PLT Praxis 5625 - From Cirrus Practice Booklet
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
198 Terms
Abraham Maslow
He developed the Hierarchy of Needs, which he theorized to be the unconscious desires that motivate people.

guided practice
practicing a new concept with scaffolded support from the teacher (Bandura) essential when using social learning in lesson plans
operant conditioning
provides rewards (intrinsic or extrinsic) or punishment as a motivation for desired performance (Thorndike's research led to it. Watson performed experiments on orphaned infants. Skinner expanded on the theory - learning by responding to the environment rather than stimuli)
short-term memory
information that enters the conscious memory but is not stored for recall at a later time (less than a min unless learner consciously attempts to store it in long-term memory i.e. repetition)
verbal prompting
using words or beginning phonemes to assist students (memory - goes with nonverbal prompting or sentence stems)
inductive reasoning
conclusions are drawn by putting together known concepts and applying them to a new situation (cognitive process) can bring students close to an accurate conclusion (approximation), deductive reasoning is more accurate/absolute
conference
a meeting between teacher and student in which learning is orally assessed and evaluated (can also be to mitigate behavior)
mode
the score that appears most frequently (national, state, and district standardized assessments) Likert Scale should be interpreted using mode, not mean.
attribution theory
internal attribution is assumed when other people make mistakes or are victims, as individuals tend to see others as a predictable stereotype; when an individual makes a mistake, he or she tends to view the cause as external (see yourself as more complex than they give others credit for) Teachers need to be careful about applying internal attributions to students and help students understand others complexity.
visual impairments
problems with eyesight, such as blindness
Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972
protects students against gender discrimination in all federally funded education programs, including colleges that receive federal funding
extrinsic motivation
an external reward (people with an external PLOC - perceived locus of causality - feel outside forces are controlling their behavior and are motivated by external rewards. help students understand their PLOC so they feel more in control of their own behavior).
exit ticket
a small piece of paper that includes two to three short, literal comprehension questions; a useful tool for teachers to assess student understanding at the end of a lesson in order to better shape future lessons (for monitoring and adjusting instruction)
Lawrence Kohlberg
Worked to further develop Piaget's ideas on moral development. Identified the three levels (six stages) of moral development (Preconventional morality, Conventional Morality, Posconventional morality) Moral development in classroom=student participation in creating a social contract. Cooperative learning, role-play, and self-assessment toward stage 5.

Common Core Standards
the predominant set of standards used across most states for Math and English Language Arts
standardized test
a test administered to all students in a consistent way and then graded in the same way so that score comparisons may be accurately made. Used to measure achievement, aptitude, or ability.
Albert Bandura
a Canadian psychologist who developed the social learning theory - Learning is a combination of cognition, behavior, and environment. Change occurs when four processes are present - attention (attention to a behavior to get someone to copy), retention (must have enough meaning to be memorable), reproduction (learner has the skill and ability to recreate behavior), and motivation (positive and negative reinforcement related to behavior). (Bobo doll experiment) Social Learning Theory in classroom=using attention-getting hook, explaining learning goals, recalling background knowledge, modeling, guided practice, feedback, more guided practice, assessment, spiraling the objective into curriculum at a deeper level.

remediation
Strategies that assess the learning needs of each student and provide targeted instruction when there are gaps in a student's background.
selected response
students choose the best answer from the available choices; sometimes called multiple choice. Easy to grade and versatile. Guessing is likely and error analysis is difficult
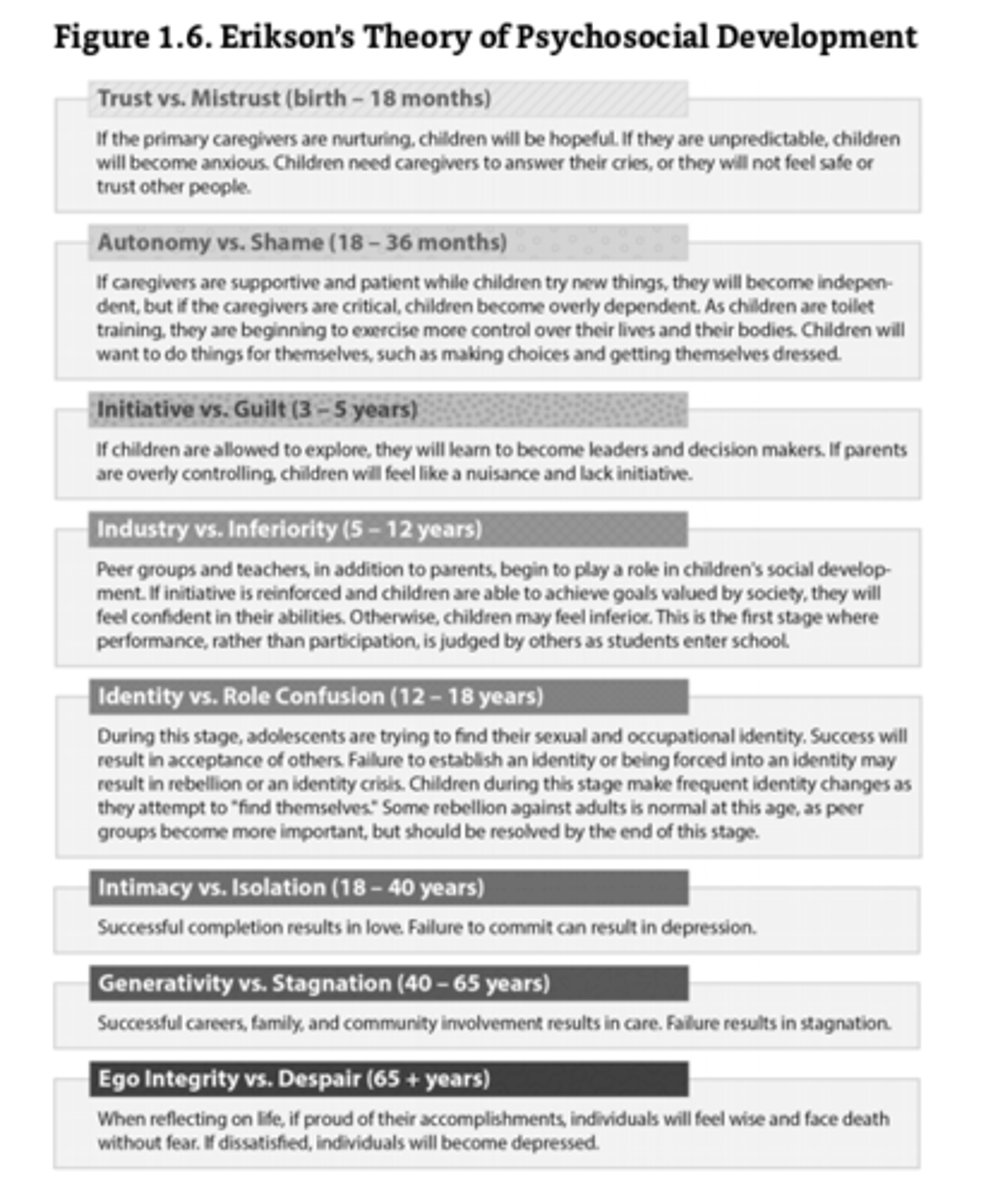
Erik Erikson
Expanded on Sigmund Freud's ideas. His theory of psychosocial development focuses on reconciling individual needs with needs of society through stages. Failure at a stage can result in personality disorders/stunt future stages. Teachers can contribute to the psychosocial development of their students in a variety of ways. Middle and high school students need teachers who model respect, expose them to career choices, and help them build confidence in their abilities.
Professional Learning Communities
small groups of professionals who share common goals that meet to collaborate about instructional practices. PLCs are formal but informal lesson planning meetings are another option.
positive reinforcement
Encouraging a behavior to continue or improve by providing the student with something he or she values such as praise, recognition, or rewards. A part of Behaviorism. Examples: Time to listen to music, homework passes, a free pass to school activity, extra computer time, positive phone call home, preferred activity time, praise, work with a peer, stickers....
paraprofessional
A trained teacher assistant provides student support as determined by the special education faculty. Teacher remains responsible for curriculum and delivering it.
diagnostic assessment
May be formal (usually summative) or informal (formative), given before a learning experience to measure the students' baseline knowledge. Throughout instruction, formative assessments help teacher's monitor student progress to adjust instruction.
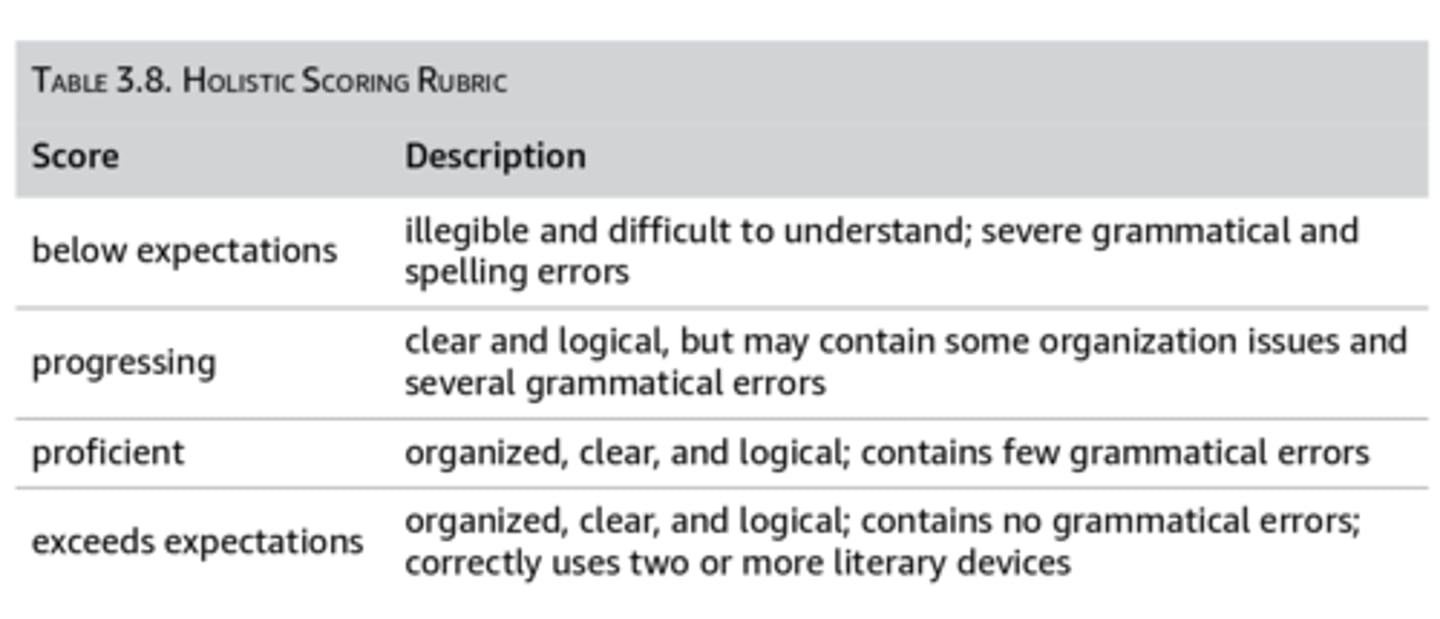
holistic scoring
Uses general categories to rate the overall outcome. Has between 3-5 levels of performance with general statements that include achievement at each level. Easy to make, provide limited feedback.
Edward Thorndike
Foundational Behaviorist, his research initially led to operant conditioning; His learning laws include the law of effect, the law of readiness, and the law of exercise

enrichment
The opportunity to learn objectives at a deeper level than outlined in the curriculum standards. Does not mean more work, means more meaningful work at a higher level of Bloom's technology.
self-regulate
to maintain control of one's own emotional responses (used by teachers who understand constructivism). Teachers who are unable to self-regulate have a negative impact on student learning.
think-pair-shares
Student as Learners and Assessment - an aspect of metacognition, students reflect on a question individually and then turn to other students nearby to share and discuss their responses
cooperative learning
the teacher places students into small groups and gives them a task to complete together. Social learning - students learn from each other. Moves students toward stage 5 in Kohlberg's stages of moral development.
Socratic Questions
a teaching technique in which a leader prompts discussion solely by asking questions and allowing the class to share and then respond to and build upon one another's ideas. Probing questions to help students critically evaluate a topic.
achievement test
tests that measure acquired knowledge or skills. determine what students know at the end of a learning experience, a unite, semester, year, or longer (ex. ACT). Critics say too much emphasis on them, should only be considered as one of multiple measures. Cultural biases persist.
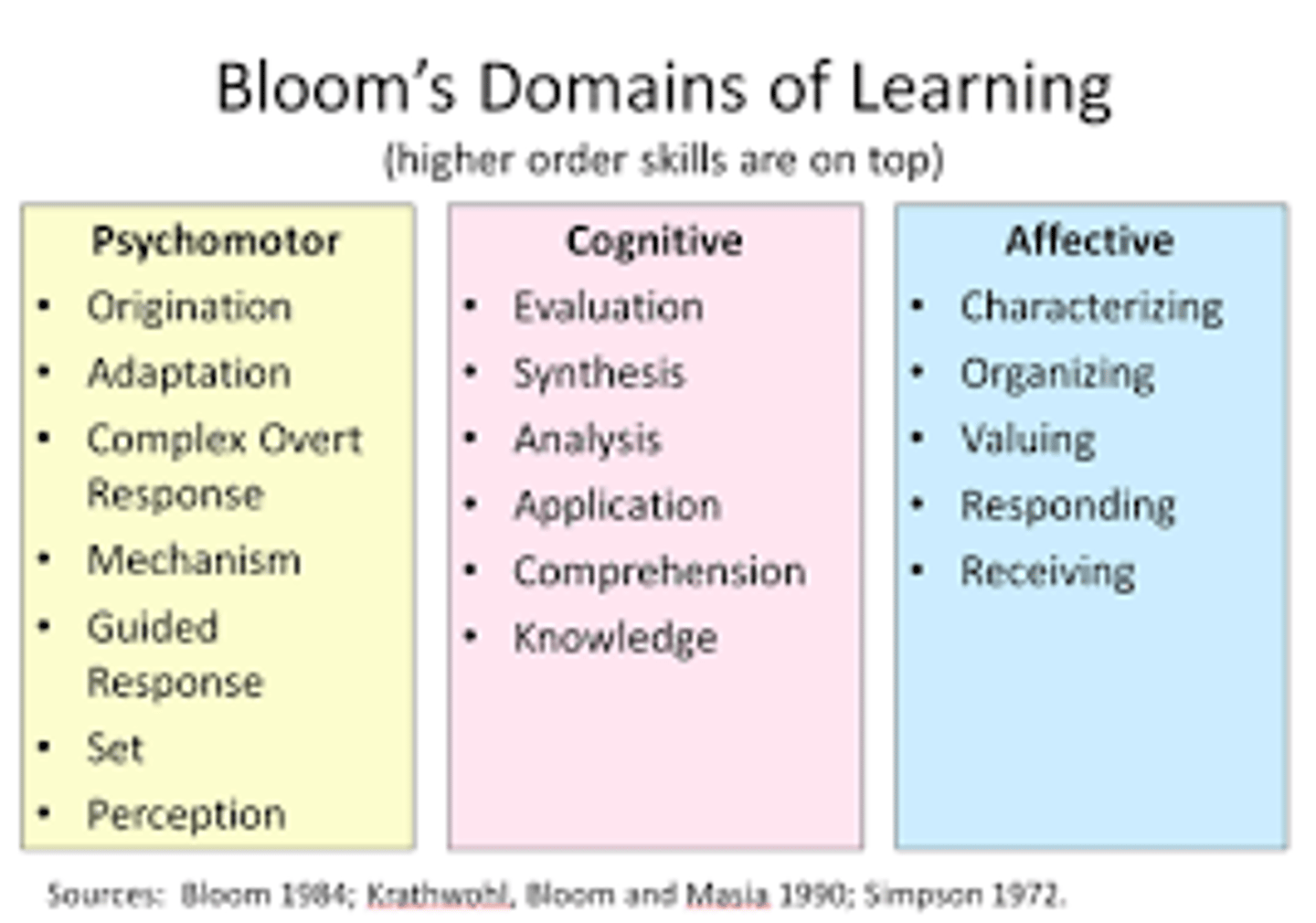
psychomotor domain
controls motor skill development (part of Bloom's more holistic approach to education)
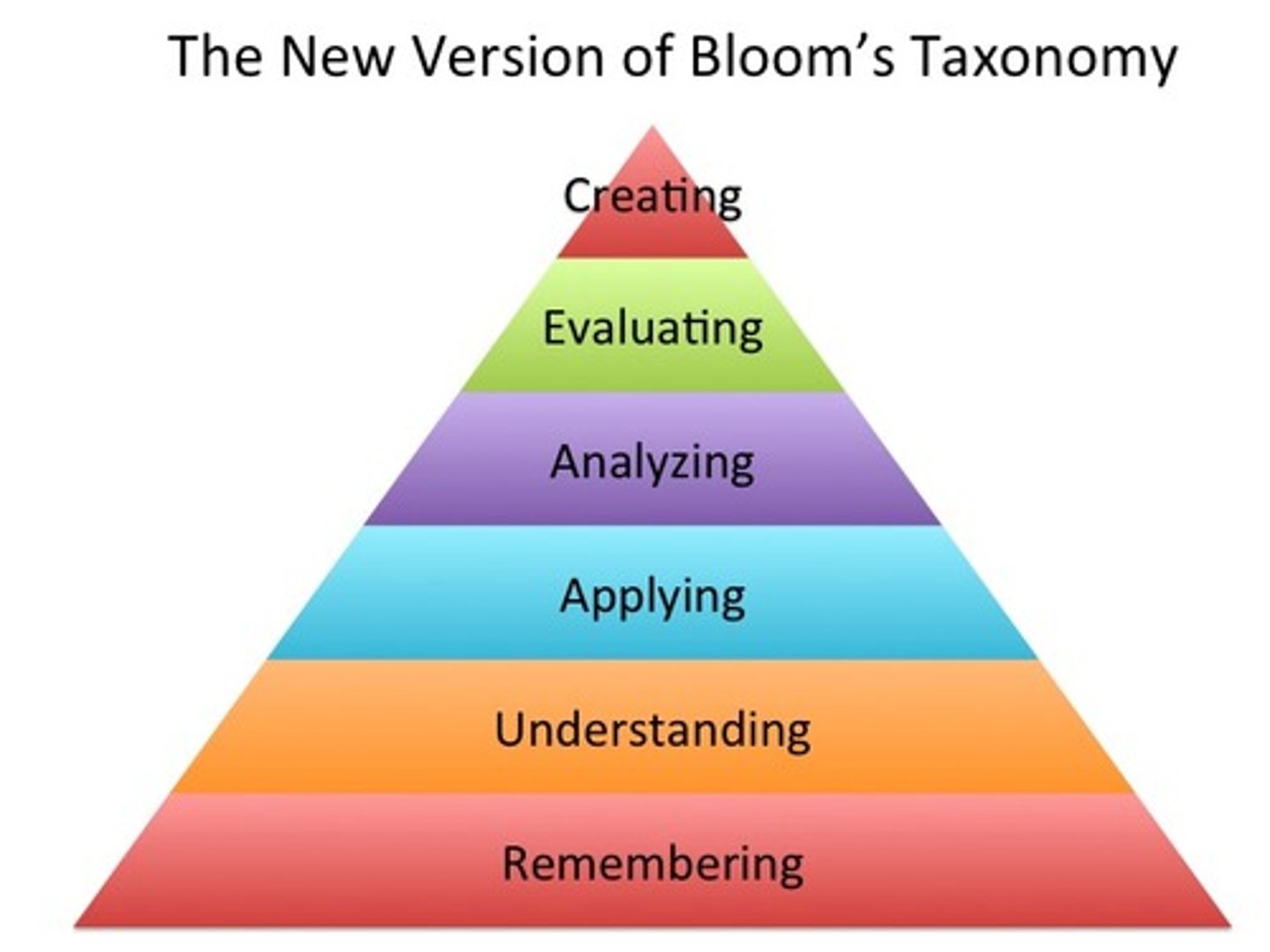
Bloom's Taxonomy
a framework for categorizing educational goals that identifies six categories based on the three domains of learning (psychomotor, affective, and cognitive). The triangle addresses levels in the cognitive domain (Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, Creating).
observation
when a teacher watches a student engaged in a learning activity to find evidence of learning. anecdotal notes are written records of a teacher's observations of a student.
affective/social domain
controls the development of emotions, values, and attitudes. Part of Bloom's holistic approach to education. Categories include receiving phenomena (attentive/aware), responding (participation), valuing (respect), organizing (balance/prioritization), and internalizing values (discriminating).
informal assessment
collected in the classroom to monitor student performance. regularly used to help make daily instructional decisions. include checklists, pop quizzes, periodic learning probes, and exit tickets.
norm referenced
standardized tests that measure students in comparison with other students of the same age. rank students.
learning contracts
agreements negotiated between a student and a teacher, with possible input from other school personnel or parents, designed for the improvement of an objective. Typically provide some degree of creativity on the part of the student, but keep focus on the mastery of learning objectives.
self-assessment
a method by which students monitor their own progress toward learning goals. helps move students toward stage 5 of Kohlberg's moral development. Keep students focused on learning.
aptitude test
a type of formal assessment. measure a person's ability to develop a particular skill. determine a student's strengths compared with other students of the same age. also used to help place Gifted Students
active listening
improves listening skills by structuring how a person listens and responds to the person who is talking. includes making a conscious effort to really hear what another person has to say without a wandering mind or preparation for a response.
Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act of 1974
(FERPA)
prohibits schools from sharing identifiable information about students. protects the confidentiality of student's education records. at age 18 the rights are transferred to the child. parents can request inaccurate or misleading records be changed.
authentic language
reading materials from books, newspapers, the Internet and other real-life sources. when ELLs are in stage one of second-language acquisition, this type of language is the most helpful. textbook language is too different from the language English speakers use in conversation.
Accommodations
Provide students access to the same curriculum as their grade level peers, but information is presented in a different way. Can be instructional or environmental. These will be outlined in a 504 or IEP.
Americans with Disabilities Act
This act prohibits discrimination based on disabilities. In schools, this includes activities that take place both on and off campus, including athletics and extracurricular activities.
B.F. Skinner
He expanded on Thorndike and Watson's work regarding operant conditioning but focused on responding to environment in lieu of responding to stimuli. Taught animals to do extraordinary things. Learning happens when the teacher facilitates self-paced learning activities and provides rewards for success. Reinforcement must be a part of learning behavior. Allow the learner time to meet learning goals with lots of praise and positive reinforcement.

Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills (BICS)
Stage three of second-language acquisition: developing. Conversational English. Professionals may be confused into thinking the student is more ready for academic independence than they are. Teaching strategies include flashcards and choral reading.
Benjamin Bloom
American psychologist. He contributed to the taxonomy of educational objectives and the theory of mastery learning. Proposed increasing cooperation over competition and using assessments as learning tools. Mastery learning gives credit for success to hard work over innate talent. Led to the development of the Head Start program. Crucial role of child development in the first four years of life. Holistic approach to education - affective, psychomotor, and cognitive domains. Teachers apply Bloom by asking questions and assigning tasks that promote higher-level thinking. Some prerequisite knowledge is necessary, but teachers should dig deeper with application and synthesis.
Classic conditioning
This practice involves learning a response to stimuli or the environment. Uses neutral or environmental stimuli to evoke a response.
Classical conditioning
A neutral stimulus becomes associated with a reflex response through conditioning. (Ivan Pavlov) One of the first learning theories to emerge. Ex: teacher rings a bell and students stop what they are doing.
Code-switching
This happens when students slip into native language while speaking their second-language, or vice versa. Happens during stage two of second-language acquisition. As new language becomes dominant, they will reverse code-switching.
Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency (CALPS)
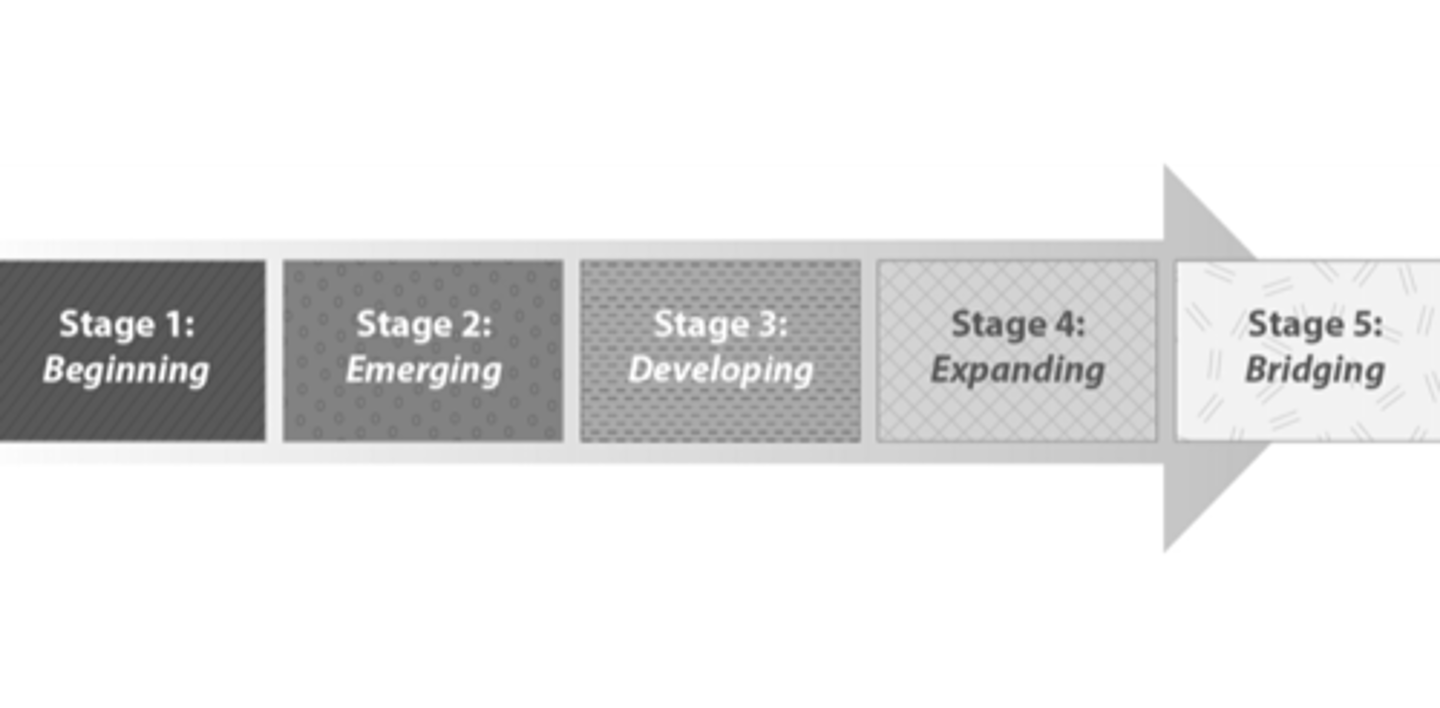
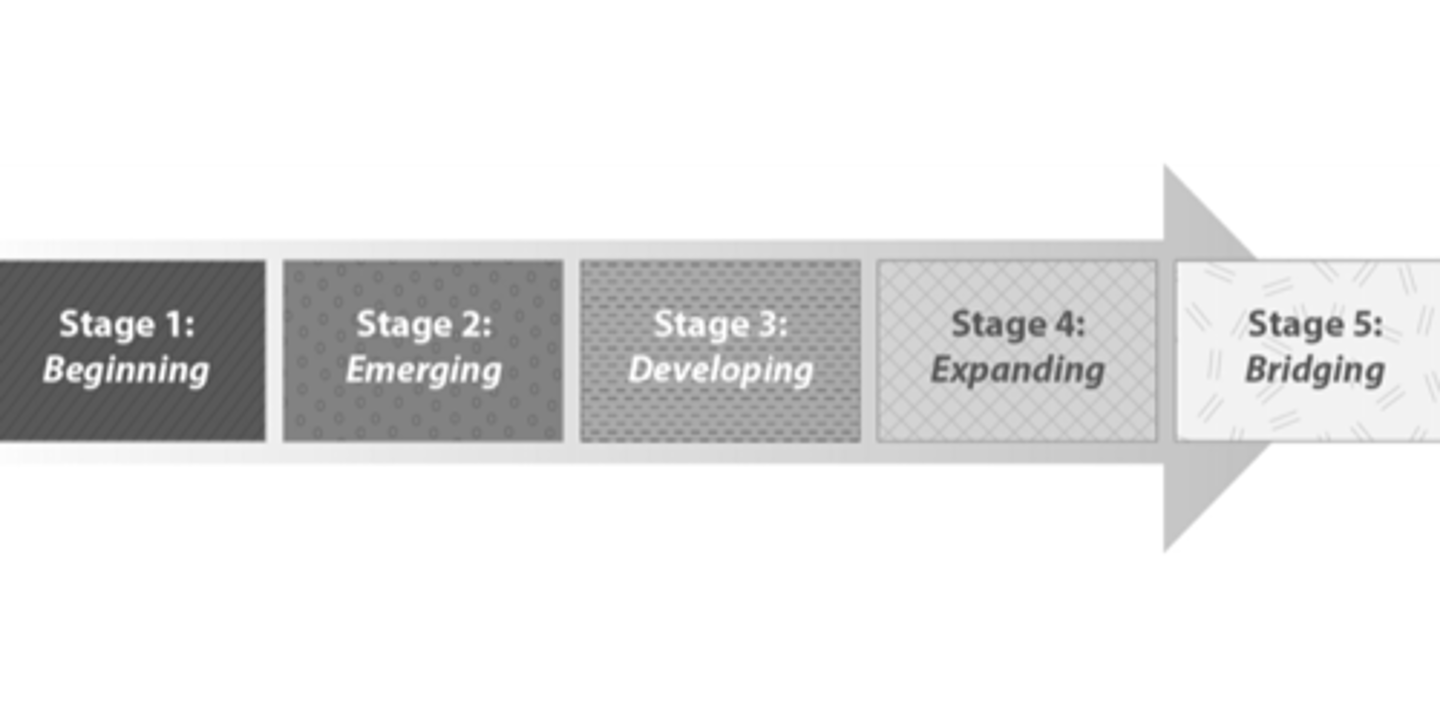
This is a student's ability to comprehend academic vocabulary in English. Part of stage five of second-language acquisition: Bridging. Even if students have achieved CALPS, they still need teacher support.
Cognitive Disabilities
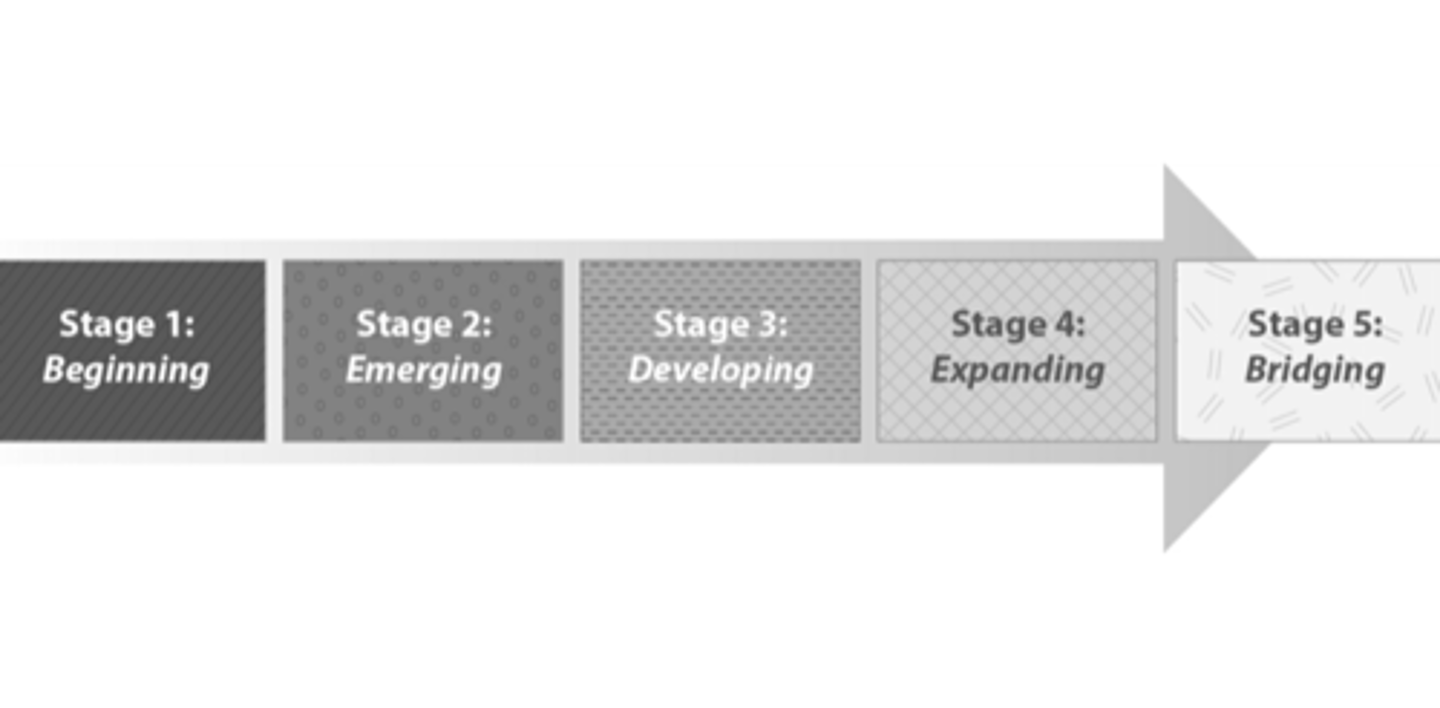
impairments in intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior. mild, moderate, or severe. IQ scores between 55 and 70=mild, moderate=30-55, severe=below 30. Can be caused by genetic disorders or injuries to the brain.
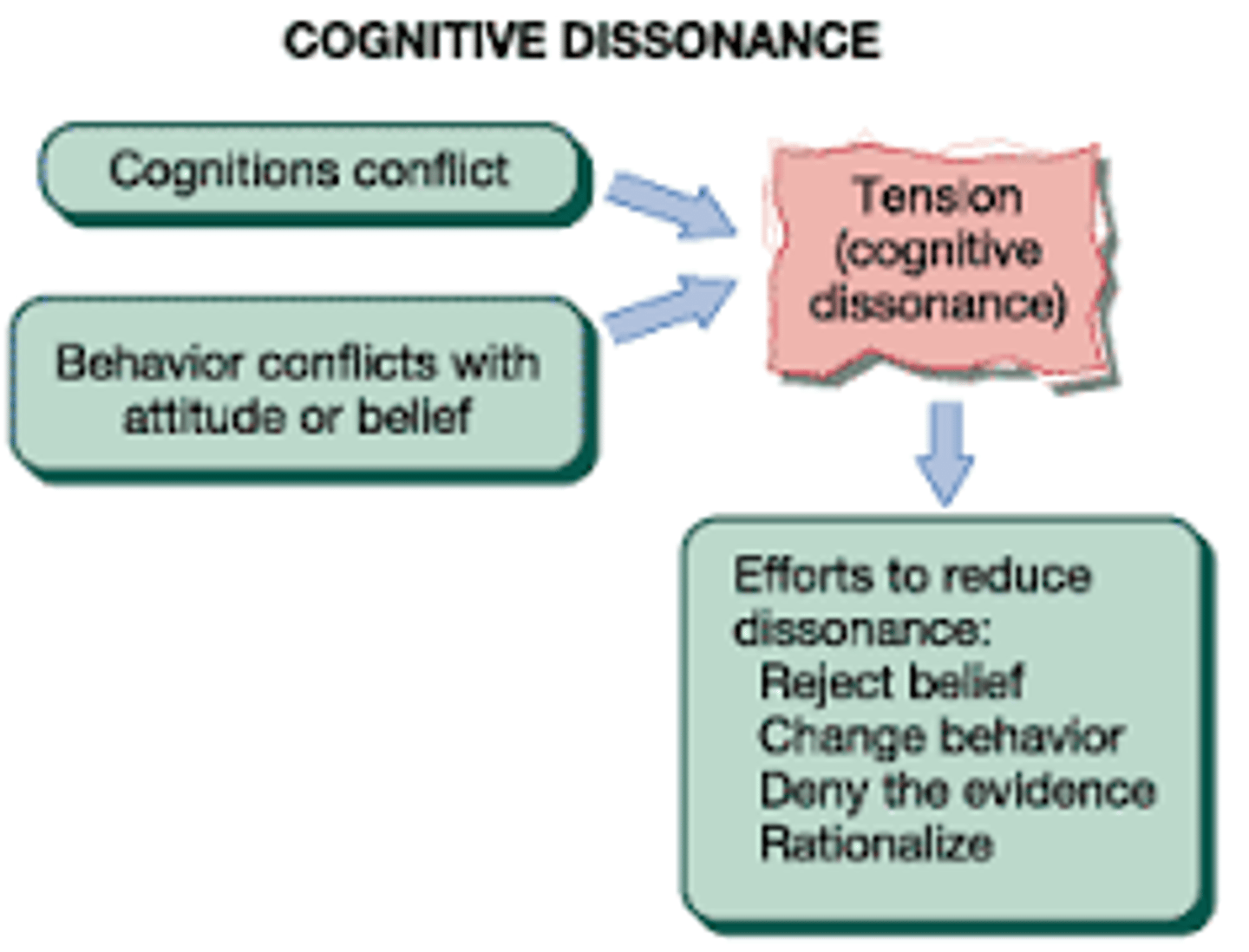
Cognitive Dissonance Theory
Uneasiness is felt when an individual has conflicting thoughts. To resolve, individuals will change their behavior, change their thoughts about the behavior, or justify their behavior. Creating cognitive dissonance=power of persuasion. Recognizing & helping students recognize it & where the internal conflict is coming from will help resolve it.
Cognitive Domain
Deals with acquiring intellect and the ways students process new information, store knowledge, and retrieve it to apply to new circumstances. Part of Bloom's holistic approach to education. See Bloom's taxonomy for the categories.
Cognitive Processes
These processes are more than just acquisition of knowledge and skills; includes the ability to apply new information to other settings and draw conclusions. Includes perception, attention, language, memory, and thinking.
Differentiation
Means providing curricula for student based on their learning styles and level. Necessary to meet the needs of all students. Successful _____ supports the use of advanced curricula that favor inquiry-based learning activities. (Includes Gifted students) Also includes remediation.
Divergent thinkers
People who think more deeply and differently from other people. Typical of Gifted students. Some may openly display eccentricities, others may hide it. What may seem like common sense to others may not make sense to them.
English-Language Learner (ELL)
Students whose native language is not English. Face a unique set of challenges, learning a new language at the same time as learning content objectives. Requires relearning language patterns. There are five stages of second-language acquisition.
English Language Proficiency Standards (ELPS)
Objectives that not only support ESL instruction but also to be used in the content areas to increase academic readiness. There are 10: 1. construct meaning from literary and info text/presentations. 2. exchange info orally & writing. 3. speak and write about literary & info text. 4. construct and defend oral & written statements. 5. solve problems w/ research. 6. critique claims of others orally & in writing. 7. make appropriate word choices orally & in writing depending on audience & purpose. 8. comprehend meaning of words in literary & info texts. 9. speak and write clearly and coherently. 10. Accurately use English when speaking and writing.

Exceptionality
A strength or weakness in academic functioning that requires extra attention to meet the needs of the student.
Foundational Theorists
The people who provided the framework by which all current knowledge of cognitive processes is based. (Bruner, Bandura, Dewey, Piaget, Vygotsky, Kohlberg, Bloom)
Individualized Education Plan (IEP)
An annual meeting for each special education student that outlines the student's learning goals and identifies the accommodations and modifications that will be offered to the student.
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
This act provides guidelines to schools to help address the individual needs of special education students.
Intellectually gifted
Students with an IQ greater than 130.
Intrinsic Motivation
Describes an internal reward. Self-motivation is the drive from within that inspires a person to work toward something.
Jean Piaget
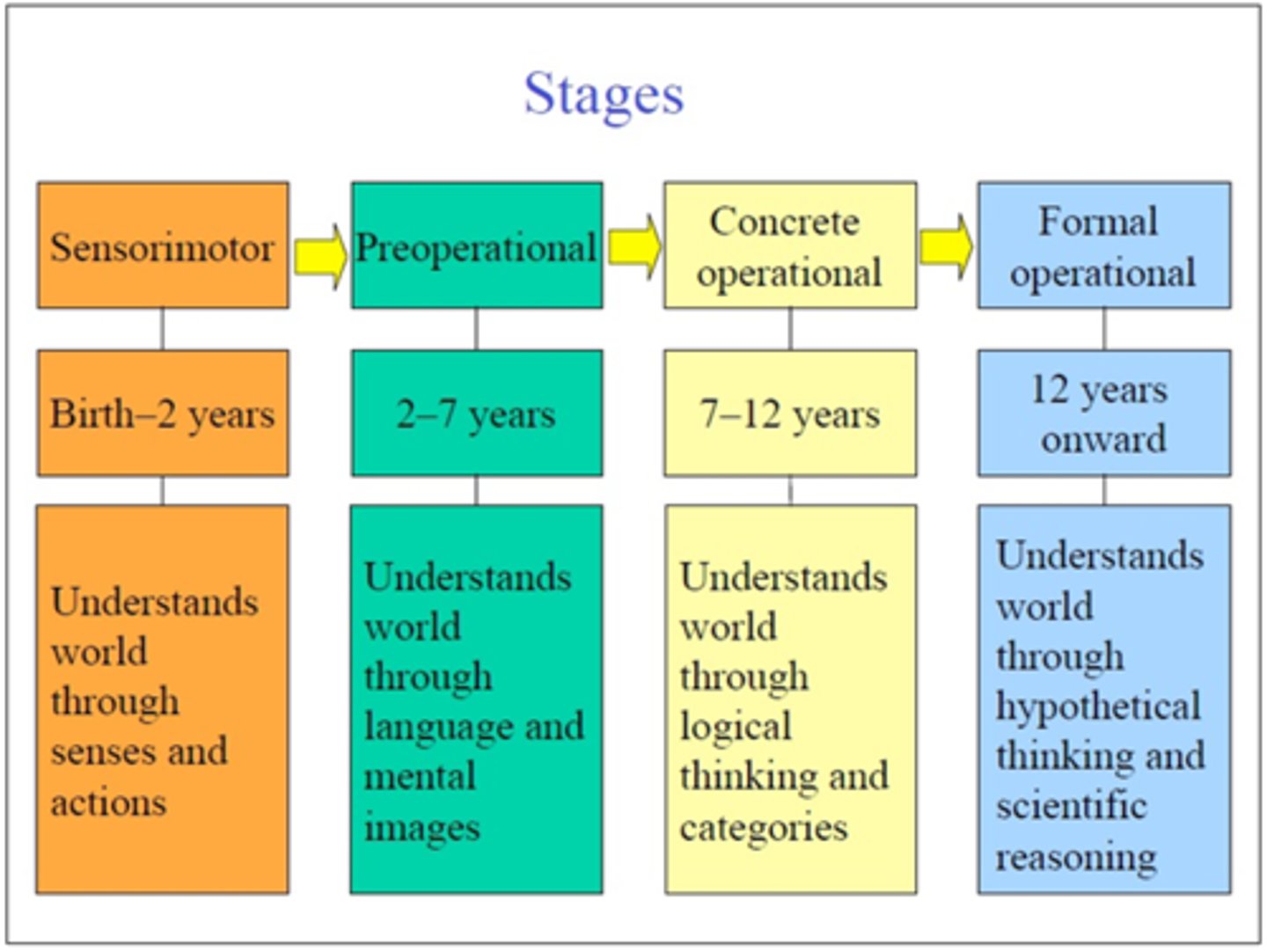
A Swiss psychologist who was the first to study cognition in children. He identified stages of development and contributed to schema learning. Stages= sensorimotor (0-2 yrs object permanence), preoperational (2-7 yrs symbolic play, no abstract or other perspectives), concrete operational (7-11 yrs logical thinking, inferences, multiple perspectives, classification), and formal operational (11-adulthood abstract thought, transfer knowledge, mentally process information). Also introduced the concepts of assimilation and accommodation and schema theory. In the classroom: teachers can include a variety of hands-on experiences for students to explore and by focusing on the PROCESS of learning rather than the end result. Understand students develop at different rates. Do not push students toward knowledge or skills before they have demonstrated readiness.
Jerome Bruner
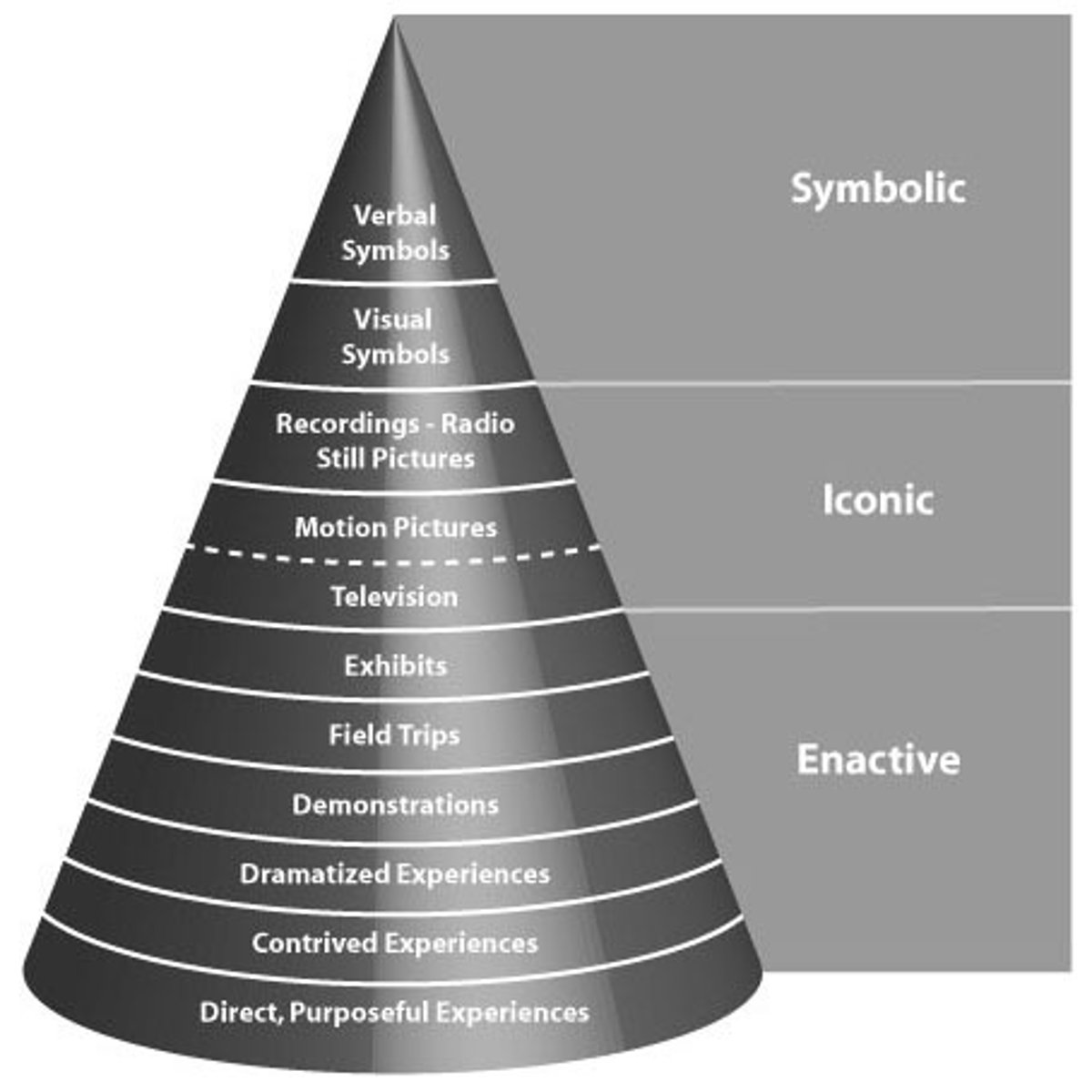
A constructivist theorist who contributed the three modes of representation to the field of cognitive development. Children integrate learnings experiences in the following order: enactive stage (up to one year) learning through action, iconic stage (1-6 years) learning through mental pictures, symbolic stage (7+) learning through abstractions like language, symbol and classification. In contrast to Piaget, said education is not about developmental readiness but about providing active & engaging experiences for students to construct own knowledge w/discovery learning and spiraling curriculum. Constructivist classroom=teacher is facilitator who promotes symbolic thinking and problem solving skills that can be applied to many situations.
John Dewey
A pragmatic philosopher who viewed learning as a series of scientific inquiry and experimentation.; he advocated real-world experiences and volunteerism. Balances the teacher's role of understanding content knowledge and modeling a passion for learning with the child's necessity to construct knowledge using hands-on and relevant learning activities. Truth is a tool for problem-solving, however, as problems change, truth also changes. In the classroom=teachers help students understand how the learning objectives relate to the world outside the classroom. Include social responsibility, tolerance, active listening, and volunteerism.
John Watson
Coined the term "behaviorism" which objectively measures behavior in response to stimuli.
Language Impairments
Students who have these struggle with comprehension.
Learning theories
Describe how genetics, development, environment, motivation, and emotions affect a student's ability to acquire and apply knowledge.
Metacognition
Thinking about the learning process
Modifications
Changes made to the curriculum because students are so far behind that they are unable to use the same curriculum as their peers.
Moral domain
Deals with the acquisition of morals and values.
Motivation Theory
Explains the driving forces behind conduct.
Motor Disabilities
Characterized by loss of movement. May be caused by injury or disease.
Physical Disabilities
Impairments that require assistance during the school day.
Physical Domain/Psychomotor Domain
Deals with all aspects of motor skill development.
Redirect
Distract students from negative behavior by channeling their attention into something positive.
Schema
Frameworks for understanding.
Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act
This section provides services to all students in federally assisted programs who have physical or mental impairments that substantially limit one or more life activities.
Self-determination Theory
Everyone has a perceived locus of causality.
Self-efficacy
When a person believes she is capable of achieving a learning goal.
Social Domain
Includes emotions, motivation, and attitudes (also called affective or social-emotional domain)
Speech Disorders
Difficulty forming words.
Transfer
To apply knowledge to make inferences about new thoughts and ideas.
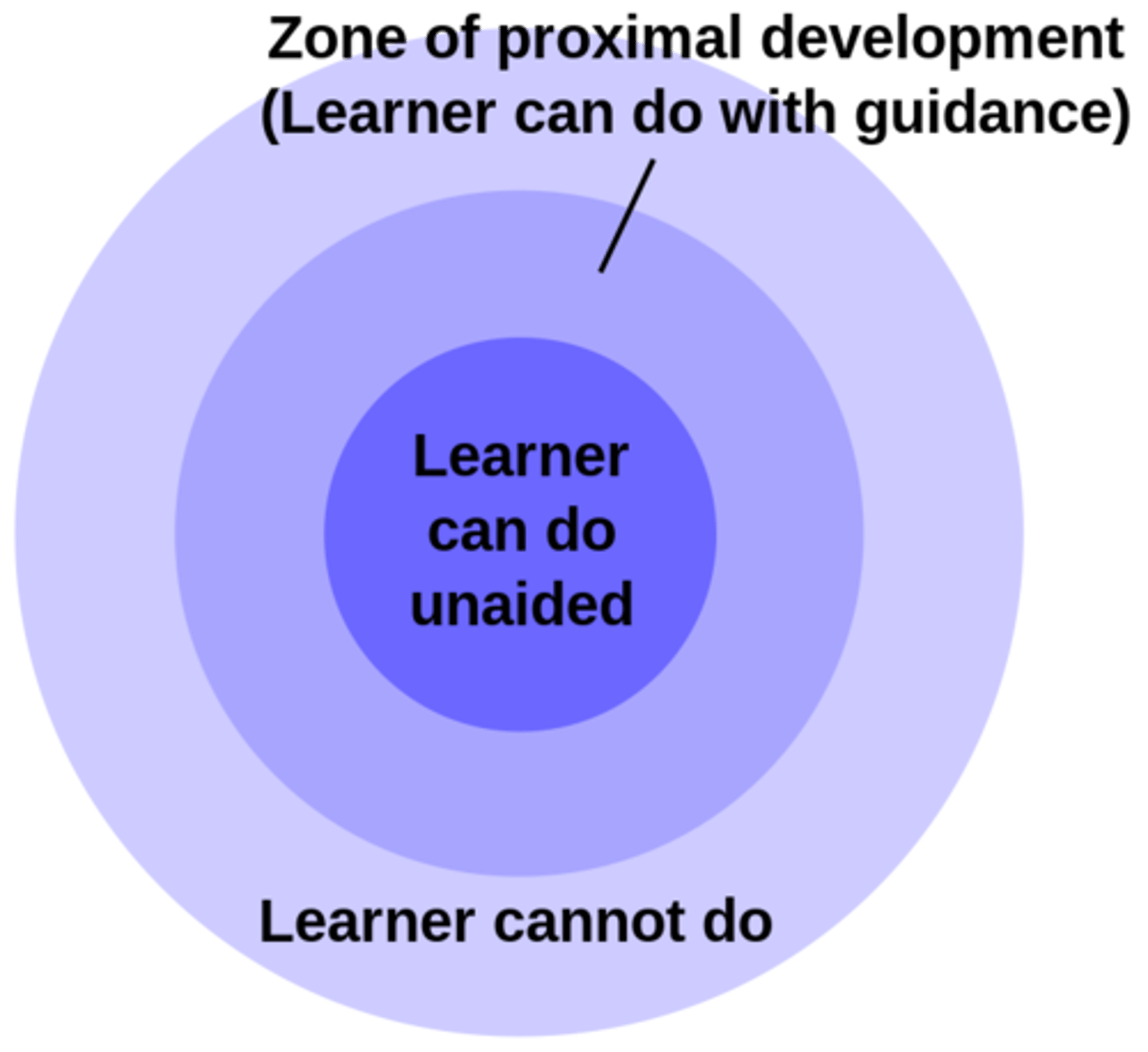
Zone of Proximal Development (ZDP)
The space between what a child can do independently and the learning goal.
Analyze
The process of inspecting something critically
Assessment
This is the process of gathering data to determine the extent to which learning goals have been met.
Audio Aid
This device amplifies the teacher's speech so that it can be heard clearly by students.
Behaviorism
The theory that describes how rewards and punishments condition student behavior and learning.
Cloze Procedures
the practice of omitting words from the text as a reading comprehension activity
Coaching
This training occurs when one person receives support from another toward the achievement of a goal.
Compare/Contrast
When students note the similarities between two or more things/the differences between two or more things.
Concept Learning
a form of learning that involves classifying information by topic
Concept Mapping
the practice of using graphic organizers to present thoughts or information
Constructivism
students construct their own knowledge through learning experiences
Critical Thinking
A form of thinking that involves looking at evidence from an objective viewpoint to make inferences or draw conclusions.