ch. 13 bioenergetics
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what is metabolism?
the sum of the chemical changes that convert nutrients into energy and the chemically complex products of the cells
what are the two types of metabolic pathways? explain the difference between them
anabolism deals with synthetic rxns/making small mol to bigger ones. This is endergonic, req input of energy and usually involves reduction. Catabolism deals with degradative rxns/breaking down larger mol to smaller. Exergonic/energy is released, involves oxidation.
anabolic pathways ___ and catabolic pathways____
anabolic pathways diverge and catabolic pathways converge
why is ATP the primary energy currency of the cell?
it is used to drive reactions because ATP hydrolysis is energetically favorable since energy is released by cutting off 1 phosphate → inorganic P + ADP (ex of transferase)
what drives conformation changes? WHY?
ATP hydrolysis because all 3 phosphate groups are negatively charged and the charges repel each other and there’s greater res. stabilization of ADP and Pi
the addition of a phosphate to a molecule does what to its potential energy?
it increases
give an example of a coupled rxn
1st step of glycolysis: glucose + pi → glucose-6-phosphate is unfavorable and ATP → ADP is favorable. Overall delta G is negative.
what is thermodynamics? What is the equation?
the study of the transformation of energy. deltaG=deltaH-TdeltaS
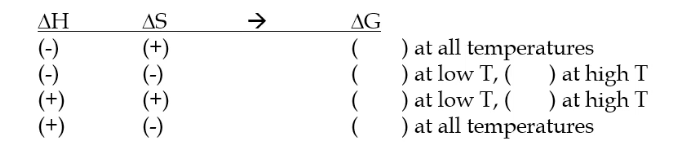
fill this out
what is standard free energy change (deltaG’o)? what does this tell us?
it is the free energy at standard conditions (1.0M, pH 7, 25Cel, 1atm) ; informs us which direction and how far a given rxn must go to reach eq. and it is an unchanging physical constant for a given rxn.
what does delta G depend on?
pH, temperature, conc. of products and reactants
what does at equilibrium mean for delta G?
it means that delta G is =0 and neither direction of the rxn is favored. DeltaG=-RTlnKeq
consider the rxn of creatine and atp, what is used when muscle cells run out of ATP? ATP___ and ADP ___
phosphocreatine is used to make ATP when cells run out of it. ATP increases and ADP decreases. RXN favors going to the left and delta G is more negative and ATP is made.
what are the 4 key processes in carbohydrate metabolism?
glycolysis
glycogenesis
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis
what is glycolysis? what are its products?
converting glucose to 2 pyruvate molecules and a small amt of energy using 10 reactions (same in every cell but rates differ). Contains 2 phases: converting glucose 6 to 2 3C sugars (G-3-P) then producing 2 pyruvates. Products: ATP, NADH, Pyruvate
where does glycolysis occur? Does this req oxygen? Does this occur in every cell?
in the cytosol, glycolysis does not req. oxygen, occurs in almost every living cell