Flexible Packaging ch4
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What is flexible packaging?
A flexible, pliable, non-rigid type of packaging.
What are the major advantages of flexible packaging?
Economy and efficient use of materials and space, resulting in a high product-package ratio.
What is an example of a flexible packaging product?
20 lbs carrot bag.
What are the primary disadvantages of flexible packaging?
No support to the load; can be difficult to open and reclose.
How can the lack of rigidity in flexible packaging be compensated?
By combining pouches with paperboard cartons, such as in breakfast cereal packages.
What are the various forms of flexible packaging?
Wraps, Bags, Pouches
What are the two types of wraps in flexible packaging?
Stretch type and Shrink type
How can bags be created in flexible packaging?
By extruding a tube and sealing the bottom or using web stock to seal the sides and bottom
What is the difference between bags and pouches in flexible packaging?
Bags are large bulk packages, while pouches are smaller packages.
What are examples of flexible packaging forms made from plastic?
Plastic films, Pouches, Retort pouch, Woven PP sacks, Flat Bottom Bag
What are examples of flexible packaging forms made from paper?
Paper sheets coated with plastic, Paper sheets coated with wax
What type of bags are considered flexible packaging?
Flat bottom bags, Plastic grocery sacks
What is one type of pouch?
Pillow Pouches
What is another type of pouch?
Three-side seal pouches
What is a third type of pouch?
Four-side seal pouches
What is the fourth type of pouch?
Stand-up pouches
What is a Pillow Pouch?
A type of packaging, such as potato chip bags.
What type of seal does a Pillow Pouch have at the back?
The back seal is either a 'fin' or 'lap' seal.
What seals are present in a Pillow Pouch?
A Pillow Pouch has top and bottom seals.
What is a characteristic feature of a Pillow Pouch?
It consists of a seam at the back.
What is a key characteristic of a Fin Seal?
The inner layer must be heat sealable.
How strong are the seams in a Fin Seal compared to a Lap Seal?
The seams in a Fin Seal are stronger than those in a Lap Seal.
What is a requirement for the materials used in a Fin Seal?
Extra material is required.
What is a key characteristic of a Lap Seal?
Both the inner and outer layers must be heat sealable.
How strong are the seams in a Lap Seal compared to a Fin Seal?
The seams in a Lap Seal are not as strong as those in a Fin Seal.
What is a requirement for the materials used in a Lap Seal?
Less material is required.
What is a three-side seal pouch?
A pouch with one side folded and the other three sides sealed.
What is the function of the folded side of a three-side seal pouch?
The folded side usually serves as the bottom of the pouch.
How are the sides of a three-side seal pouch sealed?
The remaining sides are heat sealed.
What material is needed for the inside of a three-side seal pouch?
Only the inside needs to be a heat-sealable material.
What are four-side seal pouches?
Pouches that seal all sides and may use different materials for the sides.
What is required for the inner layers of four-side seal pouches?
The inner layers must be heat-sealable.
What materials are commonly used for four-side seal pouches in the pharmaceutical industry?
Tyvek, which is made of woven fibers of HDPE, and clear plastics.
Why is Tyvek used in four-side seal pouches?
It is porous for gases and used for sterilization.
What is the advantage of using clear plastics in four-side seal pouches?
It allows the product to be visible.
Stand-up pouches
Designed to stand vertically when filled with the product. Special bottom design: Use of gussets
Display advantages compared to other styles of pouches
Types of gussets
side gussett
bottom/stand up gusset
Form Fill Seal (FFS) Machine
Horizontal FFSMachines
Vertical FFSMachines
inclined vs bucket conveyors
image
Net Weight
Vibrations are used for dispensing the product
Employ load cells
Flexible packaging in Industries
Form Fill Seal Machine (FFS)▪ Stock in roll form is bought▪ Pouch is made and filled with the product(Advantages: Comparatively less expensiveespecially for high volume applications)❖ Preformed pouches are bought▪ Comparatively less capital investment
What is the function of the forming collar in a Vertical Form Fill Seal Machine?
The forming collar shapes the flat film into a round film tube.
What do longitudinal sealing bars do in a Vertical Form Fill Seal Machine?
Longitudinal sealing bars seal the edges of the film tube.
What happens to the film in a Vertical Form Fill Seal Machine after it is weighed?
The film is pulled down.
What is the purpose of cross sealing jaws in a Vertical Form Fill Seal Machine?
Cross sealing jaws create the top and bottom seal.
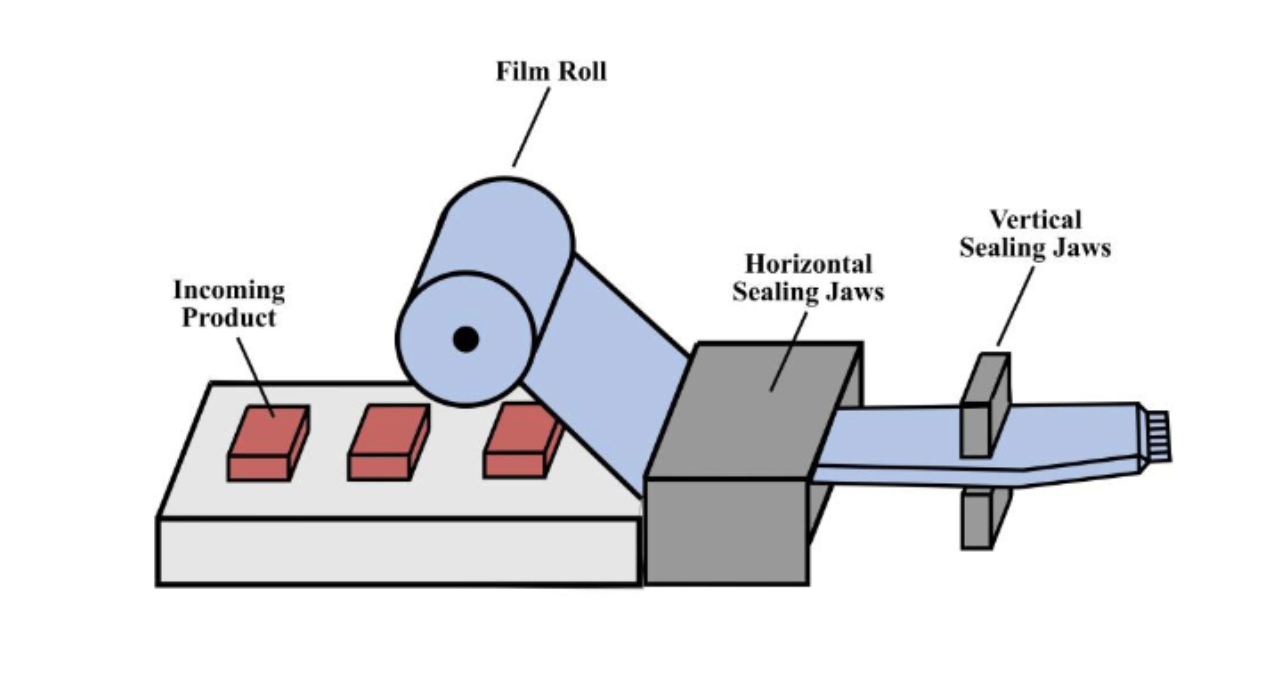
Horizontal Form Fill Seal Machine
Checkweigher
What are retort pouches designed for?
Retort pouches are designed to be filled, usually with food products, and then retorted (heat sterilized).
Do retort pouches require refrigeration?
No, retort pouches are shelf stable and do not require refrigeration.
What program started the use of retort packages in the U.S. military?
The use of retort packages started with the meals ready to eat (MRE) program.
What materials are used in the multilayer lamination of retort pouches?
The multilayer lamination of retort pouches includes an outside layer of polyester, a layer of aluminum foil, and an inside layer of polypropylene.
What is the purpose of the retorting process in food preservation?
To kill micro-organisms in canned food.
What type of steam is used in the retorting process?
Saturated steam.
What is the temperature range used during the retorting process?
113-132°C.
What is the benefit of the retorting process for food storage?
Increases shelf-stability and allows extended storage at ambient environment.
How is the food package prepared before the retorting process?
The food package is hermetically sealed.
What happens to the food and package during the retorting process?
They are heated together in a retort.
What is a Bag-in-Box packaging?
A sealed plastic bag inside a rigid outer container.
What types of products can Bag-in-Box packaging be used for?
It can be used for liquids and solids.
What materials can the outer container of Bag-in-Box packaging be made from?
Paperboard, corrugated, plastic, or wood.
Can Bag-in-Box packaging serve a dual purpose?
Yes, it can also serve as a dispenser.
What is the structure of the bag in Bag-in-Box packaging?
It can be a simple PE or a more complex structure.
Does Bag-in-Box packaging have a spout feature?
Yes, it may be spouted.
What is UV Coating also known as?
Spot varnish
What is the purpose of UV Coating in marketing?
To draw customers' attention
What type of material is UV Coating made from?
Thicker cross-linked polymer
What can happen to UV Coating if printed over a crease?
It can crack
What is photooxidation?
A process where fatty acids are prone to oxidation due to light and oxygen.
What are the key factors in photooxidation?
Light and oxygen.
What is a consequence of photooxidation in oils?
Loss of quality.
Can photooxidation be carcinogenic?
Yes, it can be carcinogenic.
What is an example of a mono-unsaturated acid?
Oleic acid.
What is a common practice to maintain product stability in packaging?
Filling pillow pouches with nitrogen (N2) gas.
Why is it critical to maintain package integrity?
To prevent photooxidation and maintain product quality.