EP1200 Sequential Logic
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
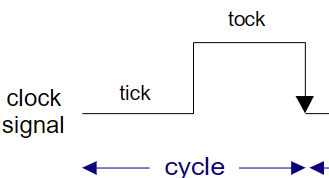
What does 1 clock cycle consist of?
Tick-phase (low), tock-phase (high)
What’s a one-bit / multi-bit register? And how is it implemented (2 chips)
A storage unit that hold a single/multiple binary digits (0/1).
if load(t-1): out(t)=in(t-1)
else: out(t)=out(t-1)
It is implemented using a Mux and DFF.
Define these RAM Design parameters:
Data Width
Memory Size
Data width = bit-width of each word
Memory size = total number of words
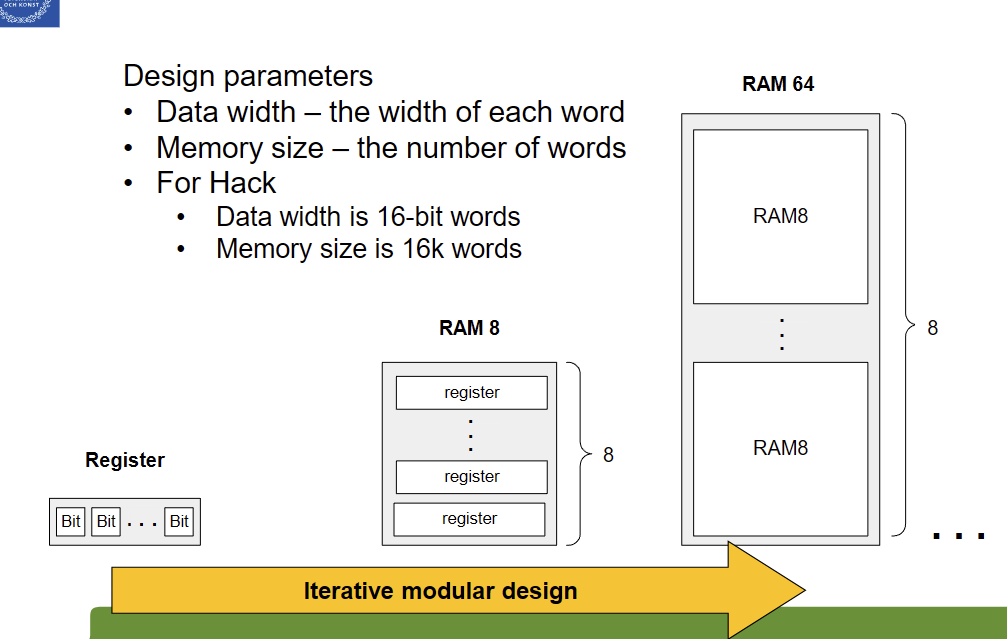
Just Acknowledge the *8 with each iteration (RAM “n”)
Order the Program Counter’s actions by priority given:
PC(in= ,load= ,inc= ,reset= ,out= );
What happens if inc=load=reset=true?
reset => load => inc => out
out=0
Just acknowledge: Why sequential logic?
1. store value over time
2. change output value [out(t+1)] only when stable