Oceans & Coasts
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
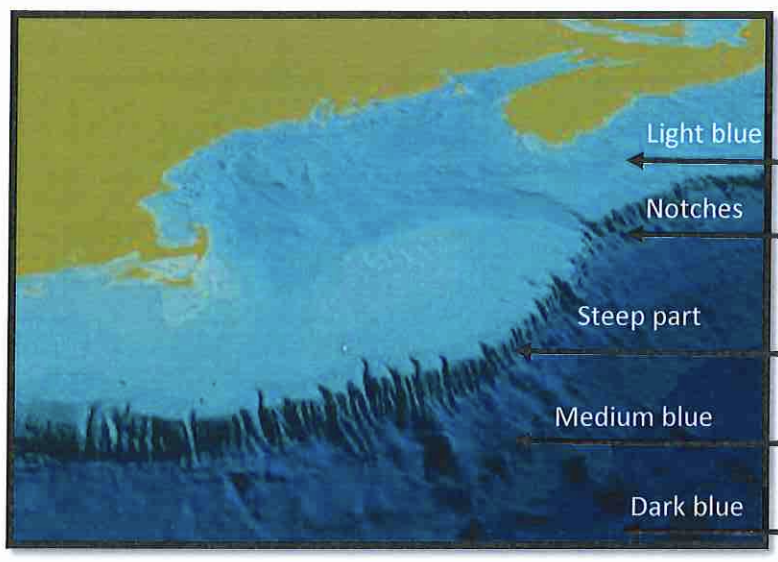
Light blue?
continental shelf
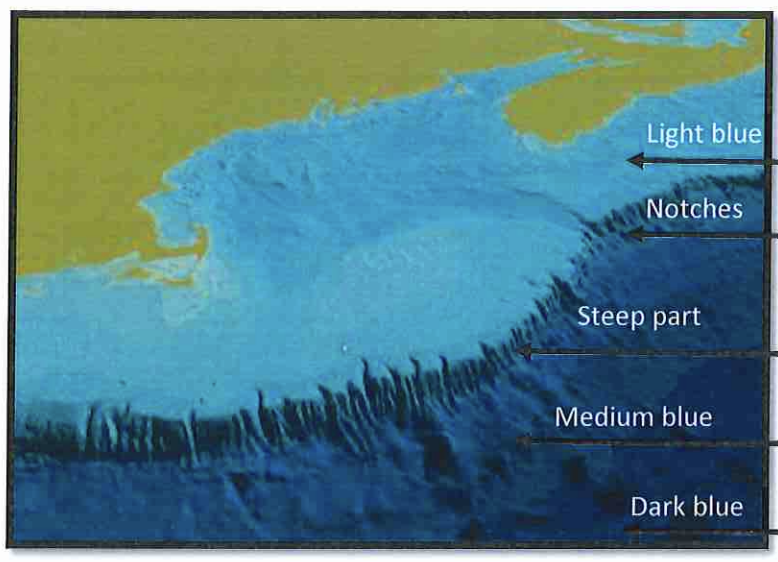
Notches?
submarine canyons
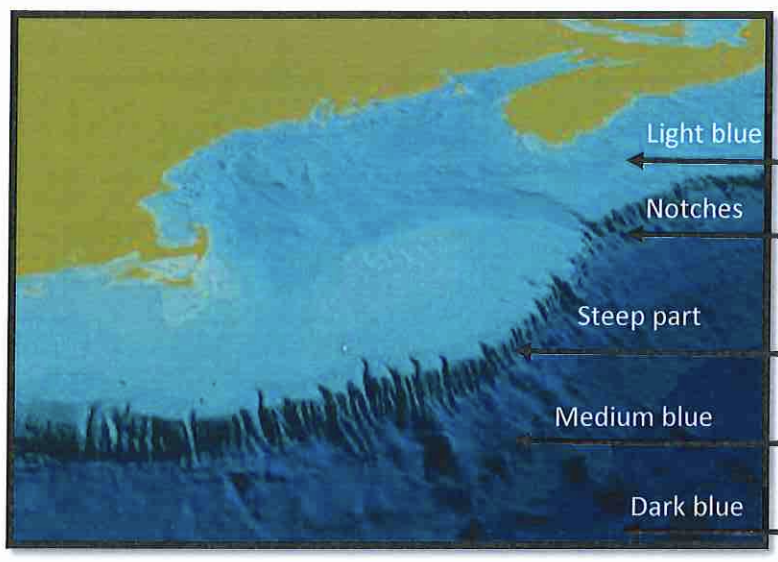
Steep Part?
continental slope
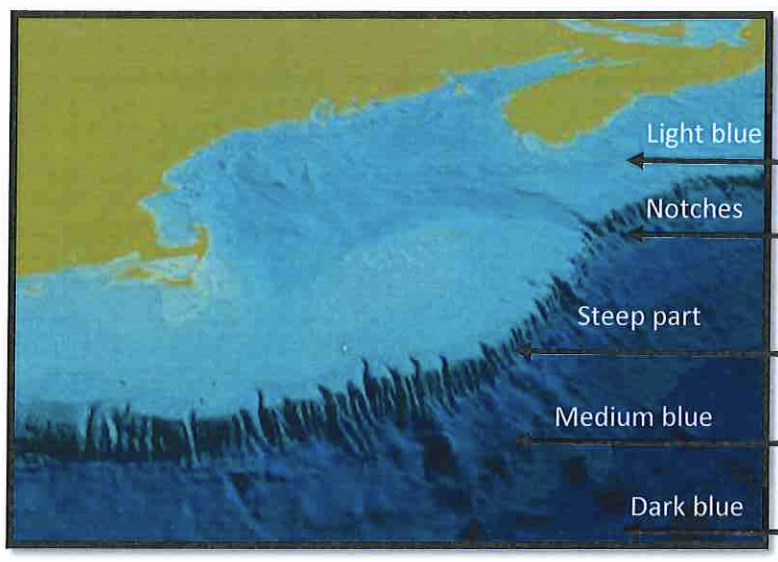
Medium Blue?
continental rise
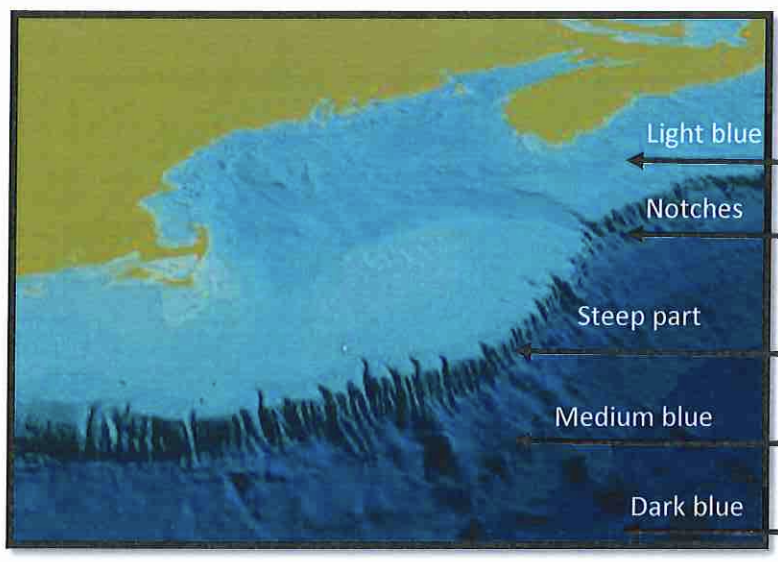
Dark Blue?
abyssal plain
What makes tides possible?
gravity
What makes waves possible?
friction (from wind)
When does a spring tide occur?
sun, moon, and earth in a straight line (full moon or new moon)
What term best describes an out-going tide?
ebb tide
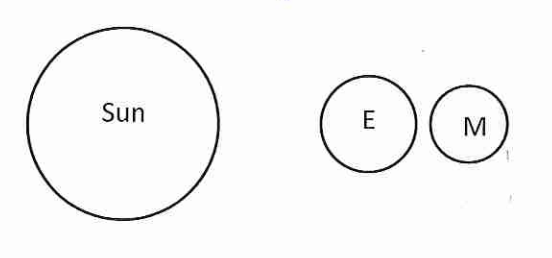
Determine what type of tide to expect based on the not to scale cartoons
spring tide
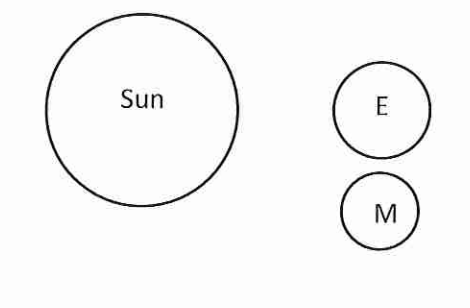
Determine what type of tide to expect based on the not to scale cartoons
neap tide

Determine what type of tide to expect based on the not to scale cartoons
neap tide
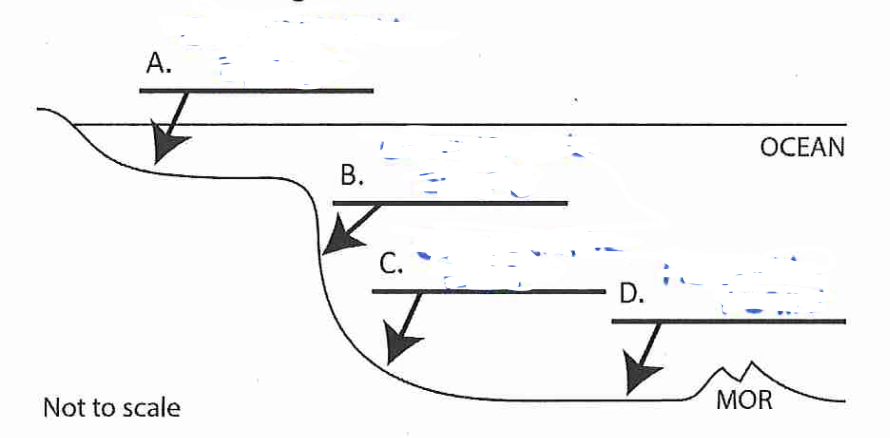
A?
continental shelf
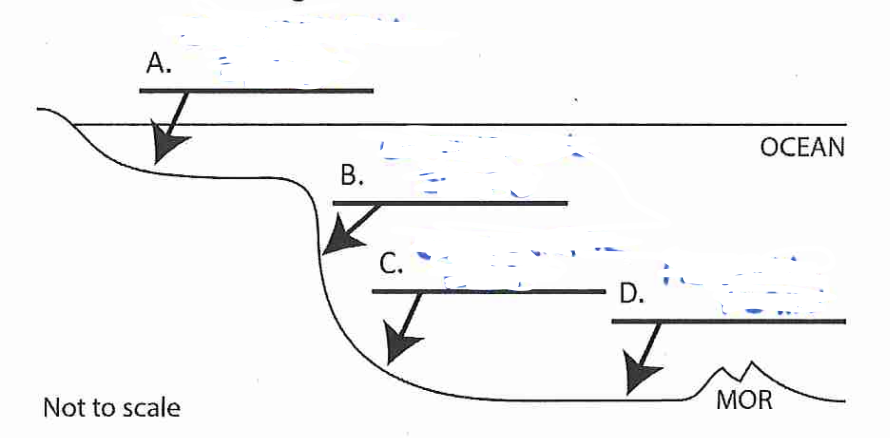
B?
continental slope
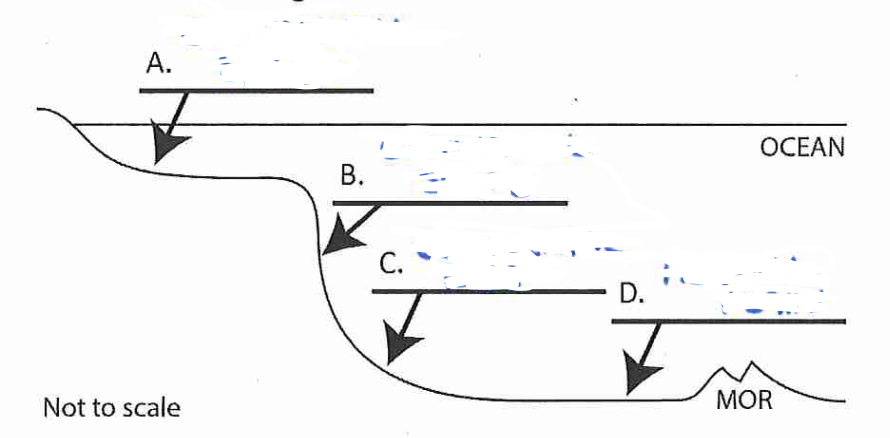
C?
continental rise
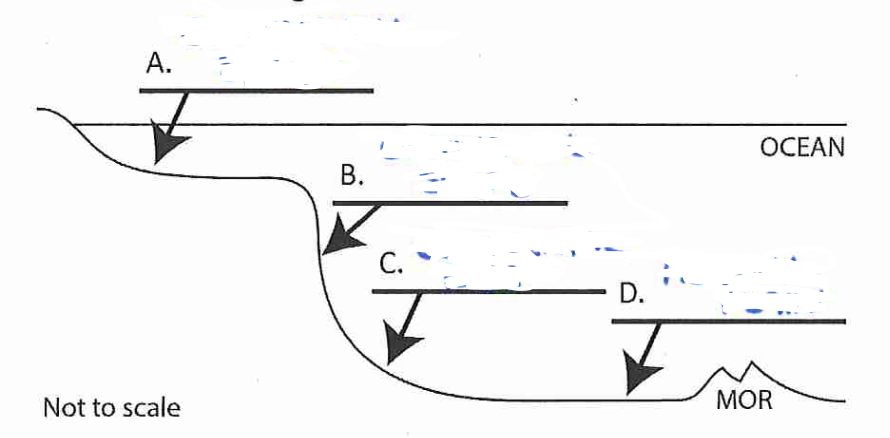
D?
abyssal plain
Key processes that shape all ocean basins?
tectonics and erosion
What are some ocean basin features?
mid ocean ridges, trenches, and abyssal plains
Costal processes involve the interactions of what 2 systems?
ocean system & atmospheric system
How do the climate system and Earth’s oceans interact?
the oceans absorb heat and co2 from the atmosphere influencing global temp and weather patterns; climate affects ocean circulation and sea level
How do the solar system and Earth’s oceans interact?
the gravitational pull of the moon and sun cause tides; sun provides energy that drives currents and the water cycle
Most marine organisms live where?
near coastlines (due to sunlight, nutrients, and shallow waters)
Continental Shelf *aka economical important source of oil, natural gas, and wind
fairly shallow, low sloping offshore area that receives sediment from continents
Continental Slope
area that descends steeply to the ocean depths
Submarine Canyon
relatively narrow and deep valleys carved into the continental shelf & slope
Continental Rise
gently sloping area of muddy and sandy sediments
Abyssal Plain *extends to the mid ocean ridge
flat area at the bottom of the ocean
Tides *usually 2 times a day
alternate rising and falling of the sea
How to make a tide?
on moon facing side, water pulled away from earth
moon also pulls earth toward it (a little bit)
causes water on opposite side of earth to “slosh away” from earth
makes high tide on moon-facing & opposite side of Earth
makes low tide at 90° from the moon-facing and opposite side of earth
Spring Tide
tide in which the difference between high and low tide is the greatest
new moon or full moon *Sun, Moon, and Earth are aligned → stronger tides
Neap Tide
tide that results in a smaller-than-average difference between high and low water levels
first or third quarter moon *Sun and Moon pull at right angles → weaker tides
Flood Tide
tide is rising
Ebb Tide
tide is falling
Tidal Range (Tidal Reach)
the difference between high and low tide
Which bay has the highest tidal range in the world?
Bay of Fundy, Canada
Wave
a disturbance that transfers energy through water, usually caused by wind
Swell
a long, regular, and low-energy wave that forms in the deep ocean
What can:
become longer, more regular, and uniform
can travel LONG distances
swell
Fetch
the distance over which the wind blows to generate waves
Wave Crest
the highest point of the wave
Wave Through
the lowest point of the wave
T/F: molecules move in roughly circular motion as the wave passes by them
true
T/F: molecules move in roughly oval motion as the wave passes by them
false
Breaker
occur because water starts to move shore, friction causes the bottom of the wave to slow down and top of the wave to tip over
Swash
the water that moves up the beach AFTER a wave breaks
Backwash
the water that flows back down the beach after the swash
Longshore Drift
sediment transport along a beach by zigzag movement
Longshore Current
shallow, offshore current that flows parallel to shore *causes longshore drift
Wave Refraction
waves bend toward shore as they approach shore
Causes waves to retreat and straighten over time?
wave refraction
Rip Current
strong current flows perpendicular to the shore
Where do rip currents form?
where longshore currents meet (water “piles up”)
What causes winds over earth’s surface?
uneven heating
Current
well defined stream of ocean water
Surface currents are driven by ___ moving across the ocean.
wind
What hemisphere do currents veer right because of earth’s rotation?
northern hemisphere
What does the veering motion make?
gyres
Gyre
large circular flow pattern of ocean’s surface currents
The inside of a gyre is ___
still
Surface water sinks to ocean basins in ____ zones
downwelling
To make deep currents deep water rises to ocean surface in ____ zones
upwelling
Upwelling & downwelling zones are driven by what?
density and temperature differences between surface and deep water
Thermohaline Circulation
the rising and the sinking of ocean water driven by temperature and density differences
What does Thermohaline Circulation do?
move water and heat from ocean basin to ocean basin
Sea Level Rise
rise of ocean water
The melting of ice will/won’t contribute to sea level rise
WILL
The melting of ice floating on ocean will/won’t contribute to sea level rise
WON’T (it already has)
Beach Erosion
beach becomes narrower when sediment removal exceeds accumulation
Hurricane
greatest storm on earth
form in tropical areas
pushed by prevailing winds
Storm Surge
dome of seawater that rises above level of surrounding ocean *one of the most destructive sides of a hurricane