Bio week 1- Nerons
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
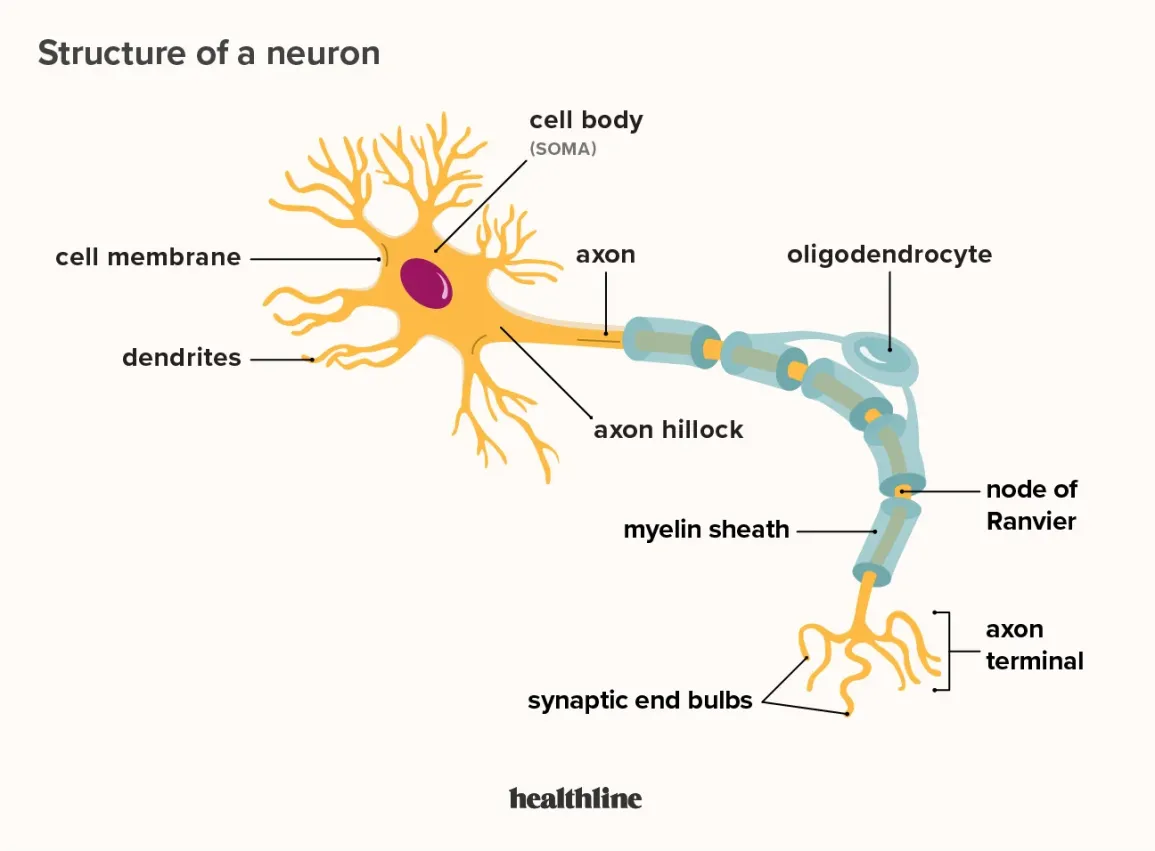
Neurons
the “wires” that transmit signals (both chemical & electrical)
Dendrites
They receive the messages from another neuron
Synapses
the space between 2 neurons where signals are passed
Axon
a tube-like stucture that feeds the electrical signals through the neuron and to the axon terminals
Axon terminals
transmits the signals using neurotransmitters through the synapse to other neurons
Soma
the cell body
Electro Chemical Signaling
the process where electrical signals become chemical signals to “jump” the synapses and be received by the postsynaptic neuron.
Synaptic plasticity
the ability to change the strength of the synaptic connections between neurons.
Glia
cells that provide support, they make sure the electrical signal is going to the right place
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the axon where the electrical signal recharges
what do neurons do before “making a decision?”
they “talk” to each other through electrical and chemical signals and synthesize
How do ions enter a neuron?
they go through ion channels in the synapses
What chemical
Depolorize
the neuron is more likely to fire
hyperpolorization
the neuron is less likely to fire
LTP
the persistent strengthing of the synaptic connections, (neurons that fire together, wire together) this also results in more AMPA receptors in the synapsis
LTD
the long-term weakening of the synaptic connections, this causes the AMPA receptors to become less responsive
glutamate
a neurotransmitter that causes the neuron to fire
how does LTP work?
glutamate attaches to the AMPA ion receptors and enters the postsynaptic neuron causing it to fire. however, this is not always enough so after repeated firing the NMDA receptor that was once blocked by a magnesium ion gets cleared allowing more glutamate and calsium through.