the mechanism of breathing
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Breathing/ventilation definition
movement of air into and out of lungs
respiration
chemical reaction to release energy in form of ATP
gaseous exchange definition
diffusion of oxygen from air in the alveoli to blood and carbon dioxide from blood into air in the alveoli
inspiration
when air pressure of atmosphere is greater than the air pressure in lungs air is forced into lungs
expiration
when the air pressure in lungs is greater than air pressure in atmosphere air is forced out of lungs
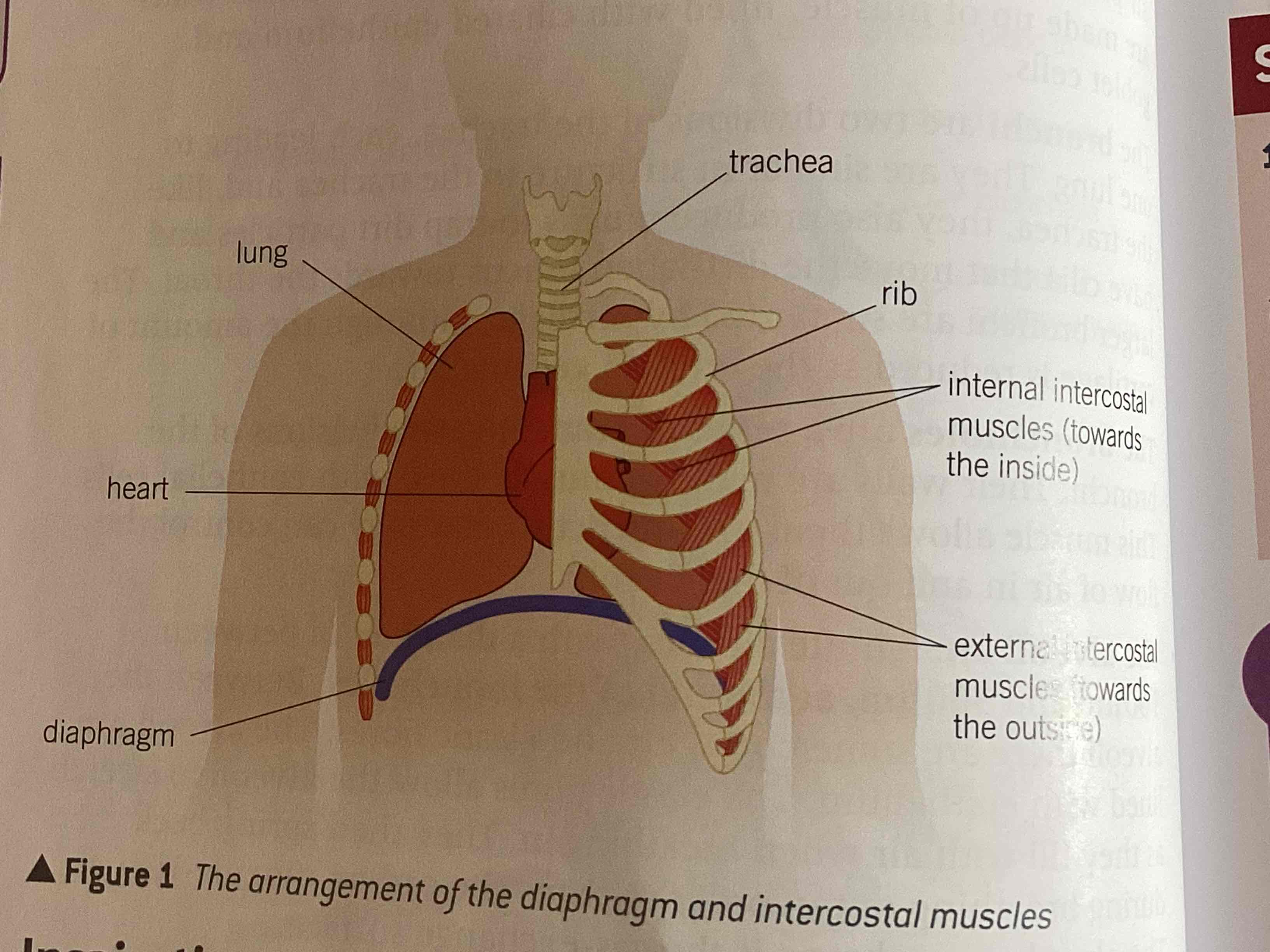
what is the diaphragm
Sheet of muscles that separate the thorax from the abdomen
where do the intercostal muscles lie
between ribs
what are the internal intercostal muscles
contraction leads to expiration
what are external intercostal muscles
contraction leads to inspiration
arrangement of lungs diagram
describe the process of inspiration (active process)
external intercostal muscles contract, and internal intercostal muscles relax
ribs pulled up and outwards, increasing volume of thorax
the diaphragm muscles contract and flatten, increasing volume of thorax
pressure reduces in lungs
atmospheric pressure is greater than pulmonary pressure so air is forced into lungs
describe process of expiration (passive)
Internal intercostal muscles contract, external intercostal muscles relax
the ribs move downwards and inwards, decreasing volume of thorax
the diaphragm muscles relax and pushed up again by abdomen. The volume of thorax is reduced.
increase pressure in lungs
the pulmonary pressure is greater than atmosphere so air is forced out of lungs
what is pulmonary ventilation rate
total volume of air that is moved into lungs during one minute
formula for pulmonary ventilation rate
tidal volume * breathing rate
what is tidal volume (dm3)
Volume of air taken in at each breath when body is at rest (0.5cm3)
breathing rate (min-1)
number of breaths taken in one minute (12-20)