Conformity
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
The theory was developed by
Hebert Kelman (1958)
Social influence theory explains how
individuals behaviors and attitudes are affected by the presence or actions of others
A types of social influence
obedience and conformity
social influences processes/ types of conformity
compliance, identification, internalisation
Effect
change in behaviour, change in behaviour and attitudes, change in behaviours and attitudes
Obedience is a type of social influence: definition:
changing a behaviour in response to a direct order by an authority figure
Conformity is a type of social influence: definition:
changing a behaviour in response to group norms or expectations of others
influencing agent
a person or group that exerts pressure over other’ attitudes and behaviours
compliance is a social influence process: defintion:
to change a behaviour and/or attitude in response to a direct request or command of another person or group
identification is a social influence process: definition:
to accept and integrate the attitude and behaviours of others into their own value systems
Compliance is due to
gaining award or approval from influencing agent, avoiding punishment or disapproval from influencing agen
For compliance, the individual
may not accept the beliefs of the influencing agent (only change in behaviour) and usually when being observed or have been identified
compliance the influencing agent normally has power so give examples
boss at work, teach, slowing down when seeing a speed camera-even if someone doesn’t approved of speed limits, not talking during a boring lesson to avoid getting detention from teacher, laughing at a friends joke even if you think its not funny
identification occurs due to
Establishing or sustaining a satisfying relationship (for mutual exchange, or to be more similar)
, Occurs when the desired relationship is attractive or satisfying, Conforming behaviour ends when relationship’s purpose stops
identification influencing agent
is an individual/group whose qualities, behaviours or beliefs are deemed desrirable
Influencing agent is an individual/group whose qualities, behaviours or beliefs are deemed desirable
a teacher grading your subject, coach, fitness trainer, lawyer, “Queen Bee” in a friendship group
Students cooperating with a teacher to get better grades or resources
A person helping another student in hopes of becoming their friend to climb a “social ladder”
A person joins run club and eats healthy around gym friends, but doesn’t at home
Why does internalisation occur?
Because the attitudes and behaviours are in line with the individual’s own values.
How does someone come to internalise attitudes and behaviours?
They come to see them as correct and valid.
What often leads to internalisation?
Repeated exposure to social norms, persuasion, or role models.
What is the effect of internalisation on behaviour?
It causes lasting change, even when the influencing agent is no longer present.
Why might someone follow a doctor’s health advice?
Because they believe health is important and trust the doctor’s expertise.
Why might someone use a sunscreen brand promoted by a TikTok influencer?
Because they value skincare and want to prevent aging, aligning with the influencer’s advice.
Give examples of influencing agents.
Religious leaders, doctors, social media influencers
Social influence theory
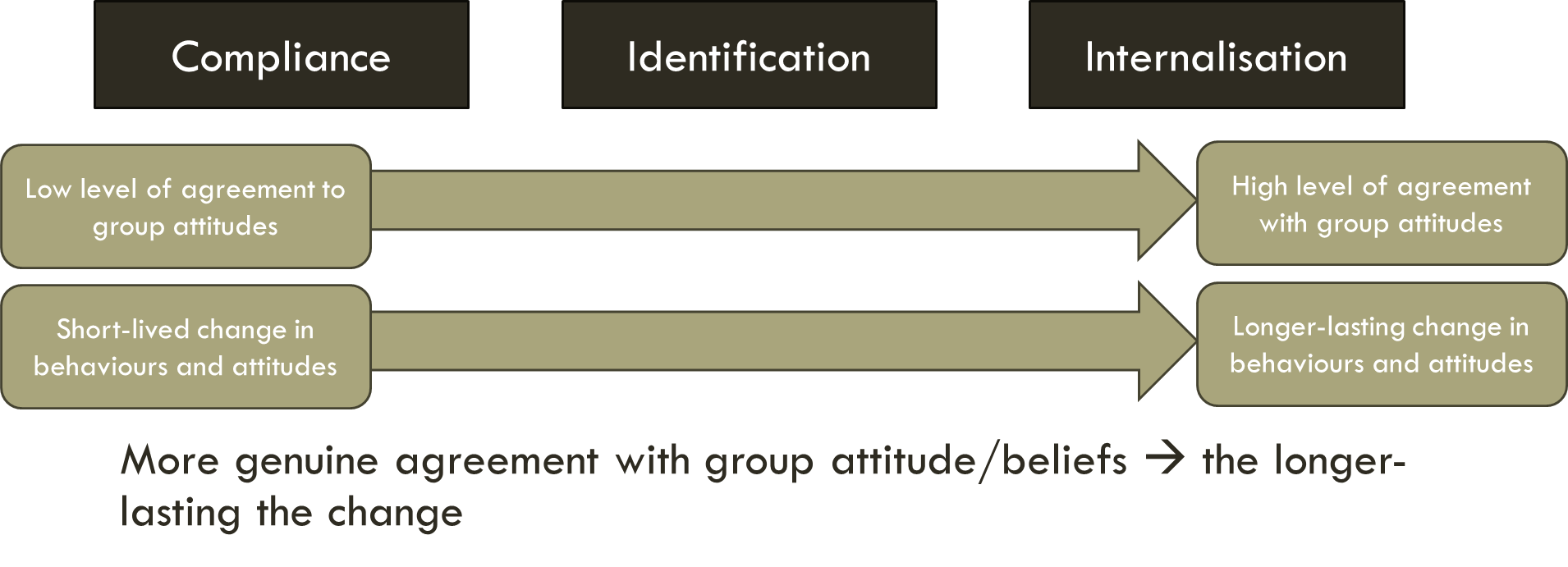
What determines how long-lasting a change in behaviour will be?
The more genuine the agreement with group attitudes or beliefs, the longer-lasting the change.
Low level of agreement to group attitudes —>
high level of agreement with group attitudes
Short lived changes in behaviours and attitudes —>
longer-lasting change in behaviorus and attitudes