Rutgers General Biology 115 Final Exam
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
179 Terms
Memory
storage
Learning
using information
Gene Expression
how your DNA is used
Signal Transduction
when your expression occurs
Neuronal Plasticity
modified after birth, meaning connections in the brain can be remodeled by experiences
Synapses
tiny spaces between neurons, tells brain what is important
encode
permanent connections in the brain
store
memory in cerebral cortex
sensory memory
experience; if you pay attention it goes to short term memory or working memory
short term memory
what you are aware of now, held for a short time. Holds 7+- 2 items
ex: plan, strategize, organize, create organizers, outline
Long term memory
permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system
ex: practice evaluations, discussions, self evals
long-term potentiation (LTP)
a process whereby communication across the synapse between neurons strengthens the connection, making further communication easier
Chunking
organizing items into familiar, manageable units
ex:
Studying in Segments
Review every few days
Determine what you know
Try to explain the material to someone else
stimulus
any event or situation that evokes a response
ex: lectures/ notes
Evolution
Change in a kind of organism over time; process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms.
emergent properties
New properties that arise with each step upward in the hierarchy of life, owing to the arrangement and interactions of parts as complexity increases.
Levels of Biological Organization (largest to smallest)
biosphere, ecosystems, communities, populations, organisms, organs and organ systems, tissues, cells, organelles, molecules
The Scientific Method
Observation, Hypothesis, Experiment, Data Collection, Conclusion, and Retest (if needed)
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
Predictions
specific statements that can be directly and unequivocally tested
Theory
A broad explanation of natural events that is supported by strong evidence.
Law
statement of what always happens/ is
CHON
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen make up 96% of living matter
Protons
Charge: +
Location: nucleus
Role in atom: identity and mass
Electrons
Charge: -
Location: orbiting nucleus
Role in atom: reactions
Neutrons
Charge: no charge
Location: nucleus
Role in atom: mass
Potential Energy
stored energy
ex: further away e- is from the nucleus, the more potential energy e- has
Molecules
Groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
chemical bonds
the attractive force that holds atoms or ions together
Electronegativty
a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons
Covalent Bonds (Nonpolar)
Strength: strongest
Between: atoms
E-Sharing: equally
Electronegativity: same
Solubility: non-polar solvents
Example: CH4, O2, H2
Covalent Bonds (Polar)
Strength: strongest
Between: atoms
E-Sharing: unequally
Electronegativity: < 2 difference
Solubility: polar solvents
Example: H2O
Ionic Bonds
Strength: Not so strong (b/c of water)
Between:atoms
E-Sharing: transferred
Electronegativity: > 2 difference
Solubility: more soluble in a polar solvent
Example: Table Salt (NaCl)
Van der Waals interactions
Strength: weak alone, strong together
Between: molecules
E-Sharing:
Electronegativity:
Solubility:
Example: Gecko Feet
Hydrogen bonds
Strength: fairly strong
Between: molecules
E-Sharing:
Electronegativity:
Solubility: Polar solvents
Example: water molecules
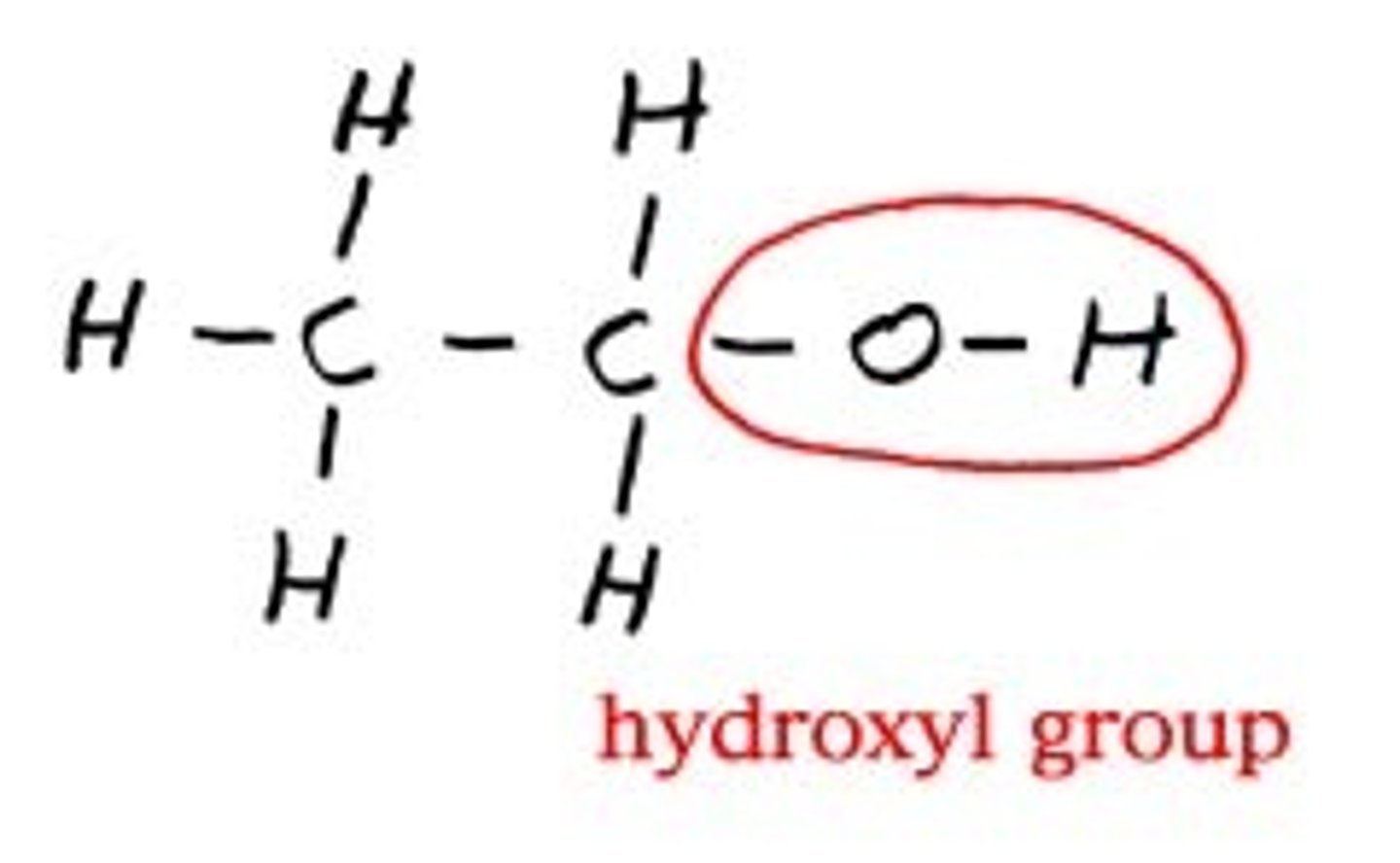
hydroxyl group (-OH)
Compound Name: alcohol
Polar/ Non: polar
Hydrophilic: yes
Acid or Base: neither
Example: Ethanol
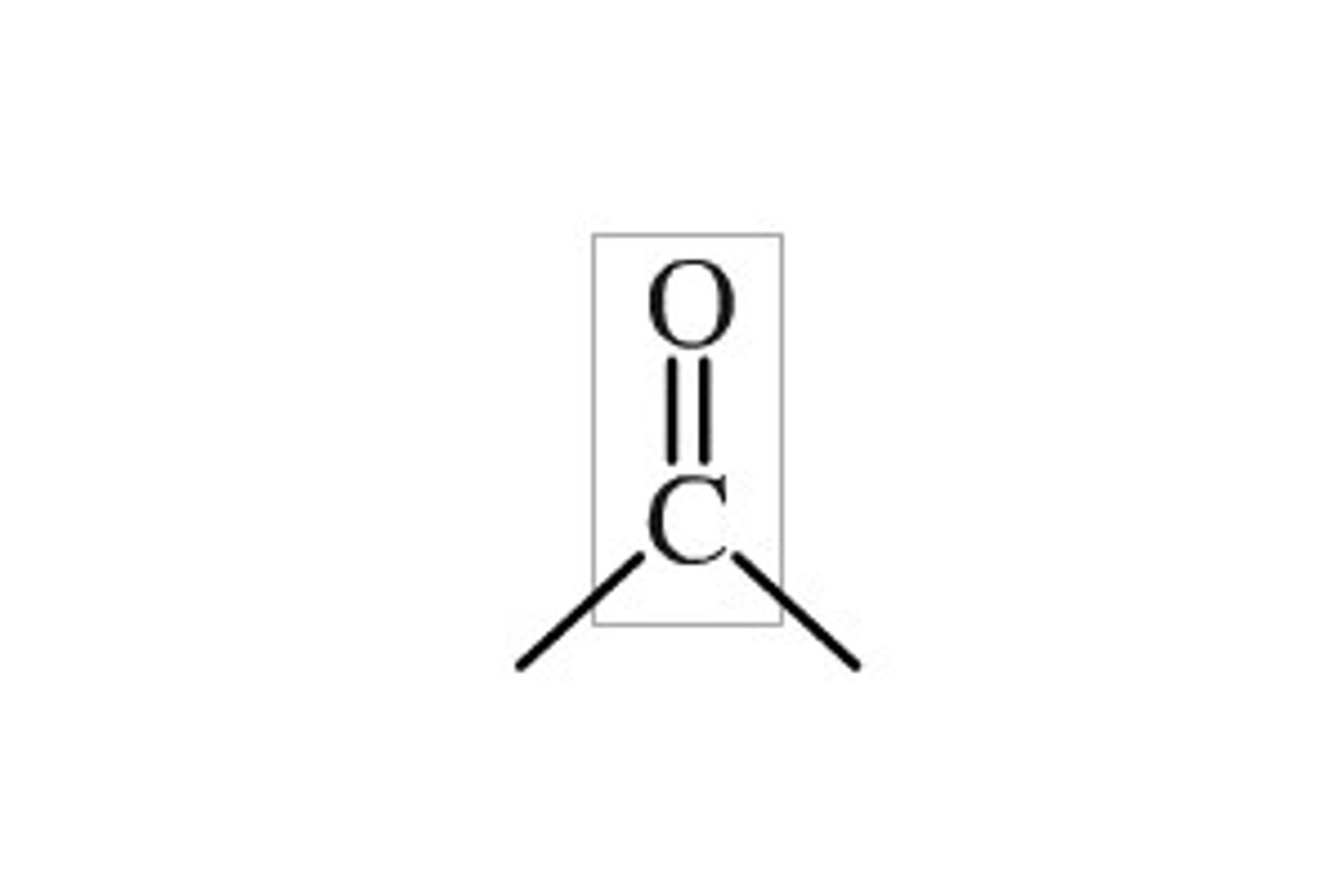
Carbonyl group (C=O)
Compound Name: Aldehyde (to the side), Ketone (surrounded)
Polar/ Non: Polar
Hydrophilic: yes
Acid or Base: neither
Example: Acetone (Ketone), Propanal (Aldehyde)
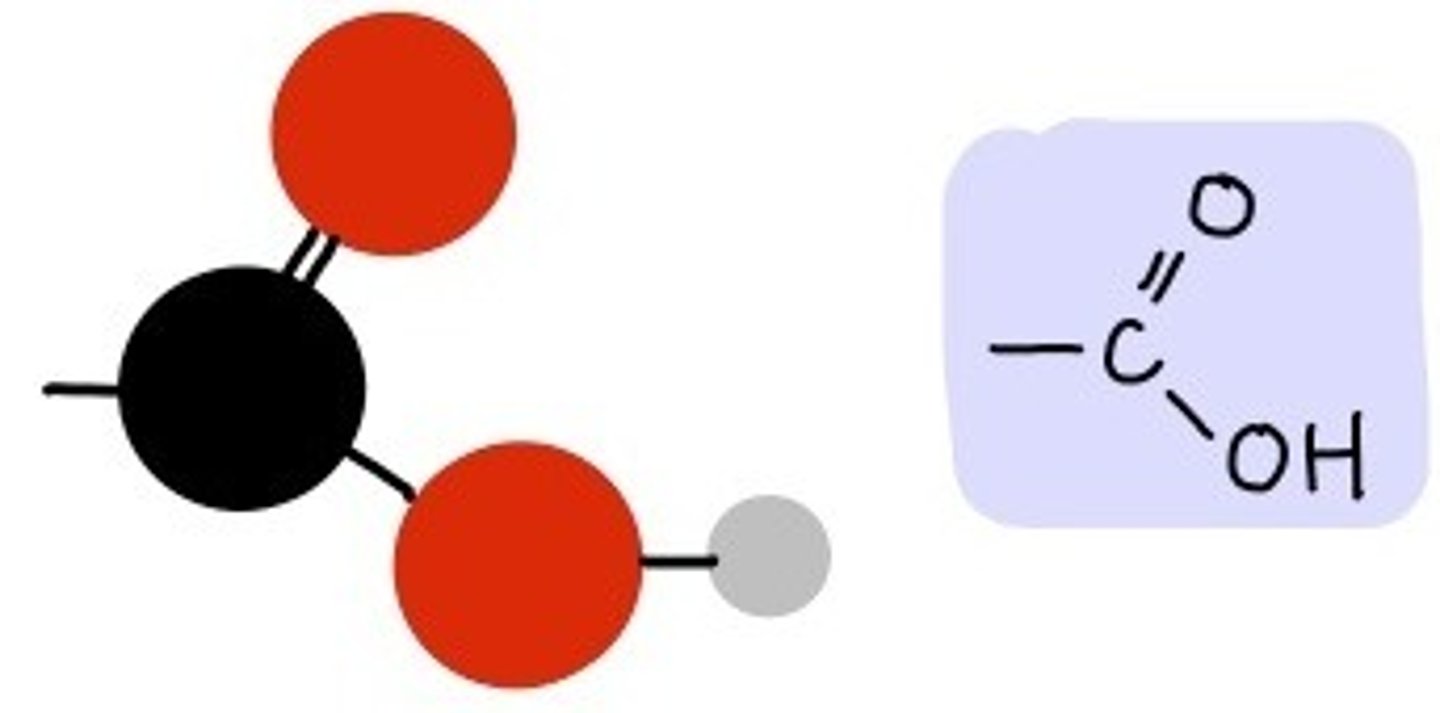
Carboxyl group (-COOH)
Compound Name: Carboxylic Acids
Polar/ Non: polar
Hydrophilic: yes
Acid or Base: acid
Example: Acetic Acid
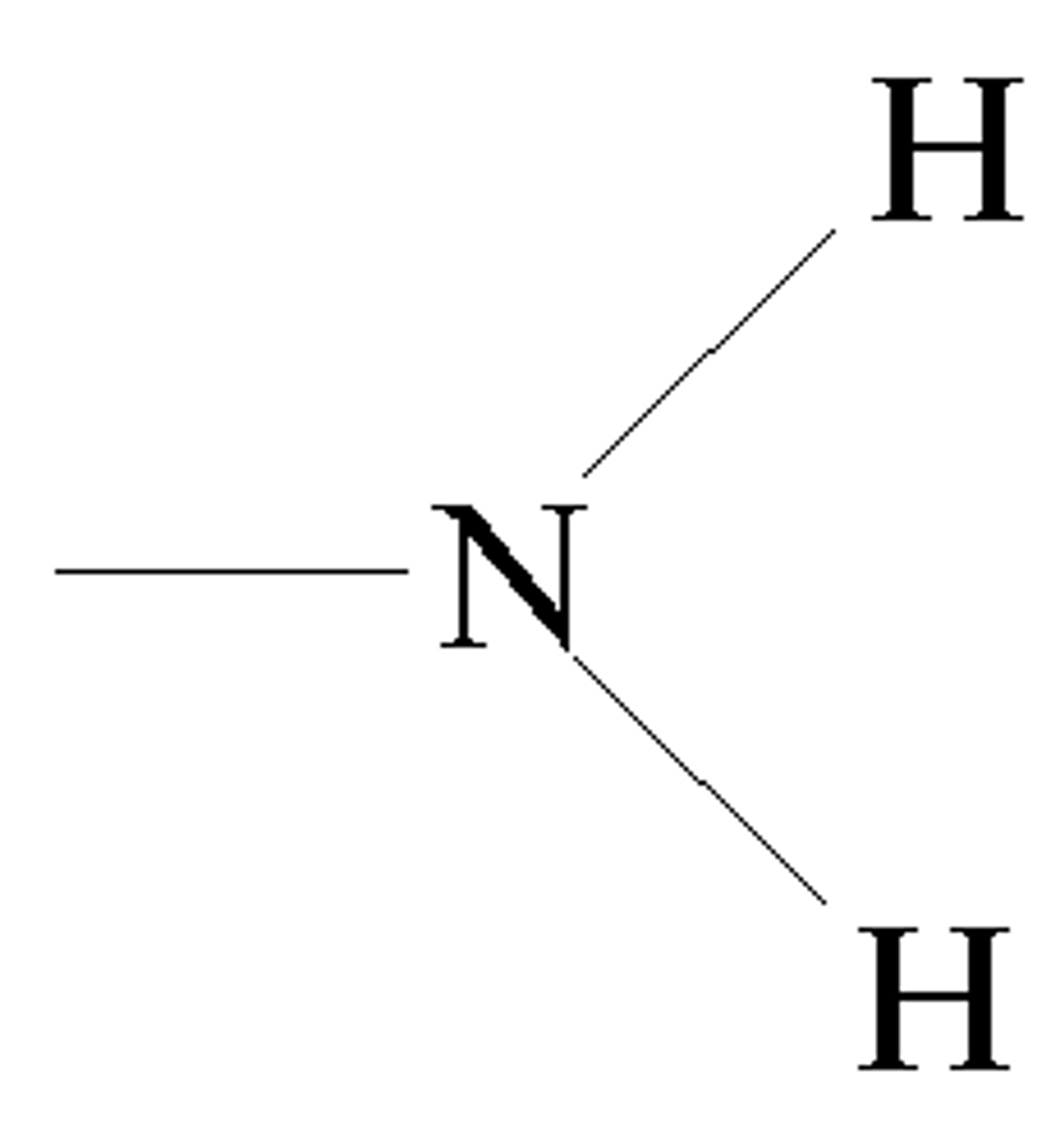
Amino group (-NH2)
Compound Name: Amines
Polar/ Non: polar
Hydrophilic: yes
Acid or Base: Base
Example: Glycine (amino acid)
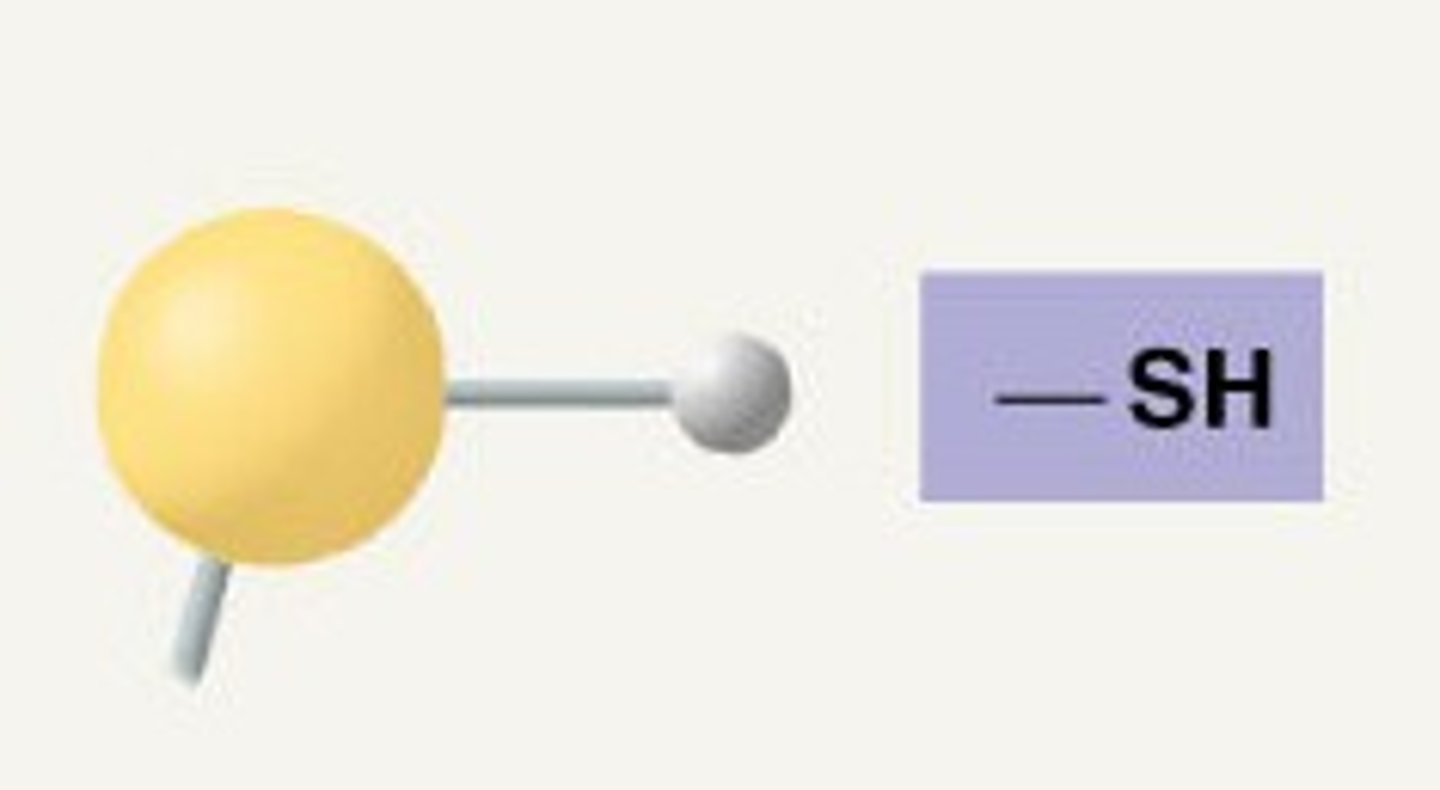
Sulfhydryl Group (SH)
Compound Name: Thiols
Polar/ Non: Polar
Hydrophilic: Yes
Acid or Base: Neither
Example: Cysteine
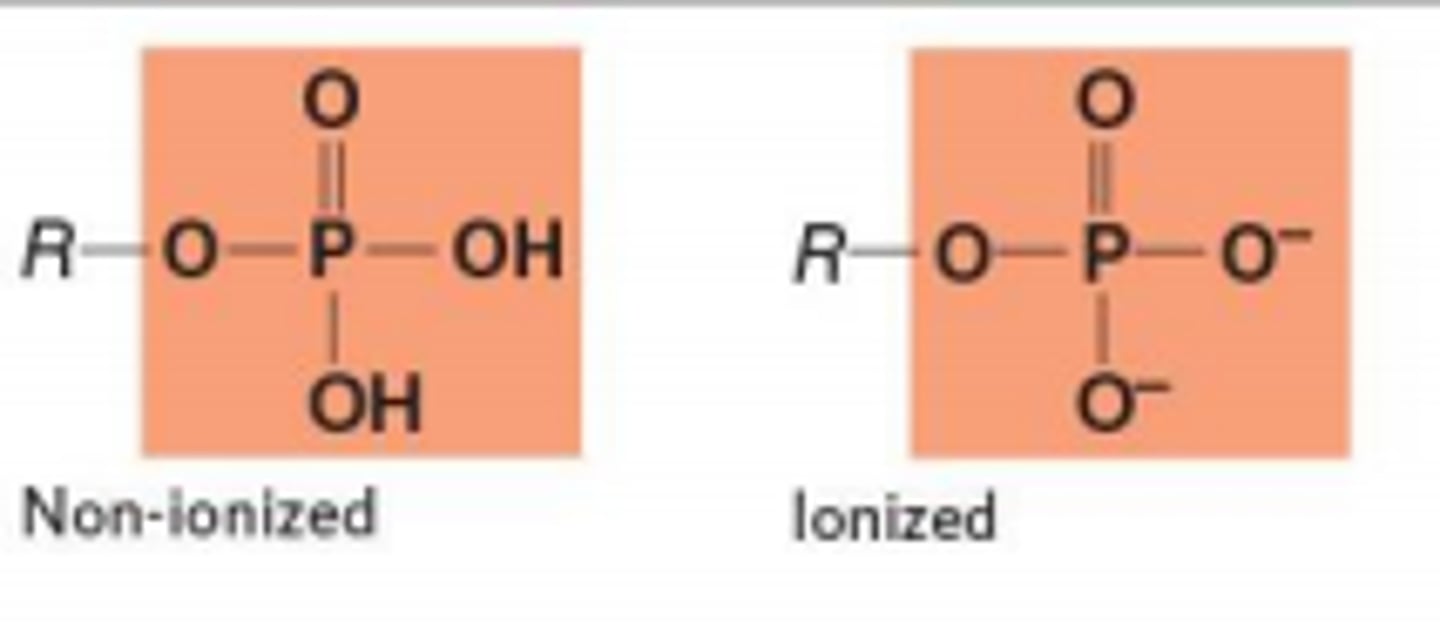
Phosphate Group (PO4H2)
Compound Name: Organic Phosphate
Polar/ Non: Polar
Hydrophilic: Yes
Acid or Base: Acid
Example: Glycerol Phosphate
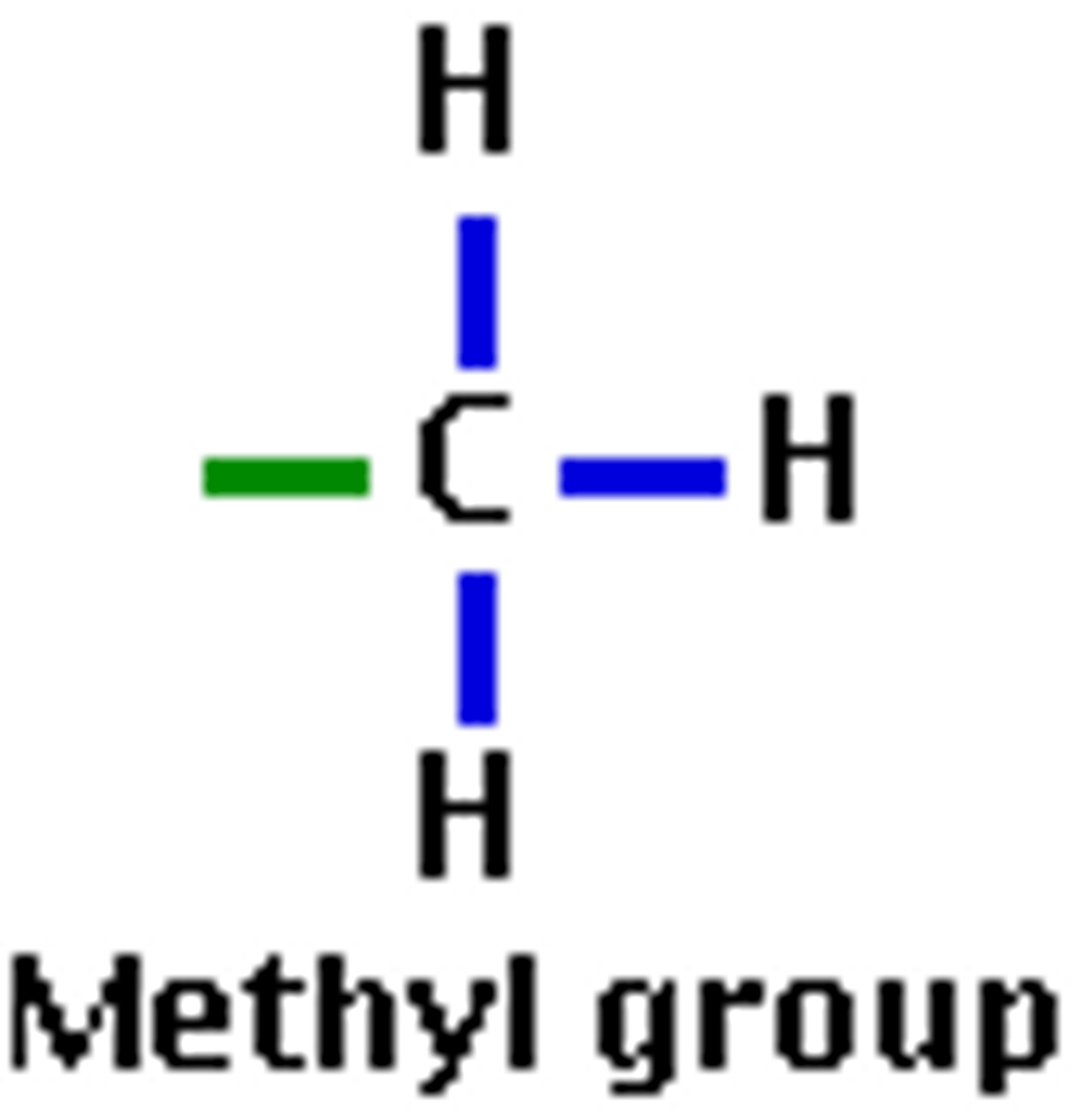
Methyl Group (CH3)
Compound Name: Methyl hydrocarbon
Polar/ Non: nonpolar
Hydrophilic: hydrophobic
Acid or Base: neither
Example: 5 methyl cytosine
Carbohydrates (CH2O)
Monomers: Monosaccharides (glucose, fructose)
Bonds between: glycosidic linkages
Polymers: Di-Saccharide (sucrose), Polysaccharide
(cellulose)
Hydro..: philic
Functional Groups: Carboxyl, Hydroxyl, Carbonyl
Functions: A) energy storage, B) structure
Examples: A)Starch, Glycogen, B)Cellulose, Chitin
Lipids
Monomers:
Bonds between: ester linkages
Polymers:
Hydro..: phobic
Functional Groups: glycerol and fatty acids
Functions: Energy storage (fats), Communication (steroids), Phospholipid membranes
Examples: saturated: butter, unsaturated: olive oil
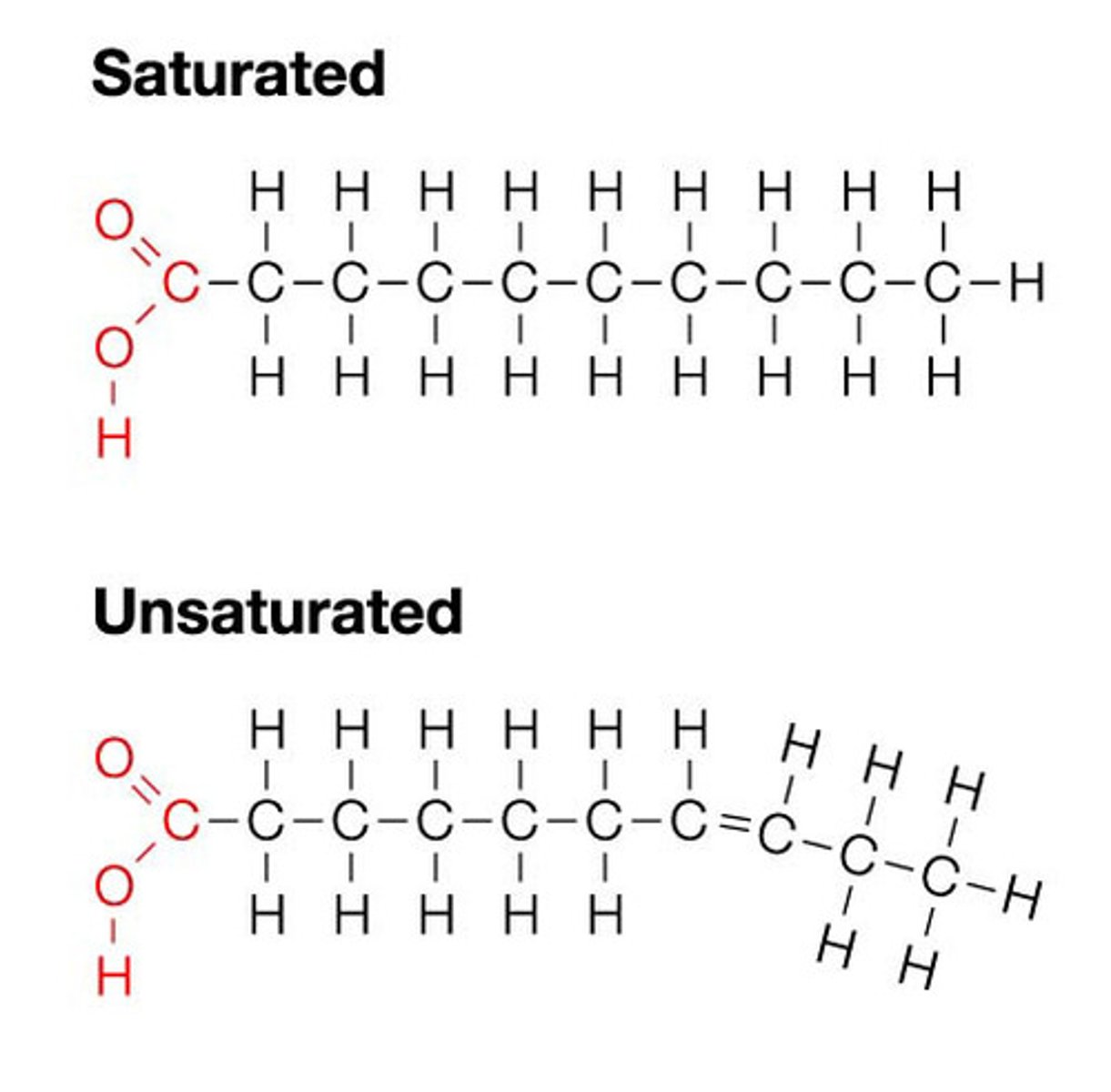
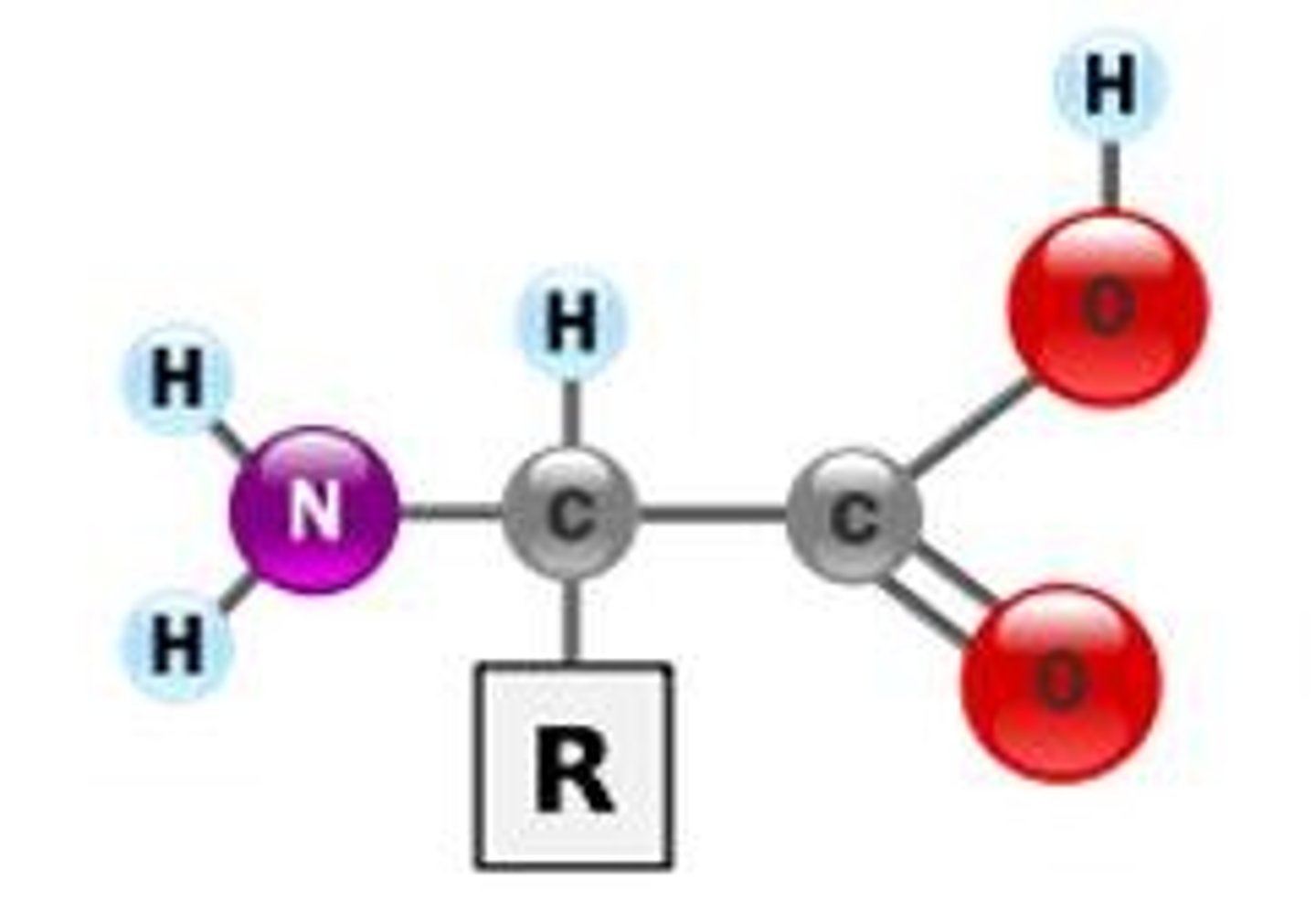
Proteins
Monomers: amino acids
Bonds between: peptide bonds
Polymers: polypeptides
Hydro..: philic and phobic
Functional Groups: amino, carboxyl
Functions: enzymes, structure, transport
Examples:
Nucleic Acid
Monomers: nucleotides
Bonds between: Phosphodiester Bonds
Polymers: DNA, RNA
Hydro..: philic
Functional Groups: phosphate
Functions: Storage of genetic info, Heredity, Protein Production
Examples: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, DNA
primary structure of protein
Bonds between: Amino Acids (Peptide bonds)
Function groups involved?: No
secondary structure of protein
Bonds between: Amines + Carboxyls (Hydrogen bond)
Function groups involved?: No
tertiary structure of protein
Bonds between: R- groups (All types of bonds)
Function groups involved?: Yes
quaternary structure of protein
Bonds between: Two or more Different folded
polypeptide chains
Function groups involved?: Yes
prebiotic soup hypothesis
Where: Surface of the Earth
Energy Source: Atmospheric discharge
(Lightning, Volcanoes, Meteoroids, Radiation)
Evidence: Miller and Urey (created synthetic atmosphere using CH4, H2O vapor, H2, and NH3)
CHON: atmosphere CH4, H2O, H2, and NH3
Catalysts:
Author: Oparin & J.B.S Haldane
iron-sulfur world hypothesis
Where: ocean floor, hypothermal vents
Energy Source: hydrothermal vents
Evidence/ Experiments:
CHON: hydrothermal vents
Catalysts: iron
Authors:
SEQ Abiogenesis
Synthesis of monomers, synthesis of macromolecules, protocells, self replication
Prokaryotic Cells
Size: 1-10 um
Organelles: no membrane bound organelles
Structures: cell wall, plasma membrane, cytosol, chromosomes, ribosomes, nucleoid
DNA Storage: nucleoid
DNA: yes
Evolutionary history: via protocells and self-replication
Eukaryotic Cells
Size: 10 -100 um
Organelles: mitochondria, nucleus, etc
Structures:
DNA Storage: nucleus
DNA: yes
Evolutionary history: endosymbiosis
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for making ribosomes, DNA, and proteins
Ribosomes
synthesize proteins/ polypeptides
Rough ER
proteins folded and modified, secrete glycoproteins, distribute transport vesicles, cell membrane factory
Smooth ER
synthesis of lipids, metabolism of carbohydrates, and detoxifies the body while storing calcium ions
Golgi
modifies ER products, sorts and packages, manufactures macromolecules, ships products using transport vesicle
Lysosomes
food vacuole stores food, contractile vacuoles pump out water, central vacuoles hold water
Plasma Membrane
exports proteins out of the cell, controls what comes in and out
mitochondria
Produces the energy a cell needs to carry out its functions
vesicles
transports materials within the cell
Exocytosis
Moves waste and proteins out of a cell as through vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes.
receptor-mediated
A type of endocytosis in which the cell acquires bulk quantities of specific substances, even though they may not be very concentrated in the extracellular fluid.
endergonic reaction
An anabolic chemical Reaction that stores free energy from its surroundings through dehydration synthesis.
exergonic reaction
A catabolic, spontaneous Chemical Reaction that releases energy through hydrolysis.
Calvin cycle products
glucose, ADP, NADP+
glycolysis products
2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
oxidation of pyruvate products
2 acetyl COA, 2 NADH, 2 CO2
Citric acid products
6NADH
4CO2
2FADH2
2ATP
oxidative phosphorylation products
2 pyruvate, 2 H2O, 2 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 H+ ions
G1 phase
Most of a cells life
Cell functions, communications, protein manufacturing
S Phase
Chromosomes duplicate (DNA synthesis)
Sister chromatids form
Kinetochores aka protein handles will form from centromere
G2 Phase
Centrosomes duplicate
Prophase (mitosis)
Chromosomes condense
nuclear envelop dissolves
mitotic spindle forms
Metaphase (mitosis)
Longest phase of Mitosis
Chromosomes align on metaphase plate
Anaphase (Mitosis)
Cohesion proteins cleaved
Sister chromatids separate
Telophase and Cytokinesis (mitosis)
2 new daughter cells form
Nuclear envelope reforms
Cytokinesis divides cytoplasm
asexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent.
sexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves two parents that combine their genetic material to produce a new organism, which differs from both parents
Prophase I (Meiosis)
homologous chromosomes pair up and form tetrads, crossing over occurs
Metaphase I (Meiosis)
Tetrads are lined up at the metaphase plate; Spindle fibers attach
Anaphase I (Meiosis)
Homologous chromosomes separate
Telophase I (Meiosis)
Cytokinesis occurs, the result are two haploid daughter cells
Prophase II (meiosis)
A new spindle forms around the chromosomes
Metaphase II (meiosis)
chromosomes line up on metaphase plate
Anaphase II (meiosis)
Sister chromatids split and head toward opposite poles
Telophase II and Cytokinesis (Meiosis)
The cells have now been formed into 4 new cells, and the nuclear membranes come back. These cells are known as haploid cells, and each has half the usual number of chromosomes
Law of Segregation
Mendel's law that states that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
law of independent assortment
Mendel's second law, stating that allele pairs separate from one another during gamete formation
Frederick Griffith Experiment
injected mice with disease- causing strain of bacteria: mice died
injected mice with harmless strain: lived
took of a culture of heat-killed harmful strain and harmless bacteria and mixed them and put in mice and mice died
Avery-MacLeod-McCarty experiment
isolate DNA, protein and others, mix with normal bacteria to prove DNA is transforming substance
Hershey-Chase Experiment
confirmed that DNA is the genetic material because only radiolabeled DNA could be found in bacteriophage-infected bacteria
Base pairing rules
Purine with pyrimidine
cytosine pairs with guanine
adenine pairs with thymine in DNA
adenine pairs with uracil in RNA
Transcription
information in DNA used to synthesize RNA
Translation
decoding of a mRNA message into a polypeptide chain