8- Capacitance, Capacitors and Dielectrics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What happens when a conductor is given charge Q?
Its electric potential rises from zero to a value V
What is capacitance?
It is the ability of a conductor to store charge per unit potential difference

What is a basic capacitor?
A capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material, storing charge on each plate.
What is the edge effect(fringing) in capacitors?
Its the distortion of the electric field near the edges of the capacitor plates, deviating from the ideal uniform field.
How can edge effects be minimized in capacitors?
By decreasing the distance between the plates relative to their other dimensions
This brings the system closer to an ideal capacitor.
How does a capacitor store energy?
It stores potential energy in the electric field created by the separation of positive and negative charges on its plates.
How do capacitors function in electric circuits?
Capacitors block direct current (DC) but allow alternating current (AC) to pass, depending on the frequency.
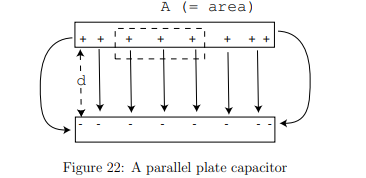
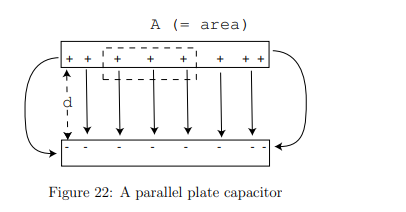
Where do the charges reside on a parallel-plate capacitor?
They accumulate on the inner surfaces of the plates due to electrostatic attraction, except near the edges where fringing effects occur.
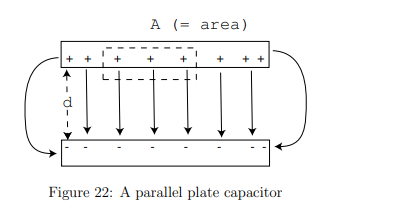
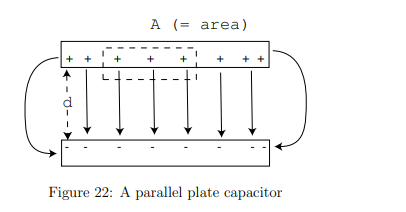
What is the charge density (σ) on the plates?
A= the plate area
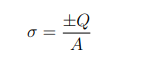
What is the electric field (E) between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor?
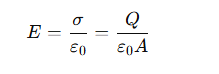
What does it mean that the plates of a capacitor are equipotential surfaces?
All points on a plate are at the same electric potential
This means there is no potential difference across any single plate.
What is the formula for the potential difference between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor?
V= the potential difference
d= the separation between the plates
Q= the charge on the plates
A= the area of each plate.
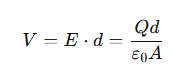
How is a capacitor charged?
A capacitor can be charged by placing it in an electric circuit with a battery.
The battery maintains a potential difference that allows the capacitor to accumulate charge.
What is the formula for the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor?
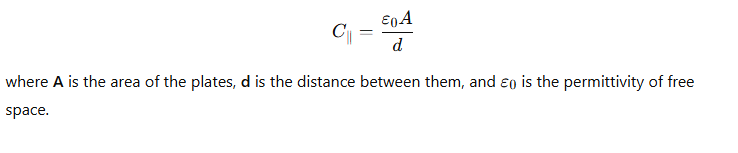
How do you calculate the capacitance of a spherical conductor?
R= the radius of the sphere
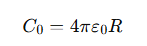
What are the two basic mechanisms through which electric fields affect dielectric molecules?
Polar dielectrics
Nonpolar dielectrics
How do polar dielectrics behave in an electric field?
Molecules like water have permanent electric dipoles that align with the applied electric field.
The alignment is not perfect due to thermal motion, but it becomes more complete as the field's magnitude increases.
How do nonpolar dielectrics behave in an electric field?
They acquire induced dipole moments when placed in an external electric field
This causes the centers of negative and positive charges within the molecule to slightly separate.