Bio Two, Exam 2, Info
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Phylogeny of land plant groups/derived traits?
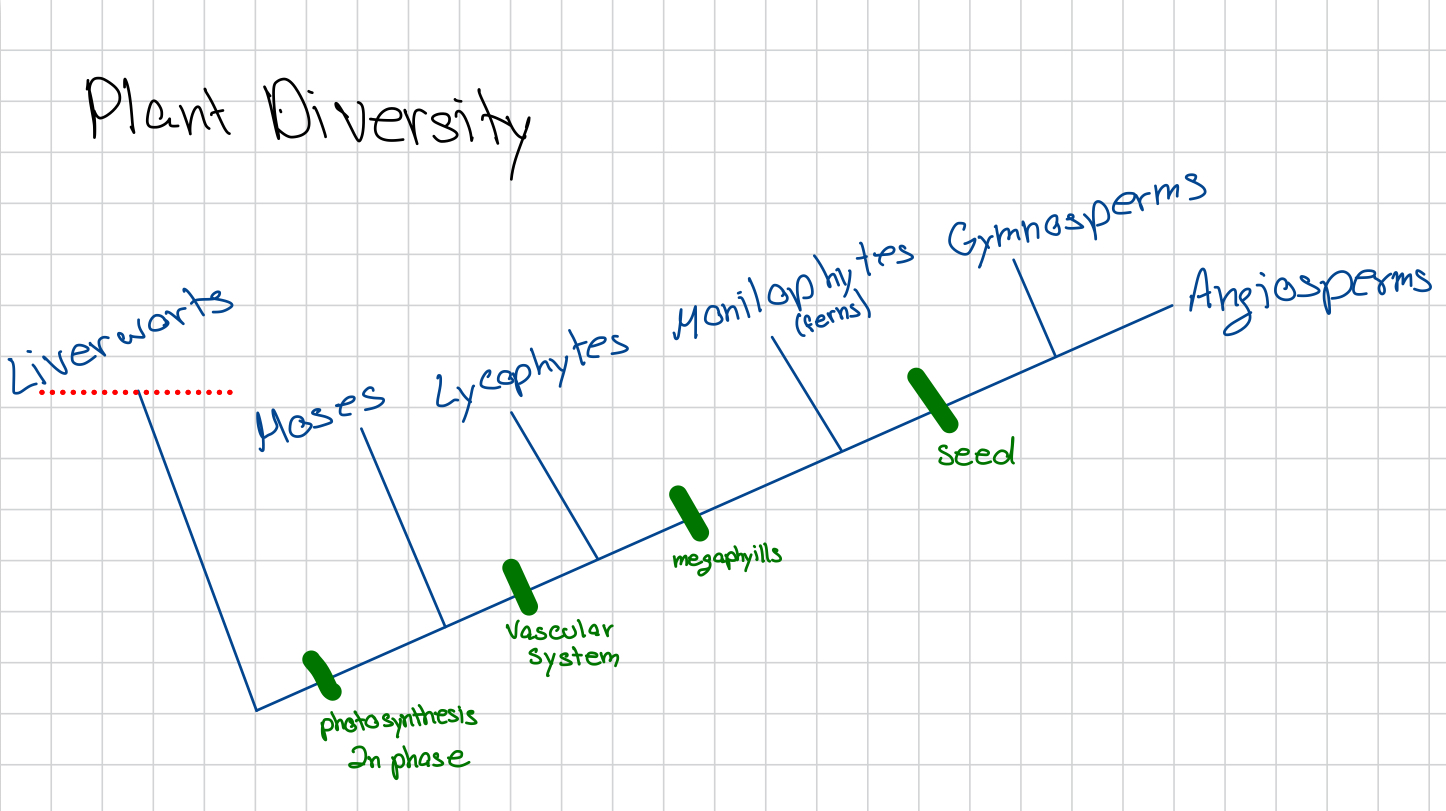
Significance of a vascular system in plants?
Having a vascular system means the plants can grow much taller and require less shade. Mosses have to grow in the shade. Other plants need a vascular system to send water from the roots and use the shoot system to send the water up. The plant has more sun expose so it needs more time in the 2n phase to resist mutations.
Types of vascular tissue?
Xylem conducts water and minerals
Takes in water and brings it from the roots to the plant. Goes up and requires true roots.
Phloem conducts sugars/organic products
Brings glucose to the nonphotosynthetic parts of the plant
Importance of lignin?
Originally the cellulose in the cell wall would soak up the liquid and not let water be transported. So lignin became a component that surrounds the water-conducting cells. This allows water to be transported. Lignin also makes the plant stronger.
Importance of seeds in angiosperms/gymnosperms?
Gymnosperns and angiosperms (flowering plants) produce seeds
*Seeds contain an embryo and its food supply (image in notes)
Functions
Allow for dormancy
Allow for dispersal (samara from maple tree and anchorn)
Anchors are fully eaten but rely on squirls to store them and forget about them to start new plants
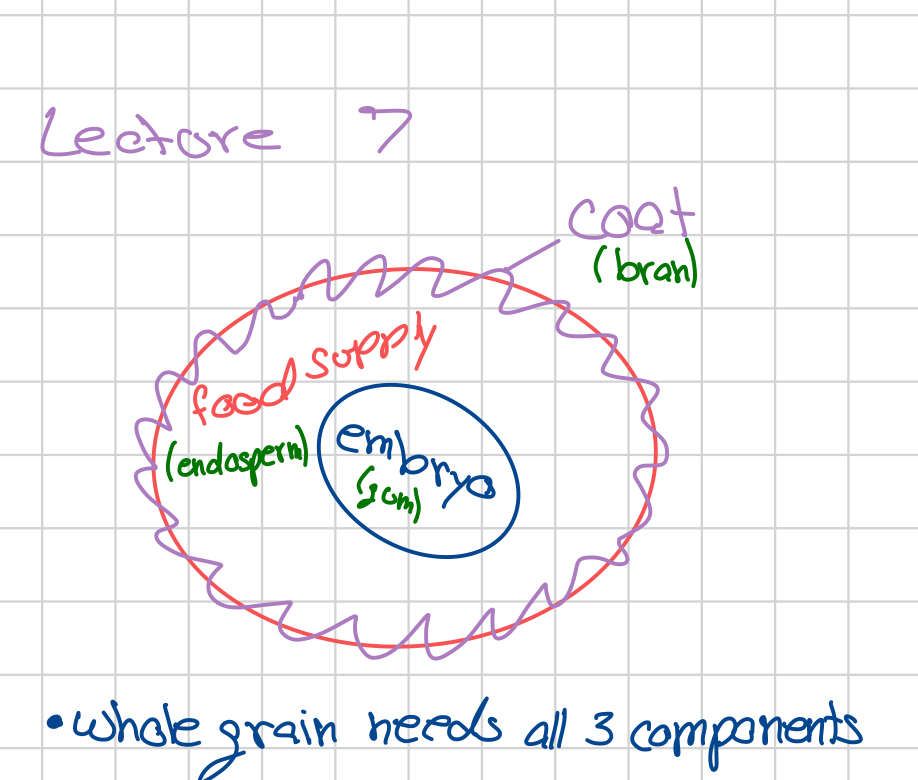
Refinement in grains?
When grains are refined, the germ and bran are removed, leaving only the food supply (endosperm). This gives the grains more shelf life.
Differences between angiosperms and gymnosperms?
Angiosperms are flowering plants
Angiosperns have an ovary surrounding their seeds. Gymnosperm seeds are “naked seeds”.
Ovary is also “fruit”
Angiosperms have a double fertilization
Double fertilization:
One sperm → zygote
One sperm → endosperm
Components of dermal tissue?
Responsible for covering a certain part
An outer covering
Protection
Dermal tissue can contain trichomes (“hair-like” extensions of dermal tissue)
Anything that tries to eat it makes the animal's skin become inflamed because of the chemicals inside the leaves to protect it, which are stored in the hairs
Root hairs increase surface area
Components of ground tissue?
Parenchyma: Make up the bulk of plant tissue
Collenchyma: Contains elongated cells for support
Stringy cells in celerly
Sclerenchyma: Lignified (usually dead) cells that protect
On top of everything
Ex: bark is dead and shows the aging of plants
Primary vs. secondary growth and how they can be advantageous?
Plant growth is indeterminate
Our cells are programmed to grow to a certain height in our DNA
Plants do not have a planned growth with their DNA (because of the meristem)
Apical meristem: Provides primary growth
Primary growth is growth in length
- only shoot
Lateral meristem: Provides secondary growth
Secondary growth: growth in diameter
Growth strategies:
Mapel tree utilities primary growth to get all
This is adventitioug for the maple tree because it focuses on getting tall then growths its leaves which causes shade and if there were acorns next to the tree it woud shade out the growth to compete with other trees. Gets tall really fast and then shades out the others.
If you have a thin trucks and there is a forest fire the maples die off and the oak trees stay
Oak trees invest in secondary growth which provides durability
Macro vs. Micronutrients?
Macronutrients: (required in large quantities)
Ex: Carbon, hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen (in plants)
Carbon, hydrogen, Oxygen (very easy to get)
Nitrogen is the limiting nutrient that determines whether it can survive or not
Nitrogen
Very hard to make a triple covalent bond
Micronutrients:(required in small quantities)
Ex: Iron, Calcium, Magnesium, and Copper
Nitrogen availability in plants/usable forms?
Plants can use nitrogen in the form of ammonium (NH4+) or nitrate (NO3-). These can be made by different types of bacteria, since plants can't break the triple covalent bond in N2.
The role of nitrogenase and how it may be incorporated into plant DNA?
Nitrogenase is the enzyme needed to break down N2 from the air, but plants don't make it. Bacteria do, so it would be possible to transfer the nitrogenase gene from bacteria to plants. The problem is that bacterial DNA is a lot different than plant DNA, so plants would have trouble reading the gene. The solution may be to transfer the gene into chloroplast DNA, which is similar to bacterial DNA.
Types of nitrogen-processing bacteria and how they function?
Ammonifying: convert amino acids from decaying organisms into NH4+ (that the plant can use)
Nitrogen-fixing: convert gaseous nitrogen (N2) into ammonium NH4+
Nitrifying: convert Ammonium (NH4+) to nitrate (NO3-) which is the ideal source of the plant
Examples of plants that acquire nitrogen without soil?
Carnivorous plants “digest” insects
Vineous fly trap
Ex: pitcher plants (insects get trapped on the edge, then fall in and cannot get out
Soil is very acidic so it consumes insects and takes away competition from their environment. Eating the plants gives them nitrogen
Types of mycorrhizae?
Ectomycorrhizae: lives on the outside of the root cells and forms a thick coating on the root (mantle)
Endomycorrhizae: penetrate the plant cell and branch out within the cell
Structure/properties of fungal hyphae?
Fungi
Cell walls made of chitin
Multicellular fungi form, long branching tubes with multiple nuclei (hyphae)
*Cells are separated by incomplete barriers (septa)
Can send things down the chain because it is incomplete
Sharing cytoplasm and incomplete divisions
Mitosis is not followed by cytokinesis
Cytokinesis: cell splits completely
Fungal symbioses?
Mutualism: both benefit
Ex: mycorrhizae
Commensal: one benefits; the other is unaffected
Ex: epiphytes and lichen
Lichen is a type of fungus that grows on tree branches, and the branch is unaffected
Lichen
*contain mycobiont (fungus) and photobiont (algae)
Parasitic: one benefits; the other is harmed
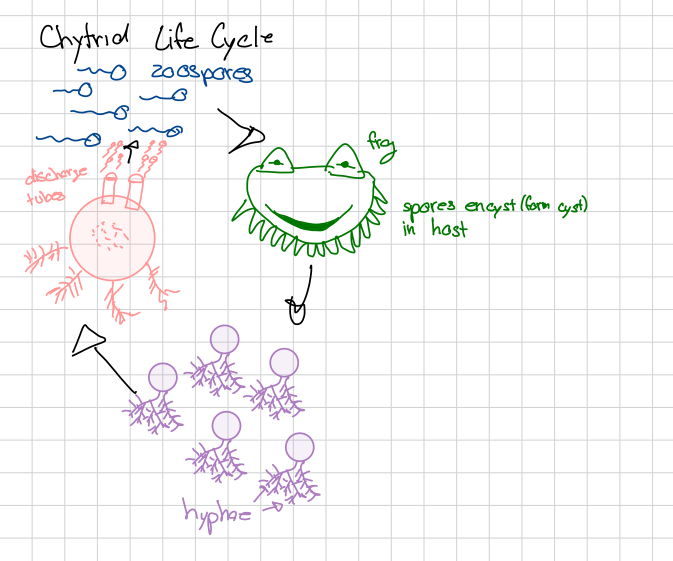
Ex: chytrid
Chytrid characteristics/life cycle?
Asexual reproduction in fungi (i.e. Zygomycota)?
Reproduce asexually by:
Hyphal fragmentation
Producing mitospores (asexual spores)