Zona Hatching
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
What is zona hatching?
When blastocyst escape from zona pellucida
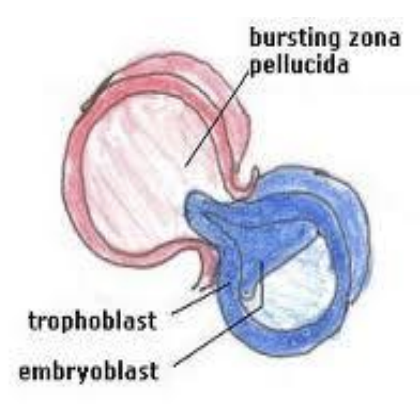
What needs to occur in order for implantation to happen?
The blastocyst needs to get rid of zona pellucida
Where does zona hatching occur?
In the uterus
How does estrogen aid in this process?
Causes softening of zona hatching
How does blastocyst escape zona pellucida?
Expansion and contraction of blastocyst result in tear in zona hatching
Post Hatching
What happens when blastocyst escape from zona pellucida
This is essential for
After hatching blastocyst enters a phase of
What is the function of conceptus migration and spacing in uterus
What is intrauterine migration and spacing
What happens when blastocyst escape from zona pellucida: Provides first cell to cell contact between conceptus (blastocyst) and maternal uterine epithelium
This is essential for: Nutrient exchange and placental development
After hatching blastocyst enters a phase of: Rapid growth (hyperplasia) and development
What is the function of conceptus migration and spacing in uterus: It physically covers a large area of endometrium to regular PGF₂α release, preventing luteolysis
What is intrauterine migration and spacing: The shifting of the conceptus from its original position within uterus
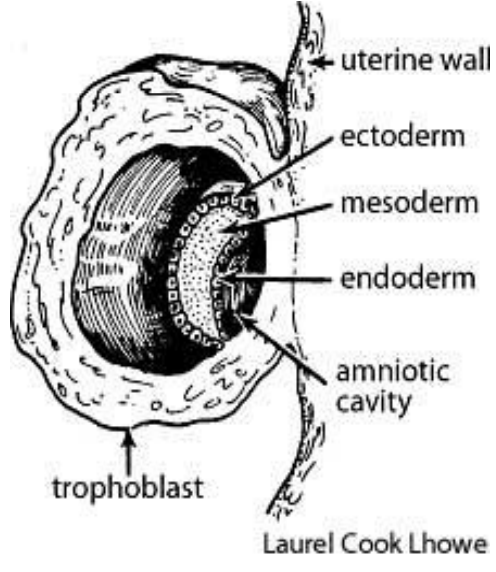
Phases in Pre-Embryonic Development
What are the 3 germ layers
What do they form
3 germ layers:
Ectoderm
Forms: External structures (skin, hair, hooves, mammary glands, neural)
Mesoderm
Forms: Heart, muscles and bones
Endoderm
Forms: Internal organs, colon, liver, pancreas