Mendelian Genetics
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Gregor Johann Mendel
Often referred to as the 'Father of Genetics'.
Parental generation (P1)
The first generation in Mendel’s experiments.
First filial generation (F1)
The second generation in Mendel’s experiments.
Second filial generation (F2)
The next generation after F1 in Mendel’s experiments.
Dominant
A trait that masks another trait.
Recessive
A trait that is masked by another trait.
Law of Segregation
Mendel’s first law that explains how alleles separate during meiosis.
Homozygous
An individual with identical alleles for a gene.
Heterozygous
An individual with two different alleles for a gene.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism.
Phenotype
The observable characteristics of an organism.
Punnett square
A diagram used to predict the outcome of a genetic cross.
Test cross
Crossing an unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual.
Law of Independent Assortment
Mendel’s second law involving genes on different chromosomes.
Lethal allele
A genotype that causes death before reproductive age.
Incomplete dominance
A heterozygous phenotype that is intermediate between both homozygotes.
Codominance
A situation where both alleles are fully expressed.
Sex-linked trait
A genetic trait that appears differently in males and females due to sex chromosomes.
Sex-limited traits
Traits expressed only in one sex despite being present in both.
Sex-influenced traits
Traits influenced by the sex of the individual.
Pedigree
A chart that shows family relationships and inherited traits.
Dihybrid cross
A 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio is typical of this genetic cross.
Monohybrid cross
A 3:1 phenotypic ratio is typical of this genetic cross.
Pedigree chart
A tool used to show inheritance patterns across generations.
Hybrid
An offspring that inherits different gene variants from each parent.
Trihybrid cross
A cross between individuals heterozygous for three different traits.
X-linked trait
A disorder caused by a gene on the X chromosome, typically affecting males more than females.
Codominance
A genetic condition where the heterozygote expresses both alleles equally.
Normal female, male
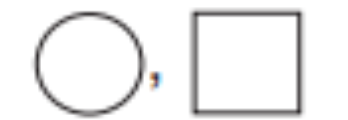
Pedigree
The term for a diagram showing inheritance of traits in a family.
Autosomal dominant inheritance
The pattern where a trait appears in every generation and affects both sexes.
Female, male who expresses trait

Female, male who carries an allele for the trait but does not express it (carrier)

Dead female, male.
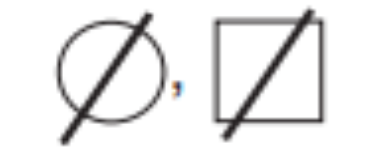
Sex unspecified.

Stillbirth
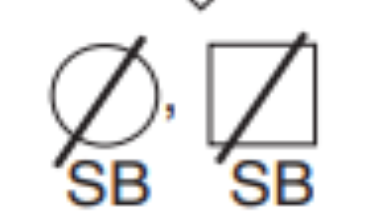
Pregnancy

Spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
Terminated pregnancy (shade if abnormal)
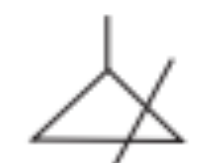
Generation
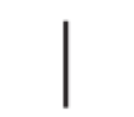
Partners

Adoption
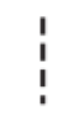
Siblings

Identical twins
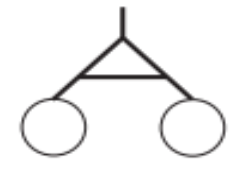
Fraternal twins
Parents closely related (by blood)

Former relationship
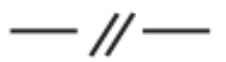
Person who prompted pedigree analysis (proband)
