Micro BIO 150 Test 1 NVCC
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
What is the biological function of an endospore?
Endospores are heat-resistant forms of bacteria, so it allows the bacteria to survive extreme conditions
What are the three domains of life that all living organisms are separated into?
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eucarya
How do you write a scientific name?
All in italics or underlined with the Genus FIRST LETTER capitalized and the species in lowercase. Many describe the microbe or honor the scientist
Are archaea more closely related to bacteria or eukarya?
Eukarya
Who developed the 3 domain system?
Carl Woese
Who is Robert Hooke?
First person to describe microbes
Who is Anton Van Leewenhook?
He was the first to describe bacteria from his own teeth
What does the Theory of Spontaneous Generation say?
organisms can arise spontaneously from non-living material
Who disproved spontaneous generation and how?
Louis Pasteur used swan-necked flasks that had a heated solution/broth. No microbes could get past the swan neck flask opening and into the solution.
pasteaurization
a process of high heat for a short time to kill harmful bacteria in beverages
How did Louis Pasteur disprove spontaneous generation?
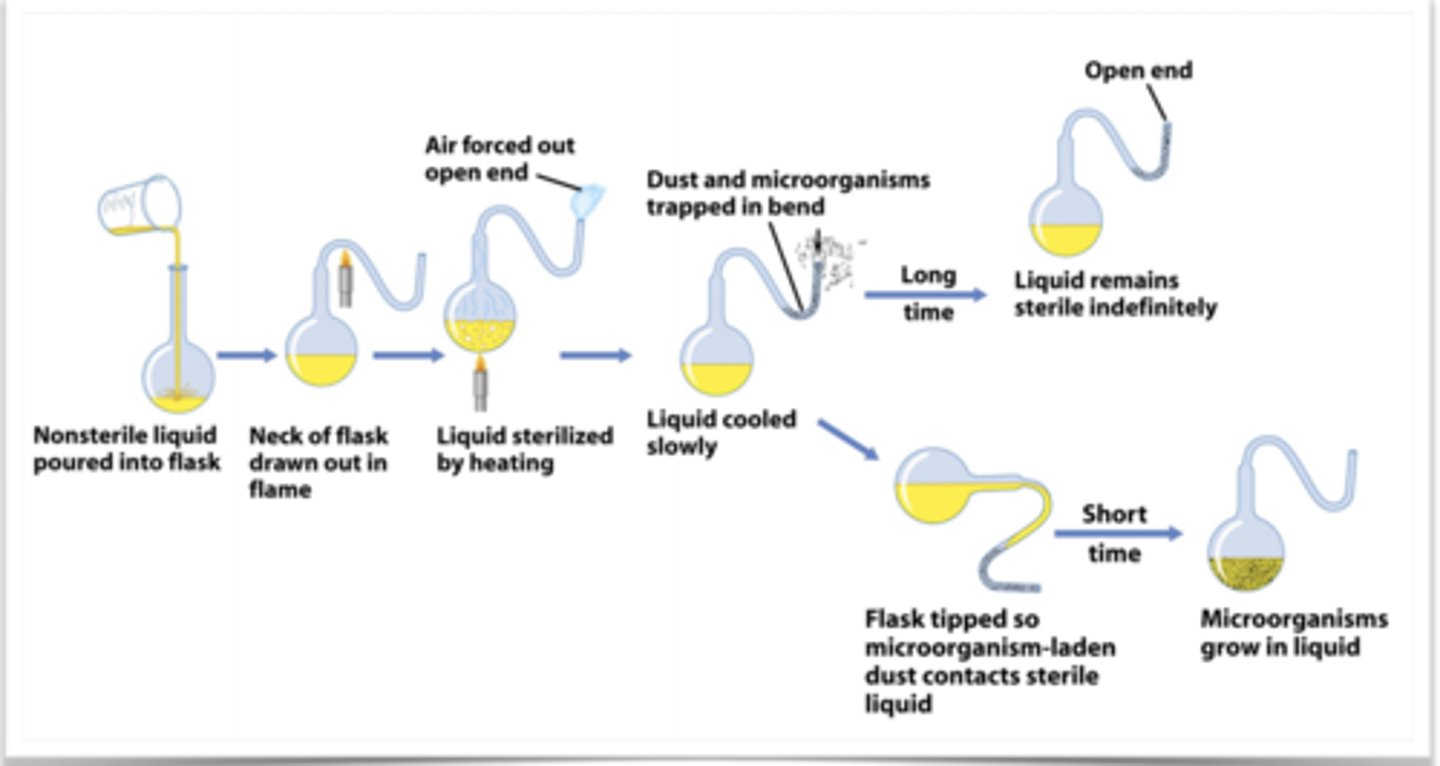
In louis pasteur's experiment, Why was the neck S shaped?
to trap the microbes in the air in the curved neck
in louis pasteur's experiment, Why was the flask heated?
to kill the microbes in the broth
in louis pasteur's experiment, Why was the flask tilted after a short time?
To introduce the trapped bacteria
Who is Robert Koch?
1. noted for developing "Koch's Postulates"
2. outlines the use of pure cultures to identify/determine the agent for infections/diseases
3. father of medical microbiology
Nobel Prize Winners
Koch and Pasteur
Koch's Postulates
a sequence of experimental steps for directly relating a specific microbe to a specific disease.
1. Draw blood- Dead rat & healthy rat
Look under microscope
Suspected pathogen spotted
Must be present in all cases of disease
2. Must be grown in pure culture (slice of potato)
Lab cultures- colonies of suspected pathogen
*Streaking isolates pathogen- pure culture
3. Inoculate healthy animal with pathogen
Does it kill rat?
4. Suspected pathogen must be isolated and shown to be same as original
5. Blood drawn from healthy dead rat and re isolated
Pure culture must be the same
Summarize Koch's postulates for linking specific microorganisms to certain diseases
-If you isolate the bacterial agent of a sick animal, you can infect a healthy individual with the same illness.
-The organism must always be present, in every case of the disease.
-The organism must be isolated from a host containing the disease and grown in pure culture.
-Samples of the organism taken from pure culture must cause the same disease when inoculated into a healthy, susceptible animal in the laboratory.
-The organism must be isolated from the inoculated animal and must be identified as the same original organism first isolated from the originally diseased host.
Microbiome
permanently colonize the host and do not cause disease under normal conditions
- prevent growth of pathogens
- produce Vitamin B and K
Normal microbiota
microbes normally present in and on the human body. example skin, oral cavity, intestines
Types of Microorganisms
Bacteria
Archaea
Fungi
Protozoa
Algae
Viruses
Multicellular animal parasites
How are Microbes in our lives?
-A few are pathogenic
-Decompose organic waste
-Are producers in the ecosystem by photosynthesis
-Produce industrial chemicals such as ethanol and acetone
-Produce fermented foods such as vinegar, cheese, bread
-Produce products used in manufacturing (eg. cellulase) and treatment (eg. insulin)
Why is knowledge of microbiology important?
It prevents the spread of disease , prevents epidemics, prevents food spoilage
Which two types of microorganisms are prokaryotic?
Bacteria and archaea
What are the characteristics of prokaryotes? (number of cells, type of nucleus, type of organelles, size) Examples?
1. single celled
2. no true nucleus (have nucleoid instead, which is not membrane bound)
3. organelles are not membrane bound
4. small and simple
5. bacteria and archaea
Characteristics of eukaryotes? Examples?
1. single or multicelled
2. true nucleus (membrane bound)
3. membrane bound organelles
4. larger, complex
5. examples: algae, protozoa, fungi
How do Archaea differ from Bacteria? How are they the same?
differ-chemical composition of cell wall (archaea do not have peptidoglycan in cell wall)
same-size, shape, appearance, movement, reproduction
Viruses are not
alive or cells, they are acellular
Which type(s) of microorganisms are eukaryotic?
Fungi, protozoa, Algae, Animal Parasites- Helminths
How do you release energy one step at a time?
Respiration and fermentation
How do enzymes speed up reactions?
By lowering the activation energy
NAME 3 Ways to phosphorylate
Substrate level phosphorylation , Photophosphorylation, Oxidative phosphorylation
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
Uses energy released by the electron transport chain to power ATP synthesis.
After Glycolysis, Where do 2 pyruvates go to further oxidize?
Krebs cycle
Where do we get 2 pyruvates from in krebs cycle?
Glycolysis
What's the starting material for glycolosis?
Glucose
Where does substrate level phosphorylation occur?
Krebs cycle and glycolysis
Where does oxidative phosphorylation occur?
electron transport chain
How was ATP creating in glycolysis?
Substrate level phosphorylation
What is respiration?
Glucose is oxidized to get ATP
1. Glycolysis
2. Krebs cycle
3. Electron transport Chain System
Catabolism
breaks down complex molecules
Anabolism
uses energy to build up complex molecules
What is fermentation?
Glycolysis & Pathway (alcohol/acid)
IN FERMENTATION how many ATPS Total from glucose?
NET: 2 ATPs
IN GLYCOLYSIS, HOW MANY ATPs net for one glucose?
2 ATP
iN GLYCOLYSIS,besides ATP - What else do you generate?
2 NADH
iN GLYCOLYSIS,What is final sub compound ?
2 Pyruvates
How is ATP GENERATED (what phosphorylation method)DURING KREBS CYCLE?
Substrate level phosphorylation
What happens when you pass the electrons down the chain?
Charged Membrane
How do you charge the membrane?
Pump the protons out of the cell
Who is the final electron acceptor in fermentation?
Pyruvate
Who uses the proton motive force?
ATP synthase
What energy does ATP synthase use?
Proton motive force
How do you generate proton motive force?
What happens during the PHOTO part of photosynthesis?
Generating ATP & NADPH
What do you need for the synthesis part of photosynthesis?
ATP and NADPH
What are peroxisomes?
Oxidizes Fatty acids; destroy H2O2 (toxic)
In Aerobic respiration, What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain
O2
Taxonomy
The scientific study of how living things are classified- degree of similarity amount organisms
Phylogeny
evolutionary history of organisms
Where did eukaryotic cells come from?
endosymbiotic theory - infoldings of prokaryotic plasma membranes
Protista
a kingdom of mostly one-celled eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophs and autotrophic
Fungi
chemoheterotrophic; unicellular or multicellular; cell walls of chitin; develop from spores or hyphal fragments
Plantae
multicellular; cellulose cell walls; undergo photosynthesis
Animalia
multicellular; no cell walls; chemoheterotrophic
Name 3 ways of classifying & identifying microorganisms
Morphological, differential staining, biochemical tests
How are endospores useful to a bacterial cell? Outline the endospore formation process
Resting cells found in certain bacterial species.
Resistant to desiccation, heat and chemicals
Can be viable for centuries
Sporulation: process of endospore formulation. NOT REPRODUCTION
1.) Spore septum begins to isolate newly replicated DNA and a small portion of cytoplasm
2.) Plasma Membrane starts to surround DNA, cytoplasm and membrane isolated in step 1
3.) Spore septum surrounds isolated portion, forming forespore
4.) Peptidoglycan layer forms between membranes
5.) Spore coat forms
6.) Endospore is freed from cell
Spontaneous Generation Theory
the theory that living organisms can rise from nonliving things
Characteristics of Microorganisms
1.) Microbes as a group show diversity, multiple domains
2.) Microbes are Ubiquitous! They're everywhere
3.) Structure=Function
What is the importance of Microbial Life on earth?
1.) Major part of food chain of all organisms
2.) Waste breakdown/nitrogen cycling in plants
3.) Food Production
4.) Drug Production
Beneficial Uses of Microbes
1.) Microbial Ecology
2.) Bioremediation
3.) Pest Control
4.) Biotechnology
What are the three domains of life and who developed it?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya. Developed by Dr. Carl Woese
What characteristics are used to classify life into three domains?
Ribosomal RNA, Single Cell/multicellular, Transferral RNA Structure
Prokaryote Bacteria
1.) Single-Celled Organisms
2.) Bacteria exist in different shape, have cell wall made of Peptidoglycan
3.) Asexual Reproduction, Binary Fission
4.) motile or Non-motile, Flagella allows it to move
Prokaryote Archaea
1.) Present in most extreme environments
2.) Methanogens, high methane environment
3.) Extreme Halophiles, high salt environment
4.) No Peptidoglycan, different cell wall
Fungi
1.) Multicellular or Unicellular
2.) Most engage in sexual reproduction, some in asexual reproduction and some can do both
3.) Mycellea made up of filaments called Hyphae
4.) Cell wall made of Kiatin
5.) Absorb organic chemicals for nutrients
Protozoa
1.) Unicellular
2.) Free living or parasitic
3.) Some are Photosynthetic
4.) sexual or asexual reproduction
5.) May be Modal, can use flagella, massive Cillia or a pseudopod "false foot" to move in environment
6.) Disease causing agents
Algae
1.) Water Plants
2.) Cellulose Cell walls
3.) Uni or multicellular forms
Helminths
1.) Parasitic flatworm/roundworm
2.) Microscopic
3.) Cysts/egg/larvae are way from going host to host
Viruses
1.) Extremely small, Acellular. Neither Prokaryote or Eukaryote
2.) Can be seen with Electron Microscope
3.) Consist of nucleic acid core either DNA or RNA
4.) Nucleic acid surrounded by protein coat, sometimes by lipids as well
5.) Parasites, only replicate in a host cell
Anton Van Leuwenhoek
Created first Microscope to look at animal cells
Robert Hooke
coined the term "cell" and redesigned microscope with light source
Edward Jenner
(vaccination) First to start idea of vaccines with cowpox. Exposed maids to cowpox before working with them
Louis Pasteur
Refutes Spontaneous Generation with beef broth experiment
Robert Koch
Postulates of Disease/Germ theory of disease- Postulates determine how germs can cause disease
Chemotherapy
Using chemical drugs to defeat disease (NOT CANCER CHEMO)
Paul Erlich and Chemotherapy
coined the term antibiotics for the "magic bullet" antimicrobials he pursued
Alexander Fleming
discovered penicillin, Penicillum inhibits growth of colonies
What are the 5 branches of Microbiology?
1.) Bacteriology- Study of Bacteria
2.) Mycology-Study of Fungi
3.) Parasitology-Study of Parasites
4.) Immunology- Study of immune system
5.) Virology- Study of Viruses
Biofilm
A surface-coating colony of one or more species of prokaryotes that engage in metabolic cooperation.
normal human microbiota
Populations of mutualistic and commensal microbes that live on and in the bodies of healthy individuals, about 100 trillion bacteria in total, representing hundreds of species
emerging infectious diseases
A new disease or one that reemerges, coronavirus
Primary Differences between Prokaryote and Eukaryote cells
1.) Prokaryotes are smallest organisms/unicellular with circular DNA in nucleoid region, Eukaryotes are larger and multicellular, have enclosed nucleus with strands of DNA
2.) Prokaryotes have cell wall for structure/protection, Eukaryotes have cytoskeleton for support
3.) Prokaryotes do Asexual Reproduction(Binary Fission), Eukaryotes do Sexual Reproduction
Baccillus Cell Shape(Rods)
SingleBaccillus- Single rod
Diplobaccillus- Two rods
Streptobaccillus- Chain of rods
Coccobaccillus-rounded rod, square shape
Coccus Cell Shape (Round/spherical)
Diplococci- Two cocci, one plane of division
Streptococci-Chain of cocci, one plane of division
Tetrad- Four cocci in a quad, two planes of division
Sarcinae- Two tetrads stacked
Staphylococci- Clump of Cocci, looks like grapes
How do Prokayotic and Eukaryotic Flagella movement differ?
Prokaryotic flagella rotate to allow them to run and tumble. Eukaryotic flagella are composed of microtubules in a 9 pairs + 2 array that allow it to bend and grappling hook twitching motility
Describe function of bacterial cell wall
Made of Peptidoglycan, sugar protein cell wall
Combats lysis, osmotic lysis
Provides strength to resist rupturing due to osmotic pressure
good antibiotic target
Explain the gram stain procedure
1.) Primary stain of crystal violet
2.) Use mordant of Iodine to allow for primary stain to stick. Intensifies the affinity of a stain to a structure
3.) Decolorizing agent of Alcohol-Acetone, determines whether gram pos or neg. Dehydrates the cell and pores in cell wall will seal. Will seal the mordant and primary stain. Gram pos cells stay purple while gram neg cells turn colorless.
4.) Counterstain of Safranin. Will turn the gram neg bacteria from colorless to red. However gram pos cells will stay purple even with counterstain.
Describe the Structure of the Plasma Membrane and its components
Plasma membrane contains a phospholipid bilayer, peripheral proteins, and Integral and Transmembrane proteins penetrate the membrane
selectively permeability and what are some processes that move materials across the plasma membrane
a property of cell membranes that allows some substances to pass through, while others cannot
Simple diffusion through the lipid bilayer
Facilitated diffusion through a nonspecific transporter
Facilitated diffusion through a specific transporter
Osmosis through the lipid bilayer and an aquaporin