Chapter 1.1 hort 3000
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Plant Physiology
A study of the nature of plants based on how they function in terms of physical and chemical processes.
Plant Taxonomy
The science that finds, identifies, describes, classifies, and names plants.
Plant Taxonomy - The SYSTEM of Plant Identification (ID)
The characterization of plants as individuals or groups based on plant structures into natural, related groups.
Classification Hierarchy
The organization of taxonomy into Kingdom, Division or Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Specific Epithet, Variety, Cultivar.
Biological Kingdoms
The major categories of life including Monera, Protista, Fungi, Animalia, and Plantae.
Plant Divisions
Categories of plants including Thallophytes, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, and Spermatophytes.
Vascular Tissues
Tissues in plants that are organized into functional structures.
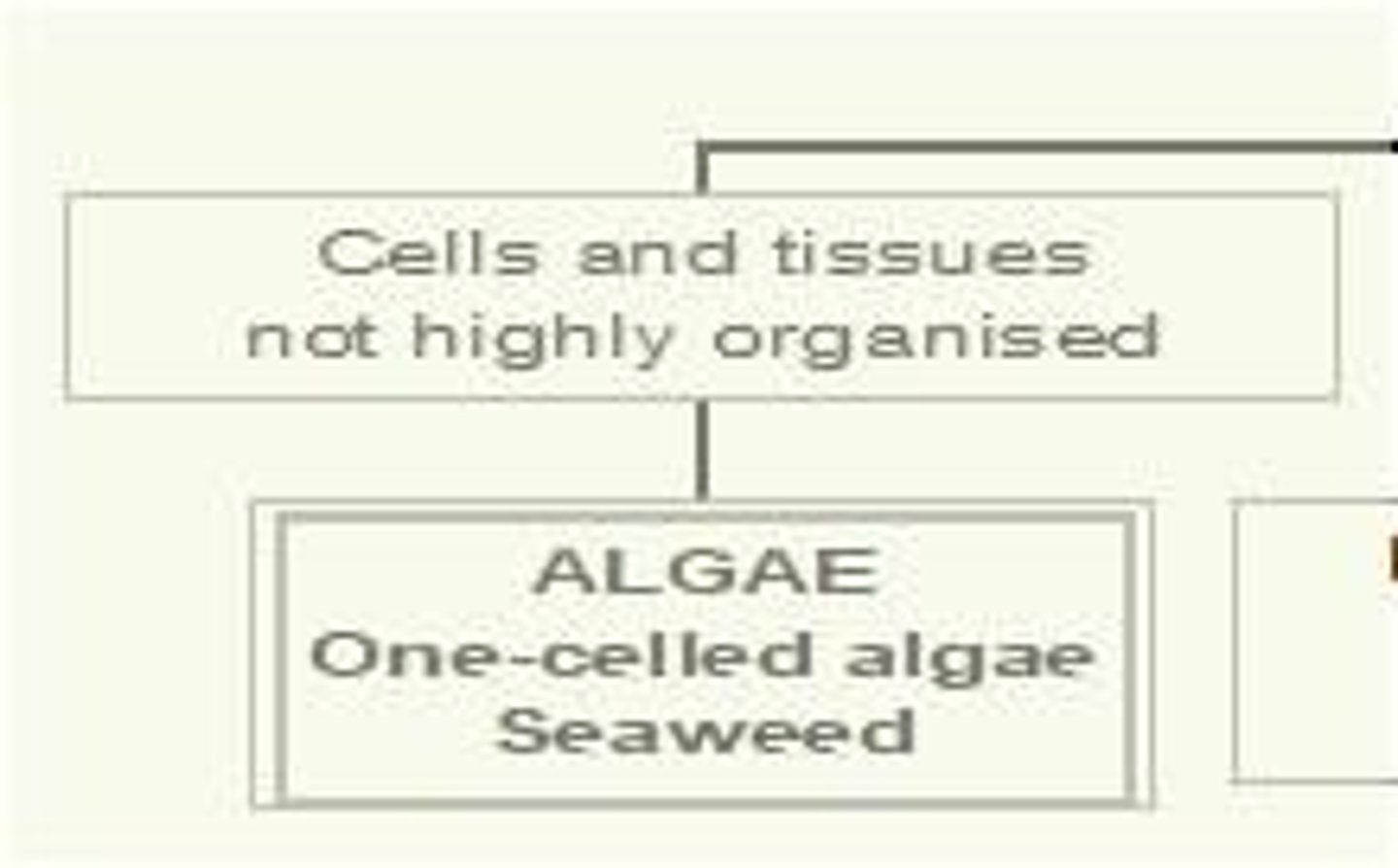
Nonvascular Tissues
Tissues in plants that are not highly organized into functional structures.
Angiosperms
Flowering plants that produce seeds enclosed in fruits.
Gymnosperms
Plants that produce seeds that are not enclosed.
Pteridophytes
Plants that reproduce via spores, including ferns and horsetails.
Bryophytes
Nonvascular plants such as mosses and liverworts.
Thallophytes
Plant-like organisms that are single-celled or multicellular and depend on water for reproduction.
Spermatophytes
Seed-producing plants, including angiosperms and gymnosperms.
Morphology
The study of the form and structure of plants.
Anatomy
The study of the internal structure of plants.
Ecologist/Botanist
A professional who studies the relationships between plants and their environment.
Ethno/Paleo-botanists
Scientists who study the relationships between ancient plants and humans.
Landscape Design/Install/Maintenance Co.
Companies that design, install, and maintain landscapes.
Extension Agents
Professionals who provide educational outreach and support in agriculture.
Ag Teachers
Educators who teach agricultural sciences.
Reproductive Strategies
Methods by which plants reproduce, including spore and seed production.
Algae
One-celled organisms that can be used as food, often found in aquatic environments.
Tracheophyta
A plant subdivision that includes vascular plants, which have specialized tissues and cells.
Spermatophyta
A subdivision of Tracheophyta that includes seed-bearing plants.
Monocotyledons
Plants with one seed leaf, including grasses, palms, and orchids.
Dicotyledons
Plants with two seed leaves, including most trees, shrubs, and perennials.
Non-vascular tissues
Tissues in plants that do not have specialized structures for water and nutrient transport.
Reproductive cells
Cells involved in the reproduction of plants, often requiring water for sexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction by spores
A method of reproduction in which single-celled spores with protective coats are produced.
Double fertilization
A process in angiosperms where one sperm fertilizes the egg and another forms endosperm.
Ovule
The structure in seed plants that develops into a seed after fertilization.
Seed production
The process by which plants produce seeds, which can be protected or unprotected.
Gymnosperm vs. Angiosperm Seeds
Gymnosperms have 'naked seeds', while angiosperms have seeds enclosed in a fruit.
Distinct tissues and organs
The specialized structures found in vascular plants that facilitate various functions.
Cultivar
A cultivated variety of a plant species, often selected for specific characteristics.
Purple coneflower
A variety of Echinacea species, known for its medicinal properties.
Kingdom Plantae
The biological classification that encompasses all plants.
Division Tracheophyta
The classification of vascular plants within the plant kingdom.