OTM 507 Neuroplasticity 8.27.19
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Neuroplasticity
The ability of neurons to change their function, chemical profile (amount and types of neurotransmitters produced), and/or structure
This is why therapy is effective
- new learning
- relearning
- memory
Includes: habituation, experience-dependent plasticity, and cellular recovery after injury
Habituation
A decrease in response to a repeated, benign stimulus
- one of the simplest forms of neuroplasticity
- 'get used to it'
- allows for multitasking
In PT and OT, __ techniques are intended to decrease neural responses to a stimulus
- visual/vestibular disorders
- complex regional pain syndrome
- autism (tactile defensiveness)
Experience-Dependent Plasticity (learning and memory)
Involves persistent long-lasting changes in the strength of synapses between neurons and within neural networks
With repetition of a task, the number of active regions of the brain is reduced
- "learning curve"
- the brain initially works harder and when skill is learned less brain activity is required
Astrocytes contribute to this
- influence synapses through modulating neurotransmitter release and receptor ability at the postsynaptic membrane
- support neurons after injury (new synapse formation after injuries like stroke)
PT and OT important for facilitating new learning patterns through this mechanism
Cell Body
Injury to the __ __ of a neuron results in cell death
Axonal inury
Damage is usually on a cellular level
- the __ swells and breaks and the cell body dies
No __ regeneration in the CNS, growth inhibiting factors released
Sprouting may occur
- collateral: neighboring axons branch to reinnervate
- regenerative: axon and target cell are damaged, so the axon branches to a new target
Exercise after injury stimulates regeneration
Recovery occurs when:
- edema(fluid buildup) /ischemia is reduced
- other receptor sites become more sensitive
- increased neurotransmitter released through intact __ branches
- silent, or unused, synapses are now used
- neurogenesis through stem cells
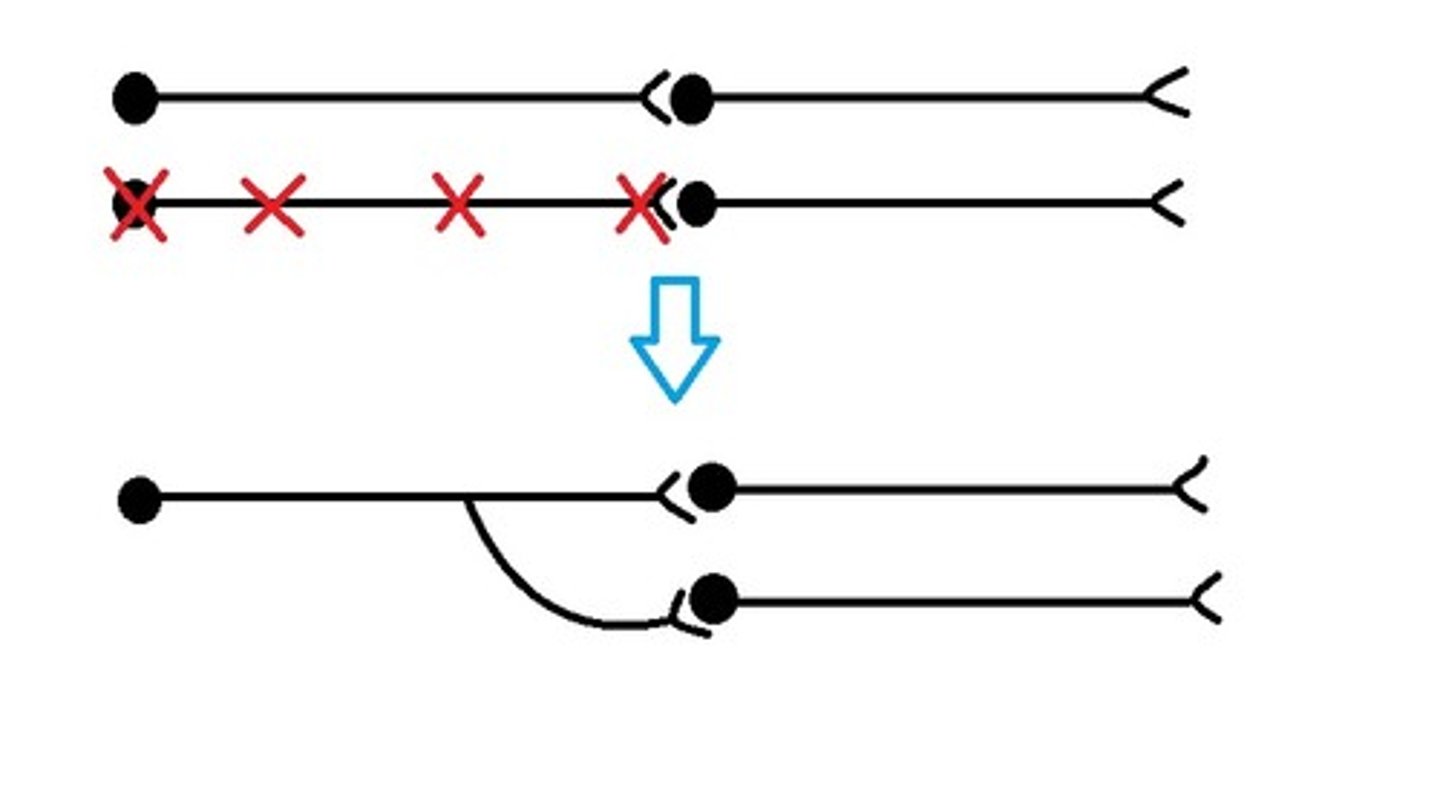
Collateral Sprouting (Axonal injury)
Which type of sprouting is occurring?
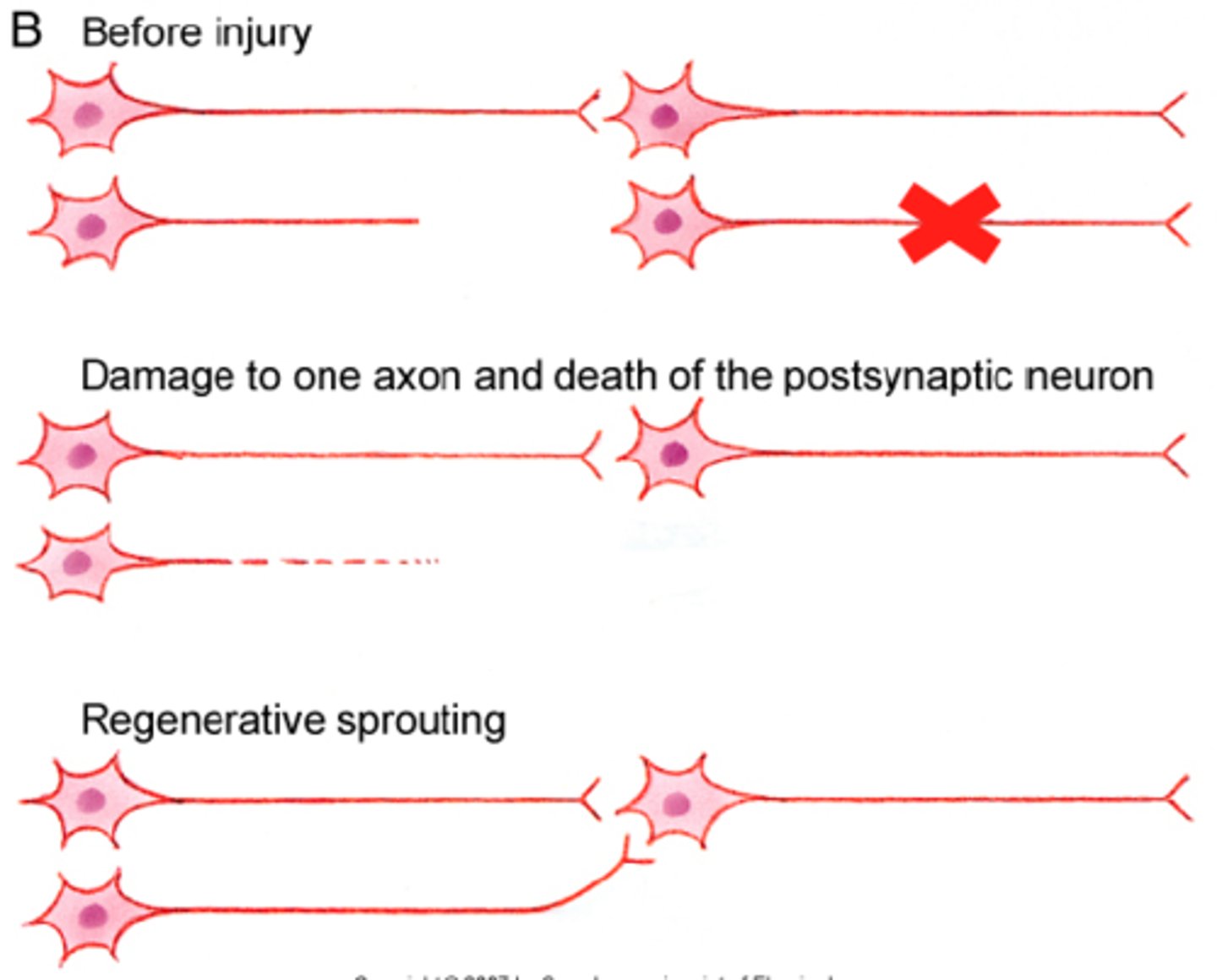
Regenerative Sprouting (Axonal injury)
Which type of sprouting is occurring?
Cortical areas
Routinely adjust the way they process info
Also have the ability to develop new functions
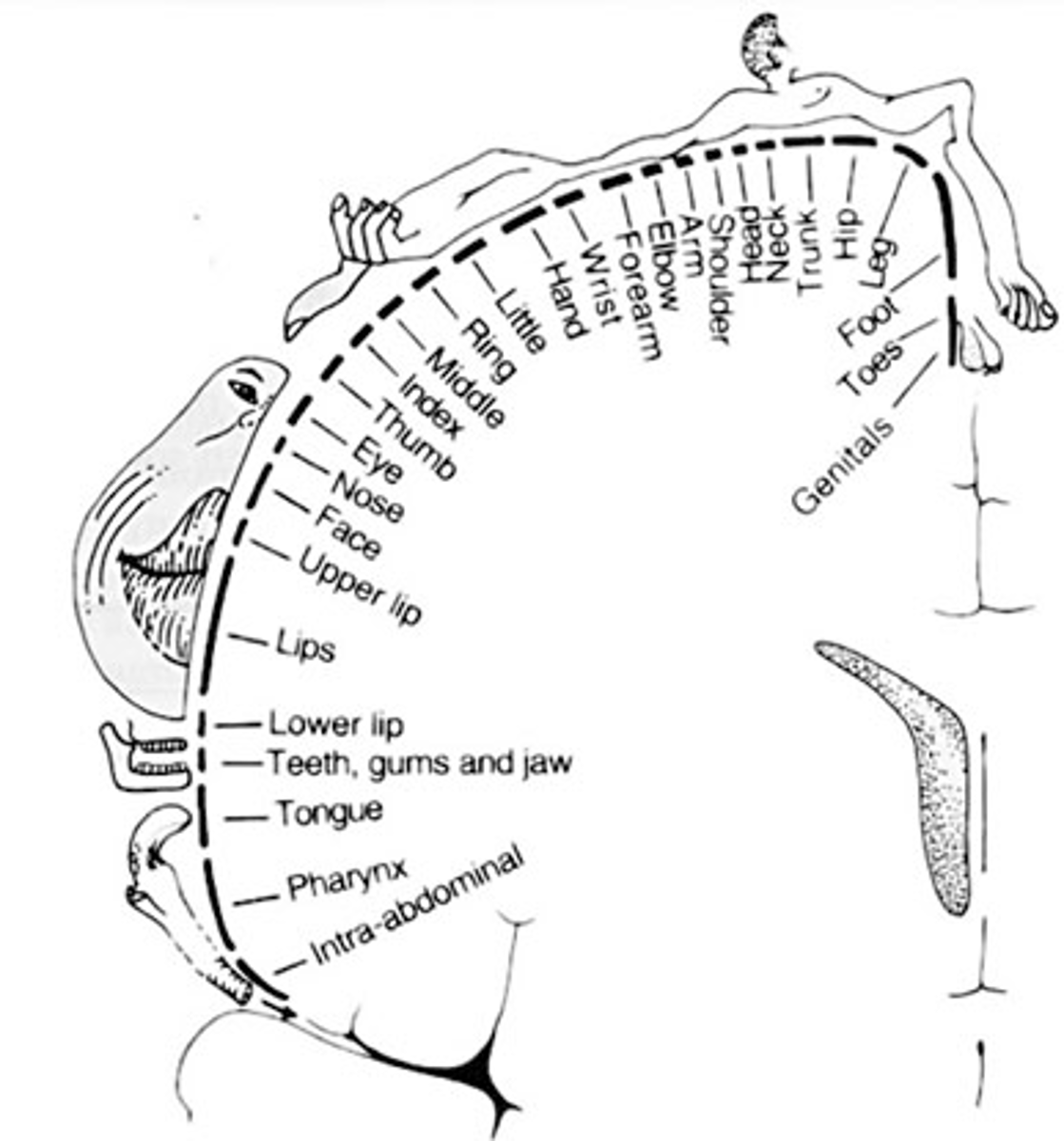
Cortical Map
Cortical representation areas; functional areas of the brain that respond to sensory or muscles stimulation
- if a person regularly performs a skilled motor task the cortical representation of that area will be enlarged
Reorganization of cerebral cortex
Brain activity shifts surrounding areas
- explains stroke recovery and why other senses are more sensitive when others are delinquent
Metabolic effects (of brain injury)
Following brain injury
Neurons are deprived of oxygen for a prolonged period of time and die without regenerating
- drugs are used to minimize detrimental effects
no (metabolic effects of brain injury)
Do any drugs cure stroke, TBI, or neurodegenerative diseases?
Rehabilitation
This is influenced by the intensity and timing of rehab
- early rehabilitation is necessary for improved outcomes
- avoid bed rest (other functioning areas of brain may suffer)
Task specific training for normal motor patterns
Constraint induced movement therapy
Often a treatment in stroke. The unaffected limb is constrained
- forcing the affected limb to function
- allows for functional reorganization
Avoid intense __ __ __ __ initially after injury because it can increase damage