2.2 The Production Possibilities Frontier and Social Choices
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Which of the following cannot be determined by using a production possibilities curve?
what combination of outputs maximizes benefits for society
how much less of one output must be produced if more of another output is produced
whether a combination of outputs can be produced
how much output can be produced from a given level of inputs
what combination of outputs maximizes benefits for society
Explanation: The production possibilities curve shows all possible combinations that can be produced, but does not indicate which one maximizes society's benefits.
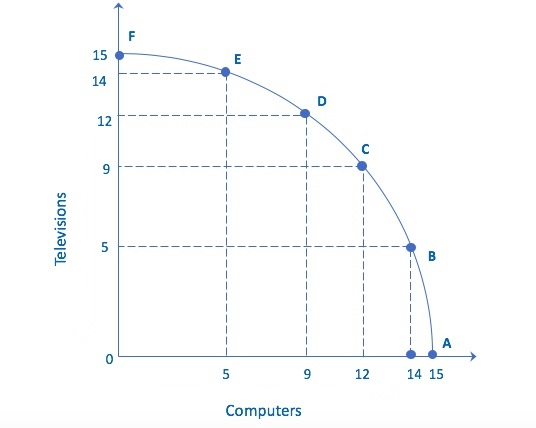
What is the opportunity cost of increasing the number of computers from 14 to 15?
5 televisions
Explanations: If we move from point B to point A, we increase production of computers by one unit. Because the slope is relatively steep here, the number of televisions decreases by 5, going from 5 units produced to 0 units produced. At this point all of the resources are being directed to production of computers.

The PPF shows the tradeoff between sugarcane and orange production. What is the opportunity cost if the production of sugarcane increases from point C to point E?
20 tons of oranages (thousands)
Explanation: With an increase in sugarcane from point C to point E (40 to 62 thousand tons of sugarcane), the production of oranges moves from 20 to 0 tons of oranges, thus the opportunity cost is 20 thousand tons of oranges.
True or false?
The law of diminishing returns states that as more variable inputs are added to production, the productivity of these inputs increases.
false
Explanation: The law of diminishing returns establishes a negative relationship between input resources and productivity. As more variable inputs are added to a fixed resource in production, the productivity of these variable inputs decreases
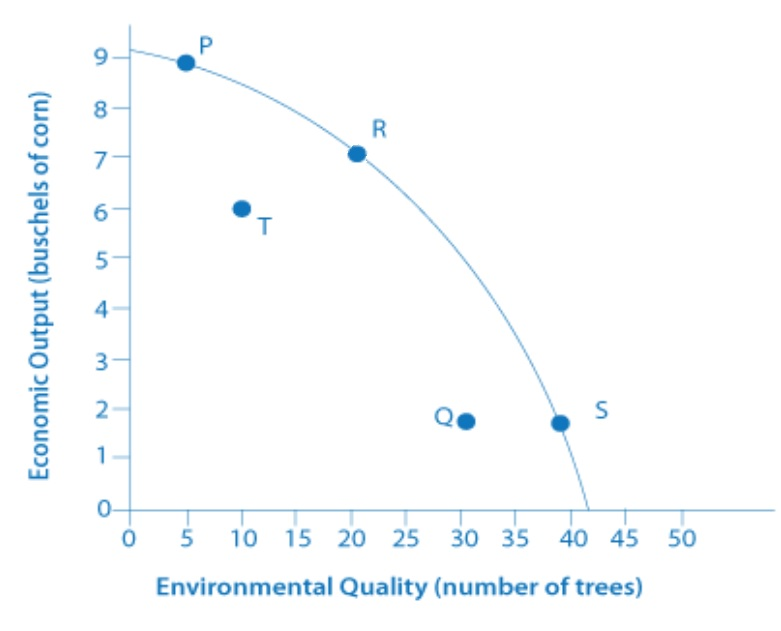
According to this production possibilities frontier, why does P demonstrate productive efficiency?
It uses all of society's available resources.
It is more desired by society than any other attainable point.
It results in the fewest number of trees.
It is one of the many points that it is possible for society to attain.
It uses all of society's available resources.
Explanation: P demonstrates productive efficiency because it is on the production possibilities frontier, which signals that this country is using all of its available resources.
Comparative advantage is a measure of _____.
profitability
advantage due to specialization
opportunity cost maximization
absolute efficiency in production
advantage due to specialization
Explanation: A country has a comparative advantage when it can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country. Therefore, comparative advantage is a measure of the advantages due to specialization in production.
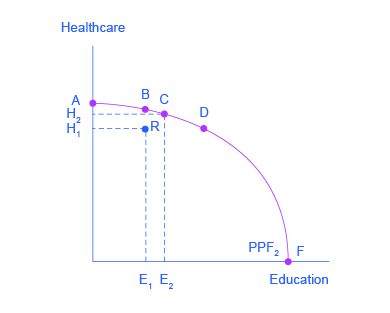
Which points in the graph below demonstrate productive efficiency?
A, F, and R, only
B, C, and D, only
R, D, and F, only
A, B, C, D, and F, only
A, B, C, D, and F, only
Explanation: Points demonstrate productive efficiency if they are located on, rather than within, the PPF. This includes the intercept points.
The law of diminishing returns states that the marginal productivity of additional resources employed_________________.
is constant
can be high initially but will eventually decrease
is always increasing
may decrease initially but will eventually increase
can be high initially but will eventually decrease
Explanation: The law of diminishing returns states that as additional increments of resources are added, the marginal benefit will decline. The reason for the decline, as pertains to the PPF curve, is that as resources are switched from the production of one good to another, the specialization of resources is an obstacle. Consider moving an engineer from designing robots to making food processors. The engineer may not be as productive working in areas he/she does not have as much experience or knowledge in.
A production possibilities frontier ___________________
is the same as a budget constraint.
is best used when a specific budget is provided.
demonstrates the constraints that society faces in production.
is a straight line.
demonstrates the constraints that society faces in production.
Explanation: A PPF demonstrates the constraints that society faces in production, while the budget constraint is best used when a specific budget and choices are presented.

True or False?
The opportunity cost of increasing production from 20 cameras to 30 cameras is 4 mobile phones.
true
Explanation: In order to move from point B to point C, the economy must move resources from producing mobile phones to cameras. In order to produce 10 more cameras they must move from 7 to 3 mobile phones, thus the the opportunity cost is 4 mobile phones.
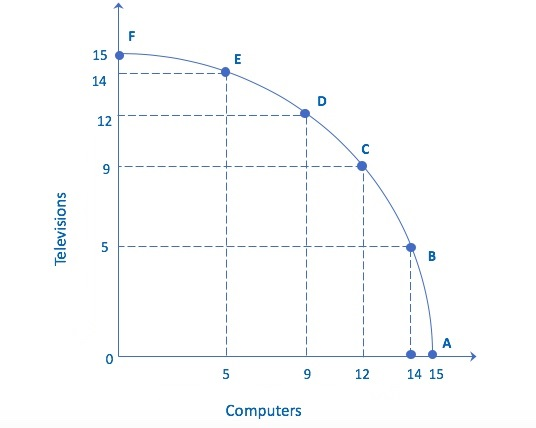
What is the opportunity cost of increasing the production of televisions from point C to point E?
7 computers
Explanation: If the number of televisions increase, resources must be reallocated from computer production to television production. If we increase the production of televisions by 5 TVs, we reduce the production of computers by 7. Therefore, the opportunity cost of moving from point C to E is 7 computers.
The opportunity cost of producing one bushel of wheat in Canada is equal to 1/2 computer. The opportunity cost of producing one bushel of wheat in the U.S. is 2 computers. If these two countries specialize according to comparative advantage and then trade with each other, which of the following is an expected outcome?
The U.S. will import wheat and export computers.
Canada will import wheat and export computers.
The U.S. will export computers and wheat.
Canada will choose not to trade with the U.S. since it can produce both products at lower costs.
The U.S. will import wheat and export computers.
Explanation: Because Canada can produce wheat at a lower opportunity cost than the U.S., it has a comparative advantage in producing wheat. Therefore, the U.S. will produce and export computers instead of wheat and import the wheat it needs from Canada.
Which scenarios would be best represented by a budget constraint? There are two correct answers.
The government of planet Mars is deciding whether it should focus on producing more spaceships or growing food in orbit.
Finn has an allowance to spend on his dog. He must decide whether to spend the allowance on new doggy treats for $10 per bag or new water balls for $3 per ball.
Narnia has resources that it can direct towards a combination of healthcare and education.
Sam has received a $500 scholarship that he can use for books and tuition.
Finn has an allowance to spend on his dog. He must decide whether to spend the allowance on new doggy treats for $10 per bag or new water balls for $3 per ball.
Sam has received a $500 scholarship that he can use for books and tuition.
Explanation: A production possibilities frontier shows the combinations of products that society can produce with its limited resources and reflects diminishing marginal returns, whereas a budget constraint shows the combinations of two goods that an individual can afford to purchase given their budget and the prices of those goods.
Finn can spend his allowance on new doggy treats for $10 per bag or new water balls for $3 per ball. Sam has received a $500 scholarship that he can use for books and tuition. Both of these scenarios reflect a consumption decision for an individual based on a budget and fixed prices of two goods, so budget constraints would best represent these situations.
The other two situations represent production decisions for entire societies given limited resources; these would be best represented by production possibilities frontiers.