CNS protective coverings, vascular distribution, PNS, cranial nerves 9-12
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
the PNS is made up of these 2 kind of nerves
afferent and efferent
afferent nerve means…
carrying toward
efferent nerves mean…
carrying away from
the two main subsystems of the PNS are
the somatic and autonomic systems
the somatic nervous system does what?
controls voluntary movements and relays sensory info to the CNS
the autonomic nervous system does what?
regulates involuntary functions like heart rate or homeostasis
the spinal cord has how many pairs of nerves?
31
gray matter is composed of…
cell bodies and terminals
white matter is composed of…
axons
what is the dorsal gray matter in the spinal cord?
a butterfly or H-shaped appearance in the center of the spinal cord
what is the ventral gray matter in the spinal cord?
cell bodies of lower motor neurons
what is the intermediate gray matter in the spinal cord?
cell bodies of autonomic neurons and interneurons
what do the dorsal columns of white matter in the spinal cord do?
carry sensory info up to the brain
what do the lateral columns of white matter in the spinal cord do?
contain both sensory and motor tracts that travel up and down the spinal cord
what do the ventral columns of white matter in the spinal cord do?
contain motor tracts that carry commands from the brain to the spinal cord
what are the key cranial nerves for speech?
5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12
what are lower motor neurons?
associated with cranial nerves. located in brainstem and spinal cord. these neurons send signals directly to the muscles
what are upper motor neurons?
they originate in the brain (primarily the motor cortex) and travel down to the spinal cord or brainstem, where they synapse with lower motor neurons
what are the 4 components of physiology of the PNS?
planning, transmission, muscle activation, movement execution
name 4 speech/swallowing disorders that can occur if the PNS is damaged
dysarthria, apraxia, aphasia, dysphagia
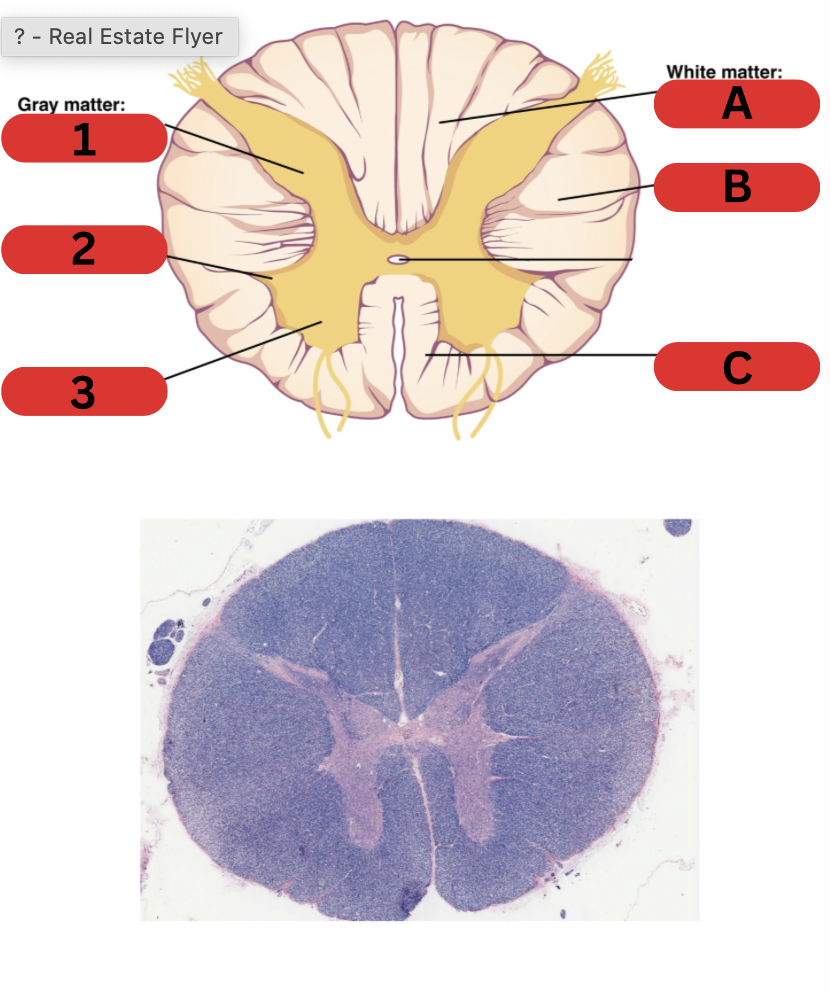
label
1: dorsal (posterior) horn
2: lateral horn
3: ventral (anterior) horn
A: dorsal column
B: lateral column
C: ventral column
what are the meninges?
3 layers that cover and protect the brain
what are the 3 layers of the meninges called?
dura mater, arachnoid, pia mater
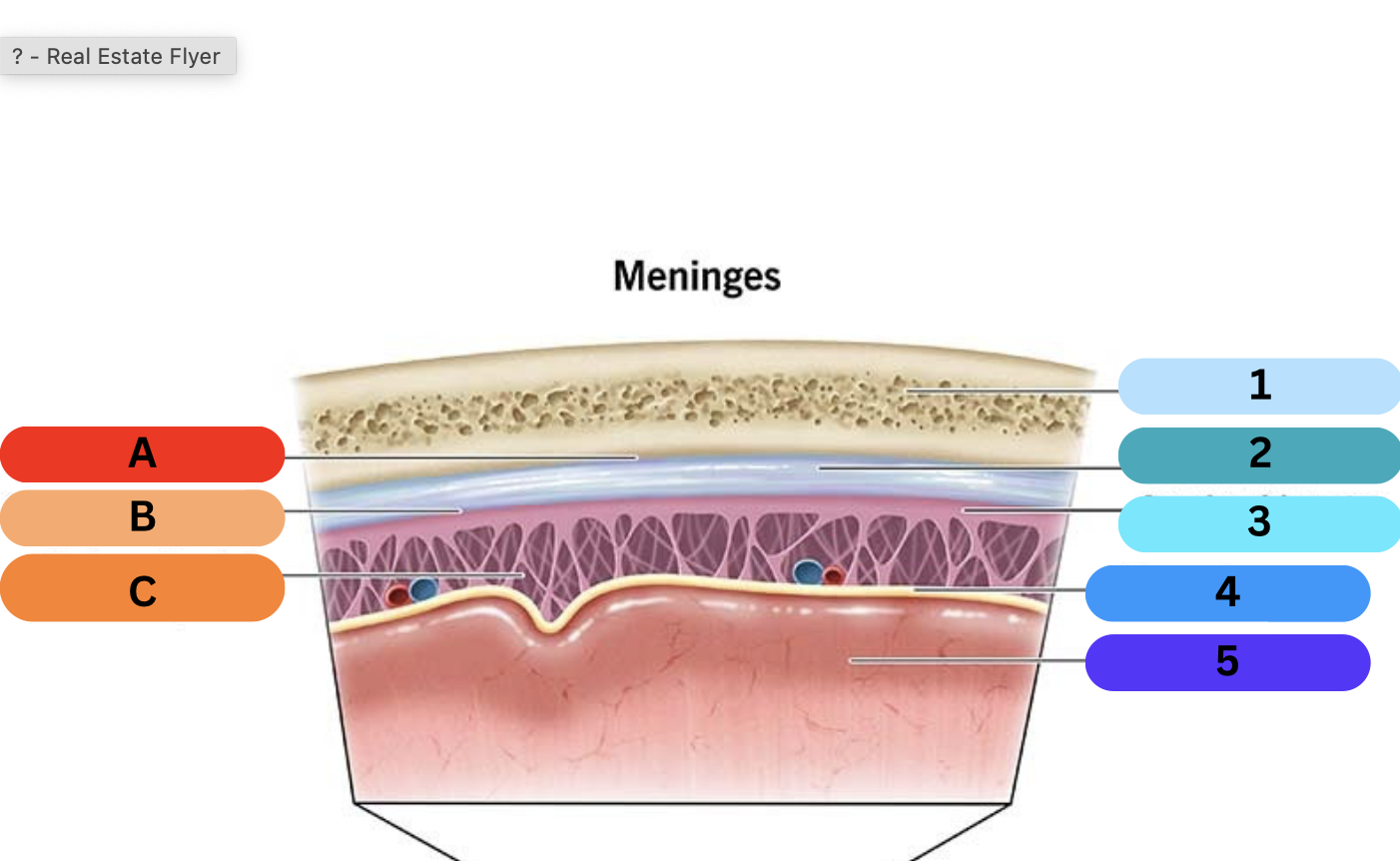
label
1: skull
2: dura mater
3: arachnoid
4: pia mater
5: brain
A: epidural space
B: subdural space
C: subarachnoid space
what is the ventricular system?
a network of fluid filled spaces in the brain. includes lateral ventricles, 3rd ventricle, and 4th ventricle
what are ventricles filled with? what is it? is it affected by disease?
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) = a mechanical buffer for protection of the CNS. consistency/pressure changes during pathologic conditions
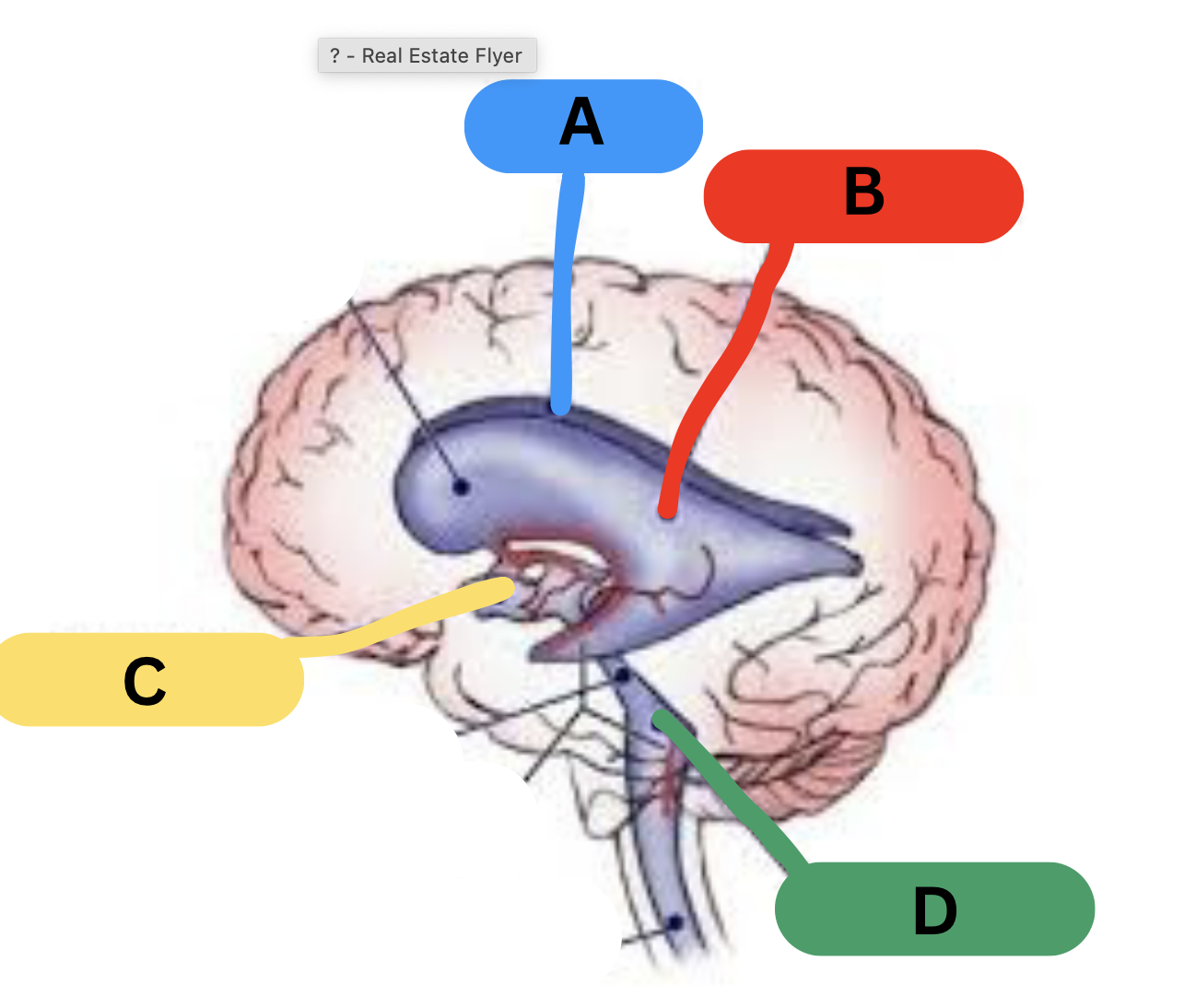
label the ventricles
A: right lateral ventricle
B: left lateral ventricle
C: third ventricle
D : fourth ventricle
the adult brain requires _____ of oxygenated blood per _____
a quarter (unknown unit) per minute
about ____% of the body’s blood and ___% of the body’s oxygen goes to the brain
20% of blood and 25% of oxygen
what are the 2 major vasculature systems? what are they connected by?
internal carotid system and vertebral-basilar system. the circle of willis
the circle of willis contains what arteries? (6)
basilar, posterior cerebral, posterior communicating, internal carotid (exits as middle cerebral), anterior cerebral, anterior communicating
the internal carotid system supplies the… (1)
cerebrum
the vertebral-basilar system supplies the… (3)
brainstem, spinal cord, cerebellum, and parts of the cerebrum
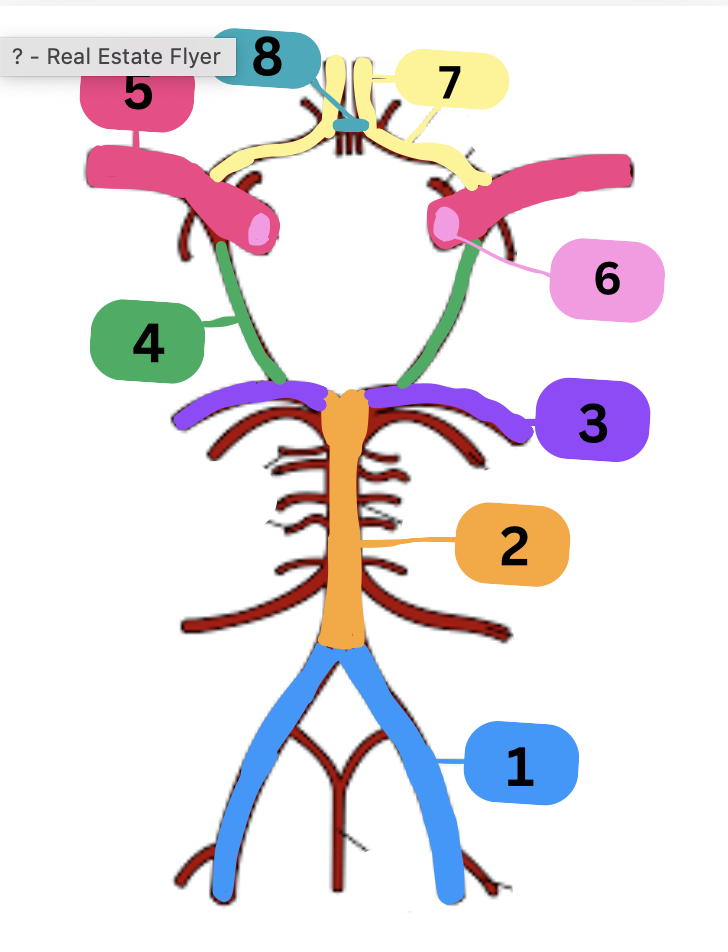
label
1: vertebral artery
2: basilar artery
3: posterior cerebral artery
4: posterior communicating artery
5: middle cerebral artery
6: internal carotid artery
7: anterior cerebral artery
8: anterior communicating artery
the common carotid artery divides into… (2)
the internal carotid and external carotid
the external carotid artery supplies what? (5)
face, forehead & oral, nasal, orbital cavities
the internal carotid artery is a major supplier to what? what does it divide into? (2)
the brain. divides into the anterior cerebral and middle cerebral
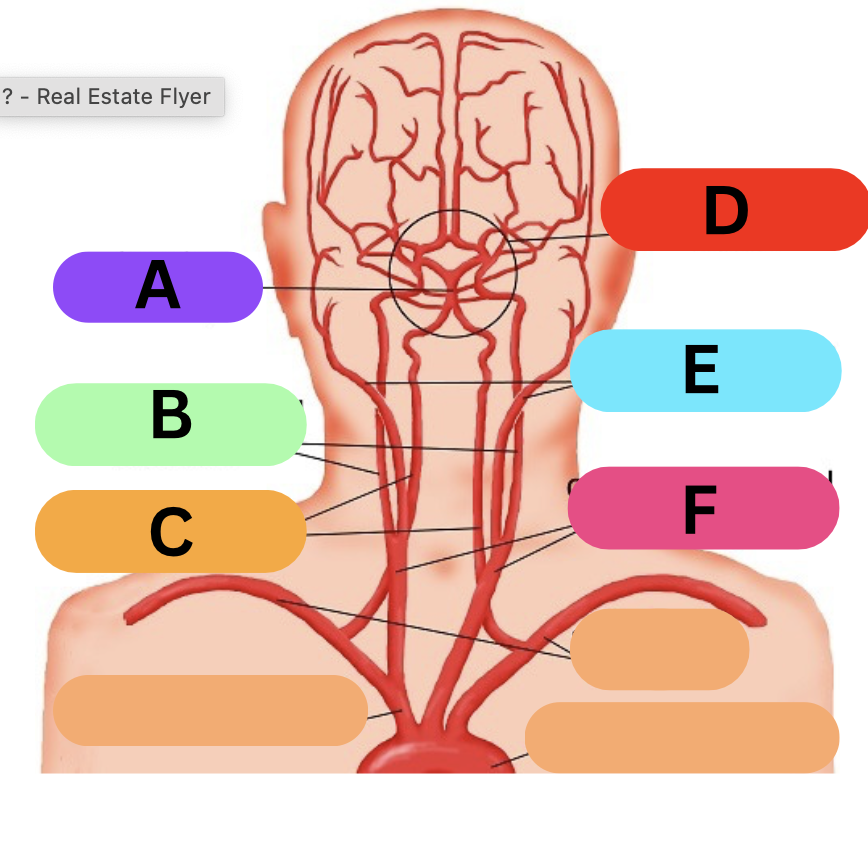
label
A: basilar
B: internal carotid
C: vetebral
D : circle of willis
E: external carotid
F: common carotid
what does the anterior cerebral artery supply?
supplies orbital and medial cortical surfaces of the prefrontal and parietal lobes. partially supplies basal ganglia and corpus callosum
what are clinical signs of interruption in the anterior cerebral arteries?
paralysis of legs, feet, and toes. prefrontal lobe symptoms. impaired executive function
the middle cerebral artery supplies…
the entire lateral surface of the cerebrum = frontal, parietal, temporal lobes. also basal ganglia and diencephalon
the blood supply of the middle cerebral artery is critical because if is related to….
speech, language, and sensorimotor function
name some clinical signs of interruption in the middle cerebral artery
aphasia, apraxia, impaired sensory functions, reading/writing deficits, hemiplegia
the posterior cerebral artery supplies blood to…
anterior and inferior temporal lobe, inferior and medial occipital lobe
name some signs of clinical signs of interruption in the posterior cerebral arteries
hemianopsia, pontine symptoms, cerebellar symptoms, blindness
blockage in the branches of the basilar artery would result in…
brainstem or cerebellar stroke
would a stroke occur if there was a blockage in the anterior communicating artery or posterior communicating artery?
no. blood can still circulate to other areas