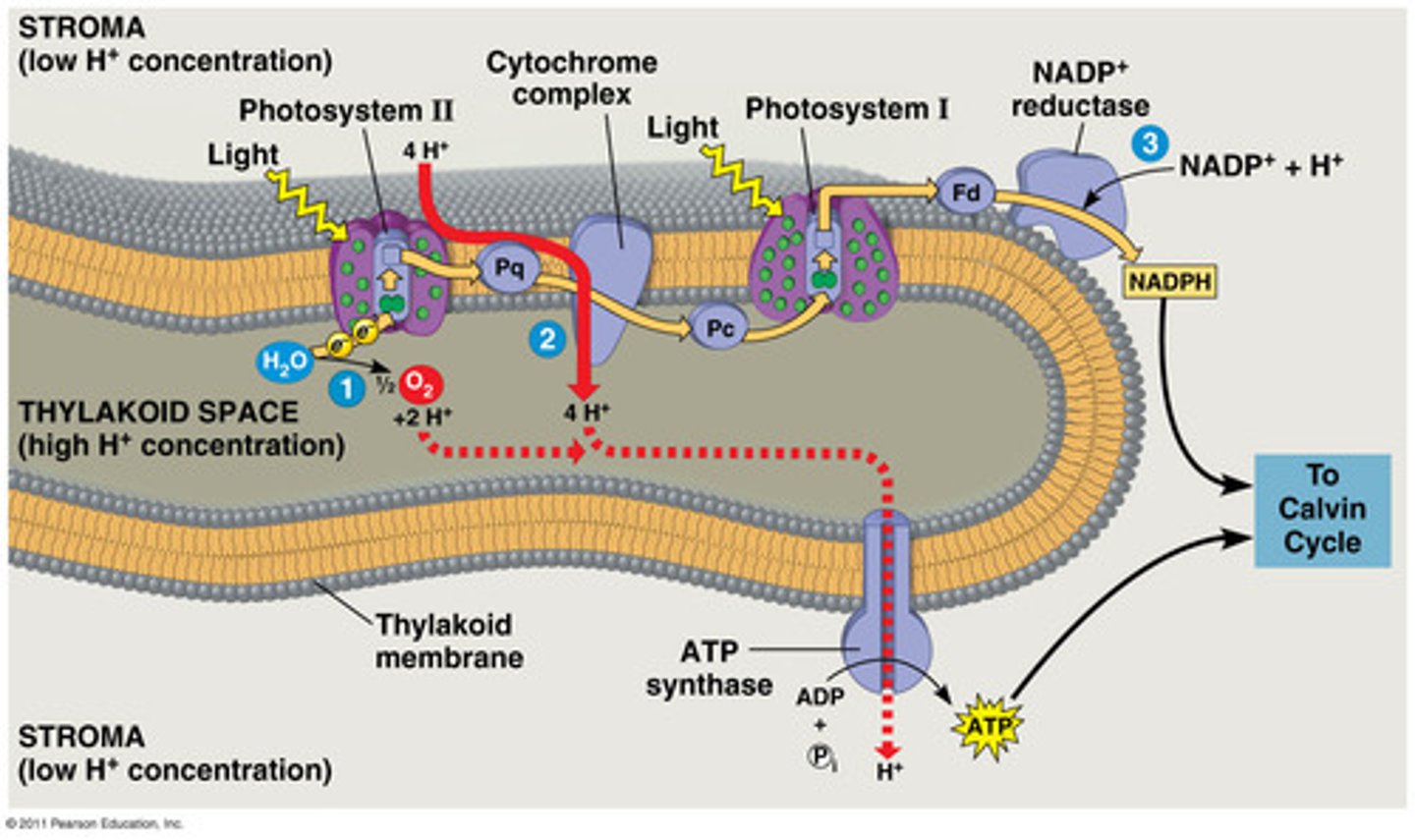
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants, algae, and some bacteria that absorbs photons of light & used to carry out photosynthesis
Excited Chlorophyll
Photons from the sun hit photosystems I and II at the same time causing the magnesium atoms to release 2 electrons
Photolysis
The light splits water into oxygen, electrons and protons.
Creation of Concentration Gradient
The electrons once it reaches cytochrome pump protons from the outside of the thylakoid to the inside of the thylakoid
light dependent reaction part 6
The excited electrons from photosystem one get on the carrier protein ferredoxin and travel to NADP Reductase once the electrons reach NADP reductase they react and create NADP+
End of Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
NADP+ through photolysis gains a proton with the assistance of NADP+ Reductase to create NADPH
Diffusion of Protons
Hydrogen ions travel through ATP synthase in order for equilibrium to be established again, ATP is formed.
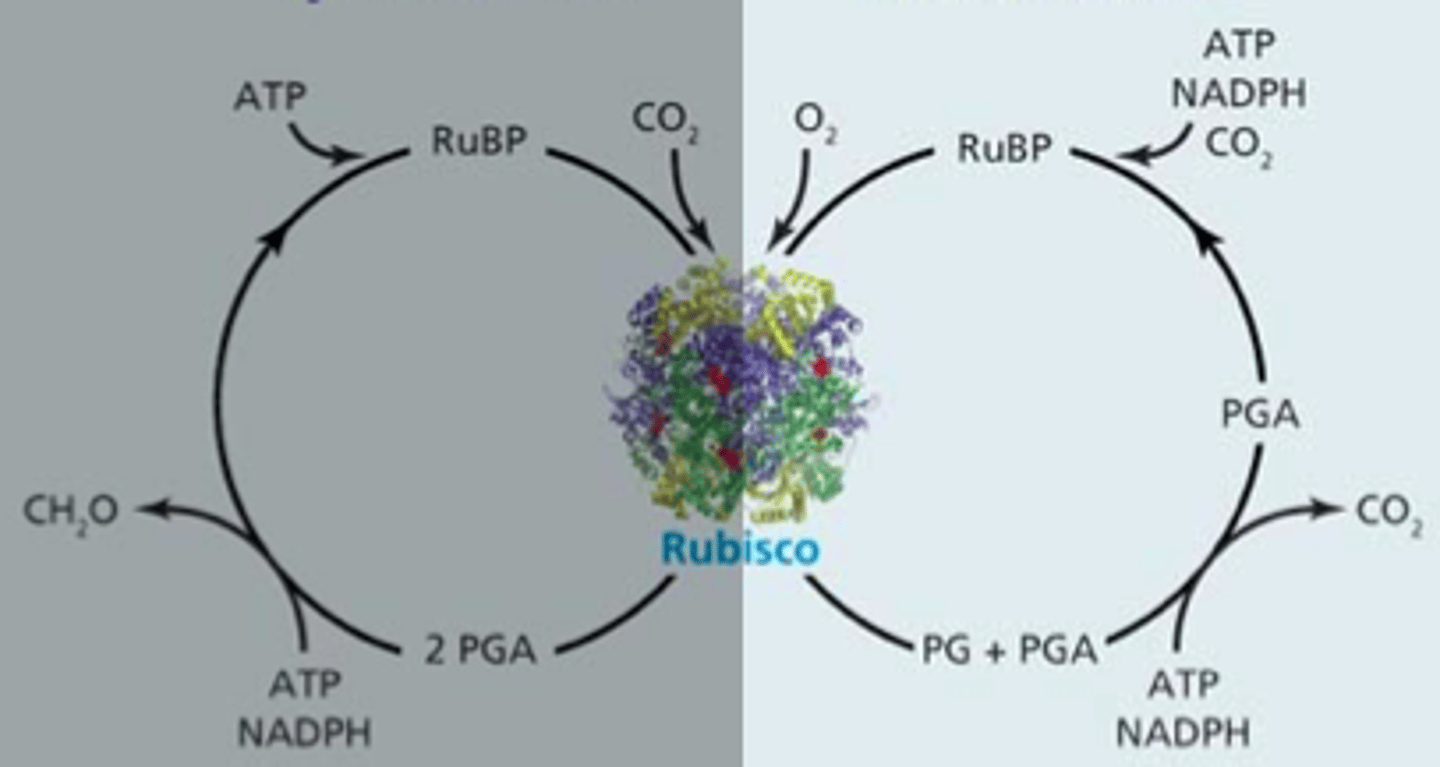
Carbon Fixation
RuBP combines with carbon dioxide by using rubisco and forms an unstable 6 carbon molecule.The 6 carbon molecule then splits into two PGA molecules.
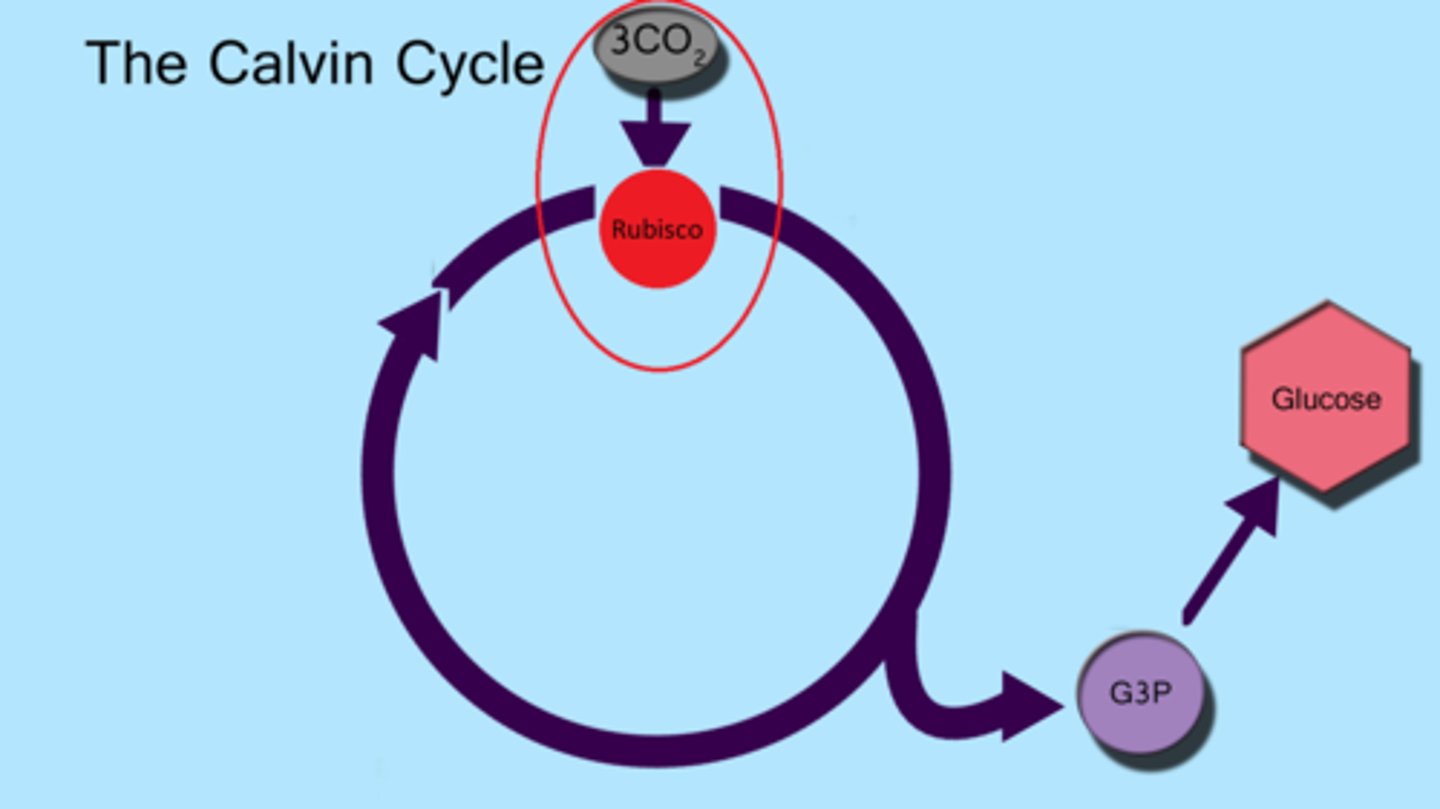
Reduction
2 NADPH are added to the two phospho glycerate molecules in order to reduce it to 2 NADP+ and the PGA molecule becomes 2 G3P.
Regeneration
With the use of 3 ATP, 5 G3P molecules go back to rubisco so more RuBPs can be made and the cycle begins again.
Calvin Cycle products
glucose, ADP, NADP+
Photorespiration
Using oxygen instead of CO2 to do carbon fixation in the Calvin cycle as a last resort to keep alive
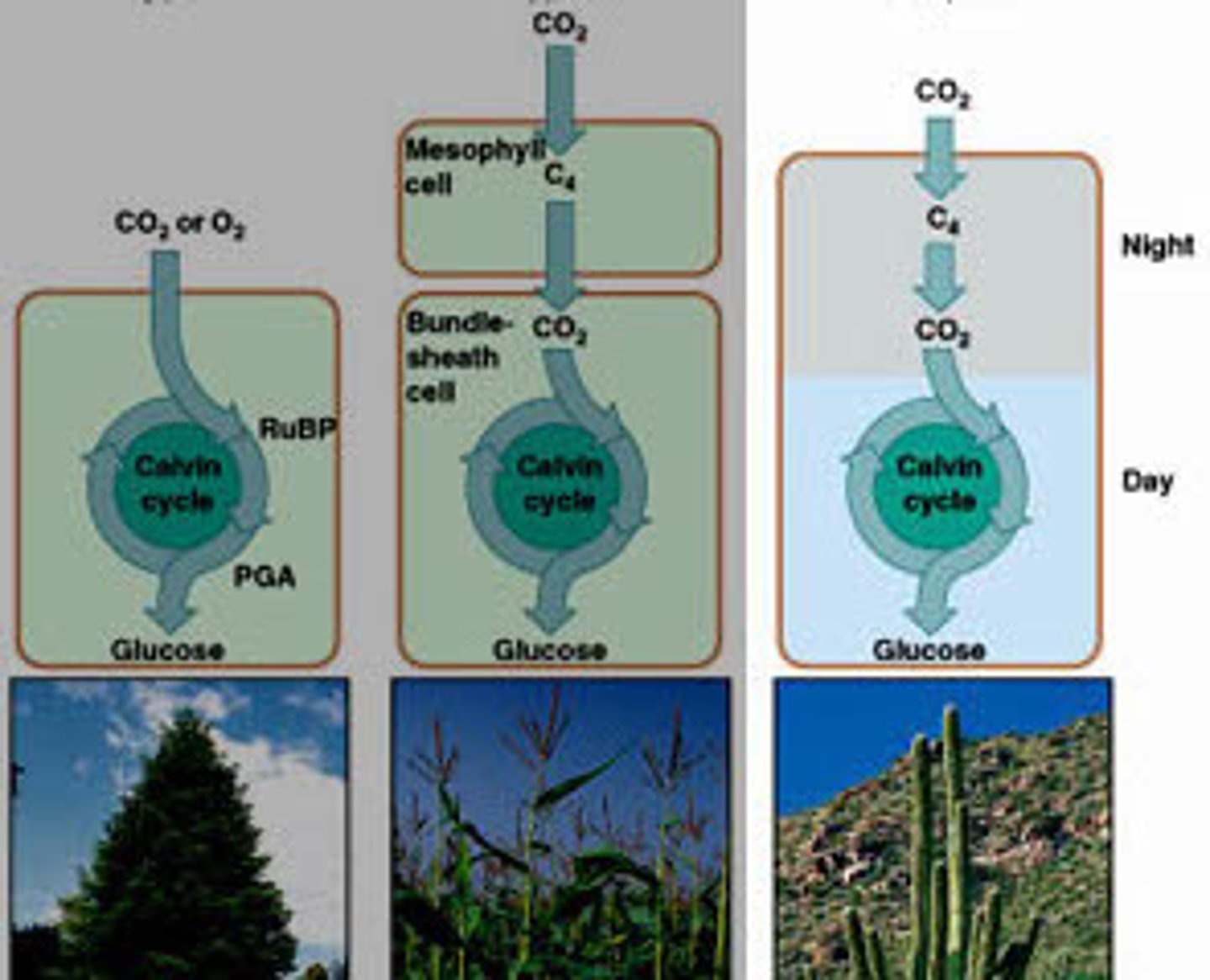
C4 plants
These plants use bundle sheath cells to prevent oxygen from entering and modify CO2 to create malate a 4 carbon molecule. Malate will then release Carbon from the bundle sheath cells into the Calvin cycle in order for it to create ATP.
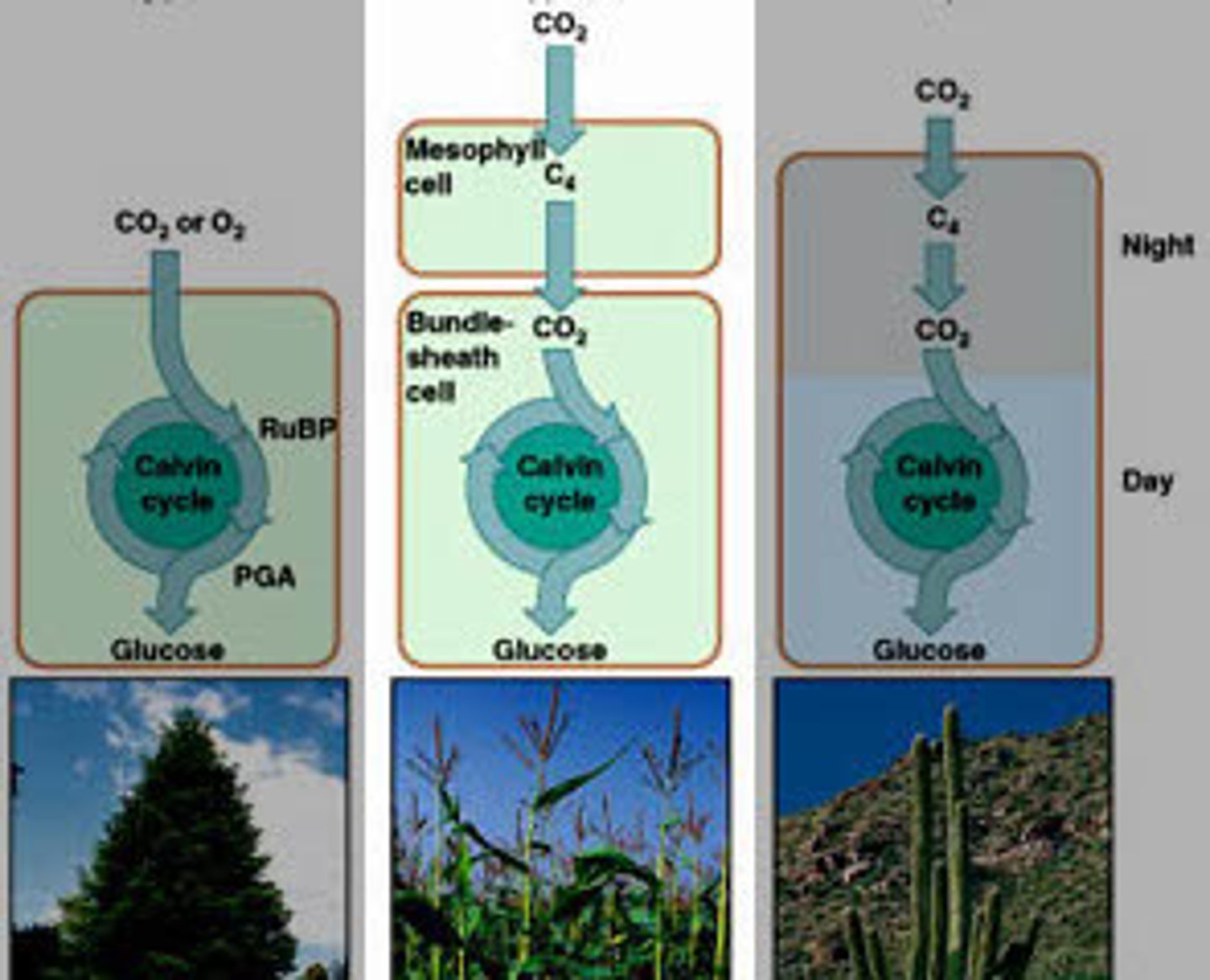
CAM plants
The stomata opens only at night in order to take in co2 and release O2, the co2 is stored as crassulaceam acid so it may be broken down during the day. Prevents excess water loss
Carbon cycle
CO2 is removed from the air by photosynthesizing organisms. The CO2 is used in the development of sugars during photosynthesis . These sugars which contain carbon are passed down through food chains and food webs through each trophic level. All organisms then releases carbon through cellular respiration replenishing the carbon in the air and starting the cycle over
Energetic hypothesis
We have short food chains due to the 10% rule of energy (90% of energy is lost as heat by metabolism of that organism only 10% of the energy is passed on to the next level)
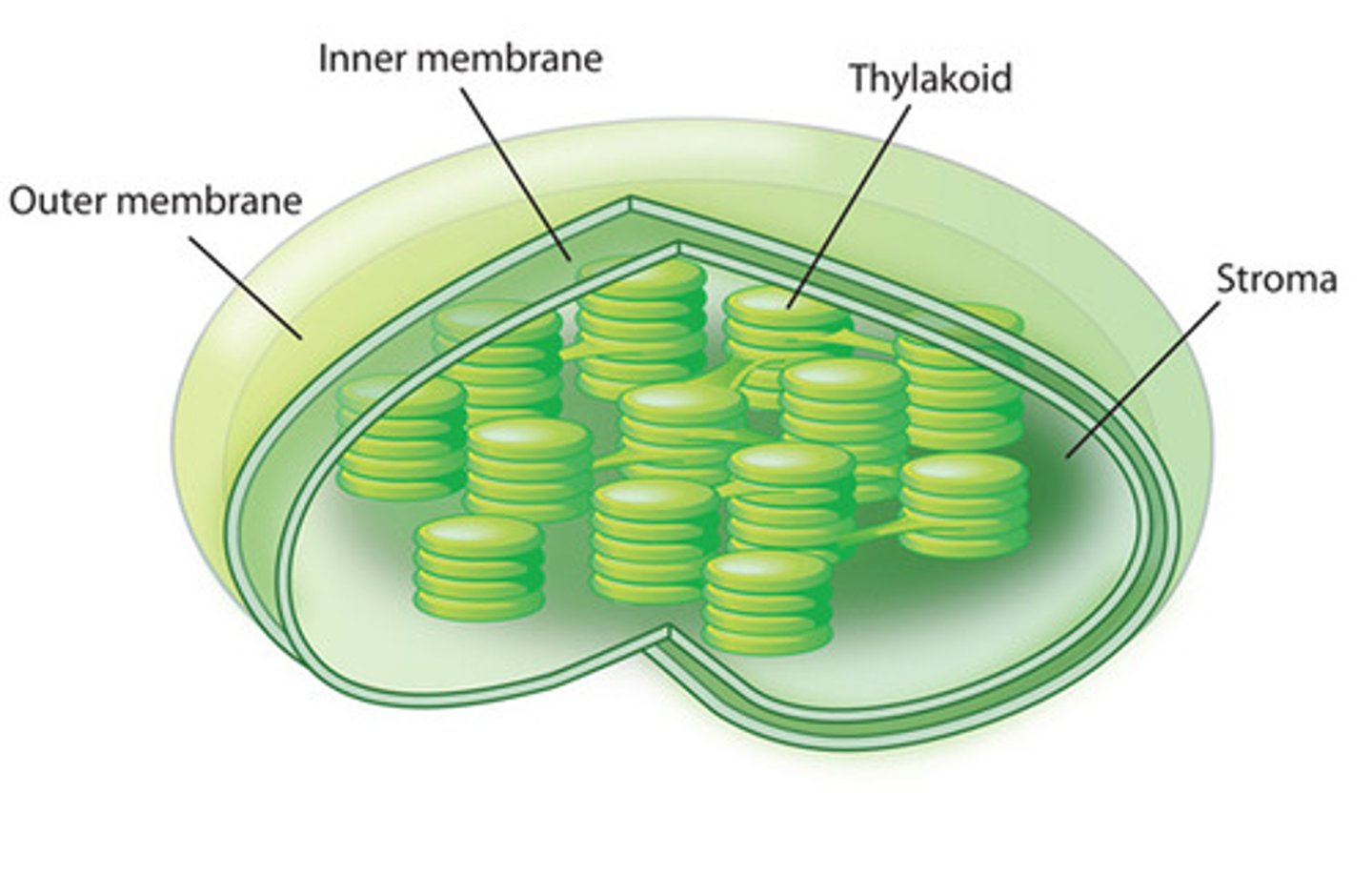
Stroma
The fluid of the chloroplast surrounding the thylakoid membrane;location of the Calvin Cycle
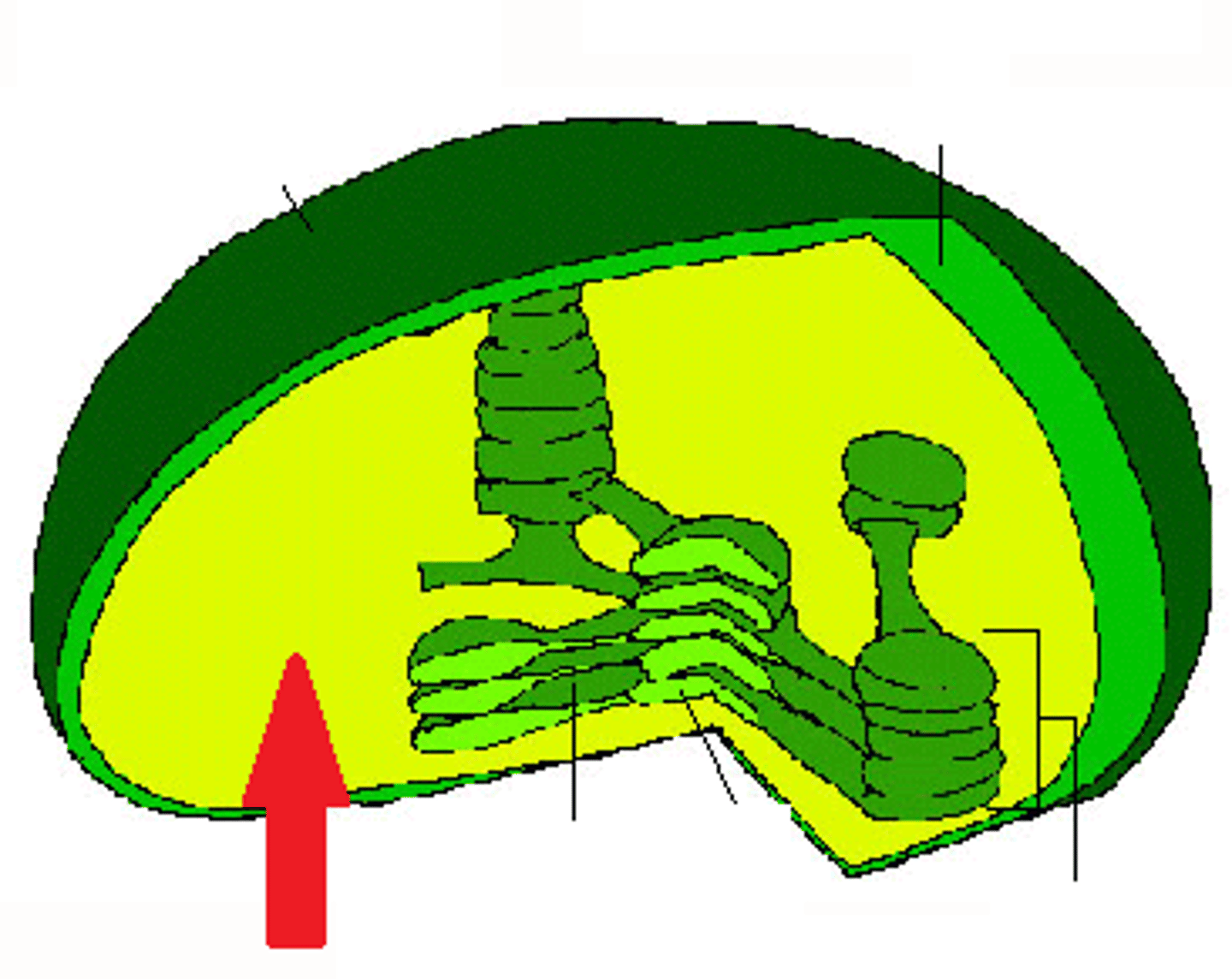
Grana (granum)
the stacks of thylakoids embedded in the stroma of a chloroplast.
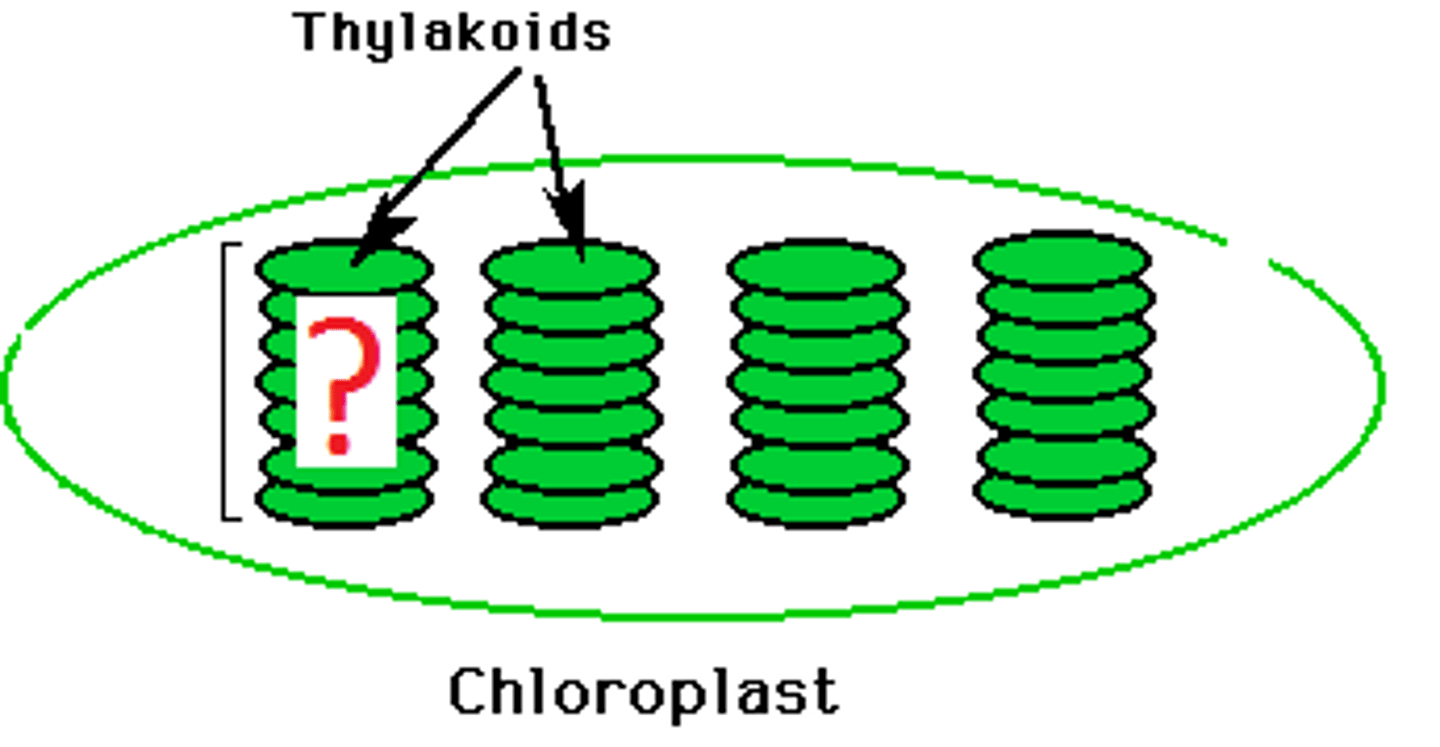
Thylakoid
The photosynthetic discs within a chloroplast that contains light-gathering pigment molecules and electron transport chains.