L37 Insufficient or overactive immune system
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Immune Deficiencies (doesn’t work as hard as it should)
Immune deficiencies can be inherited or induced by viruses, (also by medical treatments, or poor nutrition).
Tolerance to Self-Antigens
The concept where the immune system does not attack the body's own cells.
Autoimmunity
Examples include rheumatoid arthritis and type I diabetes, where immune cells attack self cells.
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
X-chromosome linked disease, more common in males (females are carriers), patients lack functional T cells and B cells. Body is extremely susceptable to infection.
Virus-Induced Immune Suppression
Measles, HIV, and many other viruses interfere with the normal host immune system.
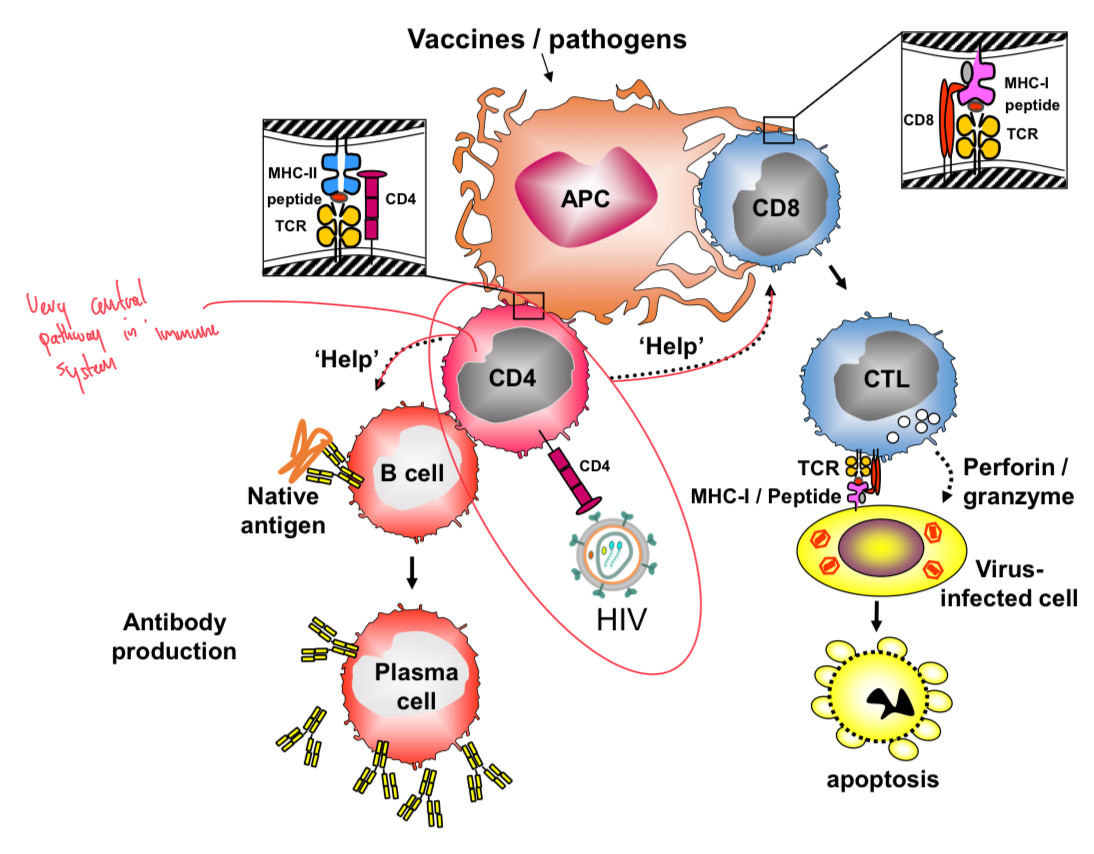
HIV
HIV receptor is CD4 molecule on CD4 T cells, so targets and can kill them, causing lack of CD4 T cells, unable to provide help for antibody and CTL responses.
HIV Infection Impact
Impacts immunity to microbes (fungi, bacterial and virus) and to cancer.
Autoimmune Disease
Normally prevented by host mechanisms of immune tolerance, although innate system can trigger or make it worse, it is normally mediated by adaptive immune response.
Immune Tolerance
Critical to avoid autoimmunity, thymus deletes autoreactive T cells, in periphery are other mechanisms to silence autoreactive B/T cells. Failures (due to genes or triggering infections) can lead to autoimmunity.
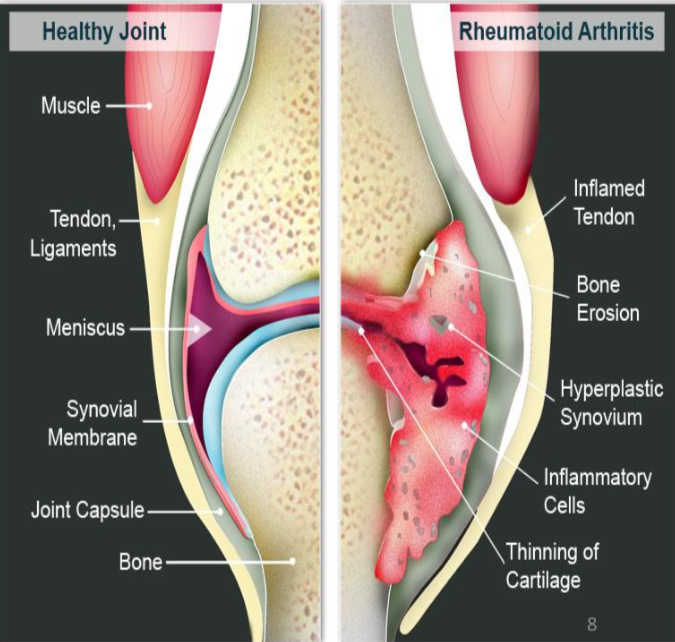
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) autoimmune example
Autoreactive T cells and B cells attack self-antigens present in joints, affects 1% of population. Often late onset in life.
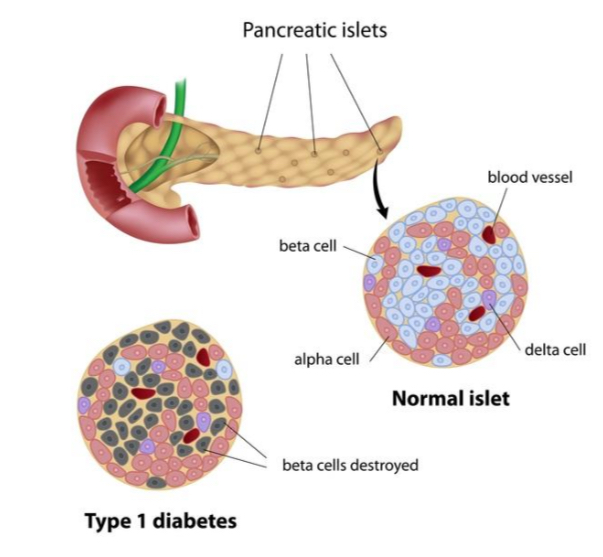
Diabetes Type 1 (autoimmune example very specific)
Insulin beta-cells are attacked. Other islet cells may escape autoimmune attack.
Allergic reactions (overactive immune system)
Allergens are antigens that trigger allergy, normally harmless environmental antigens. Chemicals can induce allergy (eg. penicillin). Large range of outcomes mild to extreme.
Allergic Reactions: Effector Response
DC present peptides from peanut proteins (allergens) to helper T cells, primed helper T cells activate B cells to secrete IgE, which binds very tightly to mast cell receptors (FcR). This triggers degranulation of mast cell and release of histamine and other inflamatory mediators.
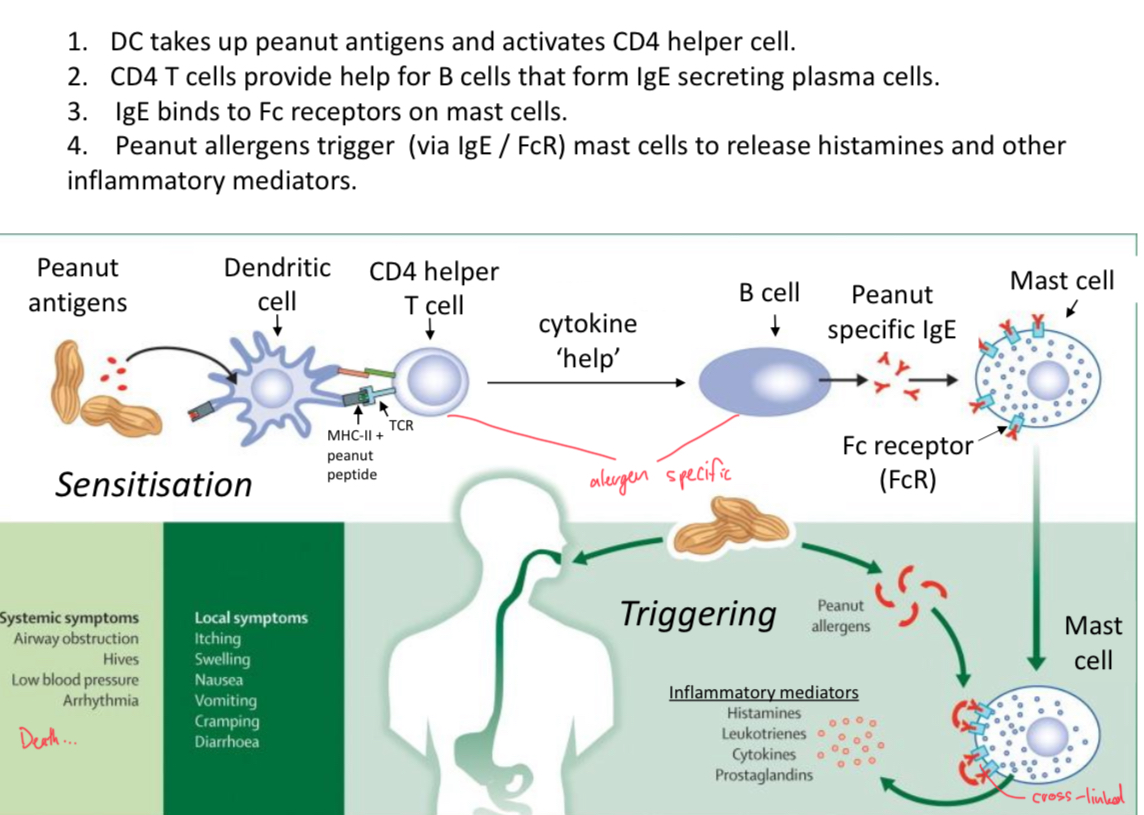
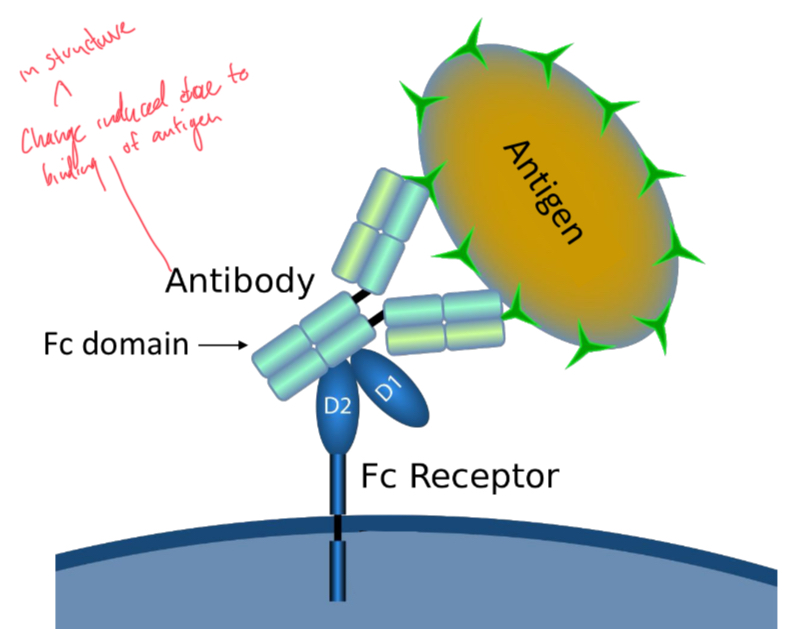
Fc Receptors (FcR)
Bind to the Fc domain (on constant region) of antibody. Facilitate phagocytosis and mast cell activation.