EXAM 4 (ch.12-14) - Dr. Jones
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
sensory receptors
specialized to respond to changes in environment (stimuli)
sensation
awareness of stimulus
perception
interpreting meaning of stimulus
mechanoreceptors
respond to touch, pressure, vibration, and stretch
thermoreceptors
sensitive to change in temperature
photoreceptors
respond to light energy
ex.retina
chemoreceptors
respond to chemicals
eg. smell, taste, change in blood chemistry
nociceptors
sensitive to pain-causing stimuli (INTENSE stimulation)
eg. extreme cold/heat, excessive pressure, inflammatory chemicals
exteroceptors
respond to stimuli arising outside body
(most special sense organs)
-receptors for touch, pressure, pain, temp
interceptors
visceroceptors
-respond to stimuli arising in organs and blood vesels
proprioceptors
respond to stretch in skeletal muscles, tendons, joints, ligaments..
-inform brain of one’s movements
somatosensory system
part of sensory sytem serving body wall and limbs
-recieves inputs from Exteroceptors, Proprioceptors, and Interoceptors; input relayed TOWARD head, but processed along the way
adaption
change in sensitivity in presence of CONSTANT STIMULUS
inhibitory endogenous opioids
pain impulse blockage; protective action by body
eg. endorphins
visceral pain
stimulation of visceral organ receptors
-felt as vague aching, gnawing, burning
referred pain
pain from one body region percieved as coming from a diff. regionn
-visceral and somatic pain fibers travel along same nerves which cause brain to assume stimulus comes from common (somatic) region
nerve
- cordlike organ that is part of the peripheral nervous system
- classified as cranial or spinal
- consists of bundles of peripheral axons enclosed by of connective tissue
endoneurium
- layer of loose connective tissue that also encloses the fibers associated with Schwann Cells
perineurium
- coarser connective tissue wrapping
- binds groups of axons
epineurium
- tough fibrous sheath
- encloses all the fascicles to form the nerve
fascicles
groups of axons binded by perineurium are called...
mixed nerves
- contain both sensory and motor fibers and transmit impulses both to and from the central nervous system
- most are mixed (both sensory and motor)
ganglia
- collections of neuron cell bodies associated with nerves in the PNS
automatic nervous system
(Part of the Motor Division of the PNS)
Made up of the Sympathetic Division and the Parasympathetic Division
-maintains homeostasis
difference of automatic nervous system and somatic nervous system
-effectors
Somatic NS : innervate skeletal muscles
ANS: inervates cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
-number of neurons in charge of transmission
-neurotransmitters depend on target
parasympathetic division
promotes maintenance functions, conserves energy
sympathetic division
mobilizes body during activity
dual innervation
all visceral organs are served by both parasympathetic and sympathetic divisons
-conserve energy or mobilize for action
parasympathetic divison
rest-and-digest
-ppupils constricted
-direct digestion, diuresis, defecation
sympathetic division
fight or flight system
-excitement, emergency
-dilated pupils
-shunt blood to skeletal muscles and heart
-cause liver to release glucose for muscles
sympathetic division
increase heart and respiratory rates and inhibits digestion and elimination
parasympathetic division
decreases heart and respiratory rates and allows for digestion and discarding of wastes
nerves
bundle of axons in PNS
cephalization
concentration of nervous tissue in the head
cerebral hemispheres
diencephalon
brain stem
cerebellum
what are the adult brain 4 regions?
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
what does the brain stem consist of?
gray matter
NON-MYELINATED NEURONS and cell bodies
white matter
MYELINATED and NONMYELINATED AXONS
-fat/lipid with protein
basic pattern found in CNS
central cavity SURROUNDED by GRAY MATTER, WHITE MATTER external to GRAY MATTER
(pattern change ascending brain stem)
cortex
what the cerebral hemispheres (cerebrum) and cerebellum contain OUTER LAYER OF GRAY MATTER
spinal cord pattern
-inner gray matter
-outer white matter
cerebrum and cerebellum pattern
-islands of gray matter (nuclei) within white matter
-cortex of gray matter
ventricles
filled with cerebrospinal fluid
-lined with ependymal cells (neuroglial cells)
-paired lateral ventricles separated by membranous septum pellucidum
diencephalon
where third ventricle lies in
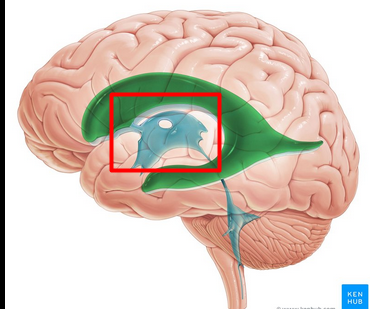
cererbral aqueduct
how third ventricle is connected to fourth ventricle
cerebral hemispheres
form superior part of brain
-account for majority of brain mass
gyri
ridges
sulci
shallow grooves
fissures
deep grooves
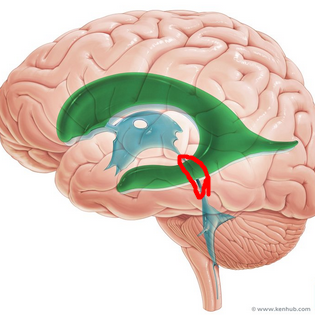
longitudinal fissure
seperates two hemispheres
transverse cerebral fissure
seperates cerebrum and cerebellum
insula
lobe buried under portions of temporal, parietal, and frontal lobes
-not visible on surface
central sulcus
Separates precentral gyrus of frontal lobe and postcentral gyrus of parietal lobe
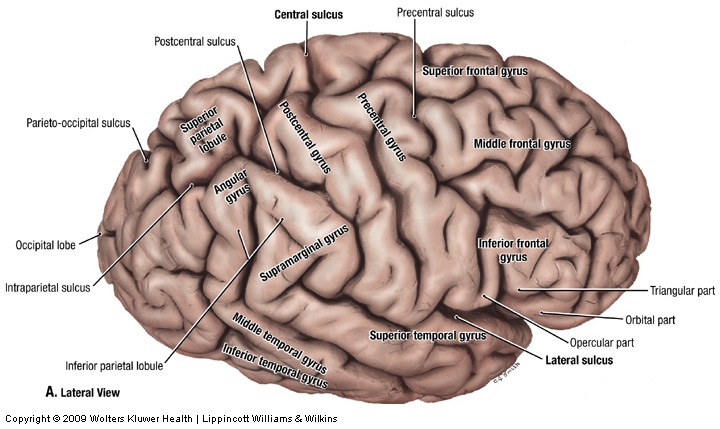
parieto-occipital sulcus
Separates occipital and parietal lobes
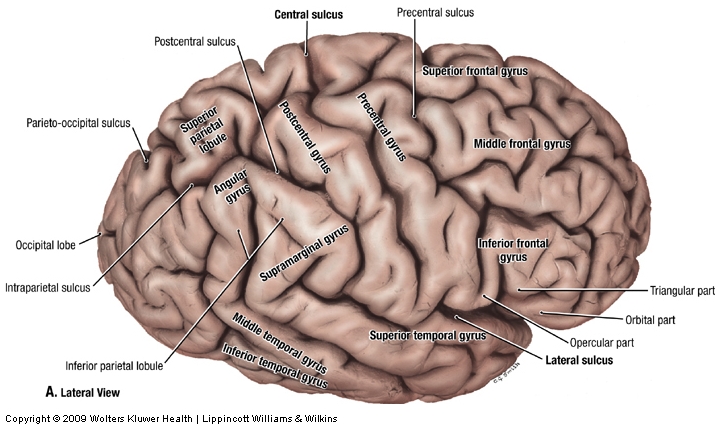
lateral sulcus
outlines temporal lobes
each hemisphere’s basic regions
-cerebral cortex of gray matter on surface
-internal white matter
-basal nuclei deep within white matter
cerebral cortex
“executive suite” of the brain
-site of CONSCIOUS MIND: awareness and sensory perception
4 considerations of CEREBRAL CORTEX
Motor areas: control voluntary movement
Sensory areas: conscious awareness of sensation
Association areas: integrate diverse info into all one unique event
Lateralization: (specialization) of cortical function occure in only ONE hemisphere
contralateral
opposite (side of body)
primary (somatic) motor cortex
stimulate skeletal muscle
-pyramidal cells: large neurons in charge of allowig control of precise, skilled skeletal muscle movement
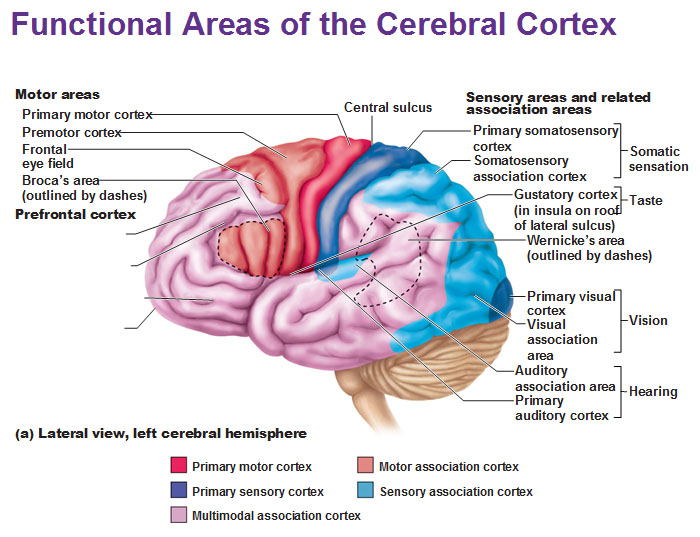
premotor cortex
helps plan movements
-ctrl learned, repeated, or patterned motor skills
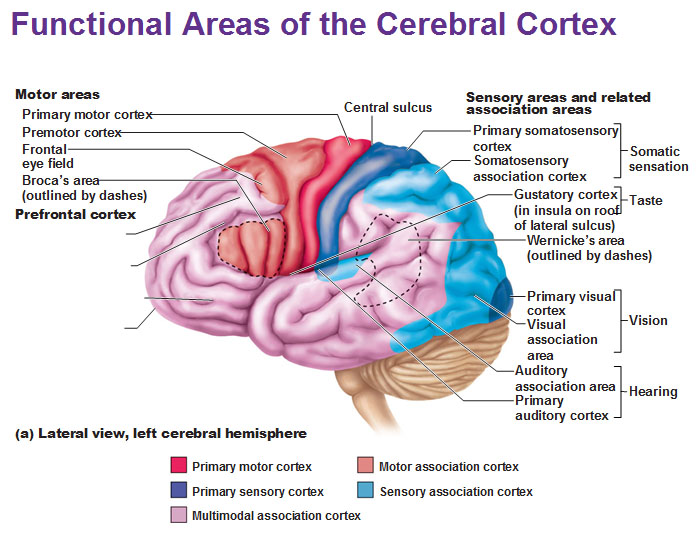
broca’s area
in charge of communication; physically initiate speech and forming words
-planning speech
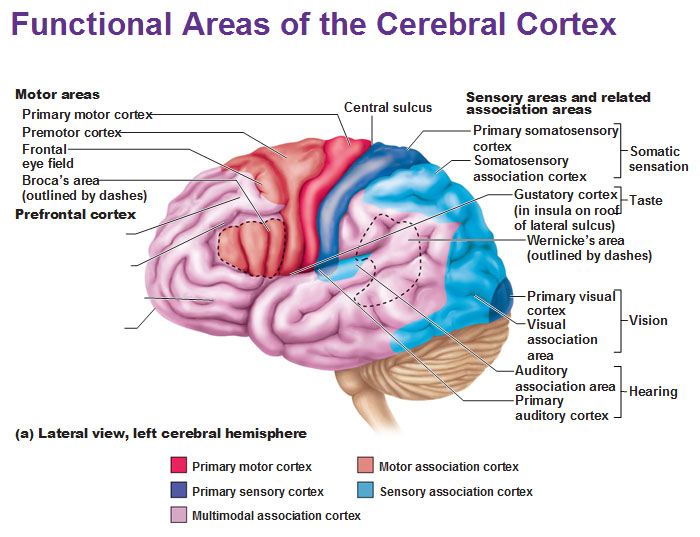
frontal eye field
control voluntary eye movements
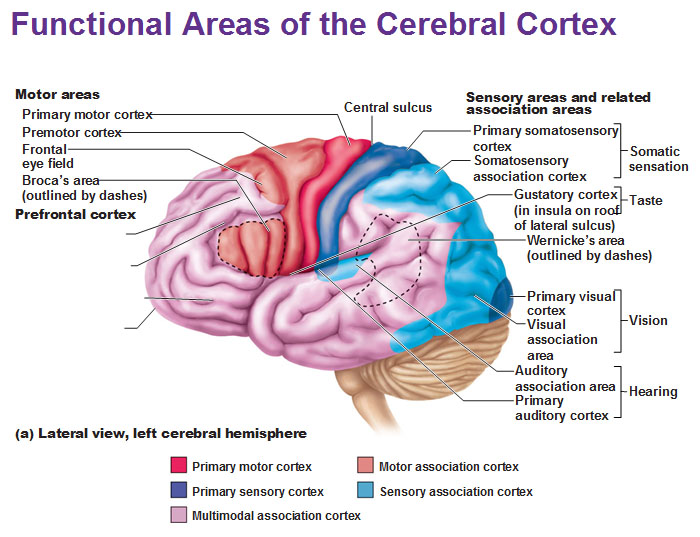
stroke or muscle paralyzation
damage to PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX results in…
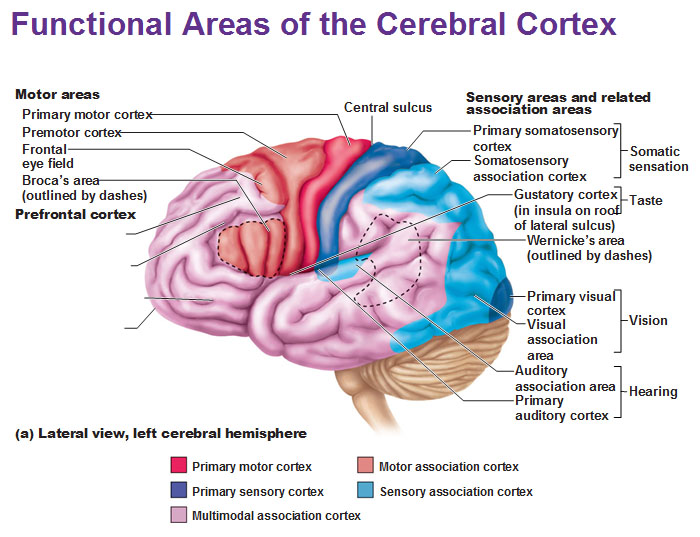
neural plasticity
ability of brain to change its function by changing its structure
-brain can rewire in certain cases to maintain function
primary somatosensory cortex
recieve sensory info from skin and proprioceptors (relating info relation to body position) of skeletal muscle, joints, tendons
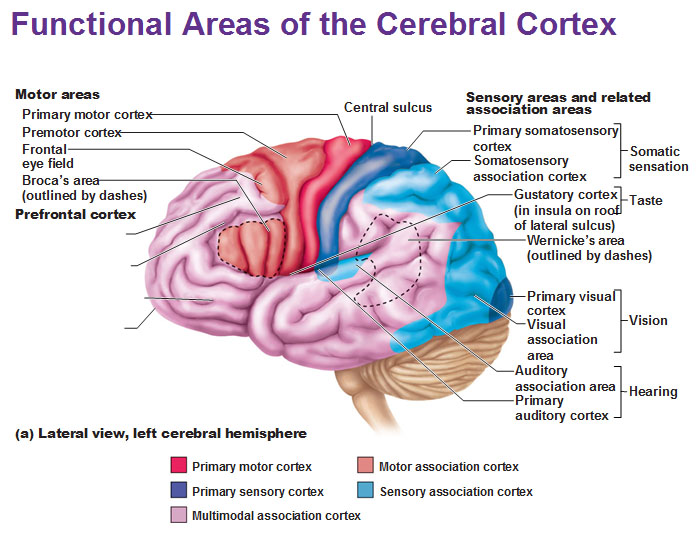
primary somatosensory cortex
capable of SPATIAL DISCRIMINATION: identification of body region being stimulated (what is the cortex?)
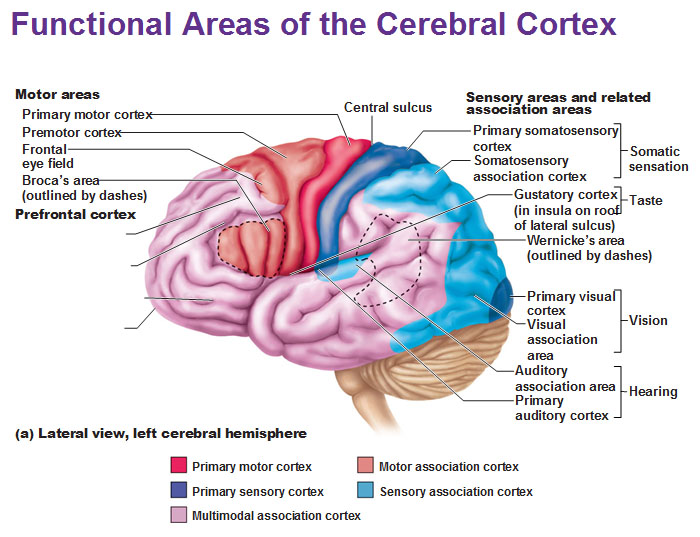
somatosensory association cortex
organize sensory neurons and understand object of sensation
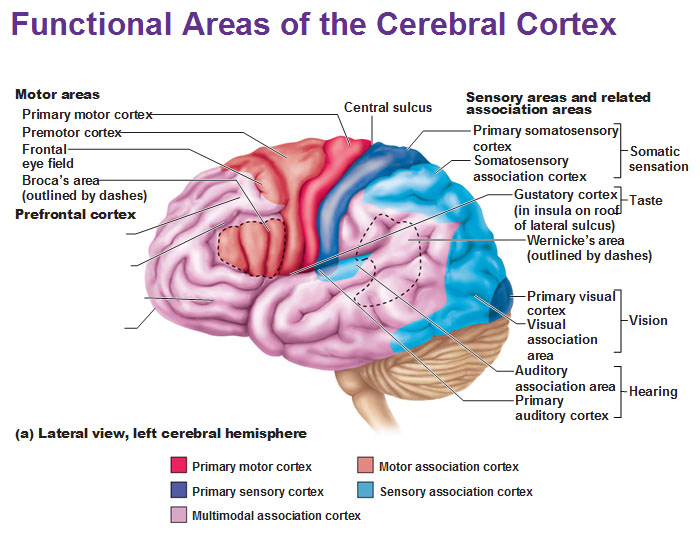
somatosensory association cortex
determines size, texture, and relationship of parts of objects being felt is the function of what cortex?
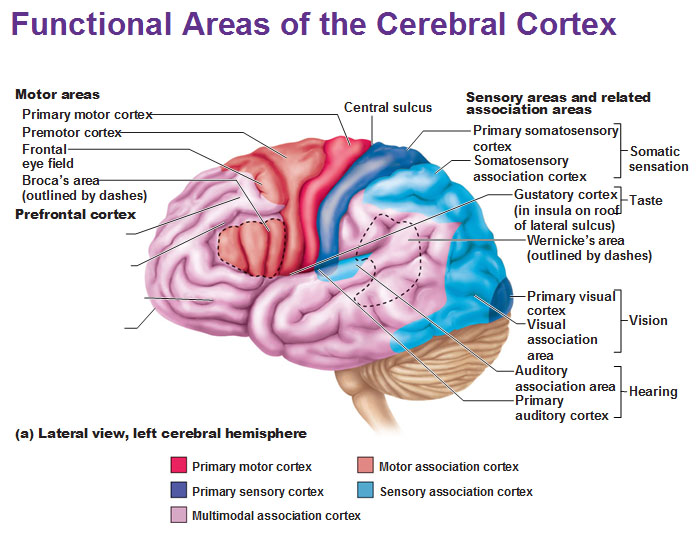
primary visual (striate) cortex
bipolar retina neuron = perceve changes in light
-recieve info from retinas
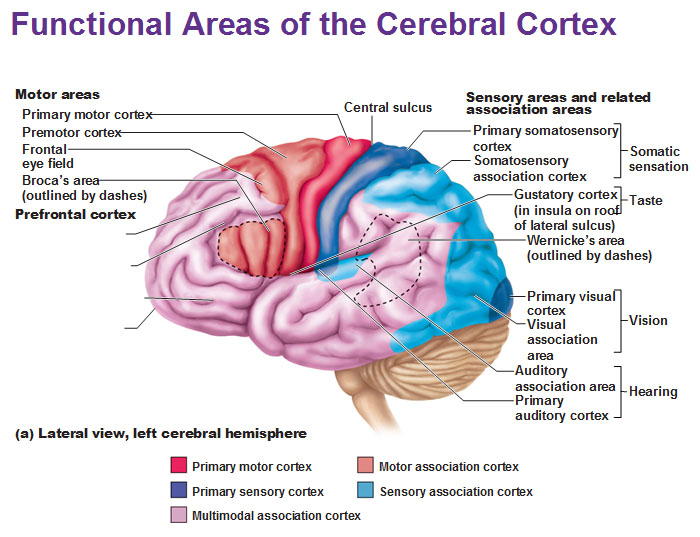
visual association area
-surrounds primary visual cortex
-uses past visual exp. to interpret visual stimuli
ex. ability to recognize faces
primary auditory cortex
interpret info from inner ear as pitch, loudness, location
-what u hear
auditory association area
store memories of sounds and allows perception of sound stimulus
-what the sound means
vestibular cortex
responsible for conscious awareness of balance (position of head in space)
-Consciously aware of position
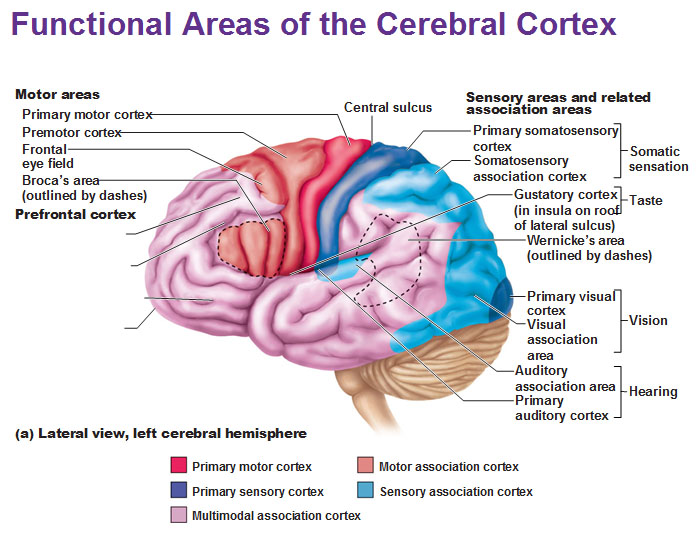
primary olfactory cortex
-conscious awareness of odors
-primative rhinencephalon, smell baby, food..
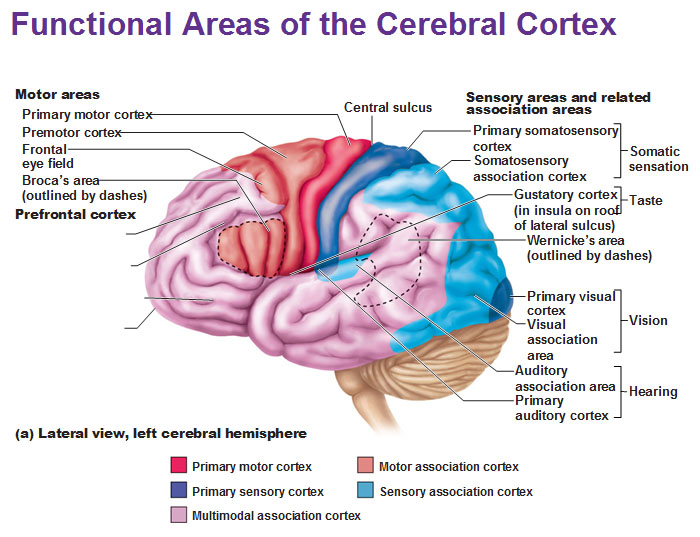
gustatory cortex
perception of taste
*taste and smell go together
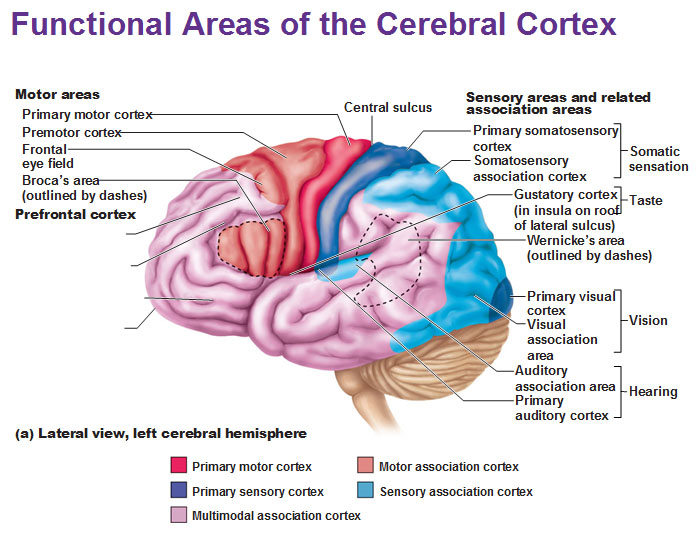
visceral sensory area
Perceive fullness or stretch of organs
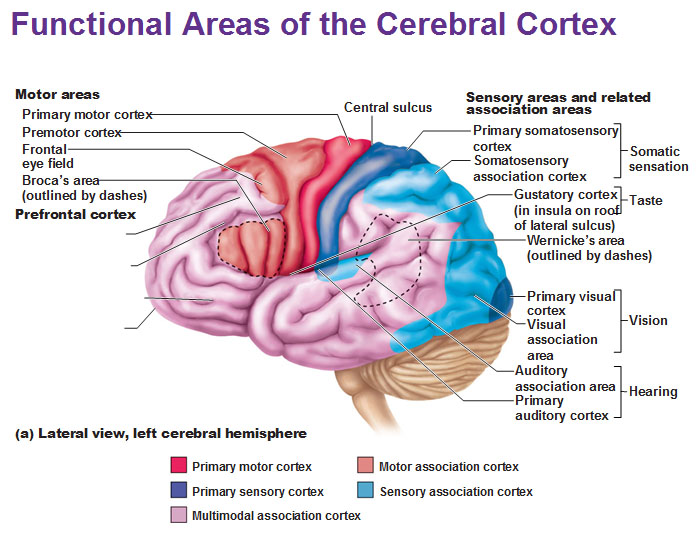
anterior of brain
where can you find motor areas of the brain?
posterior of brain
where can you find sensory areas of the brain?
damage to primary visual cortex
functional blindness; patient can see but do not comprehend what they are looking at
multimodal association areas
recieve inputs from multiple sensory areas and send outputs to multiple areas ex. we hear before we see
-gives meaning. connection to sensation, thoughts, emotions; makes us who we are
stages sensory receptors take through the brain
sensory receptors > primary sensory cortex > sensory association cortex > multimodal association cortex
prefrontal cortex / anterior association area
-unique personality
-form working memory
-reason + judgement
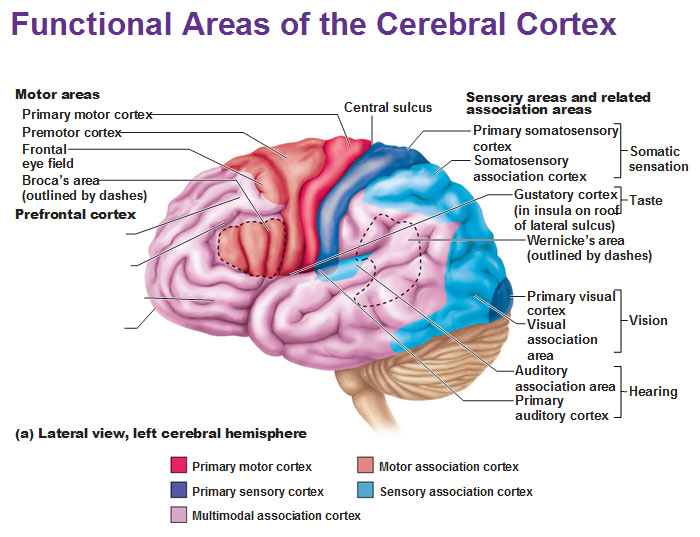
posterior association area
recognizing patterns and faces and localizing us in space
-”do i know what im looking at and where it is in relation to me?”
limbic association area
provides emotional impact that helps establish memories
cerebral dominance
hemisphere that is dominant for language (most humans have left sides dominance in brain, meaning they use right side of their body more)
lateralization
division of labor between hemispheres
-hemispheres are not identical
left hemisphere
control language, math, logic
(what is the hemisphere?)
right hemisphere
visual-spatial skills, intuition, emotion, artistic and musical skills
(what is the hemisphere?)
association fibers
horizontal running fibers that connect different parts of the same hemisphere
(white matter)
commissural fibers
horizontal fibers that connect gray matter of two hemispheres
projection fibers
vertical fibers that connect upper hemispheres with lower brain or spinal cord
basal nuclei
minimize unnecessary behaviors
-influence muscle movements, play role in cognition and emotion
Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease
disorders of basal nuclei
-eg.. tremors
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
what are the 3 paired gray matter structures in the Diencephalon
thalamus
relay station for information coming in the cortex (afferent + efferent)
-sorts, edits, relays ascending input
-EVERYTHING goes through EXCEPT olfactory (smell) >goes to olfactory cortex
hypothalamus
-influences how endocrine system work
-maintains homeostasis of automatic nervous system (blood pressure, response to emotion), AND part of limbic system(pleasure, fear)
-regulate body temp, hunger/satiety, water balance/thirst, sleep-wake cycle
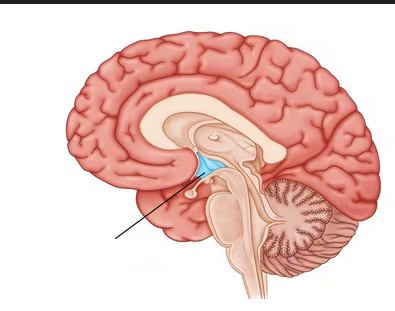
epithalamus
-contains pineal gland (secretes melatonin to regulate sleep-wake cycle; fall sleep)
automatic behaviors necessary for survival
what does the brain stem control?
superior colliculi
-connect to corpora quadrigemina
visual reflex centers
-Reflexive action to what you see