Organic Chemistry 6: Aldehydes and Ketones: Electrophilicity and Oxidation-Reduction
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
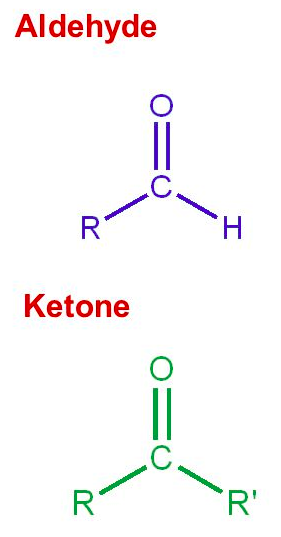
An aldehyde is a terminal functional group containing a/an [...] bonded to at least one [...]
carbonyl bonded to at least one hydrogen
[...] have the suffix -al
aldehydes
aldehydes take their name from their parent alkane chains
- the -e is removed from the end and is replaced with -al
[...] use the suffix -one and the prefixes oxo- or keto-
ketones
ketones take their name from their parent alkane chains
the ending -e is removed and replaced with -one
The aldehyde functional group is given the number [...] numbering location
1
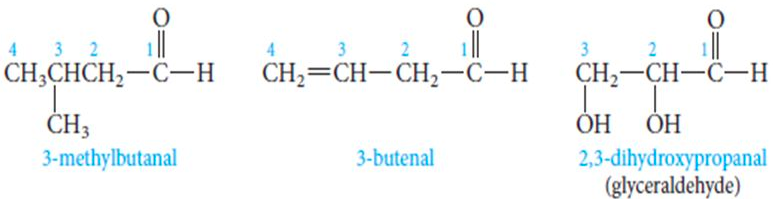
A ketone is an internal functional group containing a/an [...] bonded to two [...]
carbonyl bonded to two alkyl chains
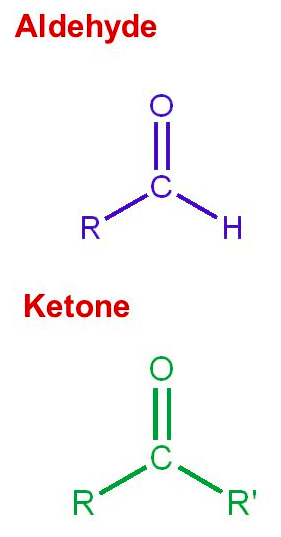
A [...] is a carbon-oxygen double bond
carbonyl group
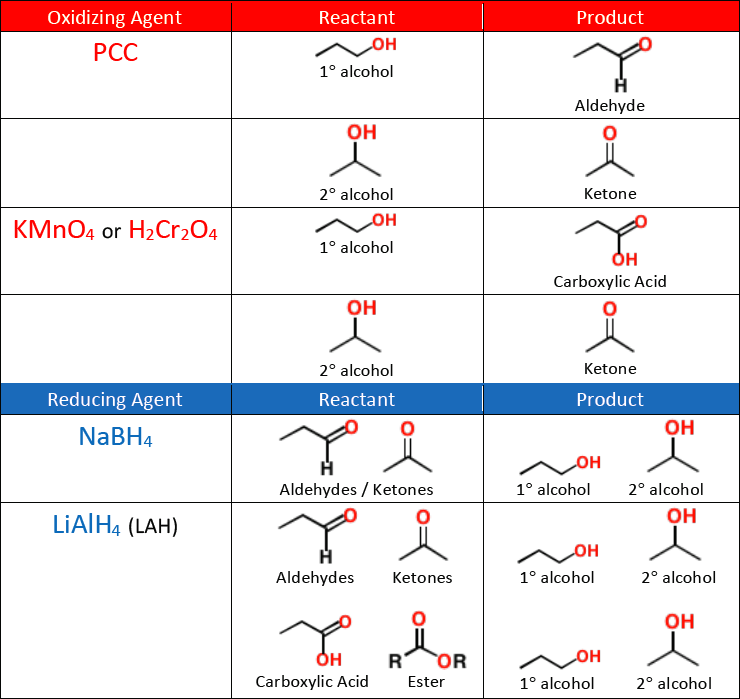
Aldehydes and ketones are synthesized from alcohols through [...]
oxidation
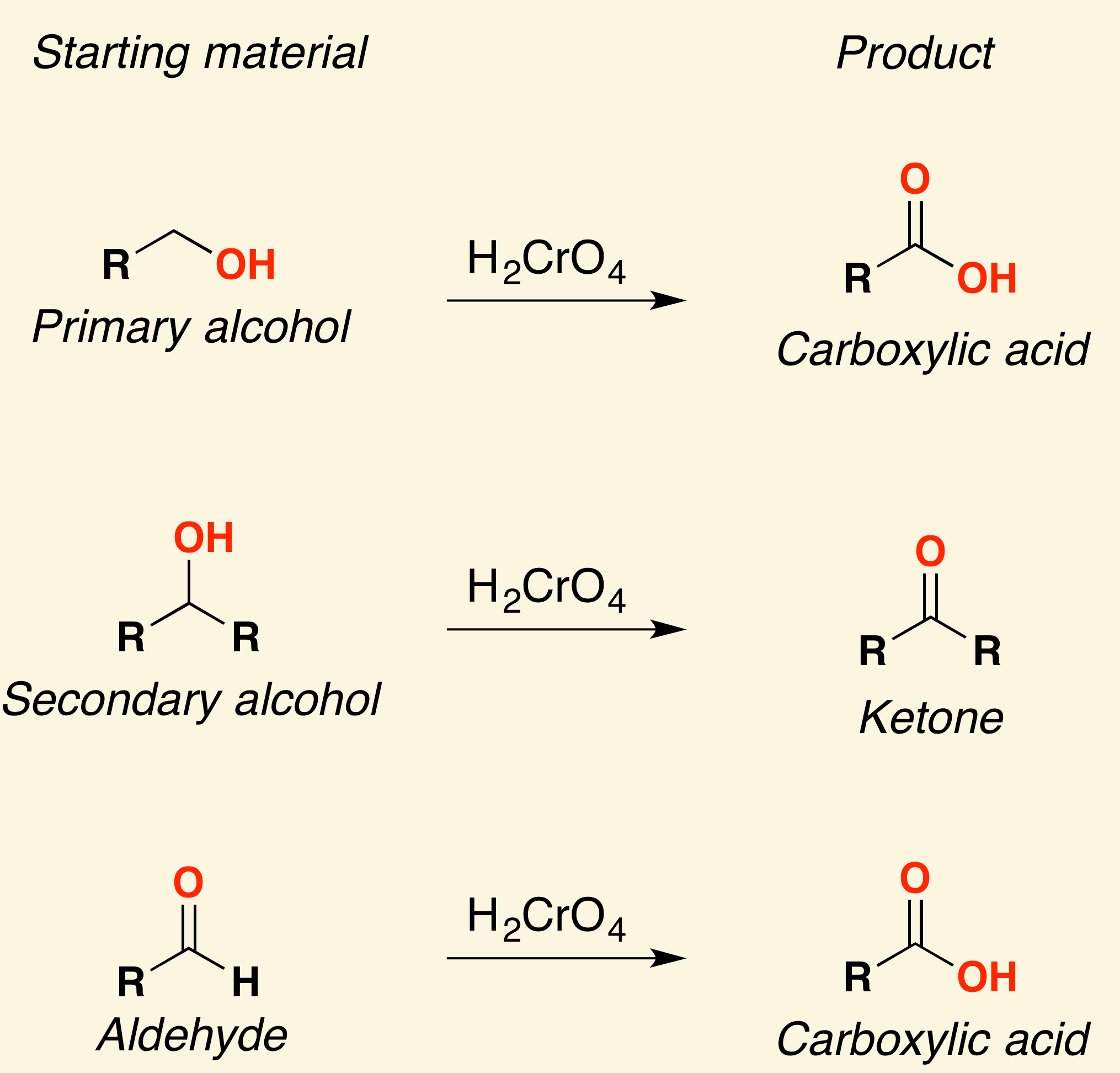
A weak oxidizing agent like [...] must be used for synthesizing aldehydes from alcohols, or else the reaction will continue oxidizing and form a carboxylic acid
pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
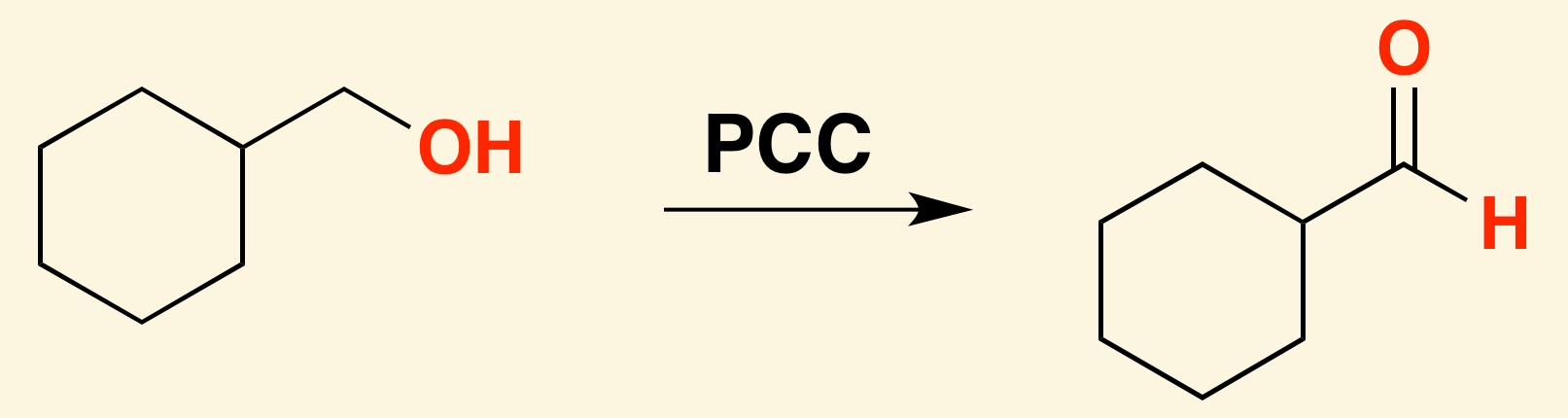
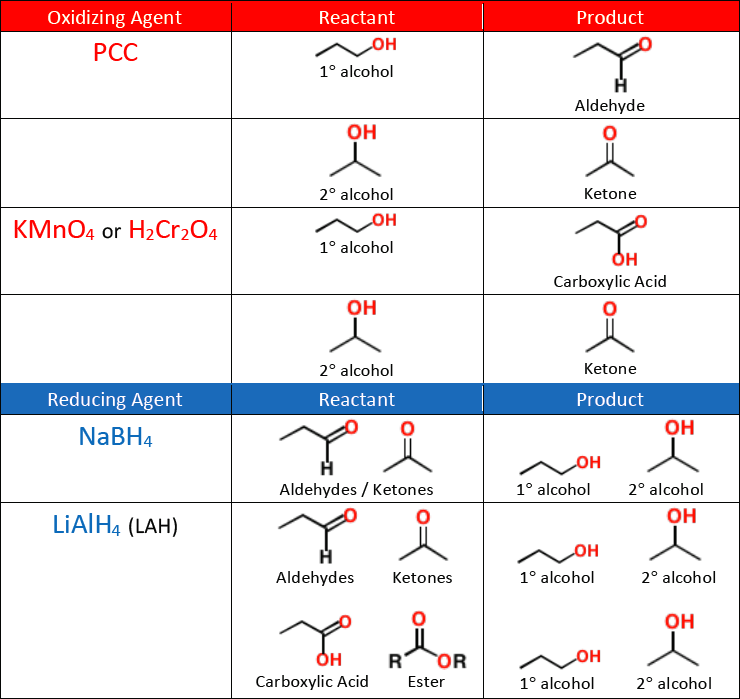
KMnO4 and H2Cr2O4 are [weak or strong] oxidizing agents
strong
they will oxidize an alcohol all the way into a ketone or carboxylic acid
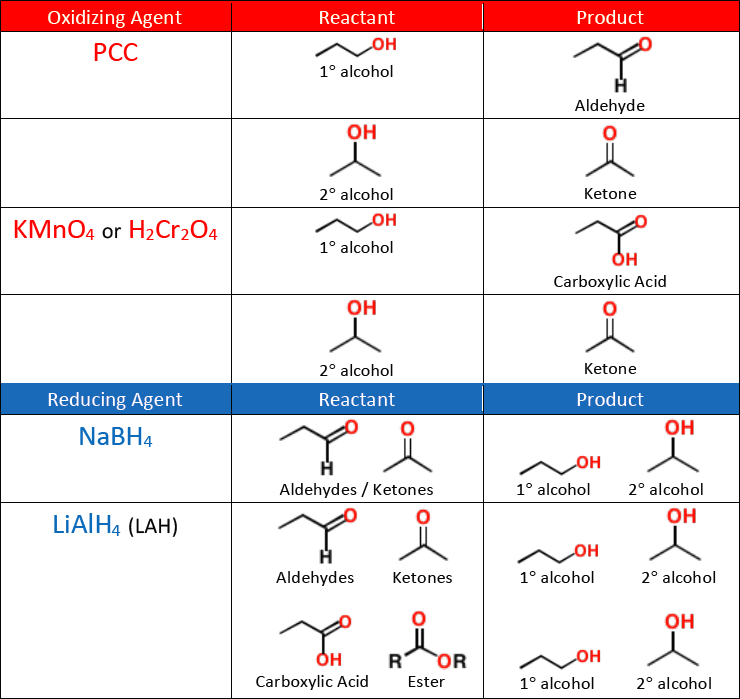
NaBH4 is a [weak or strong] reducing agent
weak
it will reduce an aldehyde or a ketone into an alcohol, but will not reduce a carboxylic acid or an ester
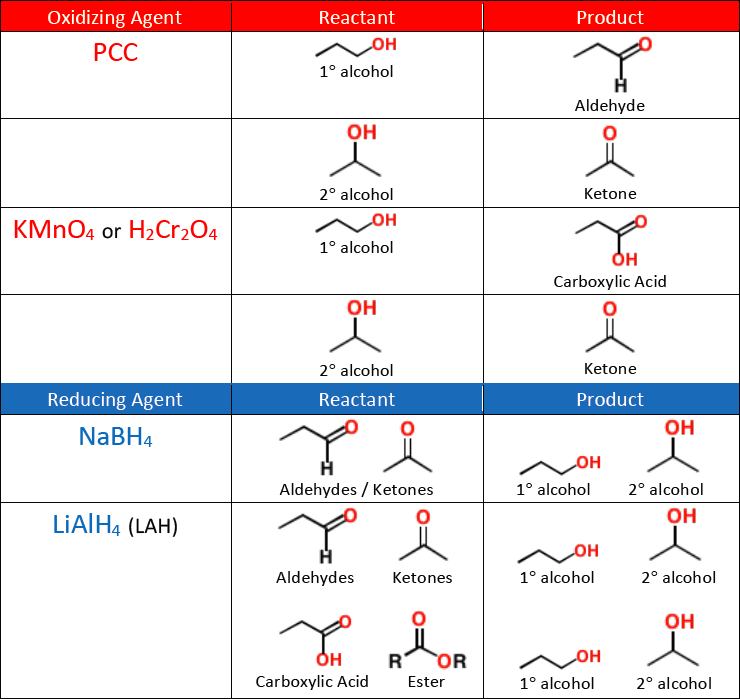
A strong reducing agent like [...] is needed to reduce a carboxylic acid or an ester into an alcohol
LiAlH4 (LAH)
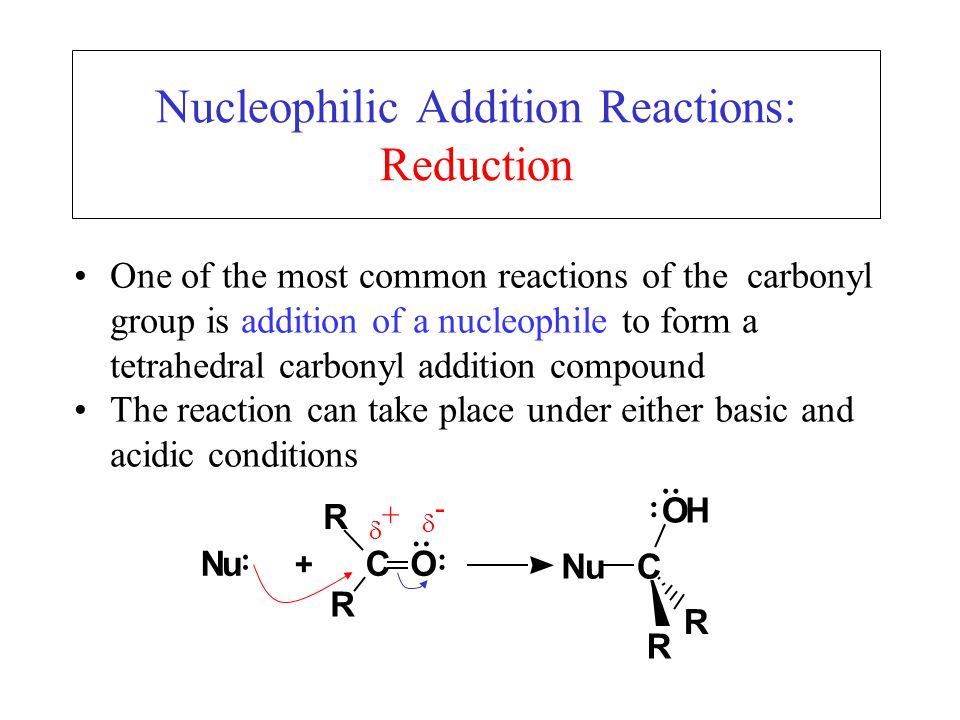
Nucleophilic addition reactions involve the attack of a nucleophile on the slightly positive [...] of a carbonyl group
carbon center
In a hydration reaction, water adds to a carbonyl and forms a/an [...]
geminal diol
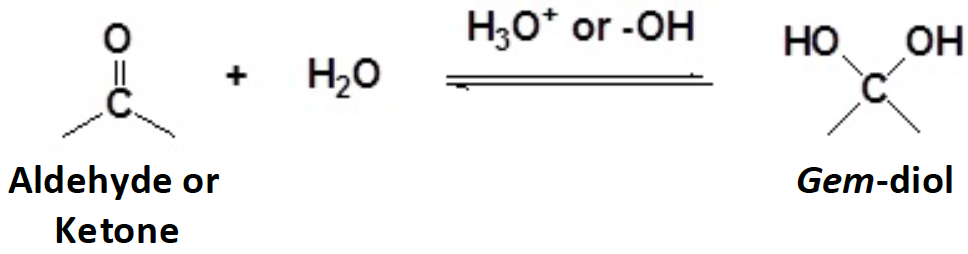
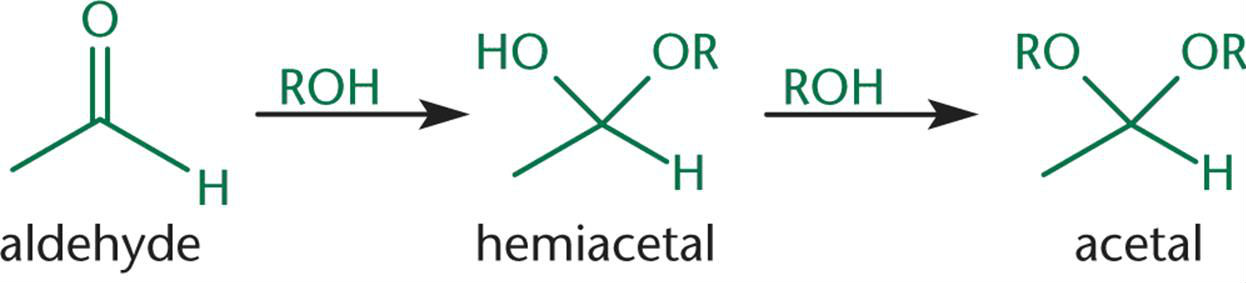
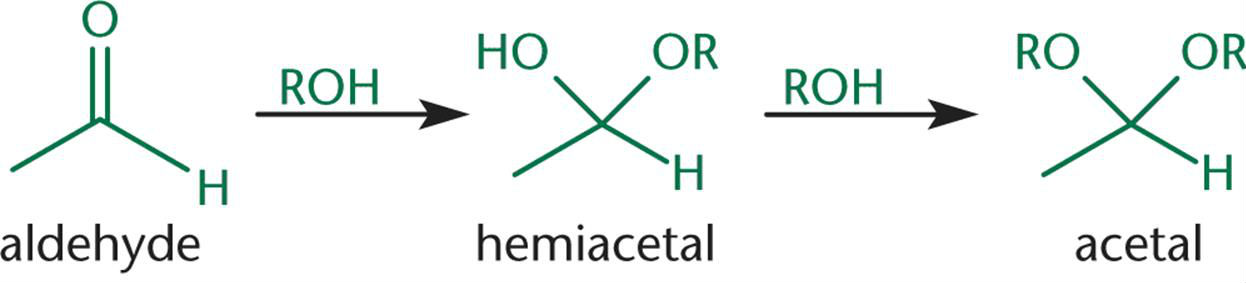
When one equivalent of alcohol reacts with an aldehyde, a/an [...] is formed
hemiacetal
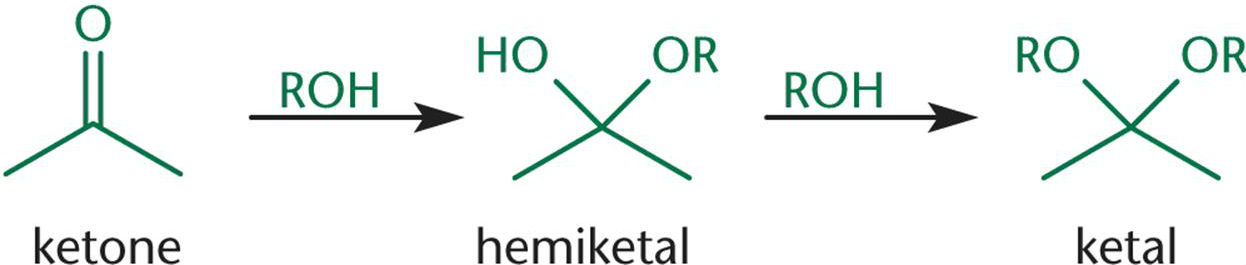
When one equivalent of alcohol reacts with a ketone, a/an [...] is formed
hemiketal
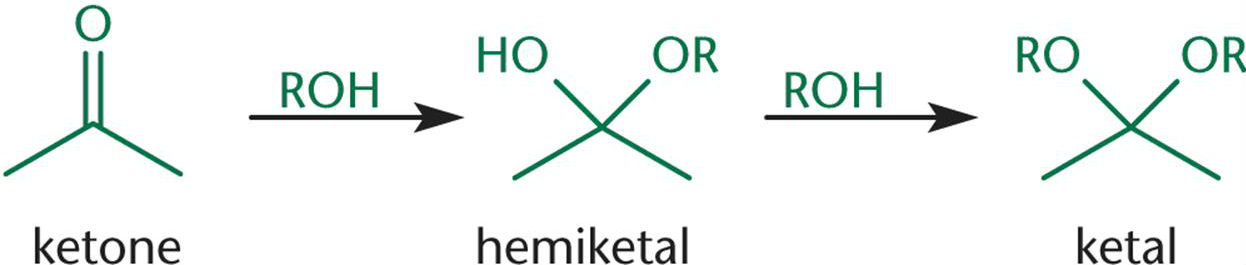
When two equivalents of alcohol react with an aldehyde, a/an[...]is formed
acetal
When two equivalents of alcohol react with a ketone, a/an [...] is formed
ketal
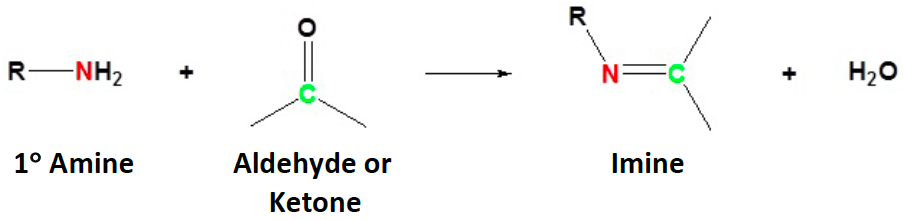
Nitrogen and nitrogen derivatives react with carbonyls to form [...]
imines
Imines can tautomerize to form [...]
enamines
tautomerization is a reaction which involves simple proton transfer
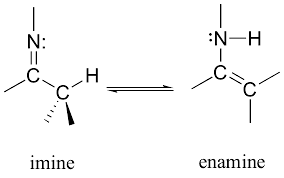
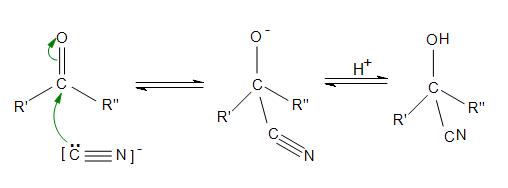
Hydrogen cyanide reacts with carbonyls to form [...]
cyanohydrins
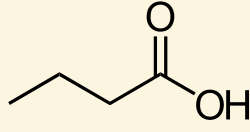
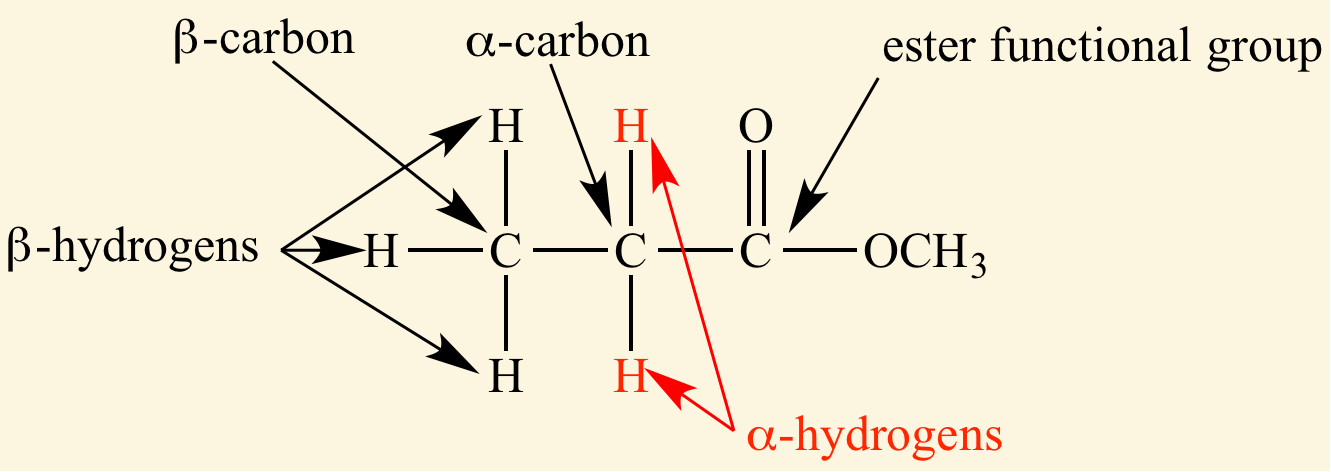
Identify the α-carbon
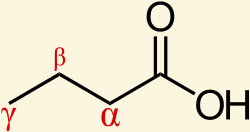
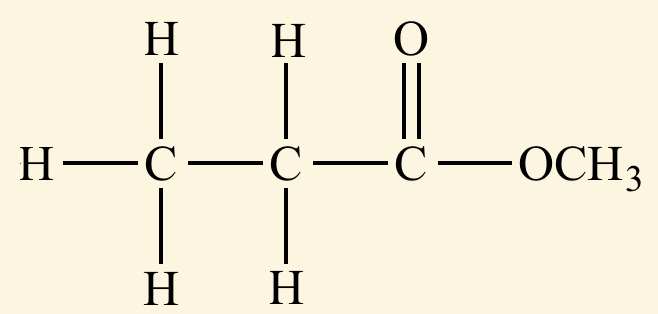
Identify the α-carbon
![<p><span>A/an </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> is formed when an </span><strong><u>α-hydrogen</u></strong><span> in the molecule of an </span><strong>aldehyde</strong><span> or a </span><strong>ketone</strong><span> is </span><strong><u>removed</u></strong></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f7750d89-4dc9-40e1-bbbf-2fe94d8f9a08.png)
A/an [...] is formed when an α-hydrogen in the molecule of an aldehyde or a ketone is removed
enolate anion
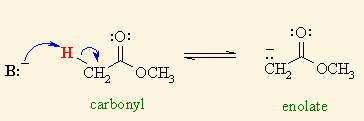
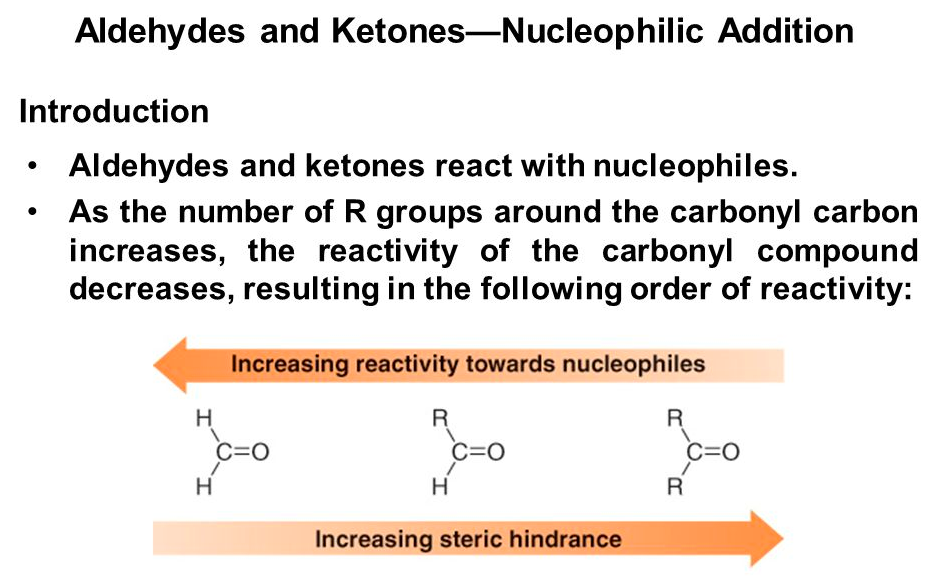
Aldehydes are usually [more or less] reactive toward nucleophilic substitutions than ketones because of both steric and electronic effects
more
![<p><span>This is the </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[keto or enol]</strong></span><span> form of acetone</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/367d35c4-b556-483a-aa4d-e275d17eb31f.png)
This is the [keto or enol] form of acetone
keto
keto form has a regular ketone or an aldehyde
enol form contains an alcohol
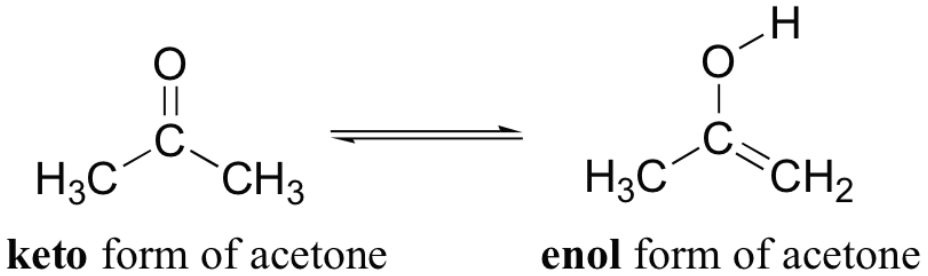
The term "enol" comes from the fact that it is a/an [...] that is also a/an [...]
alkene
alcohol
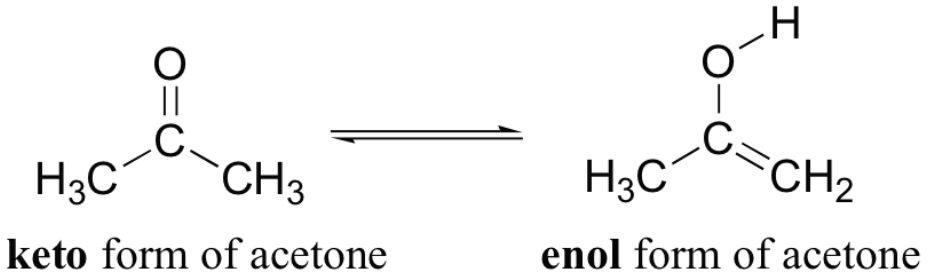
[...] refers to a chemical equilibrium between a keto form and an enol
keto-enol tautomerization
the keto and enol form are said to be tautomers of each other
they can be interconverted by moving a hydrogen and a double bond
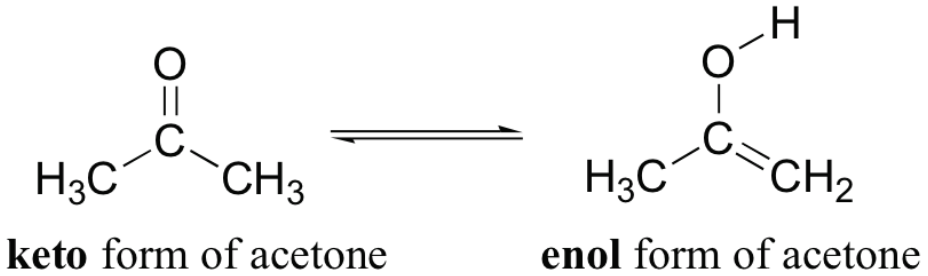
Keto form is much [more or less] common than enol form
more
can be attributed to the fact that a C+O double bond is significantly more stable (higher bond energy) then a C=C double bond
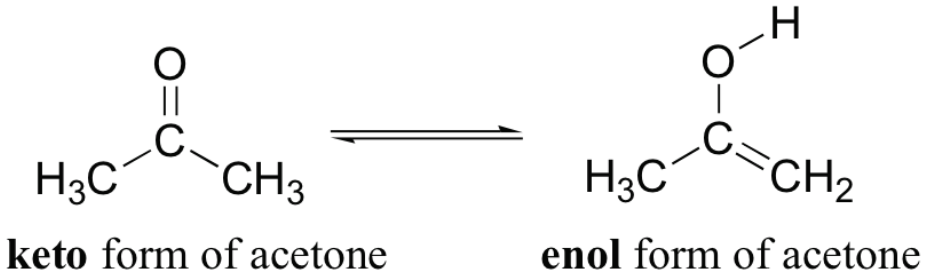
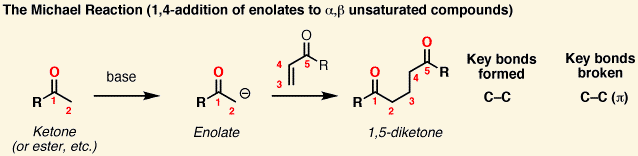
In a Michael addition, a/an [...] attacks a/an [...], creating a bond
enolate attacks a/an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl, creating a bond
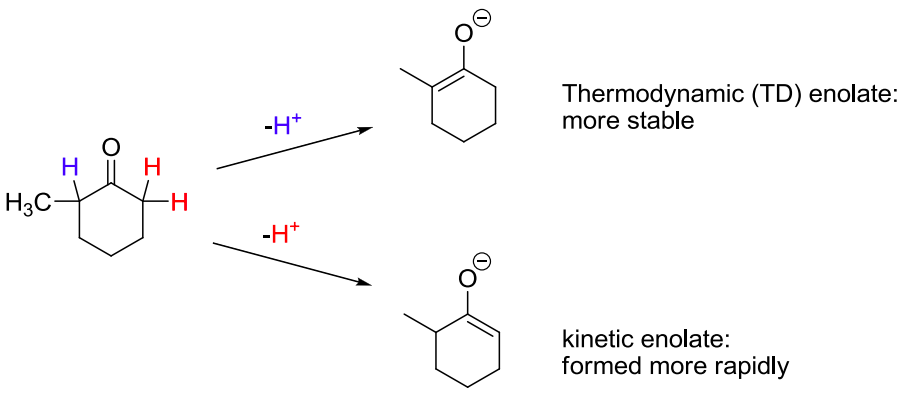
![<p><span>Removal of a proton from the</span><strong> less substituted</strong><span> (and less hindered) α-carbon gives the </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[kinetic or thermodynamic]</strong></span><span> enolate</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/83ffdb19-cb7f-4991-94e7-ce7c26704bd0.png)
Removal of a proton from the less substituted (and less hindered) α-carbon gives the [kinetic or thermodynamic] enolate
kinetic
the kinetic enolate has the less substituted C=C double bond
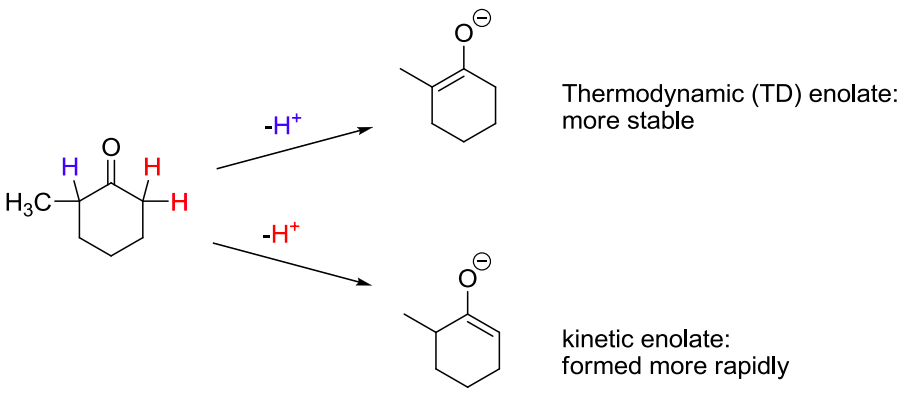
![<p><span>Removal of a proton from the </span><strong><u>more substituted</u></strong><span> (and more hindered) α-carbon gives the </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[kinetic or thermodynamic]</strong></span><span> enolate </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ce74dda5-df41-4fe2-ba37-16220b2d85f0.png)
Removal of a proton from the more substituted (and more hindered) α-carbon gives the [kinetic or thermodynamic] enolate
thermodynamic
the thermodynamic enolate has the more substituted C=C double bond
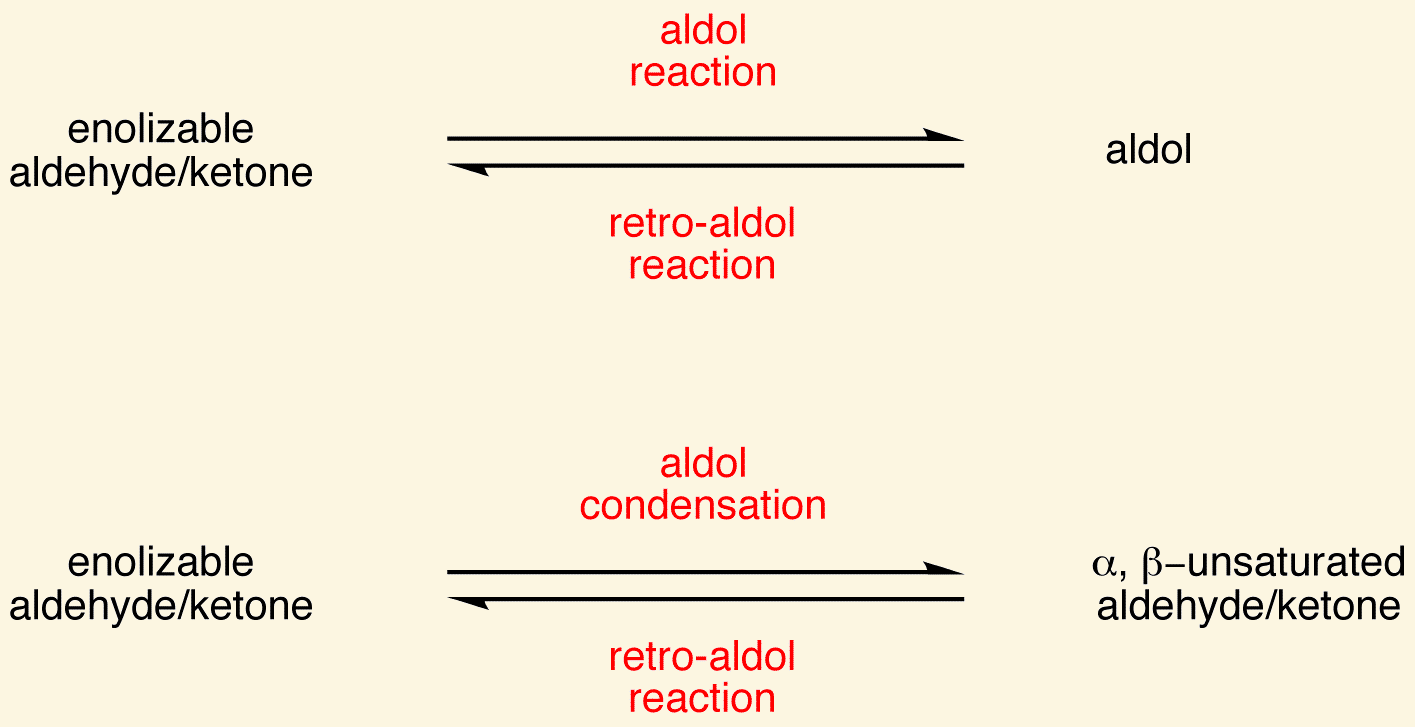
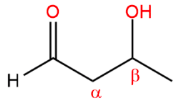
An aldol is a/an [...] plus a/an [...]
aldehyde plus a/an alcohol
Aldol addition is a powerful way to create a [...] bond
carbon-carbon
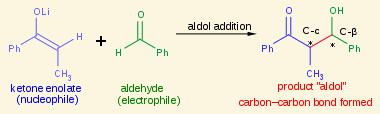
An aldol condensation starts with a/an [...] to create a/an [...]
aldol addition to create a/an aldol
then it undergoes a dehydration to give a conjugated enone (α,β-unsaturated carbonyl)
very common in the production of pharmaceuticals and refumes
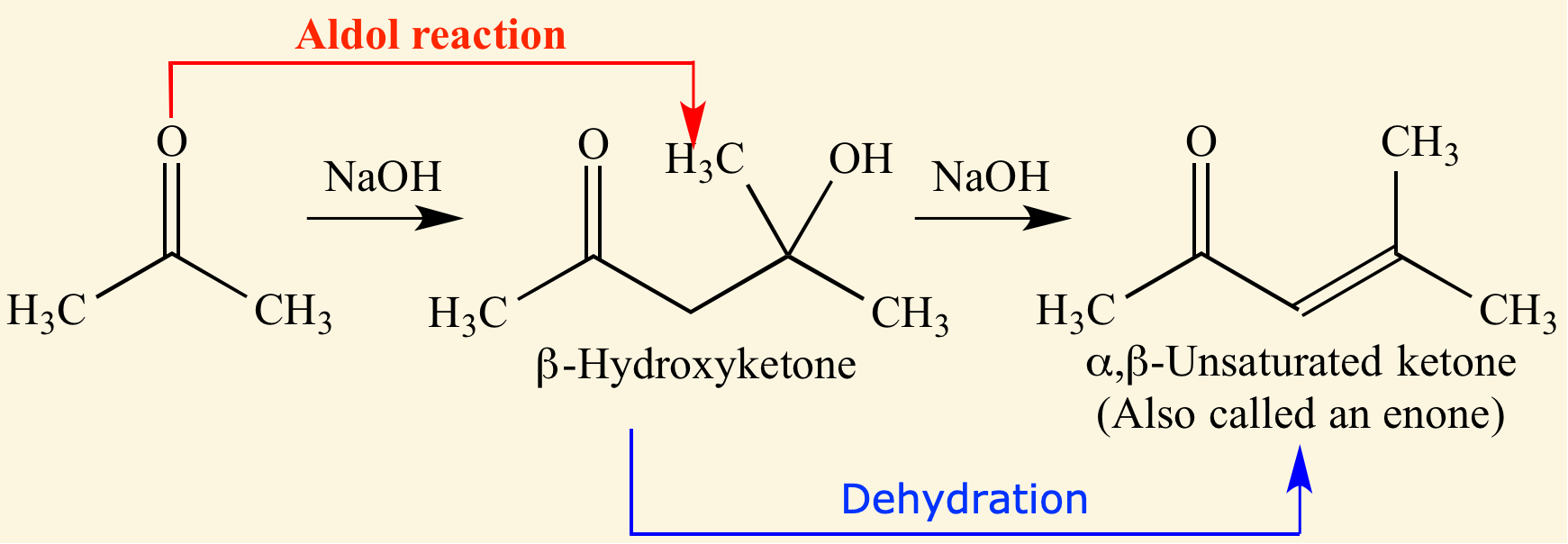
An aldol nucleophile is the [...] formed from the deprotonation of the α-carbon
nucleophile
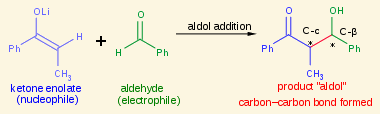
The aldol electrophile is a/an [...] or [...]
aldehyde or ketone
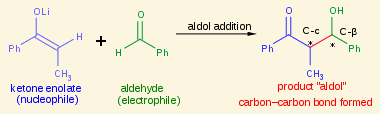
A/an [... reaction] is the reverse of an aldol reaction
reverse
the bond between the α- and β-carbon is cleaved Catalyzed by heat